Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
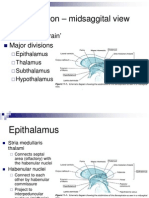
Internal Capsule and Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Transféré par
Denis QosjaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Internal Capsule and Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Transféré par
Denis QosjaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 12
Neuroanatomy – Internal Capsule & Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Horizontal Cross-Section
Section of Forebrain
Corpus callosum
(genu) Head of caudate nucleus
External capsule Putamen
Globus pallidus
Internal capsule
(anterior limb) Septum pellucidum
Fornix
Internal capsule
Claustrum
(genu)
Insular cortex
Internal capsule Thalamus
(posterior limb)
Lateral ventricle Tail of caudate nucleus
Corpus callosum
(splenium)
Optic tract
© Matt Schiller Page 1 of 5
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 12
Neuroanatomy – Internal Capsule & Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Functions and Connections of Major Forebrain Structures
Connections
Structure Function
Input/Origin Output/Termination
Amygdala Expression and (Complex – covered in lecture on limbic system)
experience of emotional
responses and formation
of emotional memories
Caudate Initiation and control of Motor cortex
nucleus gross movement
Claustrum (Poorly understood) Cerebral cortex (all lobes)
Fornix Memory formation (part Hippocampal Hypothalamus, anterior
of Papez Circuit) formation nucleus, and septal area
(limbic structures)
Globus Initiation and control of Caudate nucleus, Subthalamic nucleus and
pallidus gross movement putamen, and putamen
subthalamic nucleus
Hippocampus Memory
ry formation Parahippocampal Parahippocampal gyrus,
gyrus, septal area, septal area, hypothalamus,
and reticular and anterior nucleus
formation (limbic structures)
Hypothalamus Maintenance of (Complex)
homeostasis, regulation
of feeding, drinking and
sexual activity, circadian
rhythms, and emotional
expression
Insular cortex (Poorly understood) Cerebral cortex (particularly sensory areas)
Mamillary Memory formation Hippocampal Anterior nucleus and
body formation reticular formation
Optic radiation Transmission of visual Thalamus Primary visual cortex
impulses
Putamen Initiation and control of Motor cortex and Globus pallidus and
gross movement substantia nigra substantia nigra
Subthalamic Control of movement, Globus pallidus
nucleus by regulating activity of
globus pallidus
Thalamus Relay and integration of (Complex) Cerebral cortex
motor and sensory
information
Organisation of Basal Ganglia
Caudate
Basal ganglia / Neostriatum
Putamen
Corpus striatum Lentiform nucleus
Pallidum Globus pallidus
© Matt Schiller Page 2 of 5
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 12
Neuroanatomy – Internal Capsule & Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
White Matter of Telencephalon
Description Fibre bundle (and parts) Description/Location Tracts/Fibres
Link cortex Internal Anterior limb Between head of caudate (See following
with capsule nucleus and lentiform nucleus section)
subcortical Posterior limb Between thalamus and
structures lentiform nucleus
Projection fibres
(both Genu Junction of anterior and
directions) posterior limbs
Retrolenticular Behind lentiform nucleus
part
Sublenticular Beneath lentiform nucleus
part
External capsule External to lentiform nucleus Corticostriate fibres
Corona radiata Above caudate nucleu, fanning Fibres from internal
out to various parts of cortex and external capsules
Link Corpus Forceps major Forms splenium (posterior Fibres linking occipital
corresponding callosum part) lobes
Commissural fibres
parts of Forceps minor Forms genu (anterior part) Fibres linking
hemispheres prefrontal areas
Anterior commissure Crosses midline anterior to Fibres linking inferior
column of fornix parts of temporal
lobes (including
olfactory areas)
Hippocampal commissure Passing between fornices, Fibres linking
beneath splenium hippocampal
formations
Short – link Arcuate fibres Near cortical surface Fibres linking adjacent
adjacent areas gyri
Association fibres
of same
hemisphere
Long – link Superior longitudinal Lateral to centrum ovale Fibres linking frontal,
different fasciculus (medullary centre of parietal, and occipital
regions of hemisphere) lobes
same Arcuate fasciculus Sweeping around insula into Fibres linking auditory
hemisphere temporal lobe and speech areas
Corpus callosum subdivisions:: rostrum (A1), genu (A2), body (A3- A6), and splenium (A7)
© Matt Schiller Page 3 of 5
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 12
Neuroanatomy – Internal Capsule & Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Internal Capsule
- Superior/Middle thalamic radiation:
- Thalamus → Motor cortex
- Thalamus → Somatosensory cortex
- Corticospinal tract
- Corticobulbar tract
- Corticopontine tract
- Anterior thalamic radiation:
- Thalamus → Cingulate gyrus (limbic)
- Thalamus → Prefrontal cortex (association)
- Corticopontine tract
P
G
S
-Posterior
Posterior thalamic radiation:
- Optic radiation
- Thalamus → Cortex (association)
- Corticopontine tract
- Auditory radiation
- Optic radiation (Meyer’s loop)
Fibres carried in internal capsule (A = anterior limb; G = genu; P = posterior limb; R =
retrolenticular part; S = sublenticular part)
Thalamus
Caudate G
A
GP
P
Putamen
S
R
Medial striate artery
Lateral striate arteries
Anterior choroidal artery
Posteromedial and
posterolateal groups
Blood supply of internal capsule and related structures (N.B. not part of learning activities,
activities
but note supply of lateral striate arteries in particular)
particular
© Matt Schiller Page 4 of 5
Ageing and Endings B – Science Practical 12
Neuroanatomy – Internal Capsule & Horizontal Slices of Forebrain
Computer Tomography (CT) Scan and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
CT Scan MRI
Principle of Passing of radiation through structures Perturbation of hydrogen atoms in water by
operation and detection of resulting beam magnetic field,, and measurement of energy
(radiographic density) produced
Radiation type X-rays (ionising) Radio frequency (non-ionising)
(non
Appearance of From lighter to darker (more to less From lighter to darker (more to less water):
features dense):: bone, tissue, fluid fluid, tissue, bone (white
(w matter darker
than grey matter)
Features showing Bony structures (including inner ear) Soft tissues (including tumours)
highest detail
Other advantages • More widely available • Non-ionising
ionising radiation
• Cheaper • Possible to alter tissue contrast
• Faster • Possible to change imaging plane
• Possible for claustrophobic patients without moving patient
Selected Etymology
Term Root
Amygdala L/G: almond
Caudate L: tail
Claustrum L: barrier
Collateral L: side by side with
Commissure L: juncture
Corona L: crown
Corpus L: body
Fornix L: arch/vault
Genu L: knee/bend
Globus L: ball
Hippocampus G: seahorse
Insula L: island
Lentiform Lens-shaped
Mamillary L: nipple
Pallidus L: pale
Pellucidum L: translucent
Putamen L: shell/peel/prune
Radiata L: shine/rays
Rostrum L: beak
Septum L: partition
Splenium L/G: bandage
Striatum L: furrowed/striated
Thalamus G: bed/bedroom
Trigone L/G: triangle
© Matt Schiller Page 5 of 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Brain Anatomy: CerebellumDocument31 pagesBrain Anatomy: Cerebellumdr_mohanadPas encore d'évaluation
- Precentral Gyrus Central Sulcus Postcentral Gyrus Lateral Fissure Cerebral Hemispheres (L&R)Document14 pagesPrecentral Gyrus Central Sulcus Postcentral Gyrus Lateral Fissure Cerebral Hemispheres (L&R)kenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum DR SanyamandweDocument31 pagesCerebellum DR SanyamandweTinashe MatomboPas encore d'évaluation
- DiensefalonDocument31 pagesDiensefalonIngrid AykePas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrative Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesIntegrative Functions of The Nervous Systempuchio100% (1)
- Neuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinDocument60 pagesNeuroanatomy Overview (Inglés) (Presentación) Autor Lennart BrodinJulia AlonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- UERM GROSS Cerebrum Cerebellum and CT ScanDocument82 pagesUERM GROSS Cerebrum Cerebellum and CT Scanroxanne.viriPas encore d'évaluation
- Anat 1019 NeuroDocument37 pagesAnat 1019 NeurotakakamiseriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum Anatomy and ConnectionsDocument36 pagesCerebellum Anatomy and ConnectionssaskiabpPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsDocument17 pagesCerebellum Anatomy and FunctionsDr. NasrumminallahPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Structure and Function LectureDocument47 pagesBrain Structure and Function LecturesofiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain AnatomyDocument40 pagesBrain AnatomyMira AnggrianiPas encore d'évaluation
- L20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemDocument33 pagesL20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemSk JsPas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Structure of The BrainDocument60 pagesGross Structure of The BrainPurnomo Ponco NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument88 pagesNeuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemAchenk BarcelonistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Vesicle Secondary Vesicle Adult Derivatives NotesDocument1 pagePrimary Vesicle Secondary Vesicle Adult Derivatives NotesdammyPas encore d'évaluation
- l15 CerebrumDocument31 pagesl15 CerebrumDr. Pinki RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Diencephalon 2022Document51 pages6 Diencephalon 2022Gregory WigginsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cns ClassDocument63 pagesCns ClassAnushka SabharwalPas encore d'évaluation
- LimffffffffDocument77 pagesLimffffffffНемосјановић ЋудмилаPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum: AKA: Little BrainDocument3 pagesCerebellum: AKA: Little BrainKC White Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- EM2 Cerebellum Groups 9 17 Huzella DobolyiDocument32 pagesEM2 Cerebellum Groups 9 17 Huzella Dobolyievanjeline54Pas encore d'évaluation
- ThalamusDocument17 pagesThalamusPrafulla KasarPas encore d'évaluation
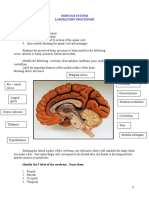
- Virtual Laboratory Activity Worksheet On Central Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesVirtual Laboratory Activity Worksheet On Central Nervous SystemAngela ParaisoPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Needed:: Nervous System Laboratory ProcedureDocument7 pagesMaterials Needed:: Nervous System Laboratory ProcedureRegina GambayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Diencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemDocument56 pagesDiencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemJoaquin GuillermoPas encore d'évaluation
- L15 CerebrumDocument27 pagesL15 CerebrumEvilneko1Pas encore d'évaluation
- CNS PDFDocument412 pagesCNS PDFSami Juggy G100% (1)
- 18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Document22 pages18 - Thalamus and Limbic System (Edited)Fotocopias LulisPas encore d'évaluation
- CerebellumDocument62 pagesCerebellumadelina.jianu9991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Decending and Ascending Tracts - Eve - 14-Oct-2022Document29 pagesDecending and Ascending Tracts - Eve - 14-Oct-2022Pyaesone AungPas encore d'évaluation
- Bates Ch 17 Neuro Study GuideDocument11 pagesBates Ch 17 Neuro Study GuidekandeePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture (17) Basal GangliaDocument13 pagesLecture (17) Basal GangliaAkashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapters 11 12 SingleDocument35 pagesChapters 11 12 Singlegeorgefromba100% (1)
- O Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusDocument11 pagesO Inferior Hypogastric Plexus/pelvis PlexusMaxinefgc BaculoPas encore d'évaluation
- SistemendokrinDocument26 pagesSistemendokrinNazwa AuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument65 pagesIlovepdf Mergedrogegir407Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Anatomy and Functions of the Cerebellum and DiencephalonDocument46 pagesThe Anatomy and Functions of the Cerebellum and DiencephalonRushi WaykulePas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Areas - Location and FunctionDocument12 pagesBrain Areas - Location and FunctionMattGilmorePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Introduction & General Features of Nervous SystemDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Introduction & General Features of Nervous Systemdaw022Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Brain: Functional Divisions: Primary and Secondary Vesicles of The Developing CNSDocument6 pagesThe Brain: Functional Divisions: Primary and Secondary Vesicles of The Developing CNSKelly FariaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 - Ii Reward System 05-09-2023Document81 pages3.1 - Ii Reward System 05-09-2023Talha TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro Written I TablesDocument6 pagesNeuro Written I TablesSolomon Seth SallforsPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusDocument7 pagesCase 6 Revision - Cognitive Impairment: Central SulcusCharlie WalkerPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cerebral Architecture: 2.1 Developmental AspectsDocument47 pagesThe Cerebral Architecture: 2.1 Developmental AspectsLuís Irajá Nogueira De Sá NetoPas encore d'évaluation
- Memory 1Document7 pagesMemory 1suman palPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Recall Neuroanatomy 4B1LEDocument8 pagesActive Recall Neuroanatomy 4B1LEAlexandryaHalePas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebral Cortex MappingDocument62 pagesCerebral Cortex MappingMORGAN LAMBERTPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of the Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesFunctions of the Nervous SystemnvhnygPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3.2 The Cerebral CortexDocument3 pagesModule 3.2 The Cerebral CortexChriscelle Ann PimentelPas encore d'évaluation
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationDocument70 pagesCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiPas encore d'évaluation
- netterDocument2 pagesnetternclov.00Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureDocument3 pages7Mm Frog: Structure GL Derivative Fate Function Cavity Misc. Info StructureJannah DangananPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding the Neurologic System in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesUnderstanding the Neurologic System in 40 CharactersMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- K3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)Document112 pagesK3. Anatomi Sistem Limbik, ARAS, Saraf Tepi, Dalam Aspek Neurologis (Dr. Ahmad Azmi Nasution, M.Biomed)AmesyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)Document3 pagesHypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)jaira_joshbiePas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Medicine Anatomy DepartmentDocument71 pagesFaculty of Medicine Anatomy Departmenteman el saeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Basal GangliaDocument9 pagesBasal Gangliasalmankhan09215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hemorrhagic FeverDocument3 pagesHemorrhagic FeverDenis QosjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Characteristics of Suicidal Attempts-Data BaseDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of Suicidal Attempts-Data BaseDenis QosjaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 2 Vitamin D Guidance Feb 2016 CCG v1 Id 589240Document2 pages4 2 Vitamin D Guidance Feb 2016 CCG v1 Id 589240Suzana VoiculescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesDenis QosjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranial NervesDocument4 pagesCranial NervesDenis QosjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument10 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFgunawanmulyana12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SystemEmilia AmmariPas encore d'évaluation
- Raw Meat vs. Cooked Meat - Which Is HealthierDocument33 pagesRaw Meat vs. Cooked Meat - Which Is HealthierMark Sloan100% (1)
- Kuliah InfeksiDocument88 pagesKuliah InfeksiuupupupPas encore d'évaluation
- English II MEDV Worksheet 1Document2 pagesEnglish II MEDV Worksheet 1CONSUELO FRANCISCA OVALLE QUEZADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Leptospirosis FactsDocument1 pageLeptospirosis FactsZenitha FauziaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiological Examination of Dairy ProductsDocument6 pagesMicrobiological Examination of Dairy ProductsLaksilu Viduraga PeirisPas encore d'évaluation
- Burch & Wartofsky Criteria For Thyroid StormDocument2 pagesBurch & Wartofsky Criteria For Thyroid StormrulisakaroziPas encore d'évaluation
- South America's Influence on the Author's Creative SpiritDocument417 pagesSouth America's Influence on the Author's Creative SpiritGabriel CasagrandePas encore d'évaluation
- Saturn or SaniDocument5 pagesSaturn or SaniAnuradha Venugopal100% (1)
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Needle CricothyroidotomyDocument9 pagesNeedle Cricothyroidotomyhatem alsrour100% (2)
- Papers 2022Document3 pagesPapers 2022MDrakePas encore d'évaluation
- Newman News Jan-Feb 2016 EditionDocument12 pagesNewman News Jan-Feb 2016 EditionSonya MathesonPas encore d'évaluation
- PTP Guideline 2014Document35 pagesPTP Guideline 2014mukeshkumar@ibasukkurPas encore d'évaluation
- Space regainers in pediatric dentistryDocument5 pagesSpace regainers in pediatric dentistryShirmayne TangPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing care for thalassemia child with priority problem of ineffective peripheral tissue perfusionDocument9 pagesNursing care for thalassemia child with priority problem of ineffective peripheral tissue perfusionnediPas encore d'évaluation
- BookfvscDocument14 pagesBookfvscburhan_magixPas encore d'évaluation
- Those Lopes - Guimarães RosaDocument3 pagesThose Lopes - Guimarães Rosaluzmoreira8448Pas encore d'évaluation
- 37981-iUBT311 Treatment Evidence Form v2Document5 pages37981-iUBT311 Treatment Evidence Form v2Aline Brito Ferreira de CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Bibliography Cards: Book Internet SiteDocument2 pagesSample Bibliography Cards: Book Internet Siteapi-30192479Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labrador Retriever: Illustrated StandardDocument14 pagesLabrador Retriever: Illustrated StandardFrancisco VilledaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Plagues of EgyptDocument9 pages10 Plagues of EgyptEdward DoenchPas encore d'évaluation
- Hasil Tesis AdelaideDocument93 pagesHasil Tesis AdelaideAndi Alfian Zainuddin100% (1)
- Omphalocele and GastroschisisDocument12 pagesOmphalocele and Gastroschisisluisisea100% (1)
- Mosquito Life CycleDocument3 pagesMosquito Life CycleRi Zu KyPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Coelom and PseudocoelomDocument2 pagesDifference Between Coelom and PseudocoelomCyanDesPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Shelters of Animals Tiger Cows Hen InformationDocument3 pagesFood Shelters of Animals Tiger Cows Hen InformationJasvinder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Case presentation of Ekakustha (27 charactersDocument36 pagesCase presentation of Ekakustha (27 charactersKARISHMA PATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Assessment of The GentialiaDocument48 pagesPhysical Assessment of The GentialiaWilliam Lim100% (2)