Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic Performance
Transféré par
Emerovsky Reyes0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues2 pagesA gas turbine engine consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine on shared shafts. Air is compressed in the compressor and mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber, producing hot combustion gas. This gas expands through the turbine, generating shaft work to power the compressor and auxiliary systems for power generation turbines, or producing thrust through high-velocity exhaust for aircraft engines. Gas turbines are designed for specific applications, with power generation turbines usually using a single shaft connecting the compressor and turbine, while aircraft engines often use twin spools with multiple compressor and turbine stages.
Description originale:
turbomaquinas
Titre original
Turbine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentA gas turbine engine consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine on shared shafts. Air is compressed in the compressor and mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber, producing hot combustion gas. This gas expands through the turbine, generating shaft work to power the compressor and auxiliary systems for power generation turbines, or producing thrust through high-velocity exhaust for aircraft engines. Gas turbines are designed for specific applications, with power generation turbines usually using a single shaft connecting the compressor and turbine, while aircraft engines often use twin spools with multiple compressor and turbine stages.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues2 pages18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic Performance
Transféré par
Emerovsky ReyesA gas turbine engine consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine on shared shafts. Air is compressed in the compressor and mixed with fuel in the combustion chamber, producing hot combustion gas. This gas expands through the turbine, generating shaft work to power the compressor and auxiliary systems for power generation turbines, or producing thrust through high-velocity exhaust for aircraft engines. Gas turbines are designed for specific applications, with power generation turbines usually using a single shaft connecting the compressor and turbine, while aircraft engines often use twin spools with multiple compressor and turbine stages.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic
Performance
A gas turbine engine is a system that consists of several turbomachinery components
and auxiliary subsystems. Air enters the compressor component which is driven by
a turbine component and is placed on the same shaft. Air exits the compressor at a
higher pressure and enters the combustion chamber, where the chemical energy of the
fuel is converted into thermal energy producing combustion gas at a temperature that
corresponds to the turbine inlet design temperature. The combustion gas expands in
the following turbine component, where its total energy is partially converted into
shaft work and exit kinetic energy. For power generation gas turbines, the shaft work
is the major portion of the above energy forms. It covers the total work required by
the compressor component, the bearing frictions, several auxiliary subsystems, and
the generator. In aircraft gas turbines, a major portion of the total energy goes toward
generation of high exit kinetic energy that is essential for thrust generation.
Gas turbines are designed for particular applications that determine their design
configurations. For power generation purposes, the gas turbine usually has a single
spool. A spool combines a compressor and a turbine that are connected together via
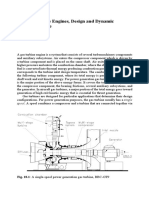
Fig. 18.1: A single-spool power generation gas turbine, BBC-GT9
474 18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic Performance
Fig. 18.2: A twin-spool Pratt & Whitney high bypass ratio aircraft engine with multi-
stage compressors and turbines
Fig. 18.3: Schematic of a twin-spool core engine with its derivatives
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SD'EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFDocument13 pagesGas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFSaadi DzPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Power CyclesDocument9 pagesGas Power CyclesWaqar YusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Sala FormatDocument82 pagesSala FormatLemuel ReñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. Objectivefarah nazPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. Objectivefarah nazPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Introduction, Gas Turbines, Applications, TypesDocument2 pages1 Introduction, Gas Turbines, Applications, TypesMostafaEslamiPas encore d'évaluation
- How Gas Turbine Power Plants WorkDocument12 pagesHow Gas Turbine Power Plants WorkLa Vien Rose100% (1)
- Gas Turbines FundamentalsDocument2 pagesGas Turbines FundamentalsMohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbines - Hassan ElBanhawiDocument3 pagesGas Turbines - Hassan ElBanhawijesus_manrique2753Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Gas Turbine Power Plants WorkDocument6 pagesHow Gas Turbine Power Plants Workchella2705100% (1)
- Gas Turbine: Principle of OperationDocument20 pagesGas Turbine: Principle of Operationwaleed paliPas encore d'évaluation
- GALGALLA - Working Assignment 3 - Gas TurbineDocument5 pagesGALGALLA - Working Assignment 3 - Gas TurbineGodfrey Jr Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument23 pagesChapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantBese Mat100% (1)
- Chapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument21 pagesChapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantBiniam Nega100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Start UpDocument131 pagesGas Turbine Start UpBaharudin Bin Kamarul Baharin100% (3)
- Gas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet ADocument82 pagesGas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet Afateh1982Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Gas Turbine: 1. Operating PrincipleDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Gas Turbine: 1. Operating PrincipleMuhammad Ridhwan100% (2)
- General Characteristics: Combustion Internal-Combustion Engine CompressorDocument4 pagesGeneral Characteristics: Combustion Internal-Combustion Engine CompressorAnshuman KatakyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument42 pagesGas Turbine Power PlantMuralikrishnan GM100% (3)
- TurbineDocument9 pagesTurbineKabir Bashir ShariffPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Thermal Power PlantDocument7 pagesGas Turbine Thermal Power PlantAkshay ManzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Power Plant PresentationDocument126 pagesGas Turbine Power Plant Presentationjehadyam100% (1)
- Gas TurbineDocument53 pagesGas TurbinedipakbagPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine DescriptionDocument8 pagesGas Turbine DescriptionSIVAPATHASEKARANPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine ReportDocument13 pagesGas Turbine Reportwaleed100% (1)
- Chapter 1 and 2 Lecture Notes - IRISDocument111 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Lecture Notes - IRISSsh keys JoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Plants Lab: Assignment 1Document3 pagesPower Plants Lab: Assignment 1Faseeh GhaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 1: Gas Turbine ConstructionDocument4 pagesFigure 1: Gas Turbine ConstructionSyed Anas Sohail100% (2)
- JET ENGINE FundamentalsDocument18 pagesJET ENGINE FundamentalsHareesha N GPas encore d'évaluation
- A Gas Turbine UnitDocument9 pagesA Gas Turbine UnitTITU NATHPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Parts: Fast Basic Guide About Components: What Is A Gas Turbine? Where Is It Used?Document6 pagesGas Turbine Parts: Fast Basic Guide About Components: What Is A Gas Turbine? Where Is It Used?Lion Tiger100% (1)
- Energy Systems: Gas Turbine System IDocument14 pagesEnergy Systems: Gas Turbine System IAbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine MaintenanceDocument146 pagesGas Turbine MaintenanceMamoun1969100% (9)
- Lesson 1 CorrectionDocument5 pagesLesson 1 CorrectionAlyanna AngelesPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance of Industrial GasturbinesDocument28 pagesPerformance of Industrial Gasturbinessomporn duangbuntaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Plant-Gas Turbine BasedDocument15 pagesPower Plant-Gas Turbine BasedmandhirPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Test and EvaluationDocument9 pagesClass Test and EvaluationJared AngPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Gas Turbines: Aero Derivative AndDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Gas Turbines: Aero Derivative And121710801027 HARI KRISHNAN SURESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesTahir MuneebPas encore d'évaluation
- Pasgt Act 3Document7 pagesPasgt Act 3Ramil SalundagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas TurbineDocument6 pagesGas Turbineusama shehrozPas encore d'évaluation
- Air and Fuel Induction - FiveDocument35 pagesAir and Fuel Induction - FiveasfsaedgarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 17Document27 pagesLecture 17Saleem KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsDocument27 pagesWorking Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsRey Danielle Navea100% (2)
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument14 pagesGas Turbine Power PlantBouhadPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo ChargerDocument23 pagesTurbo Chargerselvaraj9223100% (1)
- Gas Turbines A Manual PDFDocument74 pagesGas Turbines A Manual PDFHenry Pannell100% (1)
- DOE-Gas Turbine HandbookDocument549 pagesDOE-Gas Turbine HandbookKrasimir Ivanov88% (8)
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesD'EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesD'EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesD'EverandGas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants A Practice Treatise Setting Forth the Principles of Gas-Engines and Producer Design, the Selection and Installation of an Engine, Conditions of Perfect Operation, Producer-Gas Engines and Their Possibilities, the Care of Gas-Engines and Producer-Gas Plants, with a Chapter on Volatile Hydrocarbon and Oil EnginesPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW NmviajesDocument1 pageWWW NmviajesEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Wang Wen-Chung - Final SubmissionDocument3 pagesWang Wen-Chung - Final SubmissionEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- ACT APIs For Mechanical Guide PDFDocument52 pagesACT APIs For Mechanical Guide PDFAbhishek yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Eth 49096 02Document168 pagesEth 49096 02Emerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbojet Fyp ThesisDocument108 pagesTurbojet Fyp ThesisEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic PerformanceDocument2 pages18 Gas Turbine Engines, Design and Dynamic PerformanceEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Wang Wen-Chung - Final SubmissionDocument3 pagesWang Wen-Chung - Final SubmissionEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Can Anyone Explain The Area Used in Drag CoefficientDocument3 pagesCan Anyone Explain The Area Used in Drag CoefficientEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Published PDFDocument6 pagesPublished PDFEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Published PDFDocument6 pagesPublished PDFEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Published PDFDocument6 pagesPublished PDFEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Mechanical and Physical Properties of Corn SeDocument10 pagesSome Mechanical and Physical Properties of Corn SeEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Beltmaster Berekeningen-Transport PDFDocument16 pagesBeltmaster Berekeningen-Transport PDFyaidragonPas encore d'évaluation
- Spacex PDFDocument69 pagesSpacex PDFEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm A36 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm A36 PDFYudi Popo Fadhillah100% (3)
- Novel Stair Climbing TransformableDocument7 pagesNovel Stair Climbing TransformableEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Introducción: Nota CientíficaDocument5 pagesIntroducción: Nota CientíficaEmerovsky ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- SpaceWorks VTVL Study - ReleaseDocument13 pagesSpaceWorks VTVL Study - ReleasecrocomodxPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism Design Solman Ed4 ch3Document50 pagesMechanism Design Solman Ed4 ch3ukg12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanism Design Solman Ed4 Ch1Document26 pagesMechanism Design Solman Ed4 Ch1Ivan Alejandro Gomez AyalaPas encore d'évaluation