Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Infrastructure Technician Networking Architecture Syllabus
Transféré par
Ronald U. WacasCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Infrastructure Technician Networking Architecture Syllabus
Transféré par
Ronald U. WacasDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Making IT
good for
society
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking
and Architecture Syllabus
603/0686/5
Version 2.0
September 2017
This is a United Kingdom government regulated qualification which is administered and
approved by one or more of the following: Ofqual, Qualification in Wales, CCEA or SQA
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 1 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture
Contents
Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 4
Objectives ............................................................................................................................. 4
Course Format and Duration ................................................................................................. 4
Eligibility for the Examination ................................................................................................. 4
Format and Duration of the Examination ............................................................................... 5
Additional Time for Apprentices Requiring Reasonable Adjustments Due to a Disability ....... 5
Additional Time for Apprentices Whose Language is Not the Language of the Examination . 5
Guidelines for Training Providers .......................................................................................... 5
Syllabus ................................................................................................................................ 6
Levels of Knowledge / SFIA Levels ..................................................................................... 14
Question Weighting ............................................................................................................. 14
Format of Examination ........................................................................................................ 15
Trainer Criteria .................................................................................................................... 15
Classroom Size ................................................................................................................... 15
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 2 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Change History
Any changes made to the syllabus shall be clearly documented with a change history log.
This shall include the latest version number, date of the amendment and changes made. The
purpose is to identify quickly what changes have been made.
Version Changes Made
Number
Version 1.0 Syllabus Created
July 2016
Version 1.1 Learning outcomes reformatted in some areas & content added.
October 2016
Version 1.2 Training criteria amended.
December 2016
Version 1.3 Compliance statement added.
December 2016
Version 1.4 Module title corrected.
Version 2.0 Major amendments following full review and changed TQT.
September 2017
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 3 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Introduction
This award is the first module of the five knowledge modules required for the Level 3
Infrastructure Technician Apprenticeship. It covers the range of concepts, approaches and
techniques that are applicable to mobile and operating systems, for which apprentices are
required to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding.
Objectives
Apprentices should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of current
operating systems and mobile devices. Key areas are:
1. Understand the use of a range of cabling and connectivity, the various types of
antennas and wireless systems, and IT test equipment.
2. Understand maintenance processes and how to employ them in working practices.
3. Understand the fundamentals of computer configuration.
4. Understand the architecture of computer and business systems.
5. Understand the relevant numerical skills and the application of Binary, Octal and
Hexadecimal notation.
6. Demonstrate the networking skills necessary to maintain a secure network.
Evidence of lessons learnt in these key areas should be collected and reflected upon when
the apprentice is compiling the summative portfolio as the apprentice could identify how the
task might be done better / differently with knowledge subsequently gained.
Target Audience
The award is relevant to anyone enrolled on the Level 3 Infrastructure Technician
Apprenticeship programme.
Course Format and Duration
Candidates can study for this award by attending a training course provided by a BCS
accredited training provider. The estimated total qualification time for this award is 98.5 hours.
Eligibility for the Examination
Individual employers will set the selection criteria, but this is likely to include 5 GCSEs
(especially English, mathematics and a science or technology subject); other relevant
qualifications and experience; or an aptitude test with a focus on IT skills.
Level 2 English and Maths will need to be achieved, if not already, prior to taking the
endpoint assessment.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 4 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Format and Duration of the Examination
The format for the examination is a 1-hour multiple-choice examination consisting of 40
questions. The examination is closed book (no materials can be taken into the examination
room). The pass mark is 26/40 (65%).
Additional Time for Apprentices Requiring Reasonable
Adjustments Due to a Disability
Apprentices may request additional time if they require reasonable adjustments. Please refer
to the reasonable adjustments policy for detailed information on how and when to apply.
Additional Time for Apprentices Whose Language is
Not the Language of the Examination
If the examination is taken in a language that is not the apprentice’s native / official
language, then they are entitled to 25% extra time.
If the examination is taken in a language that is not the apprentice’s native / official
language, then they are entitled to use their own paper language dictionary (whose purpose
is translation between the examination language and another national language) during the
examination. Electronic versions of dictionaries will not be allowed into the examination
room.
Guidelines for Training Providers
Each major subject heading in this syllabus is assigned an allocated time. The purpose of
this is two-fold: first, to give both guidance on the relative proportion of time to be allocated to
each section of an accredited course and an approximate minimum time for the teaching of
each section; second, to guide the proportion of questions in the exam. Training providers
may spend more time than is indicated and apprentices may spend more time again in
reading and research. Courses do not have to follow the same order as the syllabus.
Courses may be run as a single module or broken down into two or three smaller modules.
This syllabus is structured into sections relating to major subject headings and numbered
with a single digit section number. Each section is allocated a minimum contact time for
presentation. Apprentices should be encouraged to consider their summative portfolio
throughout the modules.
Calculators
Candidates taking on-line examinations will have access to an on-screen calculator. No
other calculators or mobile technology will be allowed.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 5 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Syllabus
For each top-level area of the syllabus a percentage and K level is identified. The
percentage is the exam coverage of that area, and the K level identifies the maximum level
of knowledge that may be examined for that area.
1 Cabling and Connectivity (12.5%, K2)
In this topic, the apprentice will gain a working knowledge of a range of cabling and
connectivity, the various types of antenna and wireless systems and IT test equipment. The
successful apprentice should be able to:
1.1 Explain the key differences between cables and connector types.
• copper;
o 10Base2;
o xBaseT;
• fiber – glass / plastic;
o multi-mode;
o single-mode;
• connectors;
o RJ45;
o BNC;
o Straight Tip (ST);
o Subscriber Connector (SC);
o Local Connector (LC).
1.2 Describe the key features of Cat1-6 cables.
• identify Cat1-4 cable as older types of cable;
• describe the main features of Cat5, 5A, 6, 6A;
o capacity;
o maximum distance;
o network application;
▪ 10BastT;
▪ 100Base-TX;
▪ 1000Base-T;
▪ 10GBase-T.
1.3 Explain the different antennas types.
• directional;
• omni directional;
• point-to-point;
• point-to-multipoint;
• mobile.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 6 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
1.4 Understand the types of wireless systems.
• Bluetooth;
o features;
▪ radio communication;
▪ medium range (1-10m);
o typical purpose;
▪ wireless peripheral connection;
• Near-field communication (NFC);
o features;
▪ radio communication;
▪ very short range (6cm);
o typical purpose;
▪ contactless payments;
• IrDA / IR;
o features;
▪ uses infrared radiation;
▪ typically short range communication (1-3m);
▪ typically slow speed;
▪ line of site;
o typical purpose;
▪ communication link for older devices;
▪ control TV / setup box remote controls;
• WiFi;
o features;
▪ radio communication;
▪ longer range (up to 100m);
▪ faster;
o typical purpose;
▪ wireless network for tablet / phones / computers;
• describe the key types of WiFi networking security;
o WEP;
o WPA;
o WPA2;
▪ satellite;
o features;
▪ typically uses a microwave link;
▪ high latency;
▪ expensive;
▪ long range;
o typical purpose;
▪ where other communication links not available.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 7 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
1.5 Identify testing equipment used with wired and wireless networks.
• wired;
o multimeter;
o wire map tester;
o cable testers;
o tone generator and probe;
o loopback plug;
• wireless;
o wireless locator / WiFi analyser;
o wireless heat maps.
2 Maintenance Processes (25%, K2)
In this topic area, the apprentice will understand maintenance processes and apply them in
working practices. The successful apprentice should be able to:
2.1 Describe the typical information stored in maintenance work records.
• customer name;
• company name;
• system / device model and make;
• system ID / serial number;
• date;
• engineer name;
• description of maintenance activity;
• purpose of the maintenance activity;
• parts needed (if required).
2.2 Explain the purpose of maintenance work records.
• record of the work completed for customers;
• help with scheduling periodic routine maintenance;
• to improve quality of future maintenance work;
• identify trends that will help prevent future disruption.
2.3 Explain how to use fault related information and business process information / SLA to
select the correct outcome considering.
• the priority of the fault;
• time the fault has been outstanding;
• any required escalation.
2.4 Explain the consideration required when undertaking a task given at short notice.
• ensuring task is recorded / logged in line with organisational guidelines;
• reprioritisation of all tasks in line with SLA’s;
• potential business impact of undertaking / not undertaking short notice task.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 8 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
2.5 Describe typical status sequences of maintenance tasks.
• open – initial recording of task;
o customer details;
o description of task;
o time;
o business impact;
o system(s) impacted;
• pending – awaiting further input or information needed to progress;
• fixed – awaiting confirmation an issue is resolved;
• escalation – send the task to a more technically specialised team or more senior
member of staff;
• closed - confirmed complete with documented diagnosis and fix.
2.6 Describe the purpose and use of the following maintenance tools when maintaining
systems.
• systems backups;
• system event logging;
• antivirus;
o software and antivirus pattern updates;
o regular system scans;
o monitoring of quarantined and uninfected items;
• general tools;
o scheduling through Task Scheduler;
o Windows Control Panel – services.
2.7 Describe the purpose of updates and how to manage updates for the following:
• system updates:
o application updates;
o system updates;
o security patches;
o Windows Server Update Service;
• firmware updates.
2.8 Describe how the following tools are used to manage local storage.
• monitoring disk space through drive properties;
• Check Disk (chkdsk);
• Disk Defragmentation;
• ‘disk clean-up’ utility;
• disk format;
o FAT32;
o NTFS.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 9 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
2.9 Describe how the following tools are used to monitor system performance.
• Windows Event Viewer;
• Linux - /var/log/messages;
• Task Manager;
• Windows Resource Monitor;
• netstat -e;
• SMART monitoring tools.
3 Architecture (7.5%, K2)
In this topic area, the apprentice will understand and apply the basic elements and
architecture of computer systems and business IT architecture. The successful apprentice
should be able to:
3.1 Explain the features and purpose of basic computer systems components.
• CPU;
• motherboard;
• processor;
• memory;
• hard drive;
• NIC;
• power supply;
• fan.
3.2 Explain the purpose of:
• operating system – software used to manage the basic functions of a computer;
• applications – software designed to provide a specific task normally for end users;
• databases – used to storage and rapid retrieval of information;
• servers – provide systems resources that other computers can access;
o Active Directory;
o DNS;
o web proxy server;
o file and print;
o email;
o database;
o virtualisation;
• networking - provide managed communication links between computers;
• security – maintaining the integrity of systems and data;
• services – Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS),
Software as a Service (SaaS).
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 10 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
4 Numerical Skills (17.5%, K3)
In this topic area, the apprentice will understand where to apply the relevant numerical skills.
The successful apprentice should be able to:
4.1 Describe the configuration and use of:
• IPV4 address;
• netmask;
• default gateway;
• DNS server.
4.2 Describe key features of IPv6.
• much larger address space;
• 128 bits in size;
• 64 bits used for host address;
• 64 bits used for network address.
4.3 Identify which part of an IPv4 address refers to the network and which to the host.
4.4 Apply logical AND/OR on two 8 bit binary numbers.
4.5 Apply a binary to decimal conversion on binary numbers up to 8 bits in length.
4.6 Apply decimal to binary number conversion on decimal numbers up to 255.
5 Maintaining a Secure Network (37.5%, K2)
In this topic area, the apprentice will understand the relevant networking skills necessary to
maintain a secure network. The successful apprentice should be able to:
5.1 Identify the purpose of types of data communication platforms used in networking.
• video;
o typically requires more bandwidth than voice or data;
o individual packets can be lost and communication still works but at reduced
quality;
o impacted by jitter;
• voice;
o typically requires greater bandwidth than data less than video;
o individual packets can be lost and communication still works but at reduced
quality;
o impacted by jitter;
• data;
o typically requires less bandwidth than video or voice;
o typically, a whole message must be received for the file to be uncorrupted.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 11 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
5.2 Explain the settings needed to configure IP.
• IP address;
• netmask;
• default gateway;
• static / dynamic;
• public / private.
5.3 Explain the purpose of a DNS server.
• name resolution;
• storage of network records;
• CNAME;
• A.
5.4 Explain the purpose of configuring the IP address of DNS server on a client.
• enables DNS name resolution.
5.5 Explain how to create and configure virtual networks.
• VLAN;
• VPN;
• virtualised switch.
5.6 Describe how to configure and support networks by editing key settings.
• IP address / netmask / default gateway;
• primary and secondary DNS;
• firewall enabling / disabling;
o the entire firewall;
o ports;
▪ dhcp;
▪ dns;
▪ ftp;
▪ http;
▪ https;
▪ imap;
▪ pop3;
▪ RDP;
▪ smtp;
▪ ssh;
▪ telnet;
o applications.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 12 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
5.7 Explain the main configuration tools, what their functions are and how they are used to
maintain security.
• personal firewall;
• perimeter firewall;
• directory services (Active Directory);
o users;
o groups;
• policies (group policy);
o password policies;
o hardware restrictions;
o application and utility restrictions.
5.8 Describe how to configure remote support of systems using:
• RDP;
• VNC;
• SSH.
5.9 Describe the key purposes of domain controllers.
• centralise the management of directory services;
• centralise the management of security policies;
5.10 Describe the major steps required to install a domain controller.
• install Windows Server;
• configure networking;
• install Active Directory;
• configure a domain name.
5.11 Describe the purpose of creating and managing users and computer records within
Active Directory:
• users – centralised management of user access to organisational network;
• computers – centralised management of which computer can access a domain and
domain resources.
5.12 Describe how to create, update and delete within Active Directory.
• organisational unit (OU);
• users;
• computers.
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 13 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Levels of Knowledge / SFIA Levels
This syllabus will provide apprentices with the levels of difficulty / knowledge skill highlighted
within the following table, enabling them to develop the skills to operate at the levels of
responsibility indicated. The levels of knowledge and SFIA levels are explained on the
website www.bcs.org/levels. The levels of knowledge above will enable apprentices to
develop the following levels of skill to be able to operate at the following levels of
responsibility (as defined within the SFIA framework) within their workplace:
Level Levels of Knowledge Levels of Skill and Responsibility (SFIA)
K7 Set strategy, inspire and mobilise
K6 Evaluate Initiate and influence
K5 Synthesise Ensure and advise
K4 Analyse Enable
K3 Apply Apply
K2 Understand Assist
K1 Remember Follow
Question Weighting
Syllabus Area Target number of questions
1. Cabling and Connectivity 5
2. Maintenance Processes 10
3. Architecture 3
4. Numerical Skills 7
5. Maintaining a Secure Network 15
Total 40 Questions
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 14 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Format of Examination
Type 40 Question Multiple Choice.
Duration 1 hour. An additional 15 minutes will be allowed for apprentices sitting
the examination in a language that is not their native / mother tongue.
Pre-requisites Training from a BCS accredited training provider is strongly
recommended but is not a pre-requisite.
Supervised Yes.
Open Book No.
Pass Mark 26/40 (65%).
Calculators Calculators may be used during this examination.
Total Qualification 98.5 Hours, 37.5 GLH recommended.
Time (TQT)
Delivery Online.
Trainer Criteria
Criteria ▪ Have 10 days training experience or have a train the trainer
qualification
▪ Have a minimum of 3 years practical experience in the subject
area
Classroom Size
Trainer to 1:16
Apprentice ratio
Copyright © BCS 2017 Page 15 of 15
BCS Level 3 Award in Networking and Architecture Syllabus
Version 2.0 September 2017
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The CES Written ExaminationDocument11 pagesThe CES Written ExaminationRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Error Control Coding Fundamentals and Applications by Shu Lin PDFDocument2 pagesError Control Coding Fundamentals and Applications by Shu Lin PDFMaggie0% (1)
- ACTIVITY 4 - DeletionDocument1 pageACTIVITY 4 - DeletionRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVITY 5 - UpdateDocument1 pageACTIVITY 5 - UpdateRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2-3 Driver Power PointDocument11 pages1.2-3 Driver Power PointRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- ACTIVITY 6 - SearchDocument1 pageACTIVITY 6 - SearchRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Travelling Salesman ProblemDocument2 pagesTravelling Salesman ProblemRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Enrolment Form CollegeDocument1 pageEnrolment Form CollegeRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- And, OK, If You're Going To Use One, Which One???: Mark Branom, IT ServicesDocument68 pagesAnd, OK, If You're Going To Use One, Which One???: Mark Branom, IT ServicesRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- GP Edit and Attrib CommandDocument41 pagesGP Edit and Attrib CommandRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Proposal: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN Information TechnologyDocument23 pagesResearch Proposal: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN Information TechnologyRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Achievement Chart: Wo RK SDocument2 pagesAchievement Chart: Wo RK SRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- University Clinic Student StaffDocument1 pageUniversity Clinic Student StaffRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Research EnvironmentalDocument2 pagesResearch EnvironmentalRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Research FrameworkDocument1 pageResearch FrameworkRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- SLCB Joins 5 Niche National ConferenceDocument1 pageSLCB Joins 5 Niche National ConferenceRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Shield Pinout - Aceduino (Alexan)Document1 pageTraining Shield Pinout - Aceduino (Alexan)Alzonne Mark ManansalaPas encore d'évaluation
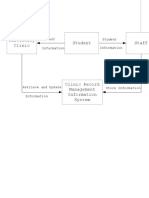
- Clinic Record Management Information System of Kalinga State UniversityDocument2 pagesClinic Record Management Information System of Kalinga State UniversityRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Format of Narrative ReportDocument17 pagesFormat of Narrative ReportRonald U. WacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto CadDocument4 pagesAuto CadNazrulMohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3Document7 pagesLecture 3xssdPas encore d'évaluation
- Populating Time DimensionDocument39 pagesPopulating Time DimensionAmit SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Office 365 Admin Center-L1Document12 pagesOffice 365 Admin Center-L1kushagra100% (1)
- Opencv2refman PDFDocument899 pagesOpencv2refman PDFrosasilbusPas encore d'évaluation
- Actix Traning - Actix BasicsDocument18 pagesActix Traning - Actix Basicsudaff4ikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lntroduction Software: Pro¡ectDocument20 pagesLntroduction Software: Pro¡ectAli Hasnat TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- Sign Language Detection: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument34 pagesSign Language Detection: Bachelor of Technology IN Electronics and Communication EngineeringshrutiPas encore d'évaluation
- GTU ReportDocument38 pagesGTU Reportchaurasiyajyoti93Pas encore d'évaluation
- X Virtual ServerDocument8 pagesX Virtual ServerAnitosh SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- G9SP Operation Manual 2010Document210 pagesG9SP Operation Manual 2010Alexandre MendesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016t EnunciatSD enDocument21 pages2016t EnunciatSD enmarioPas encore d'évaluation
- An 370 FT60X Configuration Programmer User GuideDocument15 pagesAn 370 FT60X Configuration Programmer User GuideCristian HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- VNX SPS Reemplazo de Unidad-Cambio Alimentación ElectricaDocument15 pagesVNX SPS Reemplazo de Unidad-Cambio Alimentación Electricadvecchio2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Configuring and Managing VsansDocument14 pagesConfiguring and Managing Vsansbalacool13Pas encore d'évaluation
- ContentDocument37 pagesContentAlejoTiradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cypecad Vs Etabs - En2Document33 pagesCypecad Vs Etabs - En2dskumar49100% (2)
- XVR4B04/08: 4/8 Channel Penta-Brid 1080N/720P Cooper 1U Digital Video RecorderDocument3 pagesXVR4B04/08: 4/8 Channel Penta-Brid 1080N/720P Cooper 1U Digital Video RecorderKoushik KarmakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management Systems: CSE Semester V (CSC 502) - 2018 IT Semester III (ITC 304) - 2017Document432 pagesDatabase Management Systems: CSE Semester V (CSC 502) - 2018 IT Semester III (ITC 304) - 2017Luiza Vilas Boas de OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrections in Current Adangal - Application FormDocument2 pagesCorrections in Current Adangal - Application Formmani mPas encore d'évaluation
- Block Customer Master DataDocument11 pagesBlock Customer Master DataArun DalalPas encore d'évaluation
- PLC PDFDocument20 pagesPLC PDFAnil Chandra Naidu MatchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Technologies Assignments Assignment-1: Name: V.Aravind Class: CSE 3D Roll No: 19R15A0520Document23 pagesWeb Technologies Assignments Assignment-1: Name: V.Aravind Class: CSE 3D Roll No: 19R15A0520Aravind VagaldasPas encore d'évaluation
- Content Development by Communities - Case Studies in The PhilippinesDocument15 pagesContent Development by Communities - Case Studies in The PhilippinesLiza Laith LizzethPas encore d'évaluation
- PL-2000 - Packet Light NetworksDocument2 pagesPL-2000 - Packet Light NetworksIsrael ExporterPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)Document5 pagesLesson Plan Grade 11 & 12 (Day 2)HanessyPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz App Javascript Report Css Mini Project-1Document32 pagesQuiz App Javascript Report Css Mini Project-1Kamini SalunkhePas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection Checklist Ethernet SwitchDocument16 pagesInspection Checklist Ethernet SwitchMohamed MeeranPas encore d'évaluation
- HTML FormsDocument7 pagesHTML FormsRabindra BiswalPas encore d'évaluation