Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Burn Injury: Major Burns 45% BSA
Transféré par
Kat UyTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pathophysiology of Burn Injury: Major Burns 45% BSA
Transféré par
Kat UyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
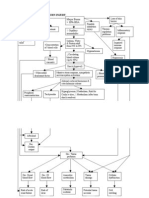
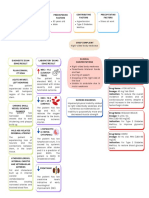
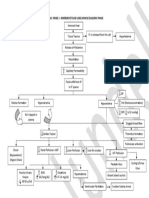
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF BURN INJURY
Major Burns Loss of skin
Cell lysis 45% BSA barrier
Inhalation injury
(singed eyebrows, eyelashes
Hemolysis ↑ Hyperkalemia & hair; soot in nares & mouth Inflammatory
(6.0 mEq/L) ↑ Capillary response
N: 3.5 – 4.5 permeability
mEq/L
Skin of face
↑ Hemoglobin is pink moist Impaired
(20g/dl) Na,H2O & immune
CHON shift & blister
N: 13.5 – 17.5g/dl ↑Concentration response
from IVS to ITS (20- 30 pus
of blood cells
(Hgb:20g/dl) cells/hpf)
Hyponatremia
(126mEq/L) Respi. Alkalosis
↓ Circulating (pH:7.49,
blood volume pCO2:32mmHg) Hypoxemia
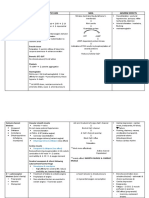
↑ Blood
viscosity Hypovolemic shock
(PR:142 bpm; RR: 36, inspiratory
BP:98/60mmHg) wheeze, sooty
sputum, Po2:60
↑ Myocardial mmHg
depressant factor Massive stress response, sympathetic
nervous system activation
↓ Blood
pressure
Adrenal corticoid hormones & (98/60mmHg)
catecholamine release
Peripheral Tachycardia Hyperglycemia (168mg/dl)
vasoconstriction (142 bpm)
Afterload
↓Cardiac
output
↓Tissue perfusion
↓ Renal ↓GI blood Anaerobic Tissue Cellular
blood flow flow metabolism damage dysfunction
Risk of acute Risk of Metabolic Thick, white Cell
renal failure paralutic acidosis leathery eschar; swelling
(BUN= ileus (pH=7.30, pain)
27mg/dl) (absent HCO3=18
bowel mEq/L
sounds)
*MAJOR BURN = THICK, WHITE LEATHERY ESCHAR ON CHEST, NECK, WHOLE BACK & MOUTH
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Drugs PharmacologyDocument75 pagesDrugs Pharmacologyapi-25987870100% (16)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Document1 pageBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testPas encore d'évaluation
- Wild Foods For Wise Women by Susun WeedDocument6 pagesWild Foods For Wise Women by Susun Weedclaricecaps100% (1)
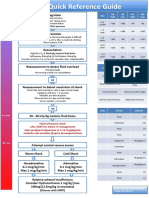
- Sepsis Quick Reference GuideDocument1 pageSepsis Quick Reference GuideRavin DebiePas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX Cram SheetDocument6 pagesNCLEX Cram Sheetaishwariyapokharel55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ozone - A Wide Spectrum Healer by Gary Null PHDDocument20 pagesOzone - A Wide Spectrum Healer by Gary Null PHDangelakimba100% (4)
- Introduction to ImmunohematologyDocument16 pagesIntroduction to ImmunohematologyJoshua TrinidadPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical InfectionsDocument310 pagesSurgical InfectionsOmar Ed ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramJessica Peñamora100% (1)
- COPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DiagramDocument2 pagesCOPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Diagramcris_198893% (15)
- Copd PathDocument2 pagesCopd Pathnursing concept maps100% (2)
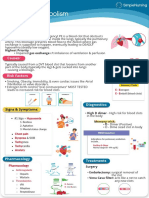
- Deadly PE Blood Clot Blocks Lung ArteriesDocument1 pageDeadly PE Blood Clot Blocks Lung ArteriesTrisha VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypovolemic Shock PathoDocument10 pagesHypovolemic Shock PathoLorebell100% (1)
- ACCA Cardiogenic and Septic ShockDocument1 pageACCA Cardiogenic and Septic ShockCatherine Morris100% (8)
- Hematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageHematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachEugen MPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC DisordersDocument8 pagesRBC DisordersDavid JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology Notes for Medical StudentsD'EverandHematology Notes for Medical StudentsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Blood Banking and Transfusion Medicine Practice QuestionsDocument45 pagesBlood Banking and Transfusion Medicine Practice QuestionsVincent Reyes85% (40)
- Fluids and Electrolytes IV FluidsDocument1 pageFluids and Electrolytes IV Fluidsnursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophys BURNDocument2 pagesPathophys BURNpaupaulala83% (6)
- ShockDocument30 pagesShockLập Trương Minh QuốcPas encore d'évaluation
- NCLEX-Crheet 240228 024718Document6 pagesNCLEX-Crheet 240228 024718rnlkjh5636Pas encore d'évaluation
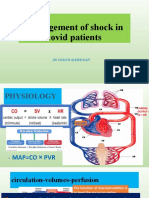
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Edema Dan PerdarahanDocument13 pagesEdema Dan PerdarahanKost Vila SakinahPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Management Post Operative Low Cardiac Output SyndromeDocument46 pages11 - Management Post Operative Low Cardiac Output SyndromeNat SPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Electrical BurnsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Electrical BurnsHanee RamonalPas encore d'évaluation
- Kuliah ShockDocument17 pagesKuliah Shockmuhammad hidayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Myocardial Infarction PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction PathophysiologyPowell TabogocPas encore d'évaluation
- Diuretics and Heart Failure Drugs Mechanisms and Side EffectsDocument3 pagesDiuretics and Heart Failure Drugs Mechanisms and Side EffectsRebecca MarshallPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of HypovolemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HypovolemiaSheana TmplPas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJessica FabroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)hasanatiya41Pas encore d'évaluation
- Follow Up Lupus NefritisDocument8 pagesFollow Up Lupus NefritisSakdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- tranzDocument22 pagestranzMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaPas encore d'évaluation
- K (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisDocument4 pagesK (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisAhmad Asyraf AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Multisystem ProblemsDocument90 pagesMultisystem ProblemsAlexander Blanche PajelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPDocument59 pagesSyok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPLuh Leni AriniPas encore d'évaluation
- Shock OverviewDocument6 pagesShock OverviewKrys Segarra GalarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- DISORDERS OF SODIUM: HYPONATREMIA CAUSES BRAIN INJURY IF CORRECTED TOO RAPIDLYDocument22 pagesDISORDERS OF SODIUM: HYPONATREMIA CAUSES BRAIN INJURY IF CORRECTED TOO RAPIDLYfaiza anwerPas encore d'évaluation
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)Document1 pagePenetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)P BPas encore d'évaluation
- Esophageal VaricesDocument1 pageEsophageal VaricesDanielle DiorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageAnemia ApproachLanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Correos Electrónicos 1. Optimizacion Cardiovascular, FluidosDocument29 pagesCorreos Electrónicos 1. Optimizacion Cardiovascular, FluidosKaren PMPas encore d'évaluation
- DM Tipe II Rasa: GDS 203 MG/DL Hba1c 7,3% APTT 22,8 DetikDocument1 pageDM Tipe II Rasa: GDS 203 MG/DL Hba1c 7,3% APTT 22,8 DetikAndrianus AtuPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 HEMA Must KnowDocument22 pages5 HEMA Must KnowSheena BlonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Trauma Management: 1. Brain InjuryDocument1 pageHead Trauma Management: 1. Brain InjuryCykaAlwiPas encore d'évaluation
- CT scan abnormalities in colon obstructionDocument1 pageCT scan abnormalities in colon obstructionAngela NeriPas encore d'évaluation
- AED Side Effects - 2Document2 pagesAED Side Effects - 2Dr zanaPas encore d'évaluation
- RBC AnomaliesDocument5 pagesRBC AnomaliesThe16LoverrPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions and Treatment of Cardiogenic and Septic ShockDocument1 pageDefinitions and Treatment of Cardiogenic and Septic Shockjose miguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Acca Cs Syok SepsisDocument1 pageAcca Cs Syok SepsisSamuel KalonkPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk factors, clinical manifestations, nursing diagnosis and management of a stroke patientDocument1 pageRisk factors, clinical manifestations, nursing diagnosis and management of a stroke patientArt Lemuel LotereñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateDocument13 pagesMedications at Red Zone: Sodium BicarbonateAiman ArifinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysio - Stemi - FinalDocument4 pagesPathophysio - Stemi - FinalPrincessDiannePas encore d'évaluation
- Antianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesAntianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsNadhirah ZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.main Regulator1 DR HanuDocument20 pages2.main Regulator1 DR Hanukoko komarudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11: Shock: Table 11 1Document6 pagesChapter 11: Shock: Table 11 1Suji MerlinePas encore d'évaluation
- Sodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Document17 pagesSodium Imbalances (Hyponatremia Vs Hypernatremia)Angel FiloteoPas encore d'évaluation
- HYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESDocument10 pagesHYPO and HYPERNATREMIA IN NEONATESraghava mbbsPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496Pas encore d'évaluation
- Burn Stage I - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBurn Stage I - Pathophysiologydecsag06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shock EditedDocument56 pagesShock EditedJeevan VelanPas encore d'évaluation
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guideline: Managing Severe Sepsis and Septic ShockDocument38 pagesSurviving Sepsis Campaign Guideline: Managing Severe Sepsis and Septic ShockSelly RizanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti ArrhythmiasDocument3 pagesAnti ArrhythmiasaqmalbaekPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinoblastoma Clinical and Pathological ClassificationDocument9 pagesRetinoblastoma Clinical and Pathological ClassificationSonia SaulésPas encore d'évaluation
- RSP20110601Document64 pagesRSP20110601Abhinav SinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- BuratDocument5 pagesBuratFreya AvellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Emergency Medical Services (EMS)Document17 pagesIntroduction To Emergency Medical Services (EMS)ishak1863Pas encore d'évaluation
- CholesteatomaDocument44 pagesCholesteatomavna297Pas encore d'évaluation
- For The Best Sinus Congestion RemediesDocument4 pagesFor The Best Sinus Congestion Remedies4zaleakuPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 1 Lecture - Introduction - Student'sDocument54 pagesWEEK 1 Lecture - Introduction - Student'smike angelo albacietePas encore d'évaluation
- Brain injury patterns in hypoxiaDocument7 pagesBrain injury patterns in hypoxiaDr.Deepak S MD,MRCPCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Suz 183Document29 pagesSuz 183Benny Chris TantoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareDocument3 pagesThe Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing CareScott PuckettPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningDocument4 pages4 - Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningABEGAIL BALLORANPas encore d'évaluation
- Bailey 5th Ed. 2014 (1125-1318) - TraumaDocument194 pagesBailey 5th Ed. 2014 (1125-1318) - TraumaelFadhlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Corpectomy Cage Surgical TechniquesDocument18 pagesCorpectomy Cage Surgical TechniquesJulian VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Substance AbuseDocument16 pagesSubstance AbuseAkansha JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 026 CoagulationDocument7 pagesChapter 026 Coagulationthubtendrolma100% (3)
- Rearrange The Jumble Letters: 10 1 10Document4 pagesRearrange The Jumble Letters: 10 1 10Shafee ArafatPas encore d'évaluation
- GERD Nursing CareDocument9 pagesGERD Nursing CareTrisha ArizalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisDocument4 pagesManage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisYeni PuspitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgeon-Performed Ultrasound As A Diagnostic Tool in AppendicitisDocument6 pagesSurgeon-Performed Ultrasound As A Diagnostic Tool in Appendicitisansar ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Committee: World Health Organization Agenda: Prevention and Cure For HIV AIDS Name: John Carlo H. Babasa Delegate of OmanDocument2 pagesCommittee: World Health Organization Agenda: Prevention and Cure For HIV AIDS Name: John Carlo H. Babasa Delegate of OmanGrinty BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Pankaj R BodadeDocument8 pages2013 Pankaj R BodadeGeorge StoicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph SignDocument2 pagesNasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph Signyeni novi yantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rohini 59284010117Document21 pagesRohini 59284010117narasimmanbiomedicalPas encore d'évaluation
- KEILMUAN DAN SENI DALM KEBIDANANDocument18 pagesKEILMUAN DAN SENI DALM KEBIDANANRizky Putri AndriantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Diseases in Pregnancy PMK HandoutDocument12 pagesThyroid Diseases in Pregnancy PMK HandoutWikrom Keng WromKiPas encore d'évaluation