Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
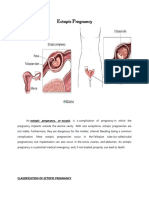
Ectopic Gestation Evaluation by Ultrasound
Transféré par
Priyanka GeorgeTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ectopic Gestation Evaluation by Ultrasound
Transféré par
Priyanka GeorgeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
50
EVALUATION OF ECTOPIC GESTATION
Commonest clinical presentation of ectopic pregnancy occurs at a mean of 7 weeks
after the last normal menstrual period, with a range of 5 to 8 weeks
Clinical Presentation
Three basic clinical presentations-
Early
Mid
Late
Early Presentation
Early symptoms are either absent or subtle.
1.Overdue periods by 1-2 weeks with bleeding PV usually mild.
2.Pain
3.Tenderness
1.Vaginal bleeding:Usually mild.
Ectopic pregnancy ---falling levels of progesterone from the corpus luteum on the
ovary cause withdrawal bleeding.
Can be indistinguishable from an early miscarriage or the 'implantation bleed' of a
normal early pregnancy
Endometrium is usually thick due to decidual reaction
2. Pain ---May be present or absent.
Pain may be confused with a strong stomach pain, it may also feel like a strong cramp
Pain while urinating
Pain and discomfort, usually mild. A corpus luteum in the ovary in a normal
pregnancy may give very similar symptoms. .
Pain while having a bowel movement
3. Tenderness--
On TVS , forniceal tenderness is commonly present when the probe is pressed against
the area of location of the sac.
Mid presentation
Commonly with 2-4 weeks overdue periods
Pain may be variable.
At times it may be very severe with fainting attacks & the patient may even come in
shock. However the pain may be similarly confused with stomach pain or pain due to
urinary infection.
Bleeding may be continuing for a number of days & as such the endometrium may be
thick or thin.
Thinning of endometrium may be when a lot of endometrium has been shed due to
bleeding.
Institute Of Ultrasound Training, New Delhi, India
51
Late (Chronic)
Lower abdominal pain commonly present but usually not very severe & in some it
may be even absent.
At times there may be a referred pain eg: when the ectopic mass is pressing on the
ureter it may cause ureteric colic with hydronephrosis.
Shoulder pain may be present in both mid & late ectopics and is due to free blood
tracking of the abdominal cavity.
Clinically patients of chronic ectopic usually do not have fever ,however mild fever
may be seen in some cases.
H/O complete ammenorrhoea is usually less common and more comonly h/o irregular
bleeding since 2-5 months is seen.
Endometrium is usually not thickened.
Sonographic presentation in ectopic-Early cases
In very early cases a small sac is seen outside the uterine cavity with or without fetal
node or yolk sac.
The margins of the sac are thick with echogenicity equal to or more than that of
endometrium.
Endometrium is thick and uterine cavity is empty.
<10% cases have a pseudosac.
Fluid is usually mild with internal echoes
Ectopic sac-Thick echogenic ring(arrow)
TVS-Ectopic sac(arrow) & thick endometrium(E). TVS-Ectopic sac (arrow head) with yolk
U-Uterus sac(arrow)
Institute Of Ultrasound Training, New Delhi, India
52
TVS-Hemorrhagic fluid(F) with thick endometrium(arrow
Pseudosac v/s true sac
Pseudo sac is fluid collection in the uterine cavity which may be anechoic or have
internal echoes of blood or decidual cast.
It is tubular unlike a true sac which is more rounded or oval.
Pseudosac commonly occupies a larger portion of uterne cavity unlike a true sac.
At times, when the true sac is abnormal and is in the process of abortion it may also
become tubular.
If yolk sac or fetal node are seen within the sac it confirms the diagnosis of intra-
uterine true sac.
However in the absence of yolk sac or fetal node presence of “double decidual ring
sign” is useful in differentiaition.
TVS-Pseudo sac(arrows) M-chronic ectopic mass
Double Ring
While presence of double ring is diagnostic of IUP ,absence does not rule out IUP since in
later cases it may be obliterated.
Mid cases
When presenting with features of shock, hemorrhagic peritoneal fluid having internal
echoes is usually moderate to marked.
A gestational sac is commonly lying within the fluid and may sometimes be difficult
to visualize.
Institute Of Ultrasound Training, New Delhi, India
53
TVS showing ectopic sac.e-endometrium TVS showing ectopic sac.Fl-fluid
TVS showing marked hemorrhagic fluid collection in pelvic peritoneal cavity (BL)
Late cases
Masses are usually big having oval appearance, commonly lying close to midline &
ileopsoas muscle.
Major part of the mass is comprised of blood clots in varying stages giving a
hetrogenous texture to the mass with only a small area occupied by the sac.
Sac may or may not be located within the mass.
Chronic ectopic mass (arrowheads). Chronic ectopic mass (M) with
U-Uterus pseudosac(arrows)
Institute Of Ultrasound Training, New Delhi, India
54
Fluid in the peritoneal cavity
It is present in almost all types of ectopic.
Early ectopics may have fluid localized only in the pelvic cavity and may be mild
while in later stages, it may be seen in various locations of upper abdomen like
Morrison's pouch and perihepatic space.
Mild fluid--Differentiation from other causes
Even a normal intra-uterine pregnancy in very early stage may have mild fluid in the
pelvic peritoneal cavity.This fluid however does not have the internal echoes which are
usually seen in cases of ectopic.Internal echoes are better visualized on TVS.
Additionally ,other features may help in differentiation:
--Visualization of ectopic sac
--If intra-uterine pregnancy sac is seen then the fluid is rarely due to ectopic (since
heterotrophic pregnancy is rare)
---The most common misdiagnosis assigned to early ectopic pregnancy is PID.
--The presence of a positive pregnancy test virtually rules out pelvic infection as it is rare
to find pregnancy with an active Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID).
D/D
Ruptured Corpus Luteum Cysts
Here the pain may or may not be associated with overdue periods.
When periods are not overdue, the confusion with ectopic does not arise. If doubts
still exist, UPT may be done which will be negative.
With overdue periods and positive UPT hemorrhagic corpus luteum cyst will be
associated with an IUP.
In very early IUP when sac is not seen and only thick endometrium is present, a
follow up scan may be done after 3-4 days to see for presence of sac
.Although fluid may be seen in both, in ectopic internal echoes are almost always seen
while in ruptured corpus luteum cyst the fluid may or may not have internal echoes.
In ectopic a sac may be seen lying outside the ovary while ruptured corpus luteum
will be seen as irregular area within the ovary.
In case, when ectopic sac is lying within the tube but close to the ovary and confusion
occurs with an eccentrically located CL cyst ,following may be helpful:
1.Sliding sign—which will show sac to move away from ovary.
2.Claw sign—A C-shaped area of ovarian tissue may be seen around an eccentric CL
cyst while in ectopic sac no such area will be seen
Other D/D-
Appendicitis
Other gastrointestinal disorder
Problems of the urinary system
Pelvic Inflammatory disease
Other gynaecologic problems
Institute Of Ultrasound Training, New Delhi, India
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ovarian Masses: Types, Ultrasound Features & Differential DiagnosisDocument5 pagesOvarian Masses: Types, Ultrasound Features & Differential DiagnosisPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Ecthopic PregnancyDocument9 pagesEcthopic PregnancyLiliani TjikoePas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy 2022 Edited 3Document40 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 2022 Edited 3apule geraldhumblePas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound measurements and findings for obstetric and gynecologic conditionsDocument4 pagesUltrasound measurements and findings for obstetric and gynecologic conditionsLoricon OlivaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809Document8 pages8412-Article Text-29472-1-10-20130809NenyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gynecologic-Nursing Part 2Document40 pagesGynecologic-Nursing Part 2jomariPas encore d'évaluation
- Vgo 411Document333 pagesVgo 411SABARI THIRUMOORTHY100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and Treatment OptionsQueenet BelingonPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal Examination DetailedDocument22 pagesAbdominal Examination Detailedsaveetha purushothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Shubrat Singh: EctopicDocument25 pagesShubrat Singh: Ectopicshubham royalPas encore d'évaluation
- Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele Diagnosis and Treatment in ChildrenDocument10 pagesInguinal Hernia and Hydrocele Diagnosis and Treatment in ChildrenShelly Stephanie BintoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Postpartal Complications PDFDocument9 pagesNursing Care of A Family Experiencing A Postpartal Complications PDFTandingco, Olivia Mari H.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Content WriterDocument51 pagesContent WriterToday ViralPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo ManongdoDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Submitted By: William Leo Manongdoliam0831Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios ExplainedDocument14 pagesPolyhydramnios and Oligohydramnios ExplainedMoses Jr KazevuPas encore d'évaluation
- Maternal Finals ReportDocument21 pagesMaternal Finals ReportLaude Sebastian DanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities Involving UterusDocument20 pagesAbnormalities Involving UterusDrRajkumar PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 51 Lecture The Gynecological ExamDocument69 pages51 Lecture The Gynecological ExamTarek TarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)Document24 pagesNursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)api-370148995% (19)
- Ectopic Pregnancy - OMDocument9 pagesEctopic Pregnancy - OMrheindPas encore d'évaluation
- Omphalocele: 1 Baskaran NDocument5 pagesOmphalocele: 1 Baskaran Nதாசன் தமிழன்Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction EctopicDocument5 pagesIntroduction EctopicRenalyn AgdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsDocument5 pagesChapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsNawaf Rahi AlshammariPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormalities Of The Testis And Scrotum: A Concise GuideDocument34 pagesAbnormalities Of The Testis And Scrotum: A Concise GuideIma MoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Ovarian CystsDocument16 pagesOvarian CystsKevin BaniwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Intussusception PresentationDocument9 pagesIntussusception PresentationAme NasokiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Presentation: "Ectopic Pregnancy"Document8 pagesCase Study Presentation: "Ectopic Pregnancy"Sherwina Alih-BieberPas encore d'évaluation
- LaborDocument19 pagesLaborAMARDEEP KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy1Document34 pagesEctopic Pregnancy1Kreshimaricon FurigayPas encore d'évaluation
- Early Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahDocument33 pagesEarly Pregnancy Complications: by Harvir Singh Supervised by DR Ranjit and DR SyafiqahShre RanjithamPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation (Er)Document32 pagesCase Presentation (Er)Apple Longos Erno100% (1)
- Family Case Study 1Document12 pagesFamily Case Study 1Mark Anthony Torcino AbianPas encore d'évaluation
- Inguinal Hernia and Hydrocele in ChildrenDocument7 pagesInguinal Hernia and Hydrocele in ChildrenIndraArdanaPas encore d'évaluation
- MANAGEMENT OF HYDRAMNIOS AND OLIGOHYDRAMNIOSDocument12 pagesMANAGEMENT OF HYDRAMNIOS AND OLIGOHYDRAMNIOSEaster Soma HagePas encore d'évaluation
- Usg Imaging: Cervical and Endometrial PolypsDocument10 pagesUsg Imaging: Cervical and Endometrial Polypsnajihah muzairi souzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scrotal AbnormalitiesDocument6 pagesScrotal AbnormalitiesmoominjunaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument61 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Diagnosis and TreatmentSuchie ILyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Abortion: Renhe Hospital Wang JunjieDocument51 pagesAbortion: Renhe Hospital Wang JunjieMadhu Sudhan PandeyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric vs Adult Hernia: Key Differences in Incidence, Presentation and ManagementDocument3 pagesPediatric vs Adult Hernia: Key Differences in Incidence, Presentation and ManagementClareen JuanicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument14 pagesEctopic PregnancytaufiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstructed Labour Causes, Symptoms, ManagementDocument5 pagesObstructed Labour Causes, Symptoms, ManagementswethashakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Tumor of The CervixDocument47 pagesBenign Tumor of The CervixjerrydanfordfxPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstructed LaborDocument41 pagesObstructed LaborHenok Y KebedePas encore d'évaluation
- Tubal pregnancy - causes, symptoms, and treatment of ectopic pregnancyDocument7 pagesTubal pregnancy - causes, symptoms, and treatment of ectopic pregnancyÄrmâÑÐ JôŠh BåùtîstâPas encore d'évaluation
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDocument9 pagesSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Obstetric Emergencies: First - Trimester Pregnancy EmergenciesDocument14 pagesObstetric Emergencies: First - Trimester Pregnancy EmergenciesdianPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - CS With BTLDocument16 pagesCase Study - CS With BTLAJ Roze Holmes100% (2)
- Abnormal Uterine ContractionDocument34 pagesAbnormal Uterine Contractionsapana shahPas encore d'évaluation
- IntussusceptionDocument10 pagesIntussusceptionshenlie100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument48 pagesEctopic PregnancyKN SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- PEDIATRIC SURGERY PROBLEMSDocument141 pagesPEDIATRIC SURGERY PROBLEMSsedaka26100% (4)
- A Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyDocument24 pagesA Woman Who Develops A Complication of PregnancyLady Jane CaguladaPas encore d'évaluation
- IntussusceptionDocument24 pagesIntussusceptionOjambo Flavia100% (1)
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesEctopic Pregnancymendato marcabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Cesarean-SectionDocument13 pagesCase Study Cesarean-SectionRenelli Anne Gonzaga100% (2)
- Pathological DeliveryDocument44 pagesPathological DeliverySitti AraPas encore d'évaluation
- Meckel Diverticulum, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandMeckel Diverticulum, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Raid Log TemplateDocument5 pagesRaid Log TemplateSabareesan SankaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Leading SAFe B&W Slides (4.6)Document100 pagesLeading SAFe B&W Slides (4.6)Priyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is AgileDocument4 pagesWhat Is AgilePriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Scrum: by Ramya PillaiDocument48 pagesScrum: by Ramya PillaiPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-2 (Two) Human Resource PlanningDocument2 pagesUnit-2 (Two) Human Resource PlanningPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- SharePoint Into A True Contract Management System.Document2 pagesSharePoint Into A True Contract Management System.Priyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Data-Driven 3D Cone Chart For Powerpoint: Sample TextDocument2 pagesData-Driven 3D Cone Chart For Powerpoint: Sample TextPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A User StoryDocument2 pagesWhat Is A User StoryPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Presentationgo: Lorem Ipsum Lorem Ipsum Lorem Ipsum Lorem IpsumDocument3 pagesPresentationgo: Lorem Ipsum Lorem Ipsum Lorem Ipsum Lorem IpsumPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- FF0166 01 Free 3d Slides Powerpoint 16x9Document10 pagesFF0166 01 Free 3d Slides Powerpoint 16x9veronika.94elisbetPas encore d'évaluation
- Competency Framework NotesDocument4 pagesCompetency Framework NotesPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Aguinis pm3 Tif 07Document15 pagesAguinis pm3 Tif 07Priyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- 08 PlacentaDocument7 pages08 PlacentaPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- 04 IugrDocument3 pages04 IugrPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- MBA-3rd Sem MDU (OCD) PDFDocument88 pagesMBA-3rd Sem MDU (OCD) PDFPriyanka George0% (1)
- 02 First TrimesterDocument6 pages02 First TrimesterPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Incompetent Cervix PDFDocument5 pages12 Incompetent Cervix PDFPriyanka George100% (1)
- General EconomicsDocument9 pagesGeneral EconomicsPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Course in OBS & GynaeDocument1 pageComprehensive Course in OBS & GynaePriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- 09 InfertilityDocument8 pages09 InfertilityPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- MU0016 Assignment Feb 11Document2 pagesMU0016 Assignment Feb 11Shantibhusan SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- IR Module 1 & 5Document45 pagesIR Module 1 & 5Priyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - FX02 PRINCE2 Sample Practitioner Paper - V1.5Document58 pages4 - FX02 PRINCE2 Sample Practitioner Paper - V1.5Priyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- HRM KtuDocument5 pagesHRM KtuPriyanka George100% (1)
- Eastern Condiments Pvt Ltd Internship Objectives and Industry AnalysisDocument101 pagesEastern Condiments Pvt Ltd Internship Objectives and Industry AnalysisPriyanka George75% (4)
- (Books - Stevenson, Buffa, Aswathapa, Adams or Any OM Book) : Production & Operations ManagementDocument20 pages(Books - Stevenson, Buffa, Aswathapa, Adams or Any OM Book) : Production & Operations ManagementPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- POM Module 2 Quality NotesDocument45 pagesPOM Module 2 Quality NotesPriyanka GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Breech PresentationDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Breech Presentationeskempertus0% (2)
- UTS 5. KOMPLIKASI POST PARTUS-English 2019Document63 pagesUTS 5. KOMPLIKASI POST PARTUS-English 2019Rafiq SamtoPas encore d'évaluation
- MENSTRUAL CYCLEI-Investigatory-project-of-biologyDocument22 pagesMENSTRUAL CYCLEI-Investigatory-project-of-biologyAkshayPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 - MHM Booklet 20191108 HRDocument12 pages08 - MHM Booklet 20191108 HRSandra Nicole SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonnie - Tam - 22S2 NUR2029 Teaching Schedule - Rev (1) (2) (3) - 5-1-23Document9 pagesBonnie - Tam - 22S2 NUR2029 Teaching Schedule - Rev (1) (2) (3) - 5-1-23Seokjin RJPas encore d'évaluation
- gynacology - revision - finalمدونة كل العرب الطبية PDFDocument14 pagesgynacology - revision - finalمدونة كل العرب الطبية PDFﻣﻠﻚ عيسىPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Also 2017 (1) (001-160)Document160 pagesManual Also 2017 (1) (001-160)Diana Calderon SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Anomalies of the Female Genital TractDocument170 pagesCongenital Anomalies of the Female Genital Tractonijino100% (1)
- Uterine MyomaDocument15 pagesUterine Myomaanon_302623176100% (1)
- Morning Report Divisi Uroginekologi OASISDocument21 pagesMorning Report Divisi Uroginekologi OASISmuhammadnurul asmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dystocia: Presented By:kushal Neupane Roll No:13 B.V.SC & A.H 8 Semester HicastDocument19 pagesDystocia: Presented By:kushal Neupane Roll No:13 B.V.SC & A.H 8 Semester Hicastkushal NeupanePas encore d'évaluation
- Cebu Doctors' University Nursing Students Present on Breast Care, Breastfeeding and Bottle FeedingDocument29 pagesCebu Doctors' University Nursing Students Present on Breast Care, Breastfeeding and Bottle FeedingDominic De GraciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Spontaneous Abortion - American Family PhysicianDocument8 pagesManagement of Spontaneous Abortion - American Family PhysicianGwEn LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDocument36 pagesAbnormal Uterine ActionMed PoxPas encore d'évaluation
- OB/GYN Student Study Guide Abbreviations and DefinitionsDocument38 pagesOB/GYN Student Study Guide Abbreviations and DefinitionsMin-Joo Esther Park100% (1)
- 2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFDocument21 pages2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFMd Rizwan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Controversies in Family Planning: How To Manage A Fractured IUDDocument5 pagesControversies in Family Planning: How To Manage A Fractured IUDPridina SyadirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan On Pregnancy PDFDocument10 pagesLesson Plan On Pregnancy PDFRuby Corazon EdizaPas encore d'évaluation
- CP102B FinalsDocument6 pagesCP102B FinalsAldrin Riel BoyanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antepartum Nursing AssessmentDocument88 pagesAntepartum Nursing AssessmentDeema AbuasiPas encore d'évaluation
- RIFbookDocument213 pagesRIFbookGaurav S DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1.5.3 Patologi Anatomi Sistem Urogenital Dan PayudaraDocument70 pages3.1.5.3 Patologi Anatomi Sistem Urogenital Dan PayudaraaiysahmirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineDocument17 pagesFinal Past Papers With Common MCQS: MedicineKasun PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory GlandsDocument29 pagesSection 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory Glandssomebody_maPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Breastfeeding WatermarkDocument83 pages2020 Breastfeeding WatermarkJasmin T. RegaspiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Case Presentation: Sevilla, Loreanne Novem Silim, Miriam Grace DDocument42 pagesA Case Presentation: Sevilla, Loreanne Novem Silim, Miriam Grace DKen StarPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalence of Postpartum Depression Among Mothers Who DeliveredDocument7 pagesPrevalence of Postpartum Depression Among Mothers Who Deliveredroven desuPas encore d'évaluation
- PCOS infertility case study treated with AyurvedaDocument3 pagesPCOS infertility case study treated with AyurvedaAlna TechnicalPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionchindobr8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labor Stages, Dystocia Causes and ManagementDocument3 pagesLabor Stages, Dystocia Causes and ManagementAllan NacinoPas encore d'évaluation