Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
My Country, The Philippines An Introduction: Official Name: REPUBLIKA NG PILIPINAS (Republic of The Philippines)
Transféré par
Mhayne Dumpas0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues3 pagesPhilippines With Region
Titre original
Philippines
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPhilippines With Region
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues3 pagesMy Country, The Philippines An Introduction: Official Name: REPUBLIKA NG PILIPINAS (Republic of The Philippines)
Transféré par
Mhayne DumpasPhilippines With Region
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
My Country, The Philippines
An Introduction
Official Name: REPUBLIKA NG PILIPINAS (Republic of the Philippines)
Titles Associated with the Philippines: "Cradle of Heroes and Heroines,"
"Pearl of the Orient Seas," "Gems of the East" and "Land of the Morning"
Map of the Philippines (Creative Commons Photo,
Courtesy of Eugene Alvin Villar or "Seav" on Wkipedia)
Location and Physical Description. The Philippines is located in
Southeast Asia. It is an archipelagic nation of more than 7,100 islands and
islets. It is surrounded by three bodies of water. On the east, it is bounded
by the Philippine Sea; on the south, it is bounded by the Celebes Sea; and
on the west and north, it is bounded by the South China Sea. The islands
and islets are grouped into three: Luzon, which is the biggest island group,
Visayas and Mindanao. Located in Luzon is Manila, the capital of the
Philippines. Located in Luzon, too, is Quezon city, the most populated city
in the Philippines and the city which was created by Commonwealth
President Manuel L. Quezon for the ordinary people so that they can live
with dignity. In terms of land area, the biggest city is Davao, which is
located in Mindanao.
Government. The Philippines adopts the democratic form of government
based on the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines (constitutional
democracy). This form of government has three branches, namely:
executive, legislative and judicial. The executive branch is composed of the
president and his or her cabinet; the president is the country's head of
state. The legislative branch (Philippine Congress) is composed of the
senators and congressional district and party-list representatives. The
senators belong to the upper house (Senate) while the congressional
district and party-list representatives make up the lower house (House of
Representatives). The Senate and the House of Representatives form the
bicameral legislature or congress. The judicial branch is composed of the
chief justice, associate justices and all the judges and members of the
various courts. The Supreme Court, which is composed of the chief justice
and associate justices, heads the judiciary, and judicial power resides in
the Supreme Court and all the lower courts as provided by law.
Socio-Political Structure. Essentially, the existing socio-political
structure in the Philippines is barangay-based (community-based). A
barangay (community) or a barrio (village) elects its barangay captain and
councilors who will manage the socio-political affairs of the barangay as
provided by law. A group of communities constitutes a municipality, a town
or a city which is headed by its duly-elected mayor and officers. A group of
municipalities and towns comprises a district whose constituents elect a
person who will represent the district in the House of Representatives. (The
city, by itself, consists of two or more congressional districts.) A bigger
group of municipalities and towns constitutes a province (state) whose
constituents elect the governor and vice-governor for the province while
the entire Filipino voters elect the senators, vice-president and president of
the Philippines.
Languages and Dialects. The national language of the Philippines is
Filipino, although the official languages are Filipino and English. These
official languages are also the media of instruction in schools. Two other
foreign languages --- Spanish and Arabic --- are to be promoted on a
voluntary and optional basis as stated in the Philippine Constitution of
1987. There are many regional languages (dialects) and these languages
are the auxiliary official languages which can be used in schools for the
purpose of enhancing and facilitating the learning process. There are eight
major dialects and these are: Bikol (Bikolano), Cebuano, Hiligaynon
(Ilonggo), Ilocano, Pampango (Kapampangan), Pangasinense, Tagalog and
Waray-Waray.
Language Info: The national language of the Philippines is Filipino, yet it is
the third largest English-speaking country in the world.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ten Best Conspiracy Websites Cabaltimes - Com-8Document8 pagesTen Best Conspiracy Websites Cabaltimes - Com-8Keith KnightPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Legal Research: Milagros Santos-OngDocument33 pagesPhilippine Legal Research: Milagros Santos-OngmikePas encore d'évaluation
- LEGAL RESEARCH by MILAGROS ONG - 1Document93 pagesLEGAL RESEARCH by MILAGROS ONG - 1Jay Tee100% (1)
- Civil Rights Movement in The USA in The 1950s and 1960sDocument20 pagesCivil Rights Movement in The USA in The 1950s and 1960sitsduhtomPas encore d'évaluation
- Client Services AgreementDocument2 pagesClient Services AgreementMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activity Sheet in Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 2 - MELC 1 To 3Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 2 - MELC 1 To 3Esther Ann Lim100% (2)
- Alpha Phi Omega PhilippinesDocument15 pagesAlpha Phi Omega PhilippinesRerbefNivra100% (1)
- The 1935 Philippine ConstitutionDocument17 pagesThe 1935 Philippine Constitutionkfbrand71100% (8)
- Toxic Charity: How Churches and Charities Hurt Those They Help (And How To Reverse IT)Document14 pagesToxic Charity: How Churches and Charities Hurt Those They Help (And How To Reverse IT)CCUSA_PSMPas encore d'évaluation
- Indigenous People in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesIndigenous People in The Philippinesabcde100% (1)
- JessaPP 1Document43 pagesJessaPP 1Nicolle Anne SartePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Line GraphDocument14 pagesLesson Plan Line GraphMhayne Dumpas100% (2)
- Constitutions of The Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionDocument18 pagesConstitutions of The Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionJoan Mila CoPas encore d'évaluation
- English in MalaysiaDocument8 pagesEnglish in MalaysiaIntan A BaizuraPas encore d'évaluation
- PreambleDocument12 pagesPreambleMary Grace PalmeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Irrational Numbers Are Non-Terminating, Non-Repeating DecimalsDocument2 pagesIrrational Numbers Are Non-Terminating, Non-Repeating DecimalsWilston BryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Philippine HistoryDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Philippine Historybatutascribd100% (1)
- Chapter 1: The Philippines and It'S People: Kilometers, 200 Nautical Miles From The ShoresDocument6 pagesChapter 1: The Philippines and It'S People: Kilometers, 200 Nautical Miles From The ShoresRussel BartolomePas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines History and Public ServiceDocument75 pagesPhilippines History and Public ServiceJP FūlgëncîöPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Philippine HistoryDocument66 pagesIntro To Philippine HistorymaricrisandemPas encore d'évaluation
- UPDATE: Philippine Legal Research: Milagros Santos-Ong Milagros Santos-OngDocument36 pagesUPDATE: Philippine Legal Research: Milagros Santos-Ong Milagros Santos-OngEis Pattad MallongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comm 5Document4 pagesComm 5oz asier cyrusPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines SymbolDocument30 pagesPhilippines SymbolJeru ElbanbuenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Political System and Structure NotesDocument18 pagesComparative Political System and Structure NotesDonnaBergadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Filipino Culture 2007 National Census: Ilocano, Pampango, Pangasinense, Tagalog, and WarayDocument1 pageFilipino Culture 2007 National Census: Ilocano, Pampango, Pangasinense, Tagalog, and WarayKevinRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Civic 1correctedDocument28 pagesCivic 1correcteddnnspetroPas encore d'évaluation
- Social StudiesDocument4 pagesSocial StudiesPaye BagnonPas encore d'évaluation
- 1935 CONSTITUTION - Dacumos and ValdezDocument20 pages1935 CONSTITUTION - Dacumos and ValdezBJ AmbatPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Legal Research: by Milagros Santos-OngDocument46 pagesPhilippine Legal Research: by Milagros Santos-Ongxeileen08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Script For The 1987 Philippine Constitution (30-Minute Video)Document13 pagesScript For The 1987 Philippine Constitution (30-Minute Video)Iana VivienPas encore d'évaluation
- Nava History Reflection PaperDocument5 pagesNava History Reflection PaperAnonymous QmnYZ5IXJIPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Government History: PhilippinesDocument17 pagesLocal Government History: PhilippinesHaRry PeregrinoPas encore d'évaluation
- UPDATE Philippine Legal Research PDFDocument35 pagesUPDATE Philippine Legal Research PDFademarPas encore d'évaluation
- CLJ 211 Project - OsilaDocument21 pagesCLJ 211 Project - OsilaJhon Louie LejanioPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines Vs SingaporeDocument11 pagesPhilippines Vs SingaporeDanah Mae EmanigPas encore d'évaluation
- Civics Notes Form OneDocument35 pagesCivics Notes Form OneIsraelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Socio-Cultural Situation in The PhilipinesDocument6 pagesThe Socio-Cultural Situation in The PhilipinesIemanzNoerPas encore d'évaluation
- Government of The PhilippinesDocument6 pagesGovernment of The PhilippinesChristine Mae Bansagale MarbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Civics NotesDocument44 pagesCivics Notesthomaspodo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- The National Legal SystemDocument28 pagesThe National Legal SystemLeslie SilverioPas encore d'évaluation
- Propose Federal-Parliamentary Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionDocument45 pagesPropose Federal-Parliamentary Republic of The Philippines ConstitutionCarlo Jose BactolPas encore d'évaluation
- Chu ChuchuDocument5 pagesChu ChuchuAldwin Briones BaylonPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesACTIVITYJoan Besa BasmayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 - Factual and SubjectiveDocument19 pagesWeek 1 - Factual and SubjectiveSophia EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Religion in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageReligion in The PhilippinesLyka ZorillaPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 1 Pre Colonial Political SystemDocument18 pagesWEEK 1 Pre Colonial Political SystemERNEST JUSTICEPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippines: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesPhilippines: Republic of The PhilippinesNigel SamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Speech of Pres QuezonDocument2 pagesSpeech of Pres Quezonjanice curagPas encore d'évaluation
- Civics Notes Form 1 - UnlockedDocument38 pagesCivics Notes Form 1 - UnlockedNyomenda Jamhuri William100% (1)
- History 3Document8 pagesHistory 3Janelle Chin MesamenPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2 Citizenship TrainingDocument29 pagesGroup 2 Citizenship TrainingJovillePas encore d'évaluation
- Group 8 LaosDocument7 pagesGroup 8 Laosjg09104350605Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 National Legal SystemDocument15 pages2 National Legal SystemPearl Nathalie S. PabalanPas encore d'évaluation
- Conclusion: Philippine HistoryDocument4 pagesConclusion: Philippine Historyian jay ranadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modules - 6-10 SS4Document50 pagesModules - 6-10 SS4Reign ManesePas encore d'évaluation
- The Legislative: Reported By: Group 3Document42 pagesThe Legislative: Reported By: Group 3Hpesoj SemlapPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine ArchitectureDocument30 pagesPhilippine ArchitectureIrrah AlvaranPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 The Contemporary World Lesson 4 Unit 2 Activity 4Document4 pages7 The Contemporary World Lesson 4 Unit 2 Activity 4Dianne RubicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Civics 1Document35 pagesCivics 1dnnspetroPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTP Citizenship Training (Final)Document17 pagesNSTP Citizenship Training (Final)sammy greyPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Constitution of The Phil. (Reaction Paper)Document3 pages5 Constitution of The Phil. (Reaction Paper)Christine Segovia IsaacPas encore d'évaluation
- Brief History of PhilippinesDocument10 pagesBrief History of PhilippinesFlorifel Eugenio TadeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Provisions in The Malaysian ConstitutionDocument50 pagesImportant Provisions in The Malaysian ConstitutionSammie Ping50% (2)
- BP 4Document9 pagesBP 4Lovely De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- BP 4Document9 pagesBP 4Lovely De CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Legal SystemDocument24 pagesPhilippine Legal SystemKhristian Joshua G. JuradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Part Time Job!!!: 2 To 3 Hours Per Day or Through Saturday and SundayDocument1 pagePart Time Job!!!: 2 To 3 Hours Per Day or Through Saturday and SundayMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Form: Professional Regulation CommissionDocument1 pageApplication Form: Professional Regulation CommissionMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mrrd-Necc: Region - IX Labason ChapterDocument2 pagesMrrd-Necc: Region - IX Labason ChapterMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chicken and Pork AdoboDocument4 pagesChicken and Pork AdoboMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Migration Theory: Java Man Peking ManDocument3 pagesMigration Theory: Java Man Peking ManMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- FamilyDocument3 pagesFamilyMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal's SurnameDocument5 pagesRizal's SurnameMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- The First FilipinoDocument4 pagesThe First FilipinoMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lumad Oct 2016 Sample Letter 0Document2 pagesLumad Oct 2016 Sample Letter 0Mhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
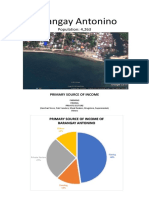
- Barangay Antonino: Population: 4,263Document10 pagesBarangay Antonino: Population: 4,263Mhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Episode 1: Your TargetDocument17 pagesEpisode 1: Your TargetMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NGDocument2 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NGMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- DILP Beneficiary ProfileDocument1 pageDILP Beneficiary ProfileMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Deaf President Named School Yields To Protests: Education NewsDocument2 pagesDeaf President Named School Yields To Protests: Education NewsMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental ProblemsDocument17 pagesEnvironmental ProblemsMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesNarrative ReportMhayne DumpasPas encore d'évaluation
- Youth Ambassadors TOR 2017-2019Document11 pagesYouth Ambassadors TOR 2017-2019Steven PalmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Leader Analysis-John MackeyDocument8 pagesLeader Analysis-John Mackeyapi-272623096Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intersectionality 101 PDFDocument17 pagesIntersectionality 101 PDFAlex BurkePas encore d'évaluation
- Tan MalakaDocument10 pagesTan MalakaLaksita NirmalasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Parents Teacher FeedbackDocument2 pagesParents Teacher FeedbackAditri ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Cultural and Trade Change Define This PeriodDocument18 pagesCultural and Trade Change Define This PeriodJennifer HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Advancing Youth Civic Engagement and Human RightsDocument88 pagesAdvancing Youth Civic Engagement and Human RightsDoug Ragan100% (1)
- BIOGRAFI (Sastra Inggris)Document8 pagesBIOGRAFI (Sastra Inggris)Ananda WindyariPas encore d'évaluation
- Buku Referensi RSMDocument2 pagesBuku Referensi RSMActiriyama SolihunPas encore d'évaluation
- Dhs Resultcum MeritDocument79 pagesDhs Resultcum Meritranjit88177Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3 Pme Hss1021Document3 pagesAssignment 3 Pme Hss1021Suraj PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comments From "Acknowledge That Aboriginals Were Victims of Genocide by The Federal Government"Document14 pagesComments From "Acknowledge That Aboriginals Were Victims of Genocide by The Federal Government"Ed TanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 JPRDocument10 pagesChapter 21 JPRMatchu VillarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Power and PoliticsDocument23 pagesPower and PoliticsfrisbeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Agueda KahabaganDocument2 pagesAgueda KahabaganKris LynnPas encore d'évaluation
- KABANATA 1 - Batas RizalDocument31 pagesKABANATA 1 - Batas Rizalthurd Digital CreativesPas encore d'évaluation
- We Shall Never Surrender - ChurchillDocument3 pagesWe Shall Never Surrender - ChurchillSachie1912Pas encore d'évaluation
- The History of Killa Saifullah (Zhob)Document2 pagesThe History of Killa Saifullah (Zhob)Killa Saifullah or Qilla SaifullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Power and The Rulling ClassesDocument399 pagesPower and The Rulling ClassesJuan FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- MGCBRNhtatore 001 Data 421Document318 pagesMGCBRNhtatore 001 Data 421nishantPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Freedom of ExpressionDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Freedom of ExpressionHussain Mohi-ud-Din QadriPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics IntroDocument2 pagesEthics IntroExekiel Albert Yee TulioPas encore d'évaluation
- Eo 11478Document3 pagesEo 11478Marla BarbotPas encore d'évaluation
- The Left Side of History by Kristen GhodseeDocument21 pagesThe Left Side of History by Kristen GhodseeDuke University Press100% (3)
- Communists Take Power in China PDFDocument2 pagesCommunists Take Power in China PDFDianePas encore d'évaluation