Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Math Symbols: Valentine Kindangen 16811015
Transféré par
Hiskia Mumu0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues3 pagesTitre original
basic math.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
28 vues3 pagesBasic Math Symbols: Valentine Kindangen 16811015
Transféré par
Hiskia MumuDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Valentine Kindangen
16811015
Basic math symbols
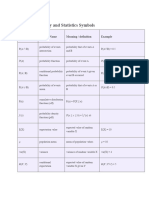
Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example
= equals sign equality 5 = 2+3
≠ not equal sign inequality 5≠4
> strict inequality greater than 5>4
< strict inequality less than 4<5
≥ inequality greater than or equal to 5≥4
≤ inequality less than or equal to 4≤5
() parentheses calculate expression inside first 2 × (3+5) = 16
[] brackets calculate expression inside first [(1+2)*(1+5)] = 18
+ plus sign addition 1+1=2
− minus sign subtraction 2−1=1
± plus - minus both plus and minus operations 3 ± 5 = 8 and -2
∓ minus - plus both minus and plus operations 3 ∓ 5 = -2 and 8
* asterisk multiplication 2*3=6
× times sign multiplication 2×3=6
∙ multiplication dot multiplication 2∙3=6
÷ division sign / obelus division 6÷2=3
/ division slash division 6/2=3
– horizontal line division / fraction
mod modulo remainder calculation 7 mod 2 = 1
. period decimal point, decimal separator 2.56 = 2+56/100
ab power exponent 23 = 8
a^b caret exponent 2 ^ 3= 8
√a square root √a · √a = a √9 = ±3
3
√a cube root 3
√a · 3√a · 3√a = a 3
√8 = 2
4
√a fourth root 4
√a · 4√a · 4√a · 4√a = a 4
√16 = ±2
n
√a n-th root (radical) for n=3, n√8 = 2
% percent 1% = 1/100 10% × 30 = 3
‰ per-mille 1‰ = 1/1000 = 0.1% 10‰ × 30 = 0.3
ppm per-million 1ppm = 1/1000000 10ppm × 30 = 0.0003
ppb per-billion 1ppb = 1/1000000000 10ppb × 30 = 3×10-7
ppt per-trillion 1ppt = 10-12 10ppt × 30 = 3×10-10
Probability and statistics symbols
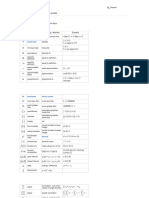
Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / definition Example
P(A) probability function probability of event A P(A) = 0.5
probability of events probability that of events A
P(A ∩ B) P(A∩B) = 0.5
intersection and B
probability of events probability that of events A or
P(A ∪ B) union B P(A∪B) = 0.5
conditional probability probability of event A given
P(A | B) P(A | B) = 0.3
function event B occured
probability density
f (x) P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫ f (x) dx
function (pdf)
cumulative distribution
F(x) F(x) = P(X ≤ x)
function (cdf)
μ population mean mean of population values μ = 10
expected value of random
E(X) expectation value E(X) = 10
variable X
expected value of random
E(X | Y) conditional expectation E(X | Y=2) = 5
variable X given Y
var(X) variance variance of random variable X var(X) = 4
σ2 variance variance of population values σ2 = 4
standard deviation of random
std(X) standard deviation std(X) = 2
variable X
standard deviation value of
σX standard deviation σX = 2
random variable X
middle value of random
median
variable x
covariance of random
cov(X,Y) covariance cov(X,Y) = 4
variables X and Y
correlation of random
corr(X,Y) correlation corr(X,Y) = 0.6
variables X and Y
correlation of random
ρX,Y correlation ρX,Y = 0.6
variables X and Y
summation - sum of all values
∑ summation
in range of series
∑∑ double summation double summation
value that occurs most
Mo mode
frequently in population
MR mid-range MR = (xmax+xmin)/2
half the population is below
Md sample median
this value
Q1 lower / first quartile 25% of population are below
this value
median / second 50% of population are below
Q2
quartile this value = median of samples
75% of population are below
Q3 upper / third quartile
this value
x sample mean average / arithmetic mean x = (2+5+9) / 3 = 5.333
population samples variance
s2 sample variance s2 = 4
estimator
sample standard population samples standard
s s=2
deviation deviation estimator
zx standard score zx = (x-x) / sx
distribution of random variable
X~ distribution of X X ~ N(0,3)
X
N(μ,σ2) normal distribution gaussian distribution X ~ N(0,3)
U(a,b) uniform distribution equal probability in range a,b X ~ U(0,3)
exp(λ) exponential distribution f (x) = λe-λx , x≥0
gamma(c,
gamma distribution f (x) = λ c xc-1e-λx / Γ(c), x≥0
λ)
χ 2(k) chi-square distribution f (x) = xk/2-1e-x/2 / ( 2k/2 Γ(k/2) )
F (k1, k2)F distribution
Bin(n,p) binomial distribution f (k) = nCk pk(1-p)n-k
Poisson(λ)Poisson distribution f (k) = λke-λ / k!
Geom(p) geometric distribution f (k) = p (1-p) k
hyper-geometric
HG(N,K,n)
distribution
Bern(p) Bernoulli distribution
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Applied Statistics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesApplied Statistics Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89Pas encore d'évaluation
- DNV Os C104 2014Document40 pagesDNV Os C104 2014Moe LattPas encore d'évaluation
- Symbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition ExampleDocument6 pagesSymbol Symbol Name Meaning or Definition Examplessrao2211Pas encore d'évaluation
- Data Assigment 1Document32 pagesData Assigment 1Sukhwinder Kaur100% (1)
- List of Mathematical SymbolsDocument21 pagesList of Mathematical SymbolsHedgeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Symbols 1Document8 pagesMathematical Symbols 1Arianne Rose FangonPas encore d'évaluation
- Math SymbolsDocument11 pagesMath SymbolsRussell MurphyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math SymbolsDocument20 pagesBasic Math SymbolsNoel O CedenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Symbols GuideDocument14 pagesMathematical Symbols GuideGoutam AcharjeePas encore d'évaluation
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematical Symbols Guide Under 40 CharactersDocument14 pagesMathematical Symbols Guide Under 40 Charactersanon_31699417100% (1)
- 1 Basic Math SymbolsDocument13 pages1 Basic Math SymbolsAlex OlivarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearden On Maxwell's EquationsDocument10 pagesBearden On Maxwell's Equationspaulsub63Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical SymbolsDocument1 pageStatistical SymbolsJaime Luis Estanislao Honrado100% (1)
- Basic Maths Symbols Names With Meaning and ExamplesDocument8 pagesBasic Maths Symbols Names With Meaning and ExamplesArianne Rose FangonPas encore d'évaluation
- Math SymbolsDocument36 pagesMath SymbolsTina Timmons100% (3)
- Citect V7.0 Error Codes PDFDocument13 pagesCitect V7.0 Error Codes PDFWahyu PrakosoPas encore d'évaluation
- CmeDocument41 pagesCmekhalis@hotmail.com100% (1)
- List of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDocument6 pagesList of Probability and Statistics SymbolsDave VillarbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Expectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition ExampleDocument2 pagesExpectation Value: Symbol Symbol Name Meaning / Definition Examplerijalul fikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Probability and Statistics Symbols GuideDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Symbols GuideChindieyciiEy Lebaiey CwekZrdoghPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument5 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListDay WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chandan Mandal 11.Document14 pagesChandan Mandal 11.jefferson sarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math SymbolsDocument24 pagesBasic Math SymbolsMuhammad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math SymbolsDocument18 pagesBasic Math SymbolsRobert KemperPas encore d'évaluation
- Danh sách ký hiệu toán họcDocument22 pagesDanh sách ký hiệu toán họcAN HOANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Symbols and Notations GuideDocument5 pagesMathematical Symbols and Notations GuideDARYL GAVINOPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Mathematical SymbolsDocument12 pagesBasic Mathematical SymbolsAllyson Angel IturiagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Symbols NameDocument19 pagesSymbols NameNoor E Alam KibriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2Document2 pagesAlgebra Symbols: When 2x 4, Then X 2AubreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebraic SymbolDocument2 pagesAlgebraic SymbolAman YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- ALGEBRA SYMBOLSDocument2 pagesALGEBRA SYMBOLSColeen Jhoy SietePas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical SymbolsDocument20 pagesMathematical SymbolsCommunity Rescue StationPas encore d'évaluation
- Simbol Matematik 2Document12 pagesSimbol Matematik 2Anonymous Ztyzc5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Symbols ListingDocument21 pagesMath Symbols ListingPhúc Hải NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- MMW CHAPTER 2aDocument10 pagesMMW CHAPTER 2aRising PhoenixPas encore d'évaluation
- SLT M1Document18 pagesSLT M1Xin Ni Chai100% (1)
- Basic Math Symbols: Equals SignDocument24 pagesBasic Math Symbols: Equals SignJella DulatrePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math SymbolsDocument16 pagesBasic Math SymbolsDương Bá LộcPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical symbols & probability symbols (μ,σ,..Document2 pagesStatistical symbols & probability symbols (μ,σ,..John Bond100% (1)
- Algebra Symbols ListDocument2 pagesAlgebra Symbols ListJohn BondPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture01 Uppsala EQG 12Document39 pagesLecture01 Uppsala EQG 12Henz RabinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math Symbols: Equals SignDocument3 pagesBasic Math Symbols: Equals SignAubreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math Symbols PDFDocument16 pagesBasic Math Symbols PDFRamnaresh Sharma0% (1)
- Basic Math SymbolsDocument3 pagesBasic Math SymbolsJeral DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic math symbols explainedDocument3 pagesBasic math symbols explainedFalse InforamationPas encore d'évaluation
- Math SymbolsDocument9 pagesMath SymbolsKeno OmićPas encore d'évaluation
- POL enDocument6 pagesPOL enPedroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical SymbolsDocument27 pagesMathematical SymbolsErica JoycePas encore d'évaluation
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document13 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)mushshrinkPas encore d'évaluation
- Taratingan, Czarina Jaya A. Assignment Deado, Marko 1 Dac Basic Math SymbolsDocument3 pagesTaratingan, Czarina Jaya A. Assignment Deado, Marko 1 Dac Basic Math SymbolsMarko JerichoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Random VariablesDocument7 pages2 Random Variablesshooky.2611Pas encore d'évaluation
- STA416 - Topic 4 - 1Document24 pagesSTA416 - Topic 4 - 1sofia the firstPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Symbols & Probability SymbolsDocument2 pagesStatistical Symbols & Probability SymbolsHugo MentzingenPas encore d'évaluation
- BU255 - All Formulas 2022fallDocument9 pagesBU255 - All Formulas 2022fallTony TheodoropoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math Symbols2Document16 pagesBasic Math Symbols2John Carl C. PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Formula SheetDocument17 pagesMath Formula SheetAnkit RajPas encore d'évaluation
- PAS Formula Tut 1-5Document5 pagesPAS Formula Tut 1-5TACN-2D-19ACN Le Thi HoaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1. Real Numbers, Intervals, and InequalitiesDocument12 pages1.1. Real Numbers, Intervals, and InequalitiesTearlëşşSufíåñPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic math symbols guideDocument15 pagesBasic math symbols guideYM Tuan IsyaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsDocument11 pagesSAT Subject Math Level 2 Facts & Formulas Numbers, Sequences, FactorsneenaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Math To Know in One Page PDFDocument3 pagesSAT Math To Know in One Page PDFhaya khaledPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3-2857Document8 pagesChapter 3-2857Kevin FontynPas encore d'évaluation
- Cagayan State University: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument21 pagesCagayan State University: Republic of The PhilippinesblessaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Castings, Welding, Qualifications of Procedures and PersonnelDocument15 pagesSteel Castings, Welding, Qualifications of Procedures and PersonnelRafael CossolinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Geology From Barmer Basin (India)Document12 pagesStructural Geology From Barmer Basin (India)Sankhajit SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Border Security Using Wireless Integrated Network Sensors (WINS)Document18 pagesBorder Security Using Wireless Integrated Network Sensors (WINS)Pradeep CheekatlaPas encore d'évaluation
- PAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorDocument2 pagesPAI Industries, Inc. - Catalog Polea de MotorAlexis VallePas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/03Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: PHYSICS 5054/03Titan XosmosPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Properties of Population Stability IndexDocument60 pagesStatistical Properties of Population Stability IndexВячеславPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle Database - Introduction To SQL Ed 2Document5 pagesOracle Database - Introduction To SQL Ed 2Miguel Alfonso DIAZ MORRISPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Refractive Index and Extinction CoefficientDocument276 pagesMaterials Refractive Index and Extinction CoefficientDr-Mandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Charts For Lognormal DataDocument7 pagesControl Charts For Lognormal Dataanjo0225Pas encore d'évaluation
- Airy stress function enables determination of stress components in pure beam bendingDocument19 pagesAiry stress function enables determination of stress components in pure beam bendingmaran.suguPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitachi ZW550Document12 pagesHitachi ZW550ForomaquinasPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluasi Mutu Fisik, Total Bakteri, Dan Sensori Minuman Sari Tempe Dengan Penambahan Bunga KecombrangDocument12 pagesEvaluasi Mutu Fisik, Total Bakteri, Dan Sensori Minuman Sari Tempe Dengan Penambahan Bunga KecombrangJosua PakpahanPas encore d'évaluation
- AP+Bio 013+Photosynthesis++Respiration+Worksheet WLDocument2 pagesAP+Bio 013+Photosynthesis++Respiration+Worksheet WLVincent SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Road Beyond 5G: A Vision and Insight of The Key TechnologiesDocument7 pagesThe Road Beyond 5G: A Vision and Insight of The Key TechnologiesSaurav SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Canon I Sensys LBP5300 5360Document192 pagesCanon I Sensys LBP5300 5360GonzaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Same Denominator or Numerator Worksheet 1Document2 pagesSame Denominator or Numerator Worksheet 1Jenny KimPas encore d'évaluation
- DBA Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDBA Roles and ResponsibilitiesMahesh Babu Sri100% (2)
- Ecen 326 - Lab 2 ReportDocument7 pagesEcen 326 - Lab 2 Reportapi-241454978Pas encore d'évaluation
- S4M Service ManualDocument522 pagesS4M Service ManualRafał Krzysztof Kowalski100% (1)
- WCB Customized Superior Quality Slewing Ring GearDocument173 pagesWCB Customized Superior Quality Slewing Ring GearWCB BEARINGPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pythagorean Spiral ProjectDocument2 pagesThe Pythagorean Spiral Projectapi-316478863Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mid-Term Engr 6201 2020Document3 pagesMid-Term Engr 6201 2020Naseri ShaunPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Prediction Studies On Electrical Insulation Navy Summary Report NAVALDocument142 pagesReliability Prediction Studies On Electrical Insulation Navy Summary Report NAVALdennisroldanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorials 1-4Document6 pagesTutorials 1-4KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation