Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP CASE STUDY - Acute Pyelonephritis
Transféré par
yasiraTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP CASE STUDY - Acute Pyelonephritis
Transféré par
yasiraDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
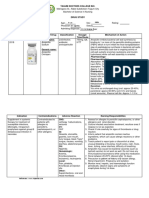
NURSING CARE PLAN
NURSING CARE PLAN- 1
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
Subjective: Acute Pain r/t At the end INDEPENDENT Goal met
acute of 8 hour 1. Established rapport. as
katong na inflammation of shift, Rationale: To get patients cooperation. evidenced
admit ko kay renal tissues patient by
sakit kaayo secondary to will: 2. Monitored VS. decreased
akong kilid acute Rationale: To have baseline data. pain scale
as verbalized pyelonephritis - report from 8/10
by the decreased 3.Assessed for referred pain, as to 2/10
patient pain scale appropriate
from 8/10 Rationale: To help determine possibility
Objective: to 2/10 of underlying condition or organ
dysfunction requiring treatment.
- (+) Facial - (-) facial
grimace, grimace 4. Accepted clients description of pain.
guarding and Rationale: Pain is a subjective
behavior guarding experience and cannot be felt by others.
behavior
- Pain scale 5. Observed non-verbal cues and pain
of 8/10 behaviors and other objective defining, as
noted.
Rationale: Observations may not be
congruent with verbal reports or may be
only indicator present when client is
unable to verbalize.
6.Provided comfort measures
Rationale: To promote non
pharmacological pain management.
7. Instructed in and encourage case of
relaxation techniques.
Rationale: To distract attention and
reduce tension.
8. encourage verbalization of feeling
about pain
Rationale: to evaluate coping abilities
and identify ideas of additional concern
9. Encouraged adequate rest period.
Rationale: To prevent fatigue that can
impair ability to manage pain.
DEPENDENT
10. Administered pain reliever as
necessary.
Rationale: To maintain acceptable level
of pain.
NURSING CARE PLAN- 2
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
Objective: Hyperthermia After 8 hours INDEPENDENT Goal met as
r/t infection of nursing 1. Established rapport. evidenced by
Temperature and intervention: Rationale: To get patients decreased
of 38.8 inflammatory cooperation. temperature
process - the from 38.8 to
skin is warm secondary to patients 2. Monitor white blood cell (WBC) 37.1, (-)
to touch acute temperature count chills
pyelonephritis will decrease Rationale: An increasing WBC count
(+) chills from 38.8 to indicates the bodys efforts to combat
37 pathogens; Very low WBC count may
urinalysis indicate a severe risk for infection.
shows WBC -the patient
count of will 3. Assess and monitor nutritional
16.61 (high) demonstrate status, weight, history of weight loss,
behaviors to and serum albumin.
promote Rationale: Patients with poor
normal body nutritional status may be anergic or
temperature unable to muster a cellular immune
response to pathogens making them
susceptible to infection.
4. Provide high caloric diet or as
indicated by the physician.
Rationale: To meet the metabolic
demand of client.
5. Monitor patients temperature and
note for presence of chills/ profuse
diaphoresis
Rationale: temperature of greater
than 37.7 (99.8 F) may indicate
infection; very high temperature
accompanied by sweating and chills
may indicate septicaemia.
6. Adjust and monitor environmental
factors like room temperature and
bed linens as indicated.
Rationale: Room temperature may
be accustomed to near normal body
temperature and blankets and linens
may be adjusted as indicated to
regulate temperature of client.
7. perform tepid sponge bath as
needed
Rationale: TSP promotes heat loss
and therefore decreasing body
temperature
8. Educate client of signs and
symptoms of hyperthermia and help
him identify factors related to
occurrence of fever; discuss
importance of increased fluid intake
to avoid dehydration.
Rationale: Providing health
teachings to client could help client
cope with disease condition and
could help prevent further
complications of hyperthermia
DEPENDENT
9. Administer antipyretics as ordered
Rationale: Antipyretics acts on the
hypothalamus, reducing
hyperthermia
10. Start intravenous normal saline
solutions or as indicated
Rationale: To replenish fluid losses
during shivering chills.
NURSING CARE PLAN- 3
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
subjective: Activity At the end of INDEPENDENT Goal met as
luya kay intolerance r/t 8 hour shift, 1. Established rapport. evidenced by
akong decreased patient will: Rationale: To get patients normal vital
paminaw, hemoglobin cooperation. signs and
murag kog secondary to - Patient will patient being
katulogun acute exhibit 2. Assess the physical activity level able to
pyelonephritis tolerance and mobility of the patient. perform ADL
during Rationale: Provides baseline independently
Objective: physical information for formulating nursing and makes
activity as goals during goal setting. use of energy
Low evidenced conservation
hemoglobin by being 3. Assess the patients nutritional techniques.
of 118 g/L able to status.
perform ADL Rationale: Adequate energy
Fatigue and with minimal reserves are needed during
lethargy or without activity.
assistance
4. Observe and monitor the patients
- Patient will sleep pattern and the amount of
use energy- sleep achieved over the past few
conservation days.
techniques. Rationale: Sleep deprivation and
difficulties during sleep can affect
the activity level of the patient
5. Assess the need for ambulation
aids (e.g., cane, walker) for ADLs.
Rationale: Assistive devices
enhance the mobility of the
patient by helping him overcome
limitations.
6. Establish guidelines and goals of
activity with the patient and/or SO.
Rationale: Motivation and
cooperation are enhanced if the
patient participates in goal setting.
7. Have the patient perform the
activity more slowly, in a longer
time with more rest or pauses, or
with assistance if necessary.
Rationale: Helps in increasing the
tolerance for the activity.
8. Gradually increase activity with
active range-of-motion exercises
in bed, increasing to sitting and
then standing.
Rationale: Gradual progression of
the activity prevents overexertion.
9. Encourage physical activity
consistent with the patients
energy levels.
Rationale: Helps promote a sense of
autonomy while being realistic
about capabilities.
10. Encourage active ROM
exercises. Encourage the patient
to participate in planning activities
that gradually build endurance.
Rationale: Exercise maintains
muscle strength, joint ROM, and
exercise tolerance. Physical
inactive patients need to improve
functional capacity through
repetitive exercises over a long
period of time.
NURSING CARE PLAN- 4
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
After 8 hours
Subjective: Risk for of nursing INDEPENDENT Goal met as
Impaired intervention: 1. Established rapport. evidenced by
Patient urinary Rationale: To get patients patient being
verbalized elimination r/t -the patient cooperation. able to
hapdus ug inflammation/ will be able maintain
sakit magihi irritation of to maintain a 2. Monitored VS. normal
bladder normal Rationale: To have baseline data. elimination
Objective: mucosa elemination pattern and
secondary to pattern 3. determine clients usual daily intake demonstrated
-High acute Rationale: to help determine level of behaviors and
creatinine pyelonephritis -the patient hydration techniques to
level of 167 will prevent
umol/L demonstate 4. ascertain clients previous pattern of urinary
techniques urine elimination infection
-Dysuria to prevent Rationale: for comparison with
urinary current situation
-Urinary infection 5. Encourage fluid intake of 2,000 to
frequency 3,000 mL of water per day, unless
contraindicated
Rationale: Fluids promote diluted
urine and frequent emptying of
bladder reducing the stasis of
urine and flushing
microorganisms
6. encourage client to verbalize fears
and concerns
Rationale: open expression allows
client to deal with feelings and
begin problem solving
7. check frequently for bladder
distention
Rationale: To reduce risk of infection
and/or autonomic hyperreflexia.
8. Instruct the female client to wipe the
area from front to back and the
avoidance of bath tubs.
Rationale: Proper perineal care helps
in minimizing the risk of
contamination and re-infection.
9. Encourage the client to void every
2-3 hours.
Rationale: To prevent the
accumulation of urine thus limiting
the number of bacteria.
10. Palpate the clients bladder every
4 hours.
Rationale: To determine the presence
of urinary retention.
NURSING CARE PLAN- 5
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation
Objective: Risk for At the end INDEPENDENT Goal met as
electrolyte of 8 hour 1. Established rapport. evidenced
Sodium level imbalance r/t shift, patient Rationale: To get patients cooperation. by patient
is 139 renal will: being able to
mmol/L dysfunction 2. Monitored VS. Maintain
secondary to - Maintain Rationale: To have baseline data. electrolyte
Potassioum acute electrolyte levels within
level is 4.19 pyelonephritis levels within 3. Assess level of consciousness and the normal
mmol/L the normal neuromuscular function, including limits and
limits sensation, strength, and movement. verbalized
Calcium level Rationale: Client is usually conscious interventions
is 1.22 - Identify and alert; however, muscular to promote
mmol/L health paresthesia, weakness, and flaccid balance.
situations paralysis may occur.
that
increase 4. Encourage frequent rest periods;
risk for assist with daily activities, as indicated.
electrolyte Rationale: General muscle weakness
imbalance decreases activity tolerance.
and
verbalize 5. Assess patients uid status
intervention Rationale: Patients who demonstrate
s to uid volume alterations are likely to
promote have electrolyte alterations as well
balance.
6. Monitor patient for physical signs of
electrolyte imbalance
Rationale: Many cardiac, neurological,
and musculoskeletal symptoms are
indicative of specic electrolyte
abnormalities.
7. Collect and evaluate serum
electrolyte results as ordered
Rationale: to allow for prompt diagnosis
and treatment of any abnormalities
8. Educate patient and family regarding
risks for electrolyte dis- turbances
associated with their particular medical
condition and possible interventions if
symptoms occur
Rationale: Early identication and inter-
vention may prevent life-threatening
complications of electrolyte imbalance.
9. Provide support and encouragement
to patient and family in their efforts to
participate in the management of the
condition.
Rationale: Positive feedback will
increase self-condence and feeling of
partnership in care
10. provide safe environment for the
patient
Rationale: Electrolyte imbalances can
cause poor coordination, weakness,
and altered gait.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Free Business Plan PresentationDocument49 pagesFree Business Plan Presentationhesziananda100% (4)
- Hunger Games ThesisDocument97 pagesHunger Games ThesisLadius PromtheusPas encore d'évaluation
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerPas encore d'évaluation
- Leaders Standard WorkDocument28 pagesLeaders Standard WorknklawPas encore d'évaluation
- R.K. Narayan Swami & FriendsDocument21 pagesR.K. Narayan Swami & FriendssriyazPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 HealthDocument42 pagesGrade 9 Healthapi-141862995100% (1)
- Academic LanguageDocument42 pagesAcademic LanguageJules Gajes50% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathySoniaMarieBalanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Sa PharmaDocument4 pagesDrug Study Sa PharmaKyle De Sagun Oteda100% (1)
- Fdar For UtiDocument2 pagesFdar For UtiCARL ANGEL JAOCHICOPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP NephrolithiasisDocument3 pagesNCP NephrolithiasisMANUEL EMERSONPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Manipulating Fast, and SlowDocument12 pagesManipulating Fast, and SlowThe Wilson Center100% (1)
- Clopidogrel - Drug StudyDocument1 pageClopidogrel - Drug StudyAcads usePas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPErl DrizPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoPas encore d'évaluation
- English, Analogy-Paired Approach Part 4: Suggested TechniqueDocument39 pagesEnglish, Analogy-Paired Approach Part 4: Suggested TechniquecellyPas encore d'évaluation
- Health TeachingsDocument7 pagesHealth Teachingstheamacias100% (2)
- NCP Acute Pain VaDocument3 pagesNCP Acute Pain VaKate ClarosPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraPas encore d'évaluation
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationllianPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (Post Op Exlap)Kay D. BeredoPas encore d'évaluation
- 4A CS File - Nursing Care of A Pregnant Family With Special Needs PDFDocument13 pages4A CS File - Nursing Care of A Pregnant Family With Special Needs PDFKimPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue NCP PediaDocument3 pagesDengue NCP Pediaraven riveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentJuliusSerdeñaTrapalPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocument8 pagesNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- Drug Study - BisacodylDocument4 pagesDrug Study - BisacodylKyla CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Pre Gabal in Drug StudyDocument1 pagePre Gabal in Drug StudyHailMarieSBarcenasPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Acute PainDocument1 pageNCP - Acute PainjsthrPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument26 pagesDrug Studyrn msnPas encore d'évaluation
- Iv Drip IsoxilanDocument1 pageIv Drip IsoxilannierbobierPas encore d'évaluation
- DeficientDocument2 pagesDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocument1 pageFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- HONRADO-Group 3 - Pedia NCPDocument7 pagesHONRADO-Group 3 - Pedia NCP2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezPas encore d'évaluation
- FDAR (After Tracheostomy)Document2 pagesFDAR (After Tracheostomy)Maribeth DantesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Database - Potassium CitrateDocument2 pagesDrug Database - Potassium CitrateReg LagartejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Analysis: Antituberculotic Agent Allergy To Aminoglycosides, Pregnancy, Lactation, Herpes Vacinia Fungal InfectionDocument1 pageDrug Analysis: Antituberculotic Agent Allergy To Aminoglycosides, Pregnancy, Lactation, Herpes Vacinia Fungal InfectionGeorge FogPas encore d'évaluation
- Date and Time Focus: D - Received Patient On BedDocument2 pagesDate and Time Focus: D - Received Patient On BedGraphaiene Neika WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Patty NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesPatty NCP HyperthermiaPatricia Jean FaeldoneaPas encore d'évaluation
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Document2 pagesSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- Rabies PJ NCPDocument3 pagesRabies PJ NCPFredrick PaderangaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Myoma 2003Document2 pagesNCP Myoma 2003grace ecм мendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dengue Discharge PlanDocument1 pageDengue Discharge PlanChris Denver BancalePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainDocument2 pagesNCP Wala Ako Ganang KumainAubrey RecierdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study NaclDocument3 pagesDrug Study NaclNicole Denise PortugalezaPas encore d'évaluation
- CatapresDocument1 pageCatapres去約翰Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJachel Kathleen LaguioPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YDocument1 pageDrug Mechanis MOF Action Indicatio N Contraindicatio N Side Effects Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilit YNica RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Actual and PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Actual and PotentialKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingPas encore d'évaluation
- FDAR Acute PainDocument1 pageFDAR Acute PainJayson OlilePas encore d'évaluation
- Ascorbic AcidDocument2 pagesAscorbic AcidJaymark Lambino100% (1)
- Definition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Case + Hyperthermia NCPCindy MariscotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Exit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseDocument2 pagesExit Ticket - Beth Taylor's CaseGayle RavanchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Crisostomo Soapie ChartingDocument2 pagesCrisostomo Soapie ChartingMica OmotsosircPas encore d'évaluation
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximekaijeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPArnold Christian QuilonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rice Is A Good Source of Calories, Carbs, Calcium, Iron, Thiamin, Pantothenic Acid, Folate, and Vitamin E, To Name A Few NutrientsDocument2 pagesRice Is A Good Source of Calories, Carbs, Calcium, Iron, Thiamin, Pantothenic Acid, Folate, and Vitamin E, To Name A Few Nutrientsmikhaela sencilPas encore d'évaluation
- Metoprolol TartrateDocument1 pageMetoprolol TartrateClifford Estilo100% (1)
- Drug Study - AmpicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Ampicillinliza sianPas encore d'évaluation
- Funda PosttestDocument11 pagesFunda PosttestRhea May Capor0% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervntion Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervntion Rationale EvaluationDeinielle Magdangal RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- SKYLA FIESTA NCP (Acute Pancreatitis)Document4 pagesSKYLA FIESTA NCP (Acute Pancreatitis)Skyla FiestaPas encore d'évaluation
- SGD Aa PDFDocument11 pagesSGD Aa PDFyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- City Real Estate Google Slides PresentationDocument36 pagesCity Real Estate Google Slides PresentationyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 2ndDocument17 pages2020 2ndyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Beta PowerPoint by GraphicpandaDocument26 pagesBeta PowerPoint by GraphicpandaAnggreanyAshariPas encore d'évaluation
- (Without Animation) Animated Timeline Free PowerPoint TemplateDocument22 pages(Without Animation) Animated Timeline Free PowerPoint TemplateAdarleny BrooksPas encore d'évaluation
- MOPI Kel 4Document37 pagesMOPI Kel 4Celia CeliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract Paper Idea Bulb Google Slides PresentationDocument36 pagesAbstract Paper Idea Bulb Google Slides PresentationAriefيوليانتوPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract Watercolored Splashes Google Slides ThemesDocument39 pagesAbstract Watercolored Splashes Google Slides ThemesputriPas encore d'évaluation
- REFERENCESDocument6 pagesREFERENCESyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Arrow Options Diagram For PowerPointDocument11 pagesFree Arrow Options Diagram For PowerPointyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract Paper Idea Bulb Google Slides PresentationDocument36 pagesAbstract Paper Idea Bulb Google Slides PresentationAriefيوليانتوPas encore d'évaluation
- Research PosterDocument1 pageResearch Posteryasira100% (1)
- Physio Tambis 1Document9 pagesPhysio Tambis 1yasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- RRL InsertDocument19 pagesRRL InsertyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tranzen1K BOIPEZADocument51 pagesTranzen1K BOIPEZAyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Katona Et Al (2011) - Factors Influencing Adolescent Blood Pressure PDFDocument9 pagesKatona Et Al (2011) - Factors Influencing Adolescent Blood Pressure PDFyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1 PrehypertensionDocument15 pagesGroup 1 PrehypertensionyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- KimDocument2 pagesKimyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Age and AlcoholDocument2 pagesAge and AlcoholyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Check List: Your Title Text HereDocument2 pagesCheck List: Your Title Text HereyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Association of Sleep Duration PDFDocument6 pagesAssociation of Sleep Duration PDFyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Association of Sleep Duration PDFDocument6 pagesAssociation of Sleep Duration PDFyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereDocument2 pagesCommunicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Location - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryDocument2 pagesLocation - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Neural Network - Your Text HereDocument2 pagesNeural Network - Your Text HereyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Design - : Your Text HereDocument2 pagesDesign - : Your Text HereyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 SlidesDocument2 pages2 SlidesyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 SlidesDocument2 pages2 SlidesyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Diversity 3rd Edition Barak Test BankDocument8 pagesManaging Diversity 3rd Edition Barak Test Bankjamesstokesmfyqdrocjp100% (32)
- Signing The Way?Document3 pagesSigning The Way?Speech & Language Therapy in PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminary Business Studies - Mindmap OverviewDocument1 pagePreliminary Business Studies - Mindmap OverviewgreycouncilPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Level Ii PDFDocument11 pagesBook Level Ii PDFMaria Alvarez AmayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Black+Box+Thinking+-+Matthew+SyedDocument16 pagesBlack+Box+Thinking+-+Matthew+Syedjasmine19jhsPas encore d'évaluation
- Essays For Academic WritingDocument79 pagesEssays For Academic Writingasma rajabPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior Seminar ProposalDocument10 pagesSenior Seminar Proposalapi-445921937Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Customer Satisfaction at 5 Floor Beauty SalonDocument40 pagesMeasuring Customer Satisfaction at 5 Floor Beauty SalonIsha MohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nepf Teacher Professional Responsibilities Rubric With EvidDocument16 pagesNepf Teacher Professional Responsibilities Rubric With Evidapi-278277795Pas encore d'évaluation
- TKT Module 1 Task Type 1 Introduction To Matching Tasks PDFDocument10 pagesTKT Module 1 Task Type 1 Introduction To Matching Tasks PDFRachel Maria RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Total Quality Management in Organizational Performance Oil Company Case in JordanDocument15 pagesImpact of Total Quality Management in Organizational Performance Oil Company Case in JordanDicky Ahmad SolihinPas encore d'évaluation
- Letter of Rec Daniel SpalingerDocument1 pageLetter of Rec Daniel Spalingerapi-334508830Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 7 Assignment 7Document9 pagesModule 7 Assignment 7api-448231075Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 SHort Essay - Ryan WongDocument2 pagesWeek 1 SHort Essay - Ryan WongRyan WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Vs DeductiveDocument2 pagesInductive Vs Deductivemnizamuddin1975Pas encore d'évaluation
- EDU 3020 JY01 J12SU QE Educational PsychologyDocument13 pagesEDU 3020 JY01 J12SU QE Educational Psychologyrachna357Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sesi 4 Systems ThinkingDocument35 pagesSesi 4 Systems ThinkingNur Fadly IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- The Attitude of Female Mass Communication Students Towards Journalism As A CareerDocument44 pagesThe Attitude of Female Mass Communication Students Towards Journalism As A CareerHaryour Bar Miey86% (7)
- Brand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesBrand Loyalty and Customer Loyalty QuestionnaireAnonymous GhyLaqEcUUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Log Book1Document11 pagesSample Log Book1RumSup MusPas encore d'évaluation
- Literacy UnitDocument8 pagesLiteracy Unitapi-463933980Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Become An Outstanding TeacherDocument4 pagesHow To Become An Outstanding Teacherapi-249997132Pas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Portfolio ENG 102Document10 pagesMidterm Portfolio ENG 102colehyatt5Pas encore d'évaluation