Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Introdruction For Icp Ms and Icp Oes PDF
Transféré par
ThejeswarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sample Introdruction For Icp Ms and Icp Oes PDF
Transféré par
ThejeswarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Sample Introduction for ICP-MS
and ICP-OES
This article discusses the key components of a typical liquid sample introduction system for
inductively coupled plasma spectroscopy, and offers troubleshooting tips for problems
commonly encountered by practitioners.
Paul Gaines
Inorganic Ventures
ample introduction can be a significant source of random Latin “nebula,” meaning mist and is defined as “an instrument
S and systematic error in the measurement of samples by
inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy
(ICP-OES) and ICP mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) systems.
for converting a liquid into a fine spray.” Therefore, a pneu-
matic nebulizer is literally an instrument for converting a liq-
uid into a fine spray that uses a gas as the driving force. The
Consequently, texts devoted to ICP have given sample intro- most popular types of ICP pneumatic nebulizers are concen-
duction considerable attention (1–4). Samples most common- tric, fixed cross-flow, and high solids.
ly are introduced as liquids. The considerations made in select- Concentric nebulizers. This basic type of nebulizer can be
ing a liquid introduction system include dissolved solids con- made from glass or plastics such as PFA and (depending upon
tent, suspended solids presence, presence of hydrofluoric acid design) is capable of handling a sample solution introduction
or caustic, detection limit requirements, precision require- rate of between 0.01 and 3 mL/min. Therefore, the “micro-
ments, sample load requirements, sample size limitations, and concentric” nebulizer (0.01–0.1 mL/min) should be consid-
operating budget. The analyst is left with the task of choosing ered when sample size is limited to 1 mL. They typically are
the best introduction components. used with cyclonic spray chambers but can be used with the
This article discusses the key components of a typical liquid Scott spray chamber (an adaptor is needed in this case). Their
sample introduction system, acquaints the reader with the basic capability of handling dissolved solids (type C better than type
options available, and addresses some common problems. A) is dependent upon how near the dissolved solid is to its sol-
ubility limit. The glass construction should not be used with
Pneumatic Nebulizers hydrofluoric acid or caustics such as the alkali hydroxides.
The term “pneumatic” is defined as “of or relating to or using Quartz construction is more resistant to chemical attack. The
air or a similar gas.” The word “nebulizer” is derived from the precision and detection limit capability of this design is excel-
ate detection limit and measurement nebulizer designs work better with one
precision. This design is used where high torch design than another. Before exper-
Torch
and suspended solids are an every day imenting with torches it is best to con-
PTFE tubing
Spray
chamber
occurrence. tact your instrument manufacturer to
Nebulizer
determine the torch design recommend-
Drain
Ultrasonic Nebulizers ed for your instrument and any design
Sound can be used instead of a gas as the specifications, operating conditions and
energy source for converting a liquid to dimensions that must be observed.
Tygon tubing
Sipper Peristalic pump
a mist. These nebulizers use an ultrason-
ic generator at a frequency of between Questions to Consider
200 kHz and 10 MHz to drive a piezo- The following are some questions you
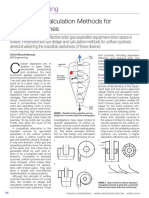
Figure 1. ICP liquid sample electric crystal. A pressure is produced might want to consider with regard to
introduction system. that breaks the surface of the liquid–air these sample introduction components,
interface. Ultrasonic nebulizers are sig- whether you are purchasing a new ICP
nificantly more expensive than the unit or already have one or more exist-
pneumatic designs but they will improve ing units:
lent with both being very dependent (that is, lower) detection limits roughly • What torch design is used and what
upon the argon gas pressure going to the by a factor of 10. are the power and argon gas flow
nebulizer. Although the sensitivity tends requirements? (You might want to cal-
to vary from nebulizer to nebulizer, Spray Chambers culate your annual argon expense.)
manufacturers have improved greatly The most common types of spray cham- • What nebulizer and spray chamber
upon their ability to reproduce this neb- bers are the Scott double-pass and the designs are available and can they be
ulizer. These nebulizers should never be cyclonic, the latter of which is relatively obtained from alternate suppliers?
used with solutions containing suspend- new but is very popular. The purpose of • Are there specific nebulizer designs
ed solids. Although delicate, this nebu- the spray chamber is to remove droplets that cannot be used with the
lizer can be used for years with the prop- produced by the nebulizer that are >8 torch–spray chamber that is recom-
er care. µm in diameter. Important considera- mended or required?
Cross-flow nebulizers. The cross-flow tions here include the wash-in time, • What are the costs of the individual
design began with a design that allowed wash-out time, stability, and sensitivity. introduction system components and
for the adjustment of the two capillary The drainage characteristics are impor- how much expense would be expected
tubes that are set at right angles to each tant in part due to pressure changes that or actually occurs throughout a year
other (5). The criticality of the capillary can occur during drainage. It is impor- of operation?
positioning led to the commercial pro- tant that the drainage process be smooth • What is the lifetime of the torch and
duction of the fixed cross-flow design. and continuous. The analyst might what is the most common reason for
The fixed cross-flow is used with the observe faster wash-in and wash-out failure?
Scott spray chamber, will provide mod- times with the cyclonic design. The • How tolerant is the system to slight
erate to good sensitivity, and generally is chamber material of construction, changes in torch alignment?
better than the concentric design for chamber surface area, volume, and flow • How tolerant is the system to air com-
high solids. It is available in materials of pattern as well as the sample matrix and ing from the nebulizer? Will it extin-
construction that resist chemical attack. the chemistry of the element influence guish after a few seconds?
It is not as delicate as the concentric neb- the wash-out times. In addition, the ana- • How tolerant is the system to the
ulizer and often is used in laboratories lyst might observe faster wash-out times introduction of organic solvents?
where the optimum in precision and with glass construction than with poly- • What is the lowest boiling point sol-
detection limit is of less importance than mers due in part to better wetability of vent that can be introduced?
having a large sample load capability. It the glass (lack of beading). • How tolerant is the system to the
is not recommended if suspended parti- torch building up coke for aromatic
cles are present. Torches and aliphatic nonpolar solvents?
High solids nebulizers. High solids neb- The two basic designs are the Greenfield • What is the most precise nebulizer
ulizers come in a variety of designs. The and Fassel torches. The Greenfield torch that can be used with your ICP system
V-groove design is very resistant to salt- requires higher plasma gas flow and and what precision should be
ing out and can be used when suspend- radio frequency power than the Fassel. obtained?
ed particles are present. Some designs Both designs produce similar detection • What are the detection limits for your
require relatively high gas pressures, limits. The Greenfield torch is more analytes of interest? Are you achieving
which might present some difficulty. rugged (less likely to extinguish due to the detection limits required for your
Designs include materials of construc- misalignment, and introduction of air) application?
tion that resist hydrofluoric acid and whereas the Fassel torch requires lower • When looking for lower detection lim-
caustic attack. In general, expect moder- argon flow and less RF power. Some its have you considered axial view
© Reprinted from SPECTROSCOPY, January 2005
ICP? Ultrasonic nebulizers? Both? background signal do you get? If the • Sipper to PTFE tubing
• Do your analytical solution samples introduction system contains glass- • PTFE tubing to peristaltic tubing
contain high levels of dissolved solids? how much hydrofluoric acid can be (both into and out of)
Any suspended solids? tolerated before signals from silicon • PTFE tubing from peristaltic pump to
• Do you experience nebulizer salting are observed? Before damage occurs? nebulizer
out? Plugging? • Nebulizer to spray chamber
• Which high solids nebulizer is recom- Avoiding Connection Problems • Spray chamber to waste drain tube
mended for your current or potential The key elements of a sample introduc- • Spray chamber to torch
ICP, and what is the precision to be tion system start with the sipper tube
expected? and end with the torch (Figure 1). They If any one of these connections is not
• How rugged is it and what does it are listed as follows: air tight the operator will experience
cost? anything from poor precision to an
• How difficult is it to connect an ultra- • Sipper – typically plastic inability to light the plasma. One of the
sonic nebulizer? • PTFE tubing going from the sipper to reasons many people prefer concentric
• Can either the Scott or cyclonic spray the peristaltic pump tubing glass nebulizers is that they are “free
chamber designs be used? • Peristaltic pump tubing flow;” that is, the liquid will flow from
• What are the washout times for mer- • PTFE tubing going from the peri- the sample container to the nebulizer
cury, boron, yttrium, and copper in staltic pump tubing to the nebulizer without assistance from the peristaltic
nitric acid? In hydrochloric acid? • Spray chamber pump. A simple check is to determine if
• Are corrosion-resistant, hydrofluoric • Torch you obtain a fine steady mist — using
acid–resistant introduction systems water as the sample — without the peri-
available? What do they cost? How The main difficulty that analysts typical- staltic pump (pressure lever released) so
easy are they to switch in and out? ly experience with introduction system that free flow can occur. This can be
• When analyzing for silicon in trace failure is that of connections between done with the nebulizer disconnected
hydrofluoric acid how much of a sili- components. The connections are listed from the spray chamber (plasma has not
con, boron, sodium, and aluminum as follows: yet been lit) so that the mist can be visu-
We Treat Labs Like Au.
Our customer service and technical support transcend the
ordinary. It’s truly an experience like no other. No hassles,
no worries – only your complete and total satisfaction.
Whether it’s a custom solution or expert advice, our specialists
are ready to work with you, one on one.
Isn’t it time your lab experienced the gold treatment?
Standards • Reagents • Quality Controls • Accessories
© Reprinted from SPECTROSCOPY, January 2005
alized easily. You also can check for the Spray chambers come in all glass, all
appearance of any small air bubbles in plastic and glass with plastic end caps. If
the PTFE tubing; bubbles should never you do not use hydrofluoric acid (all
be present and indicate a poor connec- plastic systems are needed with hydro-
tion somewhere between the sipper and fluoric acid) and therefore have the lux-
the nebulizer. ury of using glass components attempt
A connection that often is taken for to use a spray chamber without the plas-
granted is the spray chamber tic end cap. They typically are used with
drain–waste tube connection. This con- glass concentric nebulizers and use only
nection is absolutely critical. One way two O-rings to connect the nebulizer to
to test it is to put some water in the the spray chamber. The plastic end cap
spray chamber using a wash bottle and can cause longer wash-out times and
determine if it drains smoothly and carryover problems, and presents a very
without leaks. Poor precision or the large connection surface where connec-
inability to light the plasma is a com- tion problems can occur. Using a glass
mon symptom of a poor drain tube concentric nebulizer and all glass spray
connection. During this test you also chamber, a precision of between 0.2 and
should observe the absence of water 0.5% RSD should be observed. If an all-
droplets in the spray chamber (assum- glass system gives a precision of 0.6 to
ing glass construction). A dirty spray 1% RSD or greater then there is most
chamber will leave water droplets and likely a connection problem or the neb- In summary, when it comes to ICP
cause poor precision and carryover ulizer gas flow rate is too high (look for introduction systems there is no substi-
problems. Make sure the plasma is not spitting when checking the nebulizer tute for experience, so try different
lit when you perform this test. free flow and do not be afraid to lower approaches.
the gas pressure to the nebulizer).
Cleaning Components References
Glass or quartz components often are Pump Tubing 1. H.E. Taylor, Inductively Coupled Plasma
Mass-Spectrometry, Practices and
preferred because of their ease of opera- Another weak link in the introduction
Techniques (Academic Press, New York,
tion and cleaning. It is always best to start system is the peristaltic pump tubing. 2001).
the day with a clean nebulizer, spray When you start the day the tubing is 2. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spec-
chamber, and torch. Cleaning the torch fresh and the pressure can be set to give trometry, A. Mantaser, Ed. (Wiley-VCH,
daily also will extend its life. Many types a steady mist when the pump in run- New York, 1998).
3. Inductively Coupled Plasmas in Analyti-
of cleaning solutions can be used. Some ning. The problem is that the pump
cal Atomic Spectrometry, A. Montaser
of our analysts prefer 1:1 nitric acid and tubing stretches and either the nebulizer and D.W. Golighty, Eds. (VCH Publish-
water and others prefer sulfuric acid and argon pressure is not enough to drive ers, New York, 1992).
hydrogen peroxide, while others prefer the solution through the tubing or over 4. M. Thompson and J.N. Walsh, A Hand-
1:1 hydrochloric acid–nitric acid. All of tightening occurs, resulting in a pulsat- book of Inductively Coupled Plasma
Spectrometry (Blockier London, U.K.,
these cleaning solutions work depending ing mist spray. This is a problem that
1983).
upon the nature of the contaminants. each analyst has to be aware of and solve 5. R.N. Kniseley et al., Applied Spectroscopy
The sulfuric–peroxide is needed if organ- through experimentation. This problem 28, 285–286 (1974). ■
ics such as grease are suspected. is particularly troublesome for ICP-MS
Ultrasonic baths are great but never use users because the sample flow rate Paul Gaines is senior technical advisor
with Inorganic Ventures (Lakewood, NJ), a
them to clean a glass concentric nebuliz- decreases as the tubing stretches, caus-
certified reference material manufacturer
er. Glass concentric nebulizers are cleaned ing a relative increase in the sensitivity that specializes in custom standards. Visit
by leaching and occasionally by applying ratio of the higher: lower atomic num- www.inorganicventures.com for additional
a backpressure with water to remove ber elements. An option the ICP-MS spectroscopic articles and tips.
lodged particles. The use of a cleaning operator might choose to explore is free
wire or ultrasonic bath is a sure way to flow (no pump) using a micro-concen-
destroy the nebulizer. tric nebulizer.
© Reprinted from SPECTROSCOPY, January 2005 Printed in U.S.A.
Copyright Notice Copyright by Advanstar Communications Inc. Advanstar Communications Inc. retains all rights to this article. This article may only be viewed or printed (1) for personal use. User may not
actively save any text or graphics/photos to local hard drives or duplicate this article in whole or in part, in any medium. Advanstar Communications Inc. home page is located at http://www.advanstar.com.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Maintaining Lab Operations Icpoes and Icpms Support Topics April222020Document73 pagesMaintaining Lab Operations Icpoes and Icpms Support Topics April222020maulidia dwiPas encore d'évaluation
- SADCAS TR 18 - Criteria For Validation and Quality Assurance in Microbiological Testing (Issue 1)Document36 pagesSADCAS TR 18 - Criteria For Validation and Quality Assurance in Microbiological Testing (Issue 1)Augustine Gabriel YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Lod-Loq-Signal To Noise Ratio Etc. Important ArticleDocument5 pagesLod-Loq-Signal To Noise Ratio Etc. Important Articleanon_687115068Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Review Analytical Method Development and ValidationDocument5 pagesA Review Analytical Method Development and ValidationCalidad CODITEV SACPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjuvant AnalgesicDocument14 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicPradnya ParamitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Auditando Un Sistema ValidacionDocument8 pagesAuditando Un Sistema ValidacionIglesias LauraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Scientist Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesLab Scientist Job DescriptionRajeev PareekPas encore d'évaluation
- 2005 L A B Guidance Document Rev 2 PDFDocument47 pages2005 L A B Guidance Document Rev 2 PDFTony SinambelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products Revision 3 - enDocument32 pagesTraditional Herbal Medicinal Products Revision 3 - enryad bmzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook For Analytical Quality Control in Water and Wastewater LaboratoriesDocument164 pagesHandbook For Analytical Quality Control in Water and Wastewater LaboratoriesCarlos OrionPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Techniques Julia C. Drees Alan H. B. WuDocument36 pagesAnalytical Techniques Julia C. Drees Alan H. B. WuBetrearon SileshiPas encore d'évaluation
- ICP OES Maintenance TroubleshootingDocument39 pagesICP OES Maintenance TroubleshootingRonnie Sakai100% (1)
- BMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesDocument183 pagesBMT Instrumentation & LaboratoriesYogesh AnapPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebulizers Review PDFDocument24 pagesNebulizers Review PDFMelina Barbosa PeixotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectroscopy Agilent EbookDocument10 pagesSpectroscopy Agilent EbookMisse TissePas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Antiseptic - Hemostatic SolutionDocument8 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Herbal Antiseptic - Hemostatic SolutionBaru Chandrasekhar RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- PreviewpdfDocument68 pagesPreviewpdfJoel Ccallo HuaquistoPas encore d'évaluation
- An 70048 Environmental Water Applications Notebook AN70048 EDocument134 pagesAn 70048 Environmental Water Applications Notebook AN70048 EKALLIOPIPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 8 and 10 - Basic Principles of Atomic Absorption and Atomic Emission SpectrosDocument129 pagesCH 8 and 10 - Basic Principles of Atomic Absorption and Atomic Emission SpectrosfaisalPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems - Icp-Oes AgilentDocument18 pagesProblems - Icp-Oes AgilentAlma Rosa RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Procurement Qualification and Calibration of Lab InstrumentsDocument7 pagesThe Procurement Qualification and Calibration of Lab InstrumentsMowaten MasryPas encore d'évaluation
- FAQs On Elemental ImpuritiesDocument6 pagesFAQs On Elemental ImpuritiesGiriPas encore d'évaluation
- RiskISO 17025Document8 pagesRiskISO 17025paeg6512Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Trouble Shooting and Maintenance of ICP-OES SystemsDocument49 pagesGuidelines For Trouble Shooting and Maintenance of ICP-OES SystemsBashir AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Method Development of Bulk DrugsDocument40 pagesAnalytical Method Development of Bulk Drugsrishabhpharma100% (1)
- Natural Science Laws Experience "Live" - Learn Easily: For Karl Fischer TitrationDocument20 pagesNatural Science Laws Experience "Live" - Learn Easily: For Karl Fischer Titrationstepark28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals in WaterDocument7 pagesMinerals in WaterK JPas encore d'évaluation
- Coulometric Water Determination According To Karl FischerDocument6 pagesCoulometric Water Determination According To Karl Fischerlarrylchu100% (9)
- Manual QuickCODultra 07E4317 PDFDocument270 pagesManual QuickCODultra 07E4317 PDFpreciosariyazPas encore d'évaluation
- FAS 서비스 매뉴얼 3Document36 pagesFAS 서비스 매뉴얼 3ak_thimiriPas encore d'évaluation
- An 44392 Analysis of Infant Formulae and Milk Powders Using The Thermo Scientific Icap 7400 Icp Oes DuoDocument6 pagesAn 44392 Analysis of Infant Formulae and Milk Powders Using The Thermo Scientific Icap 7400 Icp Oes DuoDewi WulandhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Impurezas AgilentDocument32 pagesImpurezas AgilentArmando SaldañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods For The Determination of Limit of Detection andDocument5 pagesMethods For The Determination of Limit of Detection andFabio BottariPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Chemist Interview Part 1Document32 pagesLab Chemist Interview Part 1Viona AndhivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Millipore UF Catalog PDFDocument100 pagesMillipore UF Catalog PDFShawkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Spectroscopy Gregory Lecornet-SerbiaDocument62 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy Gregory Lecornet-SerbiaDrRameem BlochPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 17025 IntroDocument6 pagesISO 17025 Introakash batraPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1.2. Standard Solutions For Limit TestsDocument4 pages4.1.2. Standard Solutions For Limit TestsJjangyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Spectroscopy: A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and SystemDocument17 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy: A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and SystemAnonymous gpNrjv0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Control Equipment For BeveragesDocument8 pagesQuality Control Equipment For Beveragesvio.cirstoc6117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Uplc 2015Document26 pagesUplc 2015Hanumant ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Comparative Study of Pilot Plant Scale Up TechniqueDocument47 pagesA Review On Comparative Study of Pilot Plant Scale Up Techniquesai projectPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Spectroscopy 3Document36 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy 3Anonymous KzCCQoPas encore d'évaluation
- Limit of Detection Guidance DocumentDocument33 pagesLimit of Detection Guidance DocumentMomer100% (1)
- HPLC ForumDocument12 pagesHPLC ForumkiranfoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectroscopy: A ReviewDocument11 pagesInductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectroscopy: A ReviewGenetics Mipa5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sop For ICP OESDocument7 pagesSop For ICP OESRomana MasnikosaPas encore d'évaluation
- LC by DesingDocument12 pagesLC by DesingsudermanfitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument7 pagesVolumetric AnalysisZari Sofia LevistePas encore d'évaluation
- Zeenit: Quality Is The DifferenceDocument16 pagesZeenit: Quality Is The DifferenceImad Aghila50% (2)
- AA 1800C User's Manual 1Document39 pagesAA 1800C User's Manual 1Kidus YohannesPas encore d'évaluation
- KFT 190127104354Document70 pagesKFT 190127104354Aurang ZaibPas encore d'évaluation
- IPDocument26 pagesIPmonikaolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Statistik PDFDocument10 pagesJurnal Statistik PDFAni Yunita SariPas encore d'évaluation
- TocDocument11 pagesTocKwok Fai ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- IcpaesDocument37 pagesIcpaesMunawar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Uniflow CyclonesDocument10 pagesUniflow Cyclonescir74636Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Energy Costs Associated With Nitrogen Specifications: Sustainable Manufacturing FeaturesDocument8 pagesThe Energy Costs Associated With Nitrogen Specifications: Sustainable Manufacturing FeaturesJaime Andres Pardo QuinteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Calculation Methods For Uniflow Cyclones Mar19 - SP PDFDocument11 pagesDesign and Calculation Methods For Uniflow Cyclones Mar19 - SP PDFSteve Wan100% (1)
- Rasco - HV - Spray Nozzle - B.105-R.DDocument8 pagesRasco - HV - Spray Nozzle - B.105-R.DAry SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Carvedilol by Solid Dispersion Technique Using Gelucire 50/13Document5 pagesSolubility and Dissolution Enhancement of Carvedilol by Solid Dispersion Technique Using Gelucire 50/13ThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovare Academic Sciences: Original ArticleDocument7 pagesInnovare Academic Sciences: Original ArticleThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- ECA Lab Data Integrity Part 2 Data Governance PDFDocument12 pagesECA Lab Data Integrity Part 2 Data Governance PDFThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP 33v8 ParticleSizeAnalyses FINAL PDFDocument41 pagesSOP 33v8 ParticleSizeAnalyses FINAL PDFThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Jpa 119014Document2 pagesJpa 119014ThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Coreg: (Carvedilol) TabletsDocument19 pagesCoreg: (Carvedilol) TabletsThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning Validation Method DevelopmentDocument33 pagesCleaning Validation Method DevelopmentThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cleaning Validation ProtocolDocument9 pagesCleaning Validation Protocolyash143565100% (2)
- Pharma Book Final 1 PDFDocument270 pagesPharma Book Final 1 PDFThejeswar100% (1)
- Insights PT 2018 Exclusive: PolityDocument55 pagesInsights PT 2018 Exclusive: PolityThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- GS IiDocument102 pagesGS IiThejeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Yemen's Humanitarian Nightmare The Real Roots of The Conflict by Asher OrkabyDocument10 pages1 Yemen's Humanitarian Nightmare The Real Roots of The Conflict by Asher OrkabyLilia Archbold100% (1)
- Data Sheet: DEGALAN® LP 64/12Document2 pagesData Sheet: DEGALAN® LP 64/12Akhtar aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Precooling of Fruits and Vegetables - EditedDocument15 pagesPrecooling of Fruits and Vegetables - EditedMedha GujarathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Standa Modules 2022Document39 pagesStanda Modules 2022vlado_314Pas encore d'évaluation
- All OutDocument30 pagesAll OutSamreen Sabiha KaziPas encore d'évaluation
- AssamerrrDocument15 pagesAssamerrrVipul SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ship Hull ManualDocument31 pagesShip Hull ManualRajeev Balakrishnan100% (1)
- HetpDocument11 pagesHetpReginaPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative LatihanDocument3 pagesNarrative LatihanIlhamy AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Amtech ProDesign Product GuideDocument3 pagesAmtech ProDesign Product GuideShanti Naidu0% (1)
- Orchids in Thailand - A Success StoryDocument38 pagesOrchids in Thailand - A Success StoryLnw SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Indigenous Chicken Production and Marketing Systems in Ethiopia: Characteristics and Opportunities For Market-Oriented DevelopmentDocument66 pagesIndigenous Chicken Production and Marketing Systems in Ethiopia: Characteristics and Opportunities For Market-Oriented Developmentsheila antonio mapossePas encore d'évaluation
- Chandrika 8 Science CH 2Document29 pagesChandrika 8 Science CH 2Shailaja MestryPas encore d'évaluation
- Stanley 25 Amp Automatic Battery Charger BC25BS ManualDocument12 pagesStanley 25 Amp Automatic Battery Charger BC25BS ManualJoe ZhaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire On Foodpanda Vs ZomatoDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Foodpanda Vs ZomatoPoddaturi Susheel74% (42)
- McAteer Report Says Upper Big Branch Mine Explosion PreventableDocument126 pagesMcAteer Report Says Upper Big Branch Mine Explosion PreventableThe West Virginia Examiner/WV WatchdogPas encore d'évaluation
- Sistem Urinarius, Pelvis & Perineum: DR - Tri Suciati, M.KesDocument96 pagesSistem Urinarius, Pelvis & Perineum: DR - Tri Suciati, M.KeslianaalviahPas encore d'évaluation
- TELAAH Jurnal Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesTELAAH Jurnal Diabetes MellitusZefanya FanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Kasus Ke 10 (Inggris)Document5 pagesKasus Ke 10 (Inggris)Fauzan AdvantagePas encore d'évaluation
- Santos Anesthesiology 2018Document15 pagesSantos Anesthesiology 2018saeed namjooPas encore d'évaluation
- Old MacDonald LyricsDocument5 pagesOld MacDonald LyricsMariePas encore d'évaluation
- Site Manager Job DescriptionDocument4 pagesSite Manager Job DescriptionAmalina YaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Superficial Mycoses 1Document5 pagesSuperficial Mycoses 1Einstein ObladesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chm457 Fundamental Organic Chemistry: Experiment 2: Preparation of 4 - MethylcyclohexeneDocument11 pagesChm457 Fundamental Organic Chemistry: Experiment 2: Preparation of 4 - MethylcyclohexeneNur HismanizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Discussion Essay PlanDocument8 pagesDiscussion Essay PlanZulfiya beggPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 3 - Working Capital Management (WCM) - Basic Concepts WCM - Cash Management - FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, PART IDocument16 pagesQuiz 3 - Working Capital Management (WCM) - Basic Concepts WCM - Cash Management - FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, PART IAisah Reem100% (1)
- AC Service Appointment and Maintenance FormDocument11 pagesAC Service Appointment and Maintenance FormRiad RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 01 (Basics) ME141 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 01 (Basics) ME141 PDFAlteaAlPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidated Guidelines OnDocument594 pagesConsolidated Guidelines OnRICHARD EDUARDO FERNANDEZ SAENZPas encore d'évaluation
- 58 PDFDocument11 pages58 PDFMay MethaweePas encore d'évaluation