Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ANATOMY Digestive System
Transféré par
jeyssss0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
86 vues3 pagesThe digestive system is Formed of the mouth, digestive tract and appended glands. It converts ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism. The stomach mixes food with the gastric juices it secretes before emptying it into the duodenum.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe digestive system is Formed of the mouth, digestive tract and appended glands. It converts ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism. The stomach mixes food with the gastric juices it secretes before emptying it into the duodenum.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
86 vues3 pagesANATOMY Digestive System
Transféré par
jeyssssThe digestive system is Formed of the mouth, digestive tract and appended glands. It converts ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism. The stomach mixes food with the gastric juices it secretes before emptying it into the duodenum.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
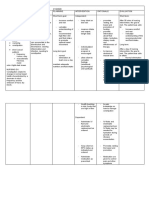
Digestive system
Formed of the mouth, digestive tract and appended glands, it converts
ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Oral cavity - Anterior cavity of the digestive tract enabling ingestion
of food; it also aids in breathing.
Tongue - Flexible muscular structure of the oral cavity; it helps in
tasting, masticating and ingesting food, and also facilitates
speech.
Salivary glands - Each of the three pairs of organs secreting a liquid
(saliva) that contains a digestive enzyme; it is used to moisten
food to facilitate its ingestion.
Pharynx - Muscular membranous channel connecting the nasal cavity
to the larynx and the oral cavity to the esophagus; it enables
breathing, ingestion of food and speech.
Esophagus - Muscular membranous channel of the anterior section of
the digestive tract; it allows food to reach the stomach.
Stomach - Dilated section of the digestive tract; it stores, stirs and
mixes food with the gastric juices it secretes before emptying it
into the duodenum.
Duodenum - Anterior section of the small intestine; secretions from
the liver and pancreas, as well as food partially digested in the
stomach, empty into it.
Pancreas - Digestive gland connected to the duodenum; produces
secretions and hormones (especially insulin).
Small intestine - Narrow section of the digestive tract, about 20 ft
long, between the stomach and cecum, where a part of
digestion and food absorption occurs.
Liver - Viscera secreting substances, including bile, that help digestion
and break up certain toxins contained in the blood.
Gallbladder - Small reservoir where bile secreted by the liver gathers
before emptying into the duodenum during digestion. Bile helps
in the digestion of fatty substances.
Jejunum - Middle section of the small intestine between the
duodenum and the ileum; the majority of nutrients are
absorbed here.
Ileum - Terminal part of the small intestine between the jejunum and
cecum.
Vecum - Anterior part of the large intestine; it receives food particles
from the ileum.
Vermiform appendix - Tubular extension of the cecum; this
appendage is occasionally the site of appendicitis, a severe
inflammation.
Large intestine - Last wide section of the digestive tract, about 5 ft
long, where the final stage of digestion and elimination of waste
occurs; it includes the colon and the rectum.
Ascending colon - First segment of the colon; it absorbs water from
food residue before it is excreted.
Transverse colon - Second segment of the colon (middle section of
the large intestine). The right colon (the ascending colon plus
half the transverse colon) mainly enables absorption of water.
Descending colon - Third segment of the colon; it stores waste
before it is eliminated.
Sigmoid colon - Fourth segment of the colon; it carries waste to the
rectum.
Rectum - Terminal section of the large intestine preceding the anus.
Anus - Terminal orifice of the digestive tube controlled by a sphincter
enabling ejection of fecal matter.
Sphincter muscle of anus - Muscle ensuring the contraction and
relaxation of the anus and enabling defecation.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Digestive System: Carbohydrate, Protein and Fat DigestionDocument45 pagesDigestive System: Carbohydrate, Protein and Fat DigestionhiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DiverticulitisDocument6 pagesNCP DiverticulitisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Topic-Nutrition (Extra Question) : Chapter - Life ProcessesDocument3 pagesTopic-Nutrition (Extra Question) : Chapter - Life Processes7A04Aditya MayankPas encore d'évaluation
- You Are What You EatDocument10 pagesYou Are What You EatsathishrajsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Mucus On Drug Transport and Its Potential To Affect Therapeutic OutcomesDocument16 pagesThe Role of Mucus On Drug Transport and Its Potential To Affect Therapeutic OutcomesSolcan RamonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology in MBBSDocument10 pagesPhysiology in MBBSPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- ICD-10 v2007Document1 097 pagesICD-10 v2007Glessica YouPas encore d'évaluation
- AmavataDocument14 pagesAmavataSamhitha Ayurvedic ChennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rat Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesRat Digestive SystemAnkit NariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cheng Man-Ching 37 Tai Chi Form PDFDocument3 pagesCheng Man-Ching 37 Tai Chi Form PDFAlbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Questions For Microboilogy, Virology 2022-2023Document10 pagesExam Questions For Microboilogy, Virology 2022-2023Amirus RussPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalDocument6 pages7.1 7.2 Animal Nutrition Alimentary CanalgesPas encore d'évaluation
- Grdds ReviewDocument33 pagesGrdds ReviewvaibhavbpatelPas encore d'évaluation
- ART230 Summary 9Document5 pagesART230 Summary 9Joseph SibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Git System (Gastroinstestinal Tract)Document37 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Git System (Gastroinstestinal Tract)Nishi RuciPas encore d'évaluation
- Postmortem and Antemortem InspectionDocument10 pagesPostmortem and Antemortem InspectionNarmadhaa AiswaaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- FeasibilityDocument5 pagesFeasibilityDiana RejanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes by CatheyDocument27 pagesEnzymes by CatheyChad Ashley VandenbergPas encore d'évaluation
- Package Leaflet SulfaguanidinDocument4 pagesPackage Leaflet SulfaguanidinddubokaPas encore d'évaluation
- NEC-Microbioma, Metaboloma y Mediadores Inflamatorios-SFNMDocument6 pagesNEC-Microbioma, Metaboloma y Mediadores Inflamatorios-SFNMlizmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestion and Absorption: SolutionsDocument12 pagesDigestion and Absorption: SolutionsSeekerPas encore d'évaluation
- Jackman2020 Article Medium-chainFattyAcidsAndMonogDocument15 pagesJackman2020 Article Medium-chainFattyAcidsAndMonogIgor BaltaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Grade BiologyDocument29 pages9th Grade BiologyNarendran Sairam93% (27)
- Advances in Microbial Ecology Volume 8Document315 pagesAdvances in Microbial Ecology Volume 8Fabio OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Elixir of LifeDocument124 pagesThe Elixir of LifejhPas encore d'évaluation
- Necrotic Enteritis in ChickensDocument3 pagesNecrotic Enteritis in ChickensHendra PranotogomoPas encore d'évaluation
- GIT Fluid BalanceDocument33 pagesGIT Fluid BalanceMaryPas encore d'évaluation
- JUNE 2003 Comprehensive Test IIIA Set A: B. "I Will Call My Doctor If Steven Has Persistent Vomiting and Diarrhea."Document20 pagesJUNE 2003 Comprehensive Test IIIA Set A: B. "I Will Call My Doctor If Steven Has Persistent Vomiting and Diarrhea."iamweena17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digestivesystem Demo Stem11Document71 pagesDigestivesystem Demo Stem11Kathrine BeldaPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Assessment - Lecture: Musculoskeletal SystemDocument21 pagesHealth Assessment - Lecture: Musculoskeletal SystemphoebePas encore d'évaluation