Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hooke's Law
Transféré par
Vikash Kumar SinghTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Hooke's Law
Transféré par
Vikash Kumar SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS TECHNOLOGY LLP
RAJA COLONY, BEHIND HANUMAN TEMPLE, KANTATOLI
RANCHI-834001, JHARKHAND. Website: www.labinstech.com
Email: info@labinstech.com Contact: +91-70045-57472
1 Manufacture of Physics, Electronics and Electrical Equipment’s and Supplier of Chemistry,
Mechanical and Civil Engineering Lab Instruments. Email: info@labinstech.com
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS TECHNOLOGY LLP
RAJA COLONY, BEHIND HANUMAN TEMPLE, KANTATOLI
RANCHI-834001, JHARKHAND. Website: www.labinstech.com
Email: info@labinstech.com Contact: +91-70045-57472
Objective
To find the force constant of a helical spring by plotting a graph between load and extension.
Theory
What is a helical spring?
The helical spring, is the most commonly used mechanical spring in which a wire is wrapped
in a coil that resembles a screw thread. It can be designed to carry, pull, or push loads.
Twisted helical (torsion) springs are used in engine starters and hinges.
Let’s study how we can use the helical spring to do our experiment.
The helical spring is suspended vertically from a rigid support. The pointer is attached
horizontally to the free end of
spring. A metre scale is kept vertically in such a way that the tip of the pointer is over the
divisions of the scale; but does not touch the scale.
2 Manufacture of Physics, Electronics and Electrical Equipment’s and Supplier of Chemistry,
Mechanical and Civil Engineering Lab Instruments. Email: info@labinstech.com
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS TECHNOLOGY LLP
RAJA COLONY, BEHIND HANUMAN TEMPLE, KANTATOLI
RANCHI-834001, JHARKHAND. Website: www.labinstech.com
Email: info@labinstech.com Contact: +91-70045-57472
Helical spring works on the principle of Hooke’s Law. Hooke’s Law states that within the
limit of elasticity, stress applied is directly proportional to the strain produced.
When a load ‘F’ is attached to the free end of a spring, then the spring elongates through a
distance ‘l’ .Here ‘l’ is known as the extension produced. According to Hooke’s Law,
extension is directly proportional to the load.
This can be represented as:
where ‘k’ is constant of proportionality. It is called the force constant or the spring constant
of the spring.
A graph is drawn with load M in kg wt along X axis and extension, l in metre along the Y
axis. The graph is a straight line whose slope will give the value of spring constant, k .
Materials required
A spring
A rigid support
Weight hanger
50g or 20 g slotted weights
A vertical wooden scale
A fine pointer
Procedure
1. The helical spring is suspended vertically from a rigid support.A pointer is attached
horizontally at the free end of the spring.
2. A metre scale is kept vertically in such a way that the tip of the pointer is over the
divisions of the scale, but does not touch the scale.
3. A dead weight, w0 gwt is suspended by the weight hanger to keep the spring vertical.
The reading of the pointer on the metre scale is noted.
4. Now, gently add a suitable load of 50 g slotted weights to the hanger and the reading
of the pointer is noted.
5. The weights are added one by one till the maximum load is reached. In each case, the
reading of the pointer is noted.
3 Manufacture of Physics, Electronics and Electrical Equipment’s and Supplier of Chemistry,
Mechanical and Civil Engineering Lab Instruments. Email: info@labinstech.com
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS TECHNOLOGY LLP
RAJA COLONY, BEHIND HANUMAN TEMPLE, KANTATOLI
RANCHI-834001, JHARKHAND. Website: www.labinstech.com
Email: info@labinstech.com Contact: +91-70045-57472
6. The weights are then removed one by one and the reading of the pointer is noted in
each case of unloading.
7. The average of the readings for each load during loading and unloading is calculated
in each case. Let z0, z1, z2, z3…etc.., be the average readings of the pointer for the
loads w0, (w0+50), (w0+100), (w0+150) etc.
8. From this, extension, l (in m) for the loads (w0+50), (w0+100), (w0+150) etc. , are
calculated as (z1-z0), (z2-z0), (z3-z0) respectively.
9. In each case, k =mg/l is calculated. The average value of k gives the spring constant in
N/m.
10. A graph is drawn with load M in kg wt along X axis and extension, l in metre along
the Y axis. The graph is a straight line. The reciprocal of the slope of the graph is
determined. It gives spring constant in kg wt/m. The spring constant in N/m is
obtained by multiplying this with g=9.8 m/s2.
Observations: Table for load and extension:
Load on Reading of position of pointer tip
Serial Tension
hanger(W) =
No of = Mg Mean,
applied force Extension
Obs. (N) Loadin
(F)(kg wt) Unloadin l=z x 10-2(m) N/m
g
g Y(cm)
X(cm)
(cm)
4 Manufacture of Physics, Electronics and Electrical Equipment’s and Supplier of Chemistry,
Mechanical and Civil Engineering Lab Instruments. Email: info@labinstech.com
LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS TECHNOLOGY LLP
RAJA COLONY, BEHIND HANUMAN TEMPLE, KANTATOLI
RANCHI-834001, JHARKHAND. Website: www.labinstech.com
Email: info@labinstech.com Contact: +91-70045-57472
Mean k=…………N/m.
Spring constant, k from load extension graph
AB=---------kgwt
BC=---------m
= ---------Nm-1
Result
By calculation, the force constant of the given spring = .............N/m.
From load-extension graph, the force constant of the given spring =……….N/m
5 Manufacture of Physics, Electronics and Electrical Equipment’s and Supplier of Chemistry,
Mechanical and Civil Engineering Lab Instruments. Email: info@labinstech.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Toyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service ManualDocument98 pagesToyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service Manualmidgo100% (2)
- Anchor Bolt Design - Apdx D - ACI318-05Document4 pagesAnchor Bolt Design - Apdx D - ACI318-05Manoj JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
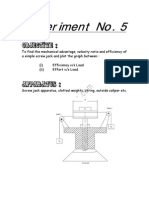
- To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of A Simple Screw JackDocument12 pagesTo Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of A Simple Screw Jackitsmeersaurabh69% (13)
- Simple Euler StrutDocument16 pagesSimple Euler StrutDaniel MabengoPas encore d'évaluation
- s2 Bending MomentDocument22 pagess2 Bending MomentismailPas encore d'évaluation
- tp6140 PDFDocument72 pagestp6140 PDFjohnPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 812-124 1989Document29 pagesBS 812-124 1989Muhamed RiskhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Material Lab ReportDocument47 pagesMechanics of Material Lab ReportMuhammad Junaid Tabassum50% (2)
- Aeron Chairs Service InstructionsDocument182 pagesAeron Chairs Service InstructionsMatt Wang0% (1)
- Principles of Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Electromechanical Energy ConversionJehovah CoelhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lab Report (Final)Document76 pagesPhysics Lab Report (Final)Waseem Akram50% (2)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresD'EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- SN 14 Lab Manual CO1Document8 pagesSN 14 Lab Manual CO1prateekbansalxcPas encore d'évaluation
- Hall EffectDocument10 pagesHall EffectGautam ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys101lab 03Document13 pagesPhys101lab 03nmadakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aadrika Deokathe - Physics (Amrita Virtual Labs)Document13 pagesAadrika Deokathe - Physics (Amrita Virtual Labs)Aadrika DeokathePas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Physics Laboratory Subject Code: Phs 383 Reg No:19U10781Document34 pagesSubject: Physics Laboratory Subject Code: Phs 383 Reg No:19U10781ShanmukhPas encore d'évaluation
- CE2100 Lecture 6Document19 pagesCE2100 Lecture 6SaiRamPas encore d'évaluation
- Hall EffectDocument10 pagesHall EffecttaruniisermPas encore d'évaluation
- Report 3Document8 pagesReport 3Tuan NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019phy1065 Prabhjot Expt-4Document5 pages2019phy1065 Prabhjot Expt-4va560426Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practical-1 Aim: Apparatus: Theory:: Enrolment No: Tca2009012 Name: Divyansh JainDocument13 pagesPractical-1 Aim: Apparatus: Theory:: Enrolment No: Tca2009012 Name: Divyansh Jainsamyak jainPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 AJC Prelim H2 Physics P1Document18 pages2011 AJC Prelim H2 Physics P1Aletheia LaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Haal Lab PDFDocument11 pagesHaal Lab PDFanon_487489119Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Novel Pull-In Accelerometer Based On Cantilever Beam Mass StructureDocument4 pagesA Novel Pull-In Accelerometer Based On Cantilever Beam Mass StructureAnjireddy ThatiparthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Theory and Waves Unit 3 Step 4Document24 pagesElectromagnetic Theory and Waves Unit 3 Step 4trabajos unad unadPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Material Job 2Document20 pagesStrength of Material Job 2Ayesha AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 3Document13 pagesExam 3Michael Janusa100% (1)
- Electricity: Confirming Coulomb's Law - Measuring With The Torsion Bal-Ance, Schürholz DesignDocument4 pagesElectricity: Confirming Coulomb's Law - Measuring With The Torsion Bal-Ance, Schürholz DesignJairo LugoPas encore d'évaluation
- SA Lab ManualDocument32 pagesSA Lab ManualAnonymous nSvmh3s67% (3)
- Force, Torque and StrainDocument22 pagesForce, Torque and StrainLungie MbathaPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining The Charge Carriers The Hall EffectDocument8 pagesExamining The Charge Carriers The Hall EffectEpic WinPas encore d'évaluation
- Coulomb Oscilloscope Lab 1Document6 pagesCoulomb Oscilloscope Lab 1Keshav SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 14lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVDocument23 pagesLecture 14lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- BEEE NotesDocument8 pagesBEEE NotesSrinathReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.105 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Fall 2003: Experiment 3 The Tension TestDocument13 pages1.105 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Fall 2003: Experiment 3 The Tension TestSuman.SPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Engineering and Technology: Lab ReportDocument33 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology: Lab ReportLiaquat Ali100% (1)
- Impulse Load Analysis of Breakdown of Overhead Transmission LineDocument8 pagesImpulse Load Analysis of Breakdown of Overhead Transmission LineTlili MahmoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- LCR Resonance Circuit: X X R ZDocument43 pagesLCR Resonance Circuit: X X R Zskiran_132902Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Tapered Beam Piezoelectric Energy HarvestersshikhamaharanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proportional Counter Report: Tomás Fernández Bouvier March 29, 2019Document27 pagesProportional Counter Report: Tomás Fernández Bouvier March 29, 2019Tomas Fernández BouvierPas encore d'évaluation
- EPHY105L LabManualDocument49 pagesEPHY105L LabManualaryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Cell & Its Application in TextileDocument27 pagesLoad Cell & Its Application in TextileSoumyajit Sarkar100% (1)
- Ephysicsl Experiment 8 - Coulombs LawDocument8 pagesEphysicsl Experiment 8 - Coulombs LawZaira Marie MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- CL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsDocument15 pagesCL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsSomila SchoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2-E-Force FieldDocument76 pagesLecture 2-E-Force Fieldapi-307330449Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsDocument29 pagesPhysics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsJuan SomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Smoothing With A CapacitorDocument9 pagesVoltage Smoothing With A CapacitorLeo LonardelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Strain Measurement Lab ReportDocument11 pagesStrain Measurement Lab ReportTyler Mehlman100% (1)
- Translines ProjectDocument8 pagesTranslines ProjectOdellien SajaPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Radicion Devido A UHVTL PDFDocument5 pages09 Radicion Devido A UHVTL PDFleriomPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient Wireless Power Transfer - Resonance Does Not Imply High EfficiencyDocument4 pagesEfficient Wireless Power Transfer - Resonance Does Not Imply High EfficiencyMihai PopaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of The Hall Coefficient in A Germanium CrystalDocument4 pagesMeasurement of The Hall Coefficient in A Germanium CrystalravisonkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hall EffectDocument8 pagesHall EffectbackupsentriePas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Fisika Dasar Physics of MotionDocument31 pages3 Fisika Dasar Physics of Motionsscarlett1231Pas encore d'évaluation
- Strain Gage RebortDocument6 pagesStrain Gage Rebortmohmmad othmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 7LABO Ganago Student Lab8Document37 pages7LABO Ganago Student Lab8Rocio Deidamia Puppi HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 25: Electric PotentialDocument11 pagesChapter 25: Electric PotentialAlexPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear LaboratoryDocument6 pagesNuclear LaboratoryMintesnot AbaynehPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisa Kesalahan Pemasangan Grounding Pada KWH Meter PrabayarDocument12 pagesAnalisa Kesalahan Pemasangan Grounding Pada KWH Meter Prabayarmamai nebePas encore d'évaluation
- Nikola Tesla - Electromagnetic EngineeringDocument13 pagesNikola Tesla - Electromagnetic EngineeringFurby HankPas encore d'évaluation
- Quotation S.No - Specifications QTY Unit Price in Rs. 1Document2 pagesQuotation S.No - Specifications QTY Unit Price in Rs. 1Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Anami 2017 Ijca 915577Document11 pagesAnami 2017 Ijca 915577Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- M/s Ganga Dhar Daya RamDocument4 pagesM/s Ganga Dhar Daya RamVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Anami 2017 Ijca 915577Document11 pagesAnami 2017 Ijca 915577Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Company DetailsDocument8 pagesCompany DetailsVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant LayoutDocument15 pagesPlant LayoutSreehari MPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit With Working Explanation - Circuits GalleryDocument8 pagesFull Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit With Working Explanation - Circuits GalleryVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Food. Clean Food.: Sortex Z+Document8 pagesSafe Food. Clean Food.: Sortex Z+Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Tapco 2008 Catalog 95Document1 pageTapco 2008 Catalog 95Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Campus BrochureDocument5 pagesDigital Campus BrochureVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- To Determine The Specific Heat Capacity of Solid and Liquid by Method of MixturesDocument5 pagesTo Determine The Specific Heat Capacity of Solid and Liquid by Method of MixturesVikash Kumar Singh0% (4)
- Thumb AxDocument35 pagesThumb AxVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 3VM Molded Case Circuit Breakers Catalog LV 31 - Catalog 2018 11 01 ENDocument92 pages3VM Molded Case Circuit Breakers Catalog LV 31 - Catalog 2018 11 01 ENCatur Aji NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue-DC Shunt MotorDocument2 pagesCatalogue-DC Shunt MotorVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SyntelDocument2 pagesSyntelHarry JustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Poem Summary - An Elementary School Classroom in A SlumDocument2 pagesPoem Summary - An Elementary School Classroom in A SlumVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 English Core Notes ReadingDocument10 pages12 English Core Notes ReadingZara HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Analysis LabDocument29 pagesStructural Analysis Labsamiee_mePas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Lab ManualDocument26 pagesConcrete Lab ManualDebabrata TrivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Bitumen Range PDFDocument4 pagesBitumen Range PDFVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Approved Institutes in 2014-15Document25 pagesList of Approved Institutes in 2014-15Vikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Thumb AxDocument35 pagesThumb AxVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure No. Name of Diagram PagenoDocument1 pageFigure No. Name of Diagram PagenoVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital PlanimeterDocument2 pagesDigital PlanimeterVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SyntelDocument2 pagesSyntelHarry JustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Principles Developed by Henri FayolDocument2 pagesManagement Principles Developed by Henri Fayolaravindvn007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Finger Print TechnalogyDocument7 pagesFinger Print TechnalogyVikash Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- T and DDocument15 pagesT and DWilson Shyam SunderPas encore d'évaluation
- General KnowledgeDocument44 pagesGeneral KnowledgeAnonymous ioNuZrgPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11John Christian De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- KEI W F List Price 12th Dec 2020Document2 pagesKEI W F List Price 12th Dec 2020Prateek Agarwal100% (1)
- 2.1 Testing MachineDocument3 pages2.1 Testing MachinekoushipriyathamPas encore d'évaluation
- Type Mao Type Mbo Type Mci: W.AriyaratneDocument1 pageType Mao Type Mbo Type Mci: W.AriyaratneLeon ZhouPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1.1 Plumbing Code ContinuationDocument2 pagesChapter 1.1 Plumbing Code ContinuationJohn roland GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ductless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Document2 pagesDuctless Fume Hood Brochure - FEB19Musz MusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) Products and ProjectsDocument4 pagesFast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) Products and ProjectsMurali Krishna ThotaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Retaining WallsDocument18 pages6 Retaining Wallsumit2699Pas encore d'évaluation
- Waste Water Treatment Using Electrocoagulation TechnologyDocument4 pagesWaste Water Treatment Using Electrocoagulation TechnologyKetan V. JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Metallurgy MM207 IIT Bombay Kashyap Sir Dislocation Grains Grain Boundary SlidesDocument97 pagesEngineering Metallurgy MM207 IIT Bombay Kashyap Sir Dislocation Grains Grain Boundary SlidesPratik BabhulkarPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Centrifugal PumpsDocument3 pagesAn Introduction To Centrifugal PumpsCaiyun LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Pranav 1Document14 pagesPranav 1DesignPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Standards SAEC Waste Disposal LandfillsDocument17 pagesEngineering Standards SAEC Waste Disposal LandfillsAhmad RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- BITZER Output Data: Created On: 16/05/2017 16:44:22Document5 pagesBITZER Output Data: Created On: 16/05/2017 16:44:22Hasan Syaiful IPas encore d'évaluation
- Hybrid Geosynthetic Paving Mat For Highway ApplicationsDocument4 pagesHybrid Geosynthetic Paving Mat For Highway ApplicationsmithileshPas encore d'évaluation
- D 6797 - 02 Rdy3otcDocument3 pagesD 6797 - 02 Rdy3otcJuan GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooper Crouse Hinds Hazardous Area Enclosures & Junction BoxesDocument46 pagesCooper Crouse Hinds Hazardous Area Enclosures & Junction BoxesrocketvtPas encore d'évaluation
- Identify The Following: Cien 3090 Construction Materials & Testing Midterm ExamDocument1 pageIdentify The Following: Cien 3090 Construction Materials & Testing Midterm Examacurvz2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cleasby Conveyors MaintenanceDocument2 pagesCleasby Conveyors MaintenanceRino AdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dow Coring Asia ManualDocument69 pagesDow Coring Asia ManualGULJAR SINGHPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Hercules AfDocument1 pageAP Hercules AfSami KahtaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Plug Valves: P4T and P6T SeriesDocument8 pagesPlug Valves: P4T and P6T SeriesKahl YeongPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitachi Power Tools Catalogue AustraliaDocument162 pagesHitachi Power Tools Catalogue AustraliaMarcio HahnPas encore d'évaluation
- ExerciseDocument4 pagesExerciseariefnur19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week13 TNT Conversion of Piezoelectric Material DataDocument7 pagesWeek13 TNT Conversion of Piezoelectric Material DataDeepak ChachraPas encore d'évaluation