Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Materials Reviewer
Transféré par
Jhun Michael LocusCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Materials Reviewer
Transféré par
Jhun Michael LocusDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
Workability
-malleability-can be flattened Material science-involves investigating
-ductility-can be drawn into wire Material Engineering-designing
Brittleness-breaks instead of deforming Material scientist-the one who develop
Elasticity-ability to return to original Material Engineer- create new products
Plasticity-retain new shape CLASSIFICATION OF MATS
Toughness-ability to absorb energy Metals-compose of one or more metallic
-resistance to fracture Ceramics-compounds between metallic
Strength-resistance to distortion Traditional ceramics-composed of clay
IMPACT-placing 2 notched specimen Polymers-have low densities
-charpytest- supported at both ends COMPOSITES-2 or more individual metals
-izodtest-supported at one end ADVANCE MATS-mats that are unitlized
TYPES OF STRESSES/FORCES Semiconductors- have electrical properties
-tension-pulling,tugofwar,slingshot Biomaterials-implanted to human body
-compression-pushing together Smart Mats-groupof newandstateof the art
-stress-strain:testing uses standardized Nanomats-we call this the bottom approach
-tensiletest-most common test Ex.Carbon nanotube
-compressiontest-applies a load
ENGINEERINGSTRESS
ENGINEERING STRAIN The density or compactness-Atomic Packing factorCT
POISSON’S RATIO-relating modulus 6 atoms is contained-hexagonal closed-pck CT
Knowledge of the CT-Density computation
Geometrical atoms-Atom Stru& InterBondng 1 or 2 atomic position-Point Defects
Smallest particle-Atom 1D-Linear Defects
+C (1.67x10-23kg)-Proton & Neu 2D-Interfacial Defects
-C(9.11x10-31kg)-Electron 3D-Bulk defects
Gives an attraction -Electrical charge Atom is missing-vacancy
Significant limitation-Bohr Atomic Model Crowded-Self-Interstitial
Outermost orbit-The Wave Mechanical Model Represent Elements of compound-Solvent/host atoms
Interaction bet 2 isolated-Atomic bonding Denote an element or compound-Solute
Number of protons in nuc-Atomic number Solubility happens-Atomic size factor
Total number of P and N-Mass number CT for metals of both atoms-Crystal structure
P is not equal to N-isotopes The more electropositive one -Electronegativity
Metallic and non metallic-Ionic Bonding Metal have more of a tendency-Valences
Adjacent atom -Covalent Bonding Light microscope is used to study-Optical Microscopy
1,2,3 valence electron-Metallic bonding Capable of much higher -Electron Microscopy
Bond are weak-2ndary Bondng Details of internal microstructural-Transmission Electron
Atoms, ions or molecules-CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Microscopy
Repeating or periodic array-Crystalline Surface of a specimen to be examined-Scanning Electron
Atomic order -Structure of unit cell Microscopy
Atoms are present only at UC-Simple cubic Microscope generates -Scanning Probe Mircroscopy
Many metals has a UC-Face-Centered CubicCT The most common method utilized by ASTM-Grain size
Atoms located at 8 corners-Body centered CubicCT determination
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Tank Size CalculatorDocument6 pagesTank Size CalculatorVijayakumar Chandrasekaran100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Nuclear ReactorsDocument45 pagesNuclear ReactorsAtul100% (3)
- Nabll Mix DesignDocument29 pagesNabll Mix DesignPIDCL WITH SUBUDHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator Certification TrainingDocument69 pagesWastewater Treatment Plant Operator Certification Trainingkokushkin02Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 4.0 Three Phase SystemsDocument41 pagesCHAPTER 2 4.0 Three Phase SystemsMUHAMMAD ALIFF DANIAL RAZMIPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonwoven Material StandardsDocument5 pagesNonwoven Material StandardsRajesh Dwivedi0% (1)
- Part Number Part Name Part Number Part Name: Weichai Power WD10 Engine Spare Parts For EngineeringDocument3 pagesPart Number Part Name Part Number Part Name: Weichai Power WD10 Engine Spare Parts For EngineeringMd. Arefin Shawon100% (1)
- Force Required to Remove Shaft from HubDocument7 pagesForce Required to Remove Shaft from HubJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Force Required to Remove Shaft from HubDocument7 pagesForce Required to Remove Shaft from HubJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 38-2023 JDL Activity ReportDocument1 pageWeek 38-2023 JDL Activity ReportJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 30-2023 JDL Activity ReportDocument1 pageWeek 30-2023 JDL Activity ReportJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
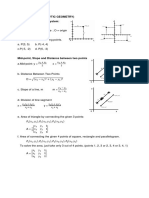
- MATHEMATICS (ANALYTIC GEOMETRY) EQUATIONSDocument4 pagesMATHEMATICS (ANALYTIC GEOMETRY) EQUATIONSJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion Without Answwer PDFDocument2 pagesConversion Without Answwer PDFJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- PPE1Document17 pagesPPE1Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework No.11: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Document6 pagesHomework No.11: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
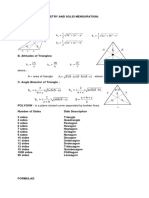
- Day 2 Plane and Solid GeometryDocument6 pagesDay 2 Plane and Solid GeometryJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 30-2023 JDL Activity ReportDocument1 pageWeek 30-2023 JDL Activity ReportJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 33-2023 JDL Activity ReportDocument1 pageWeek 33-2023 JDL Activity ReportJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics (Algebra) Properties of Inequality: F (X) G (X)Document4 pagesMathematics (Algebra) Properties of Inequality: F (X) G (X)Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PRACTICE EXAM SCOPEDocument1 pageMECHANICAL ENGINEERING PRACTICE EXAM SCOPEJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 2 1analytic GeometryDocument6 pagesDay 2 1analytic GeometryJhun Michael Locus100% (1)
- Homework No.8: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Document5 pagesHomework No.8: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Date Characters ASC. Mats ArtifactsDocument1 pageDate Characters ASC. Mats ArtifactsJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulley Key Shear Stress HomeworkDocument7 pagesPulley Key Shear Stress HomeworkJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Work No.5: BY: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Document6 pagesHome Work No.5: BY: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Seatwork No.5: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Document7 pagesSeatwork No.5: By: Jhun Michael D. Locus ME-5301Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- STUDYDocument3 pagesSTUDYJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitalization IntroDocument1 pageCapitalization IntroJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Santiago, Robert Ryan I. - PosDocument1 pageSantiago, Robert Ryan I. - PosJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Capitalization IntroDocument1 pageCapitalization IntroJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Reasearch LocusDocument1 pageProblem Reasearch LocusJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- MELAWSDocument4 pagesMELAWSJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- 5TH Year Second Sem PosDocument1 page5TH Year Second Sem PosJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- WK 3 WK 4 WK 1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4 WK 1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4 Wk1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4Document2 pagesWK 3 WK 4 WK 1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4 WK 1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4 Wk1 WK 2 WK 3 WK 4Jhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- TINADocument2 pagesTINAJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- 5TH Year Second Sem PosDocument1 page5TH Year Second Sem PosJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- 5TH Year Second Sem PosDocument1 page5TH Year Second Sem PosJhun Michael LocusPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing and Maintenance of Steam TrapsDocument8 pagesTesting and Maintenance of Steam TrapsAjaypalsinh GohilPas encore d'évaluation
- TMForumOpenAPIs EnablingAZeroIntergrationAPIeconomyDocument30 pagesTMForumOpenAPIs EnablingAZeroIntergrationAPIeconomyjdaoukPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Procedure ERLDCDocument154 pagesOperating Procedure ERLDCbramhanand vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae: Vivek PatilDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Vivek PatilVivek PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Control - Fundamental - W2 - Well Control PrincipleDocument17 pagesWell Control - Fundamental - W2 - Well Control PrincipleGilbert SunaryoPas encore d'évaluation
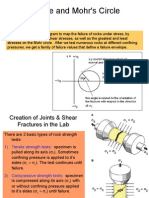
- Mohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressDocument26 pagesMohr's Circle Analysis of Rock Failure Under StressNitishPas encore d'évaluation
- QlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewDocument11 pagesQlikView Business Intelligence Tool OverviewMithun LayekPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal Drying Technology and Plant DesignDocument12 pagesCoal Drying Technology and Plant DesignJigar M. UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion Factors GuideDocument2 pagesConversion Factors GuideAndri MPPas encore d'évaluation
- Conventional Smoke DetectorDocument1 pageConventional Smoke DetectorThan Htike AungPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Inch Pipe Calculations For HydrostatDocument13 pages10 Inch Pipe Calculations For Hydrostatגרבר פליקסPas encore d'évaluation
- Vapor Pressure Experiment Data AnalysisDocument3 pagesVapor Pressure Experiment Data AnalysisRanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 General Types of Polymers Molecular StructureDocument3 pages4 General Types of Polymers Molecular StructureArgel Linard Francisco MabagaPas encore d'évaluation
- 864 Wiring Schematic: S/N 518913001-14999 S/N 516812001-14999 S/N 517512001-14999 (Printed March 2001) V-0072Document6 pages864 Wiring Schematic: S/N 518913001-14999 S/N 516812001-14999 S/N 517512001-14999 (Printed March 2001) V-0072Ataa AssaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionDocument7 pagesAcetylated Castor Oil - Preparation and Thermal DecompositionPee Hai NingPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5Document60 pagesCisco Expressway IP Port Usage For Firewall Traversal Deployment Guide X12 5JodiePas encore d'évaluation
- Gaspardo MAESTRA 2004-02 (19530520)Document78 pagesGaspardo MAESTRA 2004-02 (19530520)costelchelariuPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering Faculty Hydraulics Division: HydrologyDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering Faculty Hydraulics Division: HydrologyENA CO LTD100% (1)
- Load Case CombinationsDocument5 pagesLoad Case CombinationsFrancisco UgartePas encore d'évaluation
- Coverage of Quiz 1Document24 pagesCoverage of Quiz 1Ben RileyPas encore d'évaluation
- Remeha Gas 310 ECO: Technical InformationDocument59 pagesRemeha Gas 310 ECO: Technical InformationAdrian Blazquez MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phaser3300MFP Firmware Upgrade Instructions CWISDocument2 pagesPhaser3300MFP Firmware Upgrade Instructions CWISAlgenis De Leon RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Mks ConfigDocument5 pagesMks ConfigGabura TaniaPas encore d'évaluation