Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Hig Rise Building
Transféré par
adityaCS3Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Hig Rise Building
Transféré par
adityaCS3Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
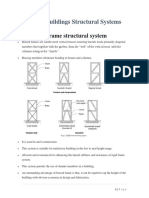
Type of High-Rise Structure
1. Braced Frame
2. Rigid Frame Structure
3. Infilled Frame Structure
4. Flat Plate and Flat Slab Structure
5. Shear wall structure
6. Coupled wall structure
7. Wall-frame structure
8. Framed tube structure
9. The trussed tube
a. Tube in tube or Hull core structure
b. Bundled tube structure
c. Core and Outriggers system
10. Hybrid structure
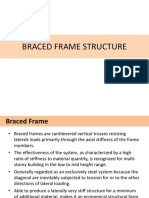
Braced Frame
Braced frames are cantilevered vertical trusses resisting laterals
loads primarily through the axial stiffness of the frame members.
The effectiveness of the system, as characterized by a high ratio of
stiffness to material quantity, is recognized for multi-storey building
in the low to mid height range.
Generally regarded as an exclusively steel system because the
diagonal are inevitably subjected to tension for or to the other
directions of lateral loading.
Able to produce a laterally very stiff structure for a minimum of
additional material, makes it an economical structural form for any
height of buildings, up to the very tallest.
Advantages:-
Girders only participate minimally in the lateral bracing action-Floor
framing design is independent of its level in the structure.
Can be repetitive up the height of the building with obvious
economy in design and fabrication.
Disadvantages:-
Obstruct the internal planning and the locations of the windows and
doors; for this reason, braced bent are usually incorporated
internally along wall and partition lines, especially around elevator,
stair, and service shaft.-
Diagonal connections are expensive to fabricate and erect
ACT Tower, Himatsu Japan
Rigid Frame Structure
Consist of columns and girders joined by moment resistant connections.
Lateral stiffness of a rigid frame bent depends on the bending stiffness of the
columns, girders, and connection in the plane of the bents. Ideally suited for
reinforced concrete buildings because of the inherent rigidity of reinforced
concrete joints. Also used for steel frame connections in steel tend to be
costly. While rigid frame of a typical scale that serve alone to resist lateral
loading have an economic height limit of about 25 stories, smaller scale rigid
frames in the for of perimeter tube typically rigid frames in combination with
shear walls or braced bents, can be economic up top much greater heights.
Advantages:-
May be place in or around the core, on the exterior, or throughout the
interior of the building with minimal constraint module.
The frame may be architecturally exposed to express the grid like nature
of the structure.
Disadvantages
The spacing of the columns in a moment resisting frame can match that
required for gravity framing. Only suitable for building up to 20 to 30
stories only; member proportions and materials cost become
unreasonable for building higher than that. buildings, but moment
Fig. WTC OSAKA JAPAN
In-filled Frame Structure
Most usual form of construction for tall buildings up to 30 stories in height.
Column and girder framing of reinforced concrete, or sometimes steel filled by
panels of brickwork, block work, or cast-in-place concrete. Because of the in-
filled serve also as external walls or internal partitions, the system is an
economical way of stiffening and strengthening of the structure. The complex
interactive behaviour of the infill in the frame, and the rather random quality of
masonry, has made it difficult to predict with accuracy the stiffness and strength
of an infilled frame.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Type of High Rise BuildingDocument2 pagesType of High Rise BuildingPrashant SunagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Highrise BuildingsDocument13 pagesHighrise BuildingsPratik ShindePas encore d'évaluation
- HGH Rise Structural SystemDocument11 pagesHGH Rise Structural SystemShubham Srivastava100% (1)
- Types of HighDocument11 pagesTypes of HighFahad AlbutiPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise .DocbuilkdingDocument1 pageHigh Rise .DocbuilkdingPrashant SunagarPas encore d'évaluation
- New Reviewer Ale October 2020 PDFDocument12 pagesNew Reviewer Ale October 2020 PDFJARMRAPas encore d'évaluation
- Brace Frame StructureDocument9 pagesBrace Frame StructureGrey YosPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of High-Rise Buildings Structural SystemsDocument12 pagesTypes of High-Rise Buildings Structural Systemsmehedi emonPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural SystemsDocument13 pagesStructural SystemscharPas encore d'évaluation
- HIGH RISE Structural SystemDocument6 pagesHIGH RISE Structural SystemFahadPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise StructuresDocument21 pagesHigh Rise StructuresJayamal Induruwa100% (1)
- High Rise StructuresDocument21 pagesHigh Rise StructuresChainsmokers ChainsmokersPas encore d'évaluation
- Lateral Resisting SystemsDocument28 pagesLateral Resisting SystemsAslam KyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal Frame: Grace Henry & Midhuna SureshDocument37 pagesPortal Frame: Grace Henry & Midhuna SureshMasroor AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Design System: Assignment: High Rise Building Structure SystemsDocument7 pagesBuilding Design System: Assignment: High Rise Building Structure SystemsUzair SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Systems For High Rise BuildingsDocument7 pagesStructural Systems For High Rise BuildingsPaulaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Multistory Building Higher Than 21m or 21 To 29 Floor Buildings With Unknown Height Described As HighDocument10 pagesA Multistory Building Higher Than 21m or 21 To 29 Floor Buildings With Unknown Height Described As HighTri Haryadi LinggialloPas encore d'évaluation
- Building Structural SystemDocument12 pagesBuilding Structural Systemannisa ersi adlyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal FrameDocument4 pagesPortal Frameakankshapen100% (1)
- Portal FrameDocument9 pagesPortal FrameAbhishek Rajgor100% (1)
- Session 4 - Structural Systems in Tall BuildingsDocument36 pagesSession 4 - Structural Systems in Tall BuildingsAlec PPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 8 - Portal Frame Construction - BSR552Document39 pagesTopic 8 - Portal Frame Construction - BSR552NURULFARHANA DAUDPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 23 PDFDocument5 pages19 23 PDFAminul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- SHRB - Struktur Utama Bangunan - 2023 PDFDocument35 pagesSHRB - Struktur Utama Bangunan - 2023 PDFYanti RahmadaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Adamson UniversityDocument20 pagesAdamson UniversityKim Yun Shik PegoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Framed Structures 1Document4 pagesFramed Structures 1Festus NgumbiPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise StructuresDocument70 pagesHigh Rise StructuresAnjalySinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of High RiseDocument3 pagesClassification of High Riseyogita guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Framed Structures: Submitted By:-Submitted ToDocument15 pagesFramed Structures: Submitted By:-Submitted ToNidhi MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Long Span Structure 050919Document63 pagesLong Span Structure 050919Ritesh LoharPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of StructuresDocument2 pagesTypes of StructuresShubham DuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal Frames Final - 2Document19 pagesPortal Frames Final - 2Ar Vivek KareliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal Frame Structure: Lect 8Document35 pagesPortal Frame Structure: Lect 8jkaliwonPas encore d'évaluation
- Precast Concrete Combined)Document13 pagesPrecast Concrete Combined)Ssu NguPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical Structure SystemsDocument51 pagesVertical Structure SystemsANJALI GAUTAMPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise BuildingsDocument7 pagesHigh Rise BuildingsjenitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Building ConstructionDocument15 pagesBuilding Constructionnikitadusing100% (1)
- Lateral Resisting Systems - Sturdy Structural PDFDocument5 pagesLateral Resisting Systems - Sturdy Structural PDFBharath m.s.v.mPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure SystemDocument12 pagesStructure SystemSAHIL KAUSHALPas encore d'évaluation
- Portal Frame-FINALDocument11 pagesPortal Frame-FINALKratiAgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Stuctures PortfolioDocument77 pagesStuctures PortfolioIndraja RmPas encore d'évaluation
- ARCH6021 LB44 2201838746 Indira Jihan Shafira-UTSDocument25 pagesARCH6021 LB44 2201838746 Indira Jihan Shafira-UTSindirajsfPas encore d'évaluation
- CE18B037 Assignment2Document9 pagesCE18B037 Assignment2Kota Thapaswini ce18b037Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Assignment 1Document4 pagesDigital Assignment 1Atul RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Systems - Vignesh.bDocument6 pagesTypes of Systems - Vignesh.bjenitaPas encore d'évaluation
- High Rise Structural Systems: Presented byDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Structural Systems: Presented byiqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iii Ce6016 Prefabricated Structures: Design PrinciplesDocument36 pagesUnit - Iii Ce6016 Prefabricated Structures: Design PrinciplesVivekPas encore d'évaluation
- Low-Rise Office BuildingDocument108 pagesLow-Rise Office BuildingDenielle Marie PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Structural SytemDocument10 pagesTypes of Structural SytemOlga KosuoweiPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrian Rollo Toisa: Portal Frame Construction & Pre Engineered Building SystemDocument31 pagesAdrian Rollo Toisa: Portal Frame Construction & Pre Engineered Building SystemdamandadinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bracing System in BuildingDocument23 pagesBracing System in BuildingSouhard MatrePas encore d'évaluation
- Portal FramesDocument13 pagesPortal FramesArun Sahani100% (2)
- Concrete PortalDocument6 pagesConcrete PortalolomizanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Highrise Construction - MMBCDocument39 pagesHighrise Construction - MMBCkareemulllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Shear WallsDocument27 pagesShear WallsRekha Tanpure100% (1)
- RCC Moment Framed RCC Flate Plate and Slab: Presented by Ashish, Bhavana, Hasita, Manoj and NaveedDocument22 pagesRCC Moment Framed RCC Flate Plate and Slab: Presented by Ashish, Bhavana, Hasita, Manoj and NaveedNidhi MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural System in High Rise BuildingDocument7 pagesStructural System in High Rise BuildingjenitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Steel DesignDocument27 pagesStructural Steel DesignLilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignD'EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsD'EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsPas encore d'évaluation
- Audio VisualDocument6 pagesAudio VisualadityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Logo MisdinarDocument4 pagesLogo MisdinaradityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- January 2017: Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri SatDocument12 pagesJanuary 2017: Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri SatadityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sea RanchDocument1 pageSea RanchadityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- ThatchDocument1 pageThatchadityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Spiral TowersDocument2 pagesSpiral TowersadityaCS3100% (1)
- Sisbang Lotte PDFDocument17 pagesSisbang Lotte PDFadityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Las Mercedes House 2Document27 pagesLas Mercedes House 2adityaCS3Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Paombong Public MarketDocument2 pagesThe Paombong Public MarketJeonAsistin100% (1)
- ETI Part BooksDocument63 pagesETI Part Booksyugopuspoyo100% (1)
- BW e S M TDocument87 pagesBW e S M TRadu GanciuPas encore d'évaluation
- Aws Aceptance Criteria VT MT PTDocument1 pageAws Aceptance Criteria VT MT PTJose MenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Armover LengthDocument2 pagesArmover Lengthjo100% (1)
- Marina Square II BrochureDocument11 pagesMarina Square II BrochureAbdul Rasyid Abdullah SebliPas encore d'évaluation
- Site and Temporary WorksDocument11 pagesSite and Temporary Worksbaluku samuelPas encore d'évaluation
- V. Project Profile and Analysis 5.1 Historical Background: Commonwealth To Post-Commonwealth EraDocument32 pagesV. Project Profile and Analysis 5.1 Historical Background: Commonwealth To Post-Commonwealth EraMr. ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Access ScaffoldingDocument19 pagesGuidelines For Access ScaffoldingAbdul Khader ShahadafPas encore d'évaluation
- Estimate The Reinforcement in Shallow FoundationDocument12 pagesEstimate The Reinforcement in Shallow FoundationEmdad Yusuf100% (2)
- Squatting WC Pan: Special FeaturesDocument2 pagesSquatting WC Pan: Special FeaturesRushan LakdimuthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Muhammad Awais: ContactDocument1 pageMuhammad Awais: ContactMian AwaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Maint Manual Swill Hydraulic PlateformDocument16 pagesOperation and Maint Manual Swill Hydraulic Plateformmicell dieselPas encore d'évaluation
- Foselev Gabon Brochure (Eng) - Rev 1Document5 pagesFoselev Gabon Brochure (Eng) - Rev 1morfeuss85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - 21 - 30Document10 pagesChapter 1 - 21 - 30MOHD ZAINUDIN JENALPas encore d'évaluation
- 0-10V AHU DX Coil Interface (LC / VRF) Installation Manual: EnglishDocument36 pages0-10V AHU DX Coil Interface (LC / VRF) Installation Manual: EnglishAhmed Salah Abd EL-WahedPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - ChecklistDocument4 pagesCase Study - Checklistsafiulla syedPas encore d'évaluation
- PSC NotesDocument87 pagesPSC Notessarath156Pas encore d'évaluation
- 328750852089918-Working HydraulicsDocument9 pages328750852089918-Working HydraulicsBestway Equipment RepairingPas encore d'évaluation
- Screw Jack DesignDocument13 pagesScrew Jack DesignIbrahimovic Elsaied78% (9)
- Economics of Lysine Production From GlucoseDocument56 pagesEconomics of Lysine Production From GlucoseIntratec Solutions50% (4)
- Installation Guidelines: 1. Preparing The SubgradeDocument3 pagesInstallation Guidelines: 1. Preparing The SubgradeElard QAPas encore d'évaluation
- Raft Foundation 2.0Document6 pagesRaft Foundation 2.0anuragPas encore d'évaluation
- FAS Data-Sheet Vantage-Seal PDFDocument10 pagesFAS Data-Sheet Vantage-Seal PDFVictor Flores ResendizPas encore d'évaluation
- LafargeDocument18 pagesLafargeMadan Mohan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- VE5C VE Commodore Hard Lid ManualDocument13 pagesVE5C VE Commodore Hard Lid ManualmathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Stirling BoilerDocument14 pagesStirling BoilerDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- 3685 Mir 006 PDFDocument1 page3685 Mir 006 PDFashishpearlPas encore d'évaluation
- Vol II KuchamanDocument556 pagesVol II Kuchamanrasun krPas encore d'évaluation
- Agri MonoblocDocument2 pagesAgri Monoblockeeprocking9777Pas encore d'évaluation