Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
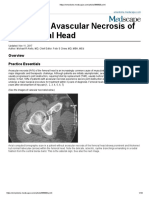
AVN Femoral Head - Causes and Diagnosis
Transféré par
Kim RamosTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AVN Femoral Head - Causes and Diagnosis
Transféré par
Kim RamosDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MUSCULAR SYSTEM 4 Introduction to Lower membrane.
As long as the epiphyseal cartilage remains, no
Extremities communication occurs between the two sources of blood. In
Gluteal Region, Posterior thigh, Hip Joint, the adult, after the epiphyseal cartilage disappears, an anastomosis
Posterior Thigh between the two sources of blood supply is established. Fractures of
Popliteal Fossa, Posterior Leg, Sole of Foot
the femoral neck interfere with or completely interrupt the blood
supply from the root of the femoral neck to the femoral head. The
Hip Joint scant blood flow along the small artery that accompanies the round
ligament may be insufficient to sustain the viability of the femoral
3. Discuss avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
head, and ischemic necrosis gradually takes place.
4. Show radiographs of normal hip joint.
Causes & Riskfactors:
Definition:
Area not receiving sufficient blood supply atraumatic causes/risk factors include the following
Cell Death due to ischemia
Excessive corticosteroid usage and alcohol
abuse account for as many as 90% of new cases.
Anatomic knowledge of the blood supply to the femoral head
Intravascular coagulation appears to be the
explains why avascular necrosis of the head can occur after
central event associated with nontraumatic AVN.
fractures of the neck of the femur. In the young, the epiphysis
(See also the Medscape Reference article
of the head is supplied by a small branch of the obturator artery, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation.)
which passes to the head along the ligament of the femoral head.
Coagulation may occur secondary to
The upper part of the neck of the femur receives a profuse blood
extravascular compression (eg, marrow fat
supply from the medial femoral circumflex artery. These branches
enlargement), vessel wall injury (eg,
pierce the capsule and ascend the neck deep to the synovial
chemotherapy, radiation), or a thromboembolic
event (eg, fat emboli).
Ischemic insult to the femoral head results in
infarcted subchondral bone. In this situation,
weakened and unrepaired necrotic bony
trabeculae fail under a compressive load,
leading to subchondral collapse (ie, crescent
sign) and, ultimately, articular collapse.
Traumatic causes of femoral head AVN include the
following:Femoral neck fractures Hip dislocation
Diagnostic Procedures:
MRI,X-Ray & Staging: Ficat 0-6, CT SCAN & Xrays
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cerebral Blood Flow and Pathophysiology: The Vascular SystemDocument3 pagesCerebral Blood Flow and Pathophysiology: The Vascular SystemJerome ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- Imaging in Avascular Necrosis of The Femoral HeadDocument44 pagesImaging in Avascular Necrosis of The Femoral Headmichaelhtun100% (1)
- CvaDocument11 pagesCvaNilo Carmelo LumanogPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's HospitalDocument152 pagesDR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's Hospitalagnes trianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Anatomy of the Head and NeckDocument9 pagesApplied Anatomy of the Head and NeckdivinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patterns of neuronal injury and markers of CNS pathologyDocument31 pagesPatterns of neuronal injury and markers of CNS pathologydenekePas encore d'évaluation
- VascularDocument3 pagesVascularalmira.s.mercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Pathology: Ronald C. KimDocument22 pagesSpinal Cord Pathology: Ronald C. KimGerardo SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's HospitalDocument152 pagesDR Zameer Ali ST Stephen's Hospitalagnes trianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurologic Conditions 4 StrokeDocument4 pagesNeurologic Conditions 4 StrokeEdward De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaDocument4 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid RhinorrheaUlises VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Review ArticleDocument10 pagesSpinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Review ArticleMeiriyani LembangPas encore d'évaluation
- SUBarachnoid HemorrhageDocument4 pagesSUBarachnoid Hemorrhagekhadzx100% (2)
- Clinical Anatomy of Spinal Cord and Nerve InjuriesDocument18 pagesClinical Anatomy of Spinal Cord and Nerve InjuriesSamia AsgharPas encore d'évaluation
- UW ObjectivesDocument171 pagesUW ObjectivesCarolina Lopez0% (1)
- PathoBCA CNSBonesWBC VisionDocument14 pagesPathoBCA CNSBonesWBC VisionNicole SarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue Boxes For Head and NeckDocument11 pagesBlue Boxes For Head and NeckhajajyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Fractures MRCSDocument4 pagesHip Fractures MRCSBlessing NdlovuPas encore d'évaluation
- Blumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 pagesBlumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryMeeraPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Shift CA Sources (Snell)Document6 pages1st Shift CA Sources (Snell)ernignacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Herniation Why Anterior ThoracicDocument5 pagesSpinal Cord Herniation Why Anterior ThoracicShahid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cauda Equina SyndromeDocument15 pagesCauda Equina SyndromeAdhi Surya NegaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Intracranial HypotensionDocument17 pagesIntracranial HypotensionNikhil TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cauda Equina and Conus Medullaris SyndromesDocument14 pagesCauda Equina and Conus Medullaris SyndromesPedro Alejandro Leon AlbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Injury PathologyDocument12 pagesHead Injury Pathologyimilosavljev@gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Layers of the Scalp and their Clinical ImplicationsDocument54 pagesLayers of the Scalp and their Clinical Implicationscristelbwee100% (2)
- InTech-Central Nervous System Vascular MalformationsDocument33 pagesInTech-Central Nervous System Vascular MalformationsmichiparisPas encore d'évaluation
- Avascular Necrosis: DR Sagar B Jaiswal JR 3 Ortho Unit "A" SSG Hospital VadodaraDocument112 pagesAvascular Necrosis: DR Sagar B Jaiswal JR 3 Ortho Unit "A" SSG Hospital VadodarasoraniphonePas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Fracture 3fDocument22 pages5-Fracture 3fRadwa TalaatPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotator Cuff TearsDocument5 pagesRotator Cuff TearsdrjorgewtorresPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument32 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjuriesPrincy VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Applied AnatomyDocument2 pagesApplied AnatomyAanavi MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Carotid Artery DiseaseDocument48 pagesCarotid Artery DiseaseAdeleye John AdebolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulnar Nerve AnatomyDocument7 pagesUlnar Nerve AnatomyAndrea AlavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Head & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFDocument113 pagesHead & Neck Notes For E-3 PDFPranavPas encore d'évaluation
- Subdural HematomaDocument5 pagesSubdural Hematomaluisse ann100% (1)
- Nuero - Brain HerniationDocument87 pagesNuero - Brain Herniationapi-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Canal Stenosis - ERHDocument56 pagesCanal Stenosis - ERHAries RHPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip JointDocument40 pagesHip Jointafeefa.gbgPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Subdural Hematoma Causes and PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAcute Subdural Hematoma Causes and PathophysiologyAngga ToragarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Atherosclerotic DiseaseDocument22 pagesPeripheral Atherosclerotic DiseaseSaleh Mohammad ShoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- CT ScanDocument84 pagesCT ScanHafiz Wajid SadiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Savitz 2005Document9 pagesSavitz 2005maria wahyuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Management of Spinal TuberculosisDocument51 pagesEpidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Management of Spinal TuberculosisLusiana PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCentral Nervous SystemMiguel Ashi GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 0019 2A Neurologia AngolDocument2 pages0019 2A Neurologia AngolMuhammad Ivan KurniawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysms: PerspectiveDocument4 pagesRuptured Cerebral Aneurysms: PerspectiveDini NanamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis - An Overview.Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis - An Overview.claudio RivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentDocument7 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke: Etiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnostics, TreatmentAfrah AbdulPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Arthroscopy in Staging Avascular Necrosis of The Femoral HeadDocument29 pagesHip Arthroscopy in Staging Avascular Necrosis of The Femoral HeadmichaelhtunPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia Regional y Sindrome Compartamental Nov 21Document5 pagesAnesthesia Regional y Sindrome Compartamental Nov 21ema moralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Aco071 020dDocument11 pagesAco071 020ddila cantikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Causes, Risks & TreatmentDocument53 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: Causes, Risks & TreatmentJulia Salvio50% (2)
- Neurosurgical EmergenciesDocument25 pagesNeurosurgical EmergenciesFarah Wahidah Abd RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Recall Vascular SurgeryDocument28 pagesSurgical Recall Vascular SurgeryAltariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parotid Gland: LocationDocument111 pagesParotid Gland: LocationFarah FarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Anatomy and Physiology VocabularyDocument13 pagesIntro To Anatomy and Physiology Vocabularywiredpsyche100% (1)
- Hip JointDocument38 pagesHip JointGaaga BritishPas encore d'évaluation
- 32999Document4 pages32999Kim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - Math in Our WorldDocument4 pagesAssignment - Math in Our WorldKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning and Teaching 3 PDFDocument63 pagesLearning and Teaching 3 PDFKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Adrenergic PharmaDocument29 pages2 - Adrenergic PharmaKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyspnea and Hypoxia (MMGP)Document7 pagesDyspnea and Hypoxia (MMGP)Kim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PATHO 2b - Repair - Dr. BailonDocument9 pages1 PATHO 2b - Repair - Dr. BailonKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Sem. Neuroana CDocument27 pages2nd Sem. Neuroana CKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Control or Prevention of Identified BiasesDocument1 pageControl or Prevention of Identified BiasesKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Research On Problems of The Dialysis Patient: FormedDocument2 pagesResearch On Problems of The Dialysis Patient: FormedKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Mayosi PenicllinDocument31 pagesB. Mayosi PenicllinKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis PDFDocument21 pages1 - Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis PDFKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Puerperium and AnalgesiaDocument12 pagesPuerperium and AnalgesiaKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Methods GuideDocument35 pagesSampling Methods GuideKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd MNC Meeting, May 3, 2018Document11 pages3rd MNC Meeting, May 3, 2018Kim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- XBs and OxidantsDocument6 pagesXBs and OxidantsKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- InstructionsDocument1 pageInstructionsKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ExamDocument2 pagesLab ExamKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaction Paper On Unethical Experiments' Painful Contributions To Today's MedicineDocument2 pagesReaction Paper On Unethical Experiments' Painful Contributions To Today's MedicineKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- (Pharma-B) 6s-1-Draft - Experiment C & eDocument3 pages(Pharma-B) 6s-1-Draft - Experiment C & eKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- ParaDocument7 pagesParaKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Adaptation, Injury and Death PathologyDocument10 pagesCell Adaptation, Injury and Death PathologyKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia G&DDocument2 pagesPedia G&DKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Y2 NS2 4th Exam ReviewerDocument17 pagesY2 NS2 4th Exam ReviewerKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Opioids and synthetic analgesicsDocument4 pagesOpioids and synthetic analgesicsKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- NS 2 3rd Shift - RAMOSDocument3 pagesNS 2 3rd Shift - RAMOSKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Fetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFDocument10 pagesFetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY- SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGIC OBSTETRICS LONG EXAMDocument9 pagesCENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY- SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGIC OBSTETRICS LONG EXAMKim Ramos100% (1)
- Quizzes: Lab. Examsd and F Cardiovascular and Git Expts. On Herbal PlantsDocument2 pagesQuizzes: Lab. Examsd and F Cardiovascular and Git Expts. On Herbal PlantsKim RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Botox 2017 PDFDocument244 pagesBotox 2017 PDFDyah Ayu Putri Midiantari50% (2)
- Daftar PustakaDocument6 pagesDaftar Pustakasatria divaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenDocument1 pagePneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Assess Hip Labral ODLICNODocument24 pagesTest Assess Hip Labral ODLICNOturbobrikPas encore d'évaluation
- Ross University 2010-2011 Pre-Residency Planning GuideDocument61 pagesRoss University 2010-2011 Pre-Residency Planning GuidescatteredbrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Bowel Preparation Colon ResectionDocument28 pagesBowel Preparation Colon ResectioncristiangallardovPas encore d'évaluation
- HaritakiDocument3 pagesHaritakirathan15Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Privileges and Duties of Registered Medical Practitioners - PDF 27777748Document6 pagesThe Privileges and Duties of Registered Medical Practitioners - PDF 27777748innyPas encore d'évaluation
- Medication Error Reporting FormDocument2 pagesMedication Error Reporting Formahmad ganiePas encore d'évaluation
- Seven Principles of Building ResilienceDocument7 pagesSeven Principles of Building ResiliencemilosvblPas encore d'évaluation
- TERRUR 1st VerDocument16 pagesTERRUR 1st VerJerome JeremiasPas encore d'évaluation
- TrichDocument30 pagesTrichwadige4668Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Personality in Sport and Physical ActivityDocument7 pagesThe Role of Personality in Sport and Physical ActivityWanRezawanaWanDaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Subfalcine Herniation Damages Cingulate GyrusDocument34 pagesSubfalcine Herniation Damages Cingulate GyrusLorenzo FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix2 Full Reccomendations Afac205Document138 pagesAppendix2 Full Reccomendations Afac205julietaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aur VedaDocument4 pagesAur VedaLalit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: DR - Yad Raouf BDS, Efb, MrcsedRabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of drug-induced gingival overgrowthsDocument14 pagesReview of drug-induced gingival overgrowthsRobins DhakalPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise and Physical Activity For Older - VanBeveren 2012 PDFDocument22 pagesExercise and Physical Activity For Older - VanBeveren 2012 PDFJuani CantellanosPas encore d'évaluation
- Closed Tibia and Fibula Fracture Case PresentationDocument30 pagesClosed Tibia and Fibula Fracture Case Presentationzhafran_darwisPas encore d'évaluation
- Narcotics and Antimigraine Agents (AE, Drug-Drug Interactions)Document5 pagesNarcotics and Antimigraine Agents (AE, Drug-Drug Interactions)ShiraishiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensional Modeling Basics For HealthcareDocument27 pagesDimensional Modeling Basics For Healthcareduwayne_willettPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlantis Implant Compatibility Chart 79214-US-1107Document2 pagesAtlantis Implant Compatibility Chart 79214-US-1107Jean-Christophe PopePas encore d'évaluation
- Denumire Comerciala DCI Forma Farmaceutica ConcentratieDocument4 pagesDenumire Comerciala DCI Forma Farmaceutica ConcentratieAlina CiugureanuPas encore d'évaluation
- (ANES) Mon 01 Epidural For Labor Analgesia (A2021)Document3 pages(ANES) Mon 01 Epidural For Labor Analgesia (A2021)Miguel SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Create Consent Form (39 charactersDocument3 pagesCreate Consent Form (39 charactersJan Diel100% (2)
- Volume 42, Issue 48 - December 2, 2011Document64 pagesVolume 42, Issue 48 - December 2, 2011BladePas encore d'évaluation
- Migraine Hemicrania and Its Homeopathic Permanent Cure - DR Bashir Mahmud ElliasDocument6 pagesMigraine Hemicrania and Its Homeopathic Permanent Cure - DR Bashir Mahmud ElliasBashir Mahmud ElliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Malaysia - Kontrak - Pusat - Ubat-Ubatan - KKM - 20.03.12Document21 pagesMalaysia - Kontrak - Pusat - Ubat-Ubatan - KKM - 20.03.12Anuj Mairh0% (1)
- Water Sealed DrainageDocument2 pagesWater Sealed DrainagefairwoodsPas encore d'évaluation