Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map Complex Care 2017
Transféré par
api-401537905Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Concept Map Complex Care 2017
Transféré par
api-401537905Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
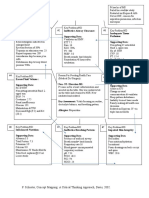
Step 1. Write the key problems the patient has based on the data collected. The key
problems are also known as the concepts. Start by centering the reason for seeking health
care (often a medical diagnosis). Next, list the major problems you have identified based
on the assessment data collected on the patient.
SLOPPY COPY
Key Problem:
Key Problem: Key Problem:
Ineffective Airway Clearance/
risk for infection Impaired Gas Exchange Risk for Deficient Fluid
Volume
Reason for Needing Health Care: Key Problem:
Key Problem:
Acute Respiratory Failure due to Pneumonia Impaired Verbal
Imbalanced Nutrition: less than Communication
body requirements 62 years old, Male, Full Code
Allergies: NKA
Key Assessment: VS with focus on respiratory
Key Problem: Key Problem:
Impaired skin integrity; Impaired Spontaneous
malnutrition and sores Ventilation
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
2
Step 2. Support problems with clinical patient data, including abnormal physical
assessment findings, treatments, medications, and IV’s, abnormal diagnostic and lab tests,
medical history, emotional state and pain. Also, identify key assessments that are related
to the reason for health care (chief medical diagnosis/surgical procedure) and put these in
the central box. If you do not know what box to put data in, then put it off to the side of
the map.
# Key Problem/ND: # Key Problems/ND: # Key Problem/ND:
Ineffective Airway Clearance/ risk for Impaired Gas Exchange Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume
infection
Supporting Data: Supporting Data:
Supporting Data: FiO2 .60 NPO
Blood tinged secretions Cancer of the Lungs Hypotension 86/69
Zosyn (pipercillin) IV Heavier Smoker Dry pink mucus membranes
Neutrophils 85 (H) Hypoxia with altered mental status Tachycardia
ETT suction every 2 hours Tachycardia
Turn every 2 hours
Diminished breath sounds all lobes
# Key Problem/ND:
# Key Problem/ND:
Imbalanced Nutrition: less than body
Impaired Verbal Communication
requirements
Reason For Needing Health Care
(Medical Dx/ Surgery) Supporting Data:
Supporting Data:
ETT placed in-patient
NPO
Acute Respiratory Failure due to Pneumonia Sedation
Endotracheal tube
Decreased ability to follow verbal
No IV fluids running
62 years old, Male, Full Code commands from nurse
Allergies: NKA
Key Assessment: VS with focus on respiratory
# Key Problem/ND: Data don’t know where to put in # Key Problem/ND:
boxes:
Impaired skin integrity; malnutrition Impaired Spontaneous Ventilation
and sores
Supporting Data:
Supporting Data: On Ventilator
NPO Mode A/C
Fluid imbalances Rate 14
ETT FiO2 60%
Sores on Coccyx TV 470
Abrasion on right hip and right foot PEEP 5
Mouth care every 2 hours
Step 3: Draw lines between related problems. Number boxes as you prioritize problems.
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
3
LASTLY- label the problem with a nursing diagnosis.
Step 4: Identification of goals, outcomes and interventions.
Step 5: Evaluation of Outcomes
Problem # _______: Ineffective Airway Clearance and risk for infection
General Goal: Increase airway clearance and no signs or symptoms of infection
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will……have patent airway with breath sounds that are
not diminished and secretions that are not blood tinged and less thick. Will also show no elevation in WBC for
signs of infection on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess breath sounds on all lobes 1. Diminished in all lobes
2. Assess the secretions 2. Blood tinged and thick
3. Give antibiotics 3. Zosyn (pipercillin) IV
4. Suction every 2 hours or PRN 4. Pt coughed when being suctioned
5. Turn every 2 hours 5. Turned with nurse pt also
6. Elevated head of bed coughed when being turned
7. Give breath treatments 6. Elevated in semi fowlers
7. Respiratory came in and gave
treatment
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
4
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patent airway with breath sounds clearing, absence of blood tinged secretions
and no signs of infection.
Problem # _______: Impaired Gas Exchange
General Goal: Increase Gas Exchange
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will……have decreased FiO2 and be able to tolerate it
on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Asses breath sounds 1. Diminished in all lobes
2. Assess ABGs 2. Sent to the lab during our shift
3. Assess the FiO2 3. Decreased for 60% to 40% on the shift
4. Elevate Head of bed 4. Elevated in semi fowlers
5. Assess the chest X-ray 5. Doctor ordered one for the patient
6. Mechanical Ventilation 6. Provides supportive care to maintain
oxygenation and ventilation
Evaluation of outcome objectives: The patient was able to decrease the FiO2 from 60% to 40% during the shift
so the patient was improving.
Step 3: Draw lines between related problems. Number boxes as you prioritize problems.
LASTLY- label the problem with a nursing diagnosis.
Step 4: Identification of goals, outcomes and interventions.
Step 5: Evaluation of Outcomes
Problem # _______: Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume
General Goal: Increase fluid volume
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will……have increase in blood pressure, moist pink
membranes, heart rate in normal ranges on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. BP 86/69 Temp 97.7 HR 117
1. Assess the vital signs 2. Skin turgor elastic, dry pink mucus
membranes
3. Didn’t vomit on shift
4. Total of 325 mL during my shift
5. Patient sweating
6. BUN was within normal limits
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
5
2. Assess skin turgor, mucus membranes
3. Assess for vomiting
4. Monitor I & O
5. Monitor for insensible losses
6. Monitor Labs like BUN
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient had a heat rate of 96 at end of shift, the skin turgor was elastic but
membranes were still dry and patient was still NPO.
Problem # _______: Imbalanced Nutrition: less than body requirements
General Goal: Improved Nutritional Status
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will……show normal lab values with BUN, will show
no signs of infection, and no abdominal distention on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess the Ng suction 1. Blood tinged
2. Provide oral mouth care 2. Every 2 hours or PRN for the patient
3. Check placement of NG 3. With a CXR everyday and air bolus prn
4. Elevate HOB 4. Patient HOB semi fowlers at all times
5. Monitor labs 5. Normal BUN
6. Assess the stool 6. Patient didn’t have a bowel movement
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient had normal BUN levels, no signs of infection, and the abdomen was
nontender soft and symmetric.
Step 3: Draw lines between related problems. Number boxes as you prioritize problems.
LASTLY- label the problem with a nursing diagnosis.
Step 4: Identification of goals, outcomes and interventions.
Step 5: Evaluation of Outcomes
Problem # _______: Impaired Verbal Communication
General Goal: Effective Communication
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will…… respond with appropriate nonverbal
behaviors to verbal commands on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
8. Neurological Assessment
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
6
9. Assess ETT tube and cuff 9. Size 7 ½ Lip Line 24
pressure 10. Patient opens eyes to command
10. Assess ability to follow verbal 11. Spoken loud enough so patient
commands could hear and just explained
11. Use soft voice and touch before touching patient
12. Administer sedation 12. Propofol 1.8 mL/hour
8. Patient was sedated
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
7
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient was able to open eyes on command but couldn’t really follow
commands like saying to lift arm up or leg.
Problem # _______: Impaired skin integrity; malnutrition and sores
General Goal: Improved skin integrity
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will…… patient will not have any further skin
breakdown during hospitalization and wounds will be kept clean and free of infection on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess site of impaired skin 1. Sore on coccyx/abrasions on R Hip/R foot
2. Assess odor, drainage, size, color 2. No odor or drainage, sores all were pink
3. Assess signs for infections 3. Lymphocytes elevated 6
4. Assess temperature 4. Not elevated
5. Change dressings as needed 5. Normal saline dressing with foam patch
6. Change diaper when stool is passed 6. Had no BM during shift and had Foley in
Evaluation of outcome objectives: check wounds every shift and change and clean dressing if there is drainage.
Step 3: Draw lines between related problems. Number boxes as you prioritize problems.
LASTLY- label the problem with a nursing diagnosis.
Step 4: Identification of goals, outcomes and interventions.
Step 5: Evaluation of Outcomes
Problem # _______: Impaired Spontaneous Ventilation
General Goal: Maintain Ventilations
Predicted Behavioral Outcome Objective (s): The patient will……tolerate ventilator on ordered settings and
have moist mucous membranes on the day of care.
Nursing Interventions Patient Responses
1. Assess Ventilator Settings 1. Decreased FiO2 during shift .60 to .40
2. Monitor SpO2 2.
3. Mouth Care 3. Did Q2 hours or PRN
4. Watch Sedation 4. 1.8 mL/hour
5. Assess the ETT and cuff pressure 5. Size 7 ½ Lip Line 24
Evaluation of outcome objectives: Patient was able to decrease the FiO2 during shift
P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument11 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-546697029Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4832 Concept MapDocument7 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-508446364Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument6 pagesConcept Mapapi-499028250Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4832 Concept MapDocument9 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-663135887Pas encore d'évaluation
- CC Concept MapDocument5 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-663024375Pas encore d'évaluation
- Step 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The KeyDocument7 pagesStep 1. Write The Key Problems The Patient Has Based On The Data Collected. The Keyapi-594625714Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map FinalDocument5 pagesConcept Map Finalapi-545001894Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapapi-546509005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map CCDocument8 pagesConcept Map CCapi-402644703Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map 2020Document4 pagesConcept Map 2020api-546505804Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument6 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-508559825Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Epidural AbcessDocument11 pagesConcept Map Epidural Abcessapi-593859653Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Part LLDocument5 pagesConcept Map Part LLapi-662892413Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brooke Baker Concept Map 4840 Complex Care: P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002Document10 pagesBrooke Baker Concept Map 4840 Complex Care: P. Schuster, Concept Mapping: A Critical Thinking Approach, Davis, 2002api-546799391Pas encore d'évaluation
- CC Concept MapDocument6 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-741058487Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Final Copy1Document7 pagesConcept Map Final Copy1api-608271845Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Critical CareDocument5 pagesConcept Map Critical Careapi-546401036Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map CCDocument7 pagesConcept Map CCapi-546473008Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4832 Concept MapDocument3 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-498427226Pas encore d'évaluation
- CC Concept Map Part LL 1Document5 pagesCC Concept Map Part LL 1api-604539767Pas encore d'évaluation
- CC - Concept MapDocument2 pagesCC - Concept Mapapi-546518436Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care PatientDocument8 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan For Critical Care Patientapi-593853954Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map Part LLDocument6 pagesConcept Map Part LLapi-455232702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept Mapapi-608044542Pas encore d'évaluation
- CC Concept MapDocument5 pagesCC Concept Mapapi-662323379Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cirrhosis: Primary Concept Nutrition Interrelated Concepts (In Order of Emphasis)Document12 pagesCirrhosis: Primary Concept Nutrition Interrelated Concepts (In Order of Emphasis)Peggy100% (1)
- Ashley Wolanzyk Concept MapDocument5 pagesAshley Wolanzyk Concept Mapapi-455796674Pas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care Concept Map Template Final 2Document6 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Template Final 2api-740444719Pas encore d'évaluation
- PediaDocument6 pagesPediaAaron Joshua PobrePas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map NewDocument13 pagesConcept Map Newapi-663972838Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Elizabeth RouxDocument6 pagesAssessment and Concept Map Care Plan: Elizabeth Rouxapi-507304905Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oral and Parenteral Medication Administration: Skills & Reasoning Case StudyDocument15 pagesOral and Parenteral Medication Administration: Skills & Reasoning Case StudyMary WamboltPas encore d'évaluation
- CC Concept Map 3-1-24Document6 pagesCC Concept Map 3-1-24api-739624128Pas encore d'évaluation
- OB Care Plan: Assessment DataDocument10 pagesOB Care Plan: Assessment Dataapi-520858833Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map - Kayla Sterling - Pediatric ClinicalDocument5 pagesConcept Map - Kayla Sterling - Pediatric Clinicalapi-498916010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Afdal Shamsa w1 Ncm116rleDocument36 pagesAfdal Shamsa w1 Ncm116rleShamsa AfdalPas encore d'évaluation
- Health ScreeningDocument3 pagesHealth Screeningpixelkum1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mohammad Hamid Sabibi - 720621465Document11 pagesMohammad Hamid Sabibi - 720621465Farida Trinovita SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Case StudyDocument44 pagesCardiac Case StudyNatalia Bernard100% (1)
- Concept Map f21 FinishedDocument5 pagesConcept Map f21 Finishedapi-601070065Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Learner'S Worksheet: Student Nameraphael Chino Aragon Date: InstitutionDocument67 pagesDigital Learner'S Worksheet: Student Nameraphael Chino Aragon Date: InstitutionRAPHAEL CHINO ARAGONPas encore d'évaluation
- Celluar and Neural Regulation StudentDocument52 pagesCelluar and Neural Regulation StudentCruz YrPas encore d'évaluation
- Careplan 2 NSG 434 CCDocument8 pagesCareplan 2 NSG 434 CCapi-509642710Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rle RequirementsDocument8 pagesRle RequirementsUzziel Galinea TolosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ocne 9 SupportDocument8 pagesOcne 9 Supportapi-349380871Pas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care Concept Map FinishedDocument7 pagesCritical Care Concept Map Finishedapi-604156447Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument8 pagesConcept Mapapi-508452270Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Concept MapDocument6 pagesPediatric Concept Mapapi-593213381Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Jim SandersonDocument6 pagesCase Study Jim SandersonJessica McAlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Concept Map: Plan of CareDocument3 pagesClinical Concept Map: Plan of Careapi-403419438Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bsn-Rs-Careplan 3-2Document12 pagesBsn-Rs-Careplan 3-2api-509646698Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4832 Concept MapDocument7 pages4832 Concept Mapapi-739571122Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brooke Baker Concept Map 4832 Nursing Care of Children and FamiliesDocument10 pagesBrooke Baker Concept Map 4832 Nursing Care of Children and Familiesapi-546799391Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Distress: Section I: Scenario DemographicsDocument6 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress: Section I: Scenario DemographicsharasthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument8 pagesConcept Mapapi-508597583Pas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map RSV 4Document10 pagesConcept Map RSV 4api-546577761Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unfolding Reasoning Dementia Physical AggressionDocument7 pagesUnfolding Reasoning Dementia Physical AggressionnoslendadnarimPas encore d'évaluation
- Thuy Functional DimensionDocument3 pagesThuy Functional DimensionTweetie PiePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangevanPas encore d'évaluation
- CE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreDocument8 pagesCE - 441 - Environmental Engineering II Lecture # 11 11-Nov-106, IEER, UET LahoreWasif RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparatory Newsletter No 3 2013Document22 pagesPreparatory Newsletter No 3 2013SJC AdminPas encore d'évaluation
- Have Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Document25 pagesHave Been Tried From Time To Time," As Churchill Famously Said (Third Paragraph) "?Aditya ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Edwards SVV HandoutDocument2 pagesEdwards SVV HandoutossinPas encore d'évaluation
- RegistryDocument4 pagesRegistryRajan KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Concordance C Index - 2 PDFDocument8 pagesConcordance C Index - 2 PDFnuriyesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abbreviations For O&G IndustryDocument38 pagesAbbreviations For O&G IndustryMike George MeyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Defining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualDocument21 pagesDefining Who Is A Volunteer ConceptualYosep Trisaputro WahyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Yealink Meeting Server Administrator Guide V10.23.0.5 PDFDocument97 pagesYealink Meeting Server Administrator Guide V10.23.0.5 PDFFatima PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- Active and Inactive Volcano LPDocument2 pagesActive and Inactive Volcano LPhorace hernandez100% (5)
- Omran WalidDocument196 pagesOmran WalidDébora AmougouPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of GrowthDocument33 pagesTheories of Growthdr parveen bathlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Try Out Ujian NasionalDocument9 pagesSoal Try Out Ujian NasionalAgung MartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Extension of MDRRMO OfficeDocument12 pagesExtension of MDRRMO OfficeJustin YuabPas encore d'évaluation
- Copper For BusbarDocument60 pagesCopper For BusbarSunil Gadekar100% (3)
- JamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateDocument23 pagesJamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateSunkilr Sönny100% (4)
- Habibillah Energi Adidaya Statement of QualificationsDocument56 pagesHabibillah Energi Adidaya Statement of QualificationsjakalegawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Salik Sa Mga Estudyante NG Hindi Wastong Pagsuot NG Uniporme NG Senior High School Sa Paaralang Ama Computer College Fairview CampusDocument1 pageSalik Sa Mga Estudyante NG Hindi Wastong Pagsuot NG Uniporme NG Senior High School Sa Paaralang Ama Computer College Fairview CampusIsrael ManansalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Conditions of The NewbornDocument46 pagesAcute Conditions of The NewbornCamille Joy BaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN Intrior Design and DecorationDocument13 pagesDIFFERENCE BETWEEN Intrior Design and DecorationSadaf khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Emerging and Less Common Viral Encephalitides - Chapter 91Document34 pagesEmerging and Less Common Viral Encephalitides - Chapter 91Victro ChongPas encore d'évaluation
- A A ADocument5 pagesA A ASalvador__DaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Business ProposalDocument35 pagesBusiness ProposalMJ MacapagalPas encore d'évaluation
- 27 Technip Energies - JD (PWD Students Only)Document1 page27 Technip Energies - JD (PWD Students Only)0901EE201067 KUNAL JOLLY SAXENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Ostrich RacingDocument4 pagesOstrich RacingalexmadoarePas encore d'évaluation
- PQS Catalogue 4 2Document143 pagesPQS Catalogue 4 2sagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Master List WDocument27 pagesMaster List Wefrem111Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Necessary Art of PersuasionDocument14 pagesThe Necessary Art of PersuasionAnugragha SundarPas encore d'évaluation
- TSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestDocument78 pagesTSR 9294 DLA3 Dragons RestLéo Duarte100% (4)