Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
29 Waves-Wave Characteristics
Transféré par
eltytanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
29 Waves-Wave Characteristics
Transféré par
eltytanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
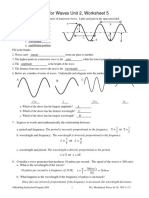
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
1. What is the wavelength of a 256-hertz sound wave 6. The diagram below represents a periodic wave.
in air at STP?
1. 1.17 × 106 m
2. 1.29 m
3. 0.773 m
4. 8.53 × 10-7 m
2. The graph below represents the relationship be- Which point on the wave is in phase with point P?
tween wavelength and frequency of waves created 1. A
by two students shaking the ends of a loose spring. 2. B
3. C
4. D
7. A periodic wave having a frequency of 5.0 hertz and
a speed of 10 meters per second has a wavelength of
1. 0.50 m
2. 2.0 m
3. 5.0 m
4. 50 m
8. A ringing bell is located in a chamber. When the air
is removed from the chamber, why can the bell be
seen vibrating but not be heard?
1. Light waves can travel through a vacuum, but
Calculate the speed of the waves generated in the sound waves cannot.
spring. [Show all work, including the equation and 2. Sound waves have greater amplitude than light
substitution with units.] waves.
3. Light waves travel slower than sound waves.
4. Sound waves have higher frequencies than light
waves.
3. What is the period of a water wave if 4 complete
waves pass a fixed point in 10 seconds? 9. The diagram below represents a transverse wave.
1. 0.25 s
2. 0.40 s
3. 2.5 s
4. 4.0 s
4. If the frequency of a periodic wave is doubled, the
period of the wave will be
1. halved The wavelength of the wave is equal to the distance
2. doubled between points
3. quartered 1. A and G
4. quadrupled 2. B and F
3. C and E
5. A 512-hertz sound wave travels 100 meters to an ob- 4. D and F
server through air at STP. What is the wavelength
of this sound wave?
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics WAV.A2 Page 161
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
10. The diagram below represents a periodic transverse wave traveling in a uniform medium.
On the diagram above, draw a wave having both a smaller amplitude and the same wavelength as the given wave.
Base your answers to questions 11 through 13 on the information and diagram below.
A longitudinal wave moves to the right through a uniform medium, as shown below. Points A, B, C, D, and E repre-
sent the positions of particles of the medium.
11. Which diagram best represents the motion of the particle at position C as the wave moves to the right?
12. The wavelength of this wave is equal to the distance between points
1. A and B
2. B and C
3. A and C
4. B and E
13. The energy of this wave is related to its
1. amplitude
2. period
3. speed
4. wavelength
Page 162 WAV.A2 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
14. Which wave diagram has both wavelength (λ) and amplitude (A) labeled correctly?
15. The diagram below represents a transverse wave moving on a uniform rope with point A labeled as
shown. On the diagram, mark an X at the point on the wave that is 180° out of phase with point A.
Base your answers to questions 16 through 18 on the information and diagram below.
Three waves, A, B, and C, travel 12 meters in 2.0 seconds through the same medium as shown in the diagram below.
16. What is the amplitude of wave C?
17. What is the period of wave A?
18. What is the speed of wave B?
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics WAV.A2 Page 163
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
Base your answers to questions 19 through 21 on the information below. [Show all work, including the
equation and substitution with units.]
A stationary submarine uses sonar to send a 1.18 × 103-hertz sound wave down through the
ocean water. The reflected sound wave from the flat ocean bottom 324 meters below the sub
is detected 0.425 seconds after it was sent from the submarine.
19. Calculate the speed of the sound wave in the ocean water.
20. Calculate the wavelength of the sound wave in the ocean water.
21. Determine the period of the sound wave in the ocean water.
22. A motor is used to produce 4.0 waves each second in The amplitude of the wave is
a string. What is the frequency of the waves? 1. 4.0 s
1. 0.25 Hz 2. 6.0 s
2. 15 Hz 3. 8 cm
3. 25 Hz 4. 4 cm
4. 4.0 Hz
26. A periodic wave is produced by a vibrating tuning
23. If the amplitude of a wave is increased, the frequency fork. The amplitude of the wave would be greater if
of the wave will the tuning fork were
1. decrease 1. struck more softly
2. increase 2. struck harder
3. remain the same 3. replaced by a lower frequency tuning fork
4. replaced by a higher frequency tuning fork
24. The time required for a wave to complete one full
cycle is called the wave’s 27. The diagram below represents a periodic wave.
1. frequency
2. period
3. velocity
4. wavelength
25. The graph below represents the displacement
of a particle in a medium over a period of time.
Which point on the wave is 90° out of phase with
point P?
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Page 164 WAV.A2 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
28. A periodic wave travels at speed v through medium A. The wave passes with all its energy into medium B. The
speed of the wave through medium B is v/2. On the diagram below, draw the wave as it travels through medium
B. Show at least one full wave.
29. The energy of a water wave is closely related to its 33. The energy of a sound wave is closely related to its
1. frequency 1. period
2. wavelength 2. amplitude
3. period 3. frequency
4. amplitude 4. wavelength
30. The diagram below represents a transverse wave. 34. The diagram below shows a periodic wave.
Which points are in phase with each other?
The distance between which two points identifies the 1. A and C
amplitude of the wave? 2. A and D
1. A and B 3. B and C
2. A and C 4. C and D
3. A and E
4. D and E 35. Which unit is equivalent to meters per second?
1. Hz∙s
31. If the amplitude of a wave traveling in a rope is 2. Hz∙m
doubled, the speed of the wave in the rope will 3. s/Hz
1. decrease 4. m/Hz
2. increase
3. remain the same 36. The sound wave produced by a trumpet has a fre-
quency of 440 hertz. What is the distance between
32. Increasing the amplitude of a sound wave produces a successive compressions in this sound wave as it
sound with travels through air at STP?
1. lower speed 1. 1.5 × 10-6 m
2. higher pitch 2. 0.75 m
3. shorter wavelength 3. 1.3 m
4. greater loudness 4. 6.8 × 105 m
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics WAV.A2 Page 165
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
Base your answers to questions 37 and 38 on the information and diagram below.
A student standing on a dock observes a piece of wood floating on the water as shown below. As a water wave
passes, the wood moves up and down, rising to the top of a wave crest every 5.0 seconds.
37. Calculate the frequency of the passing water waves. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution
with units.]
38. Calculate the speed of the water waves. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.]
39. The diagram below represents a periodic 41. A surfacing whale in an aquarium produces water
wave traveling through a uniform medium. wave crests every 0.40 seconds. If the water wave
travels at 4.5 meters per second, the wavelength of
the wave is
1. 1.8 m
2. 2.4 m
3. 3.0 m
If the frequency of the wave is 2.0 hertz, the speed of 4. 11 m
the wave is
1. 6.0 m/s 42. The diagram below represents a trans-
2. 2.0 m/s verse wave moving along a string.
3. 8.0 m/s
4. 4.0 m/s
40. Two waves having the same frequency and ampli-
tude are traveling in the same medium. Maximum
constructive interference occurs at points where the
phase difference between the two superimposed On the diagram above, draw a transverse wave that
waves is would produce complete destructive interference
1. 0° when superimposed with the original wave.
2. 90°
3. 180° 43. The product of a wave’s frequency and its period is
4. 270° 1. one
2. its velocity
3. its wavelength
4. Planck’s constant
Page 166 WAV.A2 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
Base your answers to questions 44 and 45 on the 48. A tuning fork vibrates at a frequency of 512 hertz
information below. when struck with a rubber hammer. The sound
produced by the tuning fork will travel through the
A student plucks a guitar string and the air as a
vibrations produce a sound wave with a fre- 1. longitudinal wave with air molecules vibrating
quency of 650 hertz. parallel to the direction of travel
2. transverse wave with air molecules vibrating
44. The sound wave produced can best be parallel to the direction of travel
described as a 3. longitudinal wave with air molecules vibrating
1. transverse wave of constant amplitude perpendicular to the direction of travel
2. longitudinal wave of constant frequency 4. transverse wave with air molecules vibrating
3. mechanical wave of varying frequency perpendicular to the direction of travel
4. electromagnetic wave of varying wavelengths
49. What is characteristic of both sound waves and elec-
45. Calculate the wavelength of the sound wave in air tromagnetic waves?
at STP. [Show all work, including the equation and 1. They require a medium.
substitution with units.] 2. They transfer energy.
3. They are mechanical waves.
4. They are longitudinal waves.
50. What is the wavelength of a 2.50-kilohertz sound
Base your answers to questions 46 and 47 on the infor- wave traveling at 326 meters per second through air?
mation below. 1. 0.130 m
2. 1.30 m
A transverse wave with an amplitude of 0.20 meters and 3. 7.67 m
wavelength of 3.0 meters travels toward the right in a 4. 130 m
medium with a speed of 4.0 meters per second.
51. While sitting in a boat, a fisherman observes that
46. On the diagram below, place an X at each of two complete waves pass by his position every 4
two points that are in phase with each other. seconds. What is the period of these waves?
1. 0.5 s
2. 2 s
3. 8 s
4. 4 s
52. A sound wave traveling eastward through air causes
the air molecules to
1. vibrate east and west
2. vibrate north and south
3. move eastward, only
4. move northward, only
47. Calculate the period of the wave. [Show all work,
including the equation and substitution with units.]
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics WAV.A2 Page 167
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
53. The diagram below represents a periodic wave. 58. The diagram below represents two waves, A and
B, traveling through the same uniform medium.
Which two points on the wave are out of phase?
1. A and C
2. B and F Which characteristic is the same for both waves?
3. C and E 1. amplitude
4. D and G 2. frequency
3. period
54. A distance of 1.0 × 10-2 meter separates successive 4. wavelength
crests of a periodic wave produced in a shallow tank
of water. If a crest passes a point in the tank every 59. A duck floating in a pool oscillates up and down 5.0
4.0 × 10-1 second, what is the speed of this wave? times during a 10.-second interval as a periodic wave
1. 2.5 × 10-4 m/s passes by. What is the frequency of the duck’s oscil-
2. 4.0 × 10-3 m/s lations?
3. 2.5 × 10-2 m/s 1. 0.10 Hz
4. 4.0 × 10-1 m/s 2. 0.50 Hz
3. 2.0 Hz
55. A nurse takes the pulse of a heart and 4. 50. Hz
determines the heart beats periodically
60 times in 60 seconds. The period of 60. A student produces a wave in a long spring by vi-
the heartbeat is brating its end. As the frequency of the vibration is
1. 1 Hz doubled, the wavelength in the spring is
2. 60 Hz 1. quartered
3. 1 s 2. halved
4. 60 s 3. unchanged
4. doubled
56. What is the period of a sound wave having a fre-
quency of 340 hertz? 61. The diagram below shows waves A and B in the
1. 3.40 × 102 s same medium.
2. 1.02 × 100 s
3. 9.73 × 10-1 s
4. 2.94 × 10-3 s
57. A beam of light has a wavelength of 4.5 × 10-7 meter
in a vacuum. The frequency of this light is
1. 1.5 × 10-15 Hz
2. 4.5 × 10-7 Hz Compared to wave A, wave B has
3. 1.4 × 102 Hz 1. twice the amplitude and twice the wavelength
4. 6.7 × 1014 Hz 2. twice the amplitude and half the wavelength
3. the same amplitude and half the wavelength
4. half the amplitude and the same wavelength
Page 168 WAV.A2 APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics
Name: Period:
Waves-Wave Characteristics
62. Which two points on the wave shown in the
diagram below are in phase with each other?
1. A and B
2. A and E
3. B and C
4. B and D
63. A microwave oven emits a microwave with a wave-
length of 2.00 × 10-2 meter in air. Calculate the
frequency of the microwave. [Show all work, includ-
ing the equation and substitution with units.]
APlusPhysics: Waves-Wave Characteristics WAV.A2 Page 169
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1 0wave1 11 2activityDocument10 pages1 0wave1 11 2activityNisa Hj MohamadPas encore d'évaluation
- WAVESDocument2 pagesWAVESJustus D ZatkalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz On Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesQuiz On Work, Energy, and PowerNathaniel DimaocorPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesWaves Worksheettownsenr94100% (14)
- 30 Waves-Wave BehaviorsDocument10 pages30 Waves-Wave BehaviorseltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Testbank Chapter09Document20 pagesTestbank Chapter09AldrianYanesa100% (1)
- WORKSHEET 4. DynamicsDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 4. DynamicsJoe WestPas encore d'évaluation
- Conservation of Energy QuizDocument2 pagesConservation of Energy QuizJay Noma RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/msDocument16 pagesMultiple-Choice Question 1985 Take G 10 m/s2.: Velocity/mssliversniperPas encore d'évaluation
- 33 Waves DiffractionDocument3 pages33 Waves DiffractioneltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Revision MC TestDocument36 pagesWaves Revision MC Testlove_241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Harmonic MotionDocument7 pagesSimple Harmonic MotionRaju SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 DynamicsDocument47 pagesModule 2 DynamicsTaha Kafil-HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Physics Waves Worksheet With MSDocument8 pagesIB Physics Waves Worksheet With MSpreksha spamPas encore d'évaluation
- 60 Surface Temperature & LuminosityDocument2 pages60 Surface Temperature & Luminosityvalsamis8334Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Magnetism - AllDocument14 pagesIb Magnetism - AllAarav VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinematics WorksheetDyanie PlummerPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves - Worksheet Transverse and LongitudinalDocument2 pagesWaves - Worksheet Transverse and Longitudinalschlemielz100% (1)
- Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldDocument37 pagesChapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldheyyyalePas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersDocument2 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion Review Worksheet With AnswersVicious core100% (1)
- 5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceDocument2 pages5.3 Friction On Level SurfaceBenPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave PropertiesDocument2 pagesWave PropertiesAshok Kumar Dondati100% (1)
- Motion & Force WorksheetDocument12 pagesMotion & Force Worksheethussain azizPas encore d'évaluation
- WorkEnergy P2Document26 pagesWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - WorksheetDocument12 pages4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - Worksheetkoelia100% (1)
- Work Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesWork Energy and Powerashrafrazi100% (1)
- A2 MECH Momentum QuestionsDocument8 pagesA2 MECH Momentum Questionsfootball_frenzy_2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Topic 3 Particle Physics - Lesson NotesDocument26 pagesEdexcel GCE A2 Physics Unit 4 Topic 3 Particle Physics - Lesson NotesPaul Burgess75% (4)
- 5.1.2 Worksheet 2Document3 pages5.1.2 Worksheet 2Ali AkbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Turning Effects of Forces PDFDocument6 pagesTurning Effects of Forces PDFMazharul SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Friction WorksheetDocument2 pagesFriction WorksheetNilar SanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Doppler Effect - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesThe Doppler Effect - Multiple Choice Questionsjonni sitorusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chaptest BDocument6 pagesChaptest BJun MitsuhashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Turning Effect of Forces: Chapter 5 NotesDocument5 pagesTurning Effect of Forces: Chapter 5 NotesHryan MahajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 125 Pex 5Document9 pagesPhys 125 Pex 5Richard OuPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Exploration: Temperature and Particle MotionDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Temperature and Particle MotionKimberly TaboraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 2019 Year 11 Preliminary TaskDocument11 pagesPhysics 2019 Year 11 Preliminary TaskSyed Hasan100% (1)
- AP Physics 1 Work Energy WKST From AP ProbsDocument2 pagesAP Physics 1 Work Energy WKST From AP ProbsGean GenizaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsDocument18 pagesPSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week Waves WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeek Waves WorksheetSaghir ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- 31 Waves ReflectionDocument2 pages31 Waves Reflectioneltytan100% (1)
- A2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017Document3 pagesA2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017AbhiKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Physics Revision GuideDocument78 pagesA2 Physics Revision GuideThomas Roe100% (3)
- Chap10no1 PDFDocument2 pagesChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel0% (9)
- PhysicsDocument90 pagesPhysicsAmerah Nur-Aseyah Paunte100% (1)
- 14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveDocument4 pages14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveMahad AsimPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4 - OW - (B) SuperpositionDocument59 pagesCH 4 - OW - (B) Superpositionsonali_krishPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism: (A) Magnetic Field of MagnetsDocument6 pagesElectromagnetism: (A) Magnetic Field of MagnetsLouella LaquintaPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Dynamics-Newton's 3rd LawDocument2 pages09 Dynamics-Newton's 3rd LaweltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank of Sound PDFDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank of Sound PDFSwamy Nathan100% (1)
- Voltage and ResistanceDocument4 pagesVoltage and ResistanceMark ProchaskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSDocument20 pagesElectronic Control Questions FOR IGCSE PHYSICSFahim Ahmed100% (1)
- 08 Dynamics-Newton's 2nd LawDocument9 pages08 Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Laweltytan100% (1)
- L08 Refraction of LightDocument15 pagesL08 Refraction of LightJohn JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1Document44 pagesDay 1Erika Marie D. De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves: Name - TeacherDocument47 pagesWaves: Name - TeachersaadPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.3 Waves AnswersDocument66 pages3.3 Waves Answersmarkmattesz06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Problems Worksheet IIDocument2 pagesWaves Problems Worksheet IIAnkit MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Comparing Various Types of CollisionsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Comparing Various Types of CollisionseltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceeltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: © 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights ReservedDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: © 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights ReservedeltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheeteltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Units and DimensionsDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Units and Dimensionseltytan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson: Rectilinear Motion: Graphical Representation and InterpretationeltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Document7 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Radioactivity P2Document2 pagesPhy Radioactivity P2eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- AL Applied Mathematics 1987 Paper1+2 (E)Document6 pagesAL Applied Mathematics 1987 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Graphical Method P2Document1 pagePhy Graphical Method P2eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Radioactivity P22Document5 pagesPhy Radioactivity P22eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Electronics P2Document5 pagesPhy Electronics P2eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics: Physics-MC/Electrostatics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesElectrostatics: Physics-MC/Electrostatics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics: Physics-MC/Electronics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 11Document11 pagesElectronics: Physics-MC/Electronics/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 11eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetism: Physics-MC/Electromagnetism/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesElectromagnetism: Physics-MC/Electromagnetism/By Lee Siu Hin Page 1 of 3eltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sinusoidal Wave of FDTDDocument4 pagesSinusoidal Wave of FDTDKIKIPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Dynamics - Coanda EffectsDocument23 pagesFluid Dynamics - Coanda EffectspitcabPas encore d'évaluation
- Fab Amt 4203 Prelim Module No.2Document22 pagesFab Amt 4203 Prelim Module No.2angeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Lectures On 2d Gravity and 2d String TheoryDocument200 pagesLectures On 2d Gravity and 2d String Theorymanosmagicas7340Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Quantum Physics PDFDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Quantum Physics PDFprithwiraj chatterjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Exchanger FormulasDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger FormulasAnna TrinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 2nbsped 812032790x 9788120327900 CompressDocument720 pagesFundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 2nbsped 812032790x 9788120327900 Compresssweetyjun161998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Thermodynamics - Volume 2 - Advanced Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamic Fundamentals (PDFDrive) PDFDocument647 pagesFluid and Thermodynamics - Volume 2 - Advanced Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamic Fundamentals (PDFDrive) PDFsamson pinguraiPas encore d'évaluation
- THERMODYNAMICSDocument21 pagesTHERMODYNAMICSUttam SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- SECTION A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesSECTION A: Multiple Choice QuestionsJ EJPas encore d'évaluation
- BKF2443 Chapter 8 - 04 Explicit SolutionDocument6 pagesBKF2443 Chapter 8 - 04 Explicit SolutionNur FashihahPas encore d'évaluation
- Kostic 2011Document25 pagesKostic 2011Anonymous mXicTi8hBPas encore d'évaluation
- 6) Differentiations - Questions - PDF Download 11thDocument6 pages6) Differentiations - Questions - PDF Download 11thrajatv271722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mittelstedt C Engineering Mechanics 2 Strength of MaterialsDocument328 pagesMittelstedt C Engineering Mechanics 2 Strength of MaterialsStrahinja DonicPas encore d'évaluation
- Homogenous Coordinate System: Unit 1Document52 pagesHomogenous Coordinate System: Unit 1Sanand MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tut 2Document2 pagesTut 2CK VigneshPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry of Hamiltonian Dynamics With Conformal Eisenhart MetricDocument27 pagesGeometry of Hamiltonian Dynamics With Conformal Eisenhart MetricsggtioPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Engineering MCQDocument41 pagesThermal Engineering MCQmohan rajPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE408 - Week 12 - State SpaceDocument54 pagesECE408 - Week 12 - State SpaceNishikata ManipolPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistrymc Febuary 14, 2012Document4 pagesChemistrymc Febuary 14, 2012Brandon LamPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Nonlinear Control Lecture # 4 PassivityDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Nonlinear Control Lecture # 4 PassivityZain BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Basic DefinitionsDocument20 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Basic DefinitionsVedansh KeshariPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroductionDocument24 pagesIntroductionskluxPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1 FM SD IITGDocument18 pagesLecture1 FM SD IITGRanjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023week10 PreDocument3 pages2023week10 PreNiroshan KarunarathnaPas encore d'évaluation
- ( (Diffusion) ) : Chapter (10) in VolumeDocument9 pages( (Diffusion) ) : Chapter (10) in Volumeashwaq100% (1)
- Contents of Adler, Bazin and SchifferDocument7 pagesContents of Adler, Bazin and SchifferDishant Pandya0% (1)
- Momentum Equation in Cylindrical Coordinate: Appendix BDocument8 pagesMomentum Equation in Cylindrical Coordinate: Appendix BAbdul Rauf AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Weinberg NotesDocument116 pagesWeinberg Notesjvb.hcPas encore d'évaluation