Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
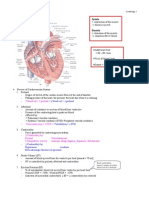
Name Four Chambers: - Receive Blood From Systemic or
Transféré par
gabiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name Four Chambers: - Receive Blood From Systemic or
Transféré par
gabiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review A &P View suggested videos in guide
Review Core concepts, structure, circulation,
Test your knowledge:
Label heart diagram
Label sequence of cardiac cycle
Take video quiz listed in weekly guide
Core Concepts
Heart = pump
Arteries and veins = circulation
(plumbing)
Capillaries = ____ & ______exchange
Pump with electrical system
Two stages R & L
Flow through ______ & _______
Sequential: ________squeeze blood into
ventricles
L Atrium provides _____%of cardiac
output
Coronary arteries = heart’s blood supply
Four heart chambers
Name four chambers:
_________ receive blood from systemic or
pulmonary venous beds, less myocardium,
low pressure
__________ L thicker than R, mean
pressure 15 vs 92
____________ divides ventricles, no blood
flow between RV and LV
R heart: receives __________blood from the body and tissues and then pumps it to the lungs to
pick up _________and dispel carbon dioxide
L heart: receives oxygenated blood returning from the lungs and pumps this blood throughout the
body to supply oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 1
Cardiac Flow
Extremely simple:
Body to ________to lungs to _____heart to the
Body
More detail:
Body> then by way of __________, Coronary
Sinus to Right Atrium (RA), To Right Ventricle
(RV), then via Pulmonary Arteries, to Left Atrium
(LA) via pulmonary veins to Left Ventricle to body
via Aorta
Detailed Cardiac blood flow..
Body> then by way of ________, Coronary Sinus
to Right Atrium (RA), To RV through ______
Valve, then via Pulmonary Arteries, to LA via
________Valve via pulmonary veins to LV through
MiTral Valve to body via ________ to Aorta
Two circulatory systems: Two circulatory systems:
Pulmonary Circulation Systemic circuit:
Blood from R heart to lungs Blood from Right or Left heart to body?________
Arteries: desaturated hemoglobin Saturated hemoglobin
Low or High Pressure? ________ High pressure or Low Pressure? __________
What have the tissues taken from this This blood is Saturated with?____________
blood leaving it
desaturated?_________________
*Position of the heart : Where would you
place your stethoscope to listen to heart
sounds?
Investigate/identify four standard points
1
2.
3
4
It may be easier for you to see Flow
in this diagram…. Either way,
become familiar with it
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 2
Heart Wall Four Heart Valves Great Vessels
___________ membranous sac RA – RV = _______ valve Superior and inferior vena cava
covers heart RV – PA (pulm artery) = Pulmonary artery
__________ main muscle of ________ valve Pulmonary vein
heart LA – LV = ________valve Aorta
_________lines inside of heart LV – Aorta = _______valve
wall, arteries & veins
Identify the layers of the pericardium and heart wall: (there are three for each)
Pericardium _________ _________ _________ Myocardium_______ _________ ____________
Positions of valves----Valves open and close in response to pressure differences
Trabeculae carnae----Note papillary muscles, chordae tendinae (heart strings): keep valves from prolapsing (purpose of
valve = 1 way flow)
Coronary Arteries Describe collateral
Heart has its own blood vessels circulation
Major arterial branches, left and right
Left: Supplies mostly the LV
L main, L anterior descending (supplies
septum and some RV)
Circumflex (LA and lateral wall of LV)
Right: mostly posterior heart
Myocardial O2 Demand Cardiac Oxygen Extraction
MVO2 – myocardial oxygen demand Heart extracts maximum amount of oxygen from hemoglobin
with wall stress (high blood pressure) Only way to increase cardiac tissue oxygenation is through
with heart rate dilation
70-75% of oxygen drawn from hemoglobin Coronary veins have abnormally low saturation compared to
from coronary capillaries rest of venous return
Increasing coronary blood flow is only
means of increasing O2 supply
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 3
Cardiac Electrophysiology The Normal Artery: Three Layers
Electrical impulse cause myocardial tissue *Tunica _____________
fibers to shorten or lengthen? (systole) •Tunica _____________
Cardiac action potential – impulse can be •Tunica _____________
passed to other myocardial cells
After short period, myocardial fibers relax
this period is called___________
Myocardial cells have ability to self fire and
do not need direct connection to nervous
system
Conduction Pathway
Sinoartial (SA) node - atrium
Atrioventricular (AV) node - septum
Bundle of his and bundle branches –
ventricles
Purkinje fibers – rest of myocardium
each node is capable of firing on own
without stimulation
*SA node – AV node conduction
contracts _________, provides “________kick” (_____% of cardiac output)
AV node: Septal and apical myocardial contraction
Action Potiential Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
Polarization: ion shifts across cell Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
membranes P -> QRS -> T waves
P wave = _________depolarization
Creates voltage difference - QRS = ventricles are ___________
60millivolts T = Ventricles _________________
Depolarization shifts ____ into cells &
______Out
Threshold for doing this can be
altered by decreased serum K
Refractory period during
repolarization
Preload and afterload
Definition Factors
The intrinsic ability of the heart to Sympathetic stimulation
Parasympathetic stimulation
increase the extent and force of
Drugs
muscle fiber shortening independent Oxygen
of preload or afterload Heart rate
Ionic environment
Cardiovascular disease
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 4
Contractility
Cardiac muscle increases strength of
contraction when stretched
End-diastolic volume = blood in ventricles
just before systole occurs
Preload = filling pressure = volume of blood
in heart
Think stretching a rubber band and how far
it will travel when released
Preload Filling pressure
R/T blood volume
Afterload Resistance to LV systole Factors r/t afterload
R/T systemic vascular resistance Outflow obstructions (AS, PS)
SVR=arterial vasoconstriction __________resistance
Î SVR = ÎÎ cardiac workload & Sympathetic tone of arterial system
decrease in cardiac output Blood viscosity
Aortic insufficiency
Cardiac Output=_______X _______
Stroke volume – __________________
Ejection fraction – blood ejected during
Systole, normal 60-75%
Heart rate – beats/min
SVR – resistance to flow
Filing pressures – amount of blood
CO = blood volume/min ~ 5L/min normal
Antiduirectic hormone
Rennin angiotensin system can increase or decrease blood volume & subsequently blood
pressure?________________
Natriuretic peptides,
adrenonmedullin
Insulin
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 5
Neural Regulation of BP
Sympathetic and parasympathetic responses
Total peripheral resistance – mostly arteriole
diameter
Hypothalmic control
Body temp high = vasodilation of arteries and
veins in skin
Body temp low = shunting of blood away
from skin
Baroreceptors in aorta and carotid sinus
Send info to medulla
Effects:
Slow heart rate
Decrease contractility by inhibiting
sympathetic
discharge
Arteriolar and venous dilation (same)
Decrease CO and SVR
Hormonal Regualtion of BP
Renin (kidneys)
Angiotensin I
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
Aldosterone
Powerful vasoconstrictor = increase
SVR
Reabsorbtion of sodium in kidneys =
increase circulatory volume
Central sympathetic
outflow directed toward
the kidneys, heart, and
peripheral vasculature,
via efferent pathways
leads to volume
retention, increased
cardiac output, and
systemic
vasoconstriction, the
harbingers of
persistently elevated
blood pressure. BNP
indicates brain
natriuretic peptide;
RAAS, renin–
angiotensin–
aldosterone system;
and SNS, sympathetic
nervous system.
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 6
An electrocardiogram (EKG, ECG) is a test that measures the electrical signals
that control heart rhythm. The test measures how electrical impulses move
through the heart muscle as it contracts and relaxes.
The electrocardiogram translates the heart's electrical activity into line tracings on
paper. The spikes and dips in the line tracings are called waves.
The ________is a record of the electrical activity through the upper heart
chambers (atria).
The _____ complex is a record of the movement of electrical impulses through
the lower heart chambers (ventricles).
The __ segment shows when the ventricle is contracting but no electricity is
flowing through it. The ST segment usually appears as a straight, level line
between the QRS complex and the T wave.
The T wave shows when the lower heart chambers are resetting electrically and
preparing for their next muscle contraction.
Determining Heart rate:
First: Find a specific R wave that peaks on a heavy black line (our "start" line)
Count off the next three lines after
"300, 150, 100" as "75, 60, 50."
Where the next R wave falls,
determines the rate. It's that simple!
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 7
What is the Heart rate here? ________
ECG of atrial fibrillation (top) and normal
sinus rhythm (bottom). The purple arrow
indicates a P wave, which is lost in atrial
fibrillation.
A & P Cardiac Summer ‘14 8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- DK Guide To The Human Body PDFDocument67 pagesDK Guide To The Human Body PDFTina Fishie Volf100% (5)
- Biyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsDocument81 pagesBiyani's Think Tank: Cell Biology & GeneticsAkshay chandrakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Trauma Life SupportDocument452 pagesAdvanced Trauma Life Supportnatalia100% (7)
- Exploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesExploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetBrian MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- 0010 (1) Science - Terms 1.154KB PDFDocument236 pages0010 (1) Science - Terms 1.154KB PDFMuhammad SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasD'EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (5)
- HemophiliaDocument27 pagesHemophiliaDorothy Pearl Loyola Palabrica100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit 10 Test Review KEYDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit 10 Test Review KEYsenjicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac SystemDocument7 pagesCardiac Systemsccctutor100% (3)
- PsychopharmacologyDocument49 pagesPsychopharmacologysazaki224Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Patricia Isabel Sandoval Martínez - Circ. Syst. ST - ANSWER SHEET 12-26Document4 pagesKami Export - Patricia Isabel Sandoval Martínez - Circ. Syst. ST - ANSWER SHEET 12-26p.sandoval.2027Pas encore d'évaluation
- Complaint Affidavit SampleDocument13 pagesComplaint Affidavit SampleGertrude PillenaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart and Circulation ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Heart and Circulation ReviewRona Carta OñatePas encore d'évaluation
- The A To Z of The HeartDocument259 pagesThe A To Z of The HeartAspenPharma100% (2)
- The Circulatory System: Circulatory System:movement of Blood Around Your BodyDocument17 pagesThe Circulatory System: Circulatory System:movement of Blood Around Your BodyStella StaryPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomyDocument18 pagesThe Ontogenetic Basic of Human AnatomymeseniaPas encore d'évaluation
- AJ Lesson 2: B4.3 The Heart: Mammalian Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesAJ Lesson 2: B4.3 The Heart: Mammalian Circulatory SystemIntelaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 13 ActivityDocument4 pagesCH 13 Activityash vldnbrPas encore d'évaluation
- Labelling The Human HeartDocument6 pagesLabelling The Human Heartchinpy088464Pas encore d'évaluation
- The circulatory system in 30 secondsDocument11 pagesThe circulatory system in 30 secondsRentika SiahaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiorespiratory System: Structure and FunctionsDocument19 pagesCardiorespiratory System: Structure and FunctionsKasam APas encore d'évaluation
- Physiol Wkst 7 The HeartDocument5 pagesPhysiol Wkst 7 The HeartritomPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 18 - The HeartDocument53 pagesLecture 18 - The HeartkiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Chevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkDocument3 pagesChevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkChevannese EllisPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart and The Pathway of BloodDocument21 pagesThe Heart and The Pathway of BloodSaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Worksheet Sheep Heart DissectionDocument3 pagesBiology Worksheet Sheep Heart DissectionFluphie Bunny0% (1)
- Manual Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesManual Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Heart Review WorksheetDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Heart Review WorksheetamongusPas encore d'évaluation
- HBS-Distance Learning - Heart Diagram LabelingDocument4 pagesHBS-Distance Learning - Heart Diagram LabelingCin CinPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulation WorksheetDocument6 pagesCirculation WorksheetKukresh TanveeraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Guided Study Notes - CardioRespiratory Unit - Part 1Document33 pages2021 Guided Study Notes - CardioRespiratory Unit - Part 1CarsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Document12 pagesClass 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Shlok JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemMuhammad Azrie0% (1)
- The Cardiovascular System: Learning ObjectivesDocument42 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Learning ObjectivesMuba sonPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Circulation and Transportion. Vena Cava Pulmonary Vein From Body From LungsDocument18 pagesBlood Circulation and Transportion. Vena Cava Pulmonary Vein From Body From Lungsnon_pakyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System Part 2Document41 pagesCirculatory System Part 2luffy proPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Task 1.6 Lesson CheckDocument3 pagesLearning Task 1.6 Lesson CheckAndrei Marie SamillanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Task 1.6 Lesson CheckDocument3 pagesLearning Task 1.6 Lesson CheckAndrei Marie SamillanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology 2 CVSDocument184 pagesPhysiology 2 CVSsinte beyuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart: Basis of Life .?Document94 pagesThe Heart: Basis of Life .?Diksha AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Circulatory System BookletDocument30 pagesThe Circulatory System BookletTroy CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 - Handout - Cardiovascular System - STUDENT'SDocument17 pages2023 - Handout - Cardiovascular System - STUDENT'SmilifacultadfcmPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart & Lung FunctionsDocument12 pagesHeart & Lung FunctionsKim Oliveri ReedPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesModule Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Failure 2022Document29 pagesHeart Failure 2022agarrido2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pedro Velazquez - Blood Vessels WorksheetDocument4 pagesPedro Velazquez - Blood Vessels Worksheetapi-391255953Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansDocument14 pagesBlood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansJames WongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Circulatory SystemDocument62 pagesThe Circulatory SystemRichele RectoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemrobhel740% (2)
- 6 2 The Transport SystemDocument18 pages6 2 The Transport Systemapi-235355872Pas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System GuideDocument3 pagesCirculatory System Guidesaleem.aitmPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument19 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomyshreya gualtiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart Activity 3 PDFDocument4 pagesThe Heart Activity 3 PDFbiancaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cardiovascular System Medical TermDocument28 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Medical TermFernando AlmaguerPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemMN NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- The Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsDocument8 pagesThe Circulatory System Pmls 2 Lecture 3 PrelimsNunai SalipadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Document91 pagesPatho - 21 HeartAdv - 211005 - 230536Puranjay ChandelPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyDocument55 pagesMedical Assisting: Powerpoint To AccompanyMarileth CoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument23 pagesCirculatory Systemhellwakeisbored12Pas encore d'évaluation
- The circulatory systemDocument1 pageThe circulatory systemTharanga HewabuhagePas encore d'évaluation
- ACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartDocument6 pagesACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartSYDNEY JILL ACHAIPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemRahul Ecka100% (1)
- The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Circulatory SystemBrettnia Angela AradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unlock SGCh13Document10 pagesUnlock SGCh13SilaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart PDFDocument67 pagesHeart PDFMuhammad Syafi'iPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 CVS PhysiologyDocument55 pages03 CVS PhysiologyMonenus KedirPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument33 pagesThe Cardiovascular System7salem7Pas encore d'évaluation
- JAMA - Dartmouth Study - Primary Care - SDH.fraze - 2019 - Oi - 190447-1Document14 pagesJAMA - Dartmouth Study - Primary Care - SDH.fraze - 2019 - Oi - 190447-1gabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Florence Nightingale - The Passionate StatisticianDocument7 pagesFlorence Nightingale - The Passionate StatisticiangabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Epidemiology and Data N7002 Syllabus Fall 2019Document14 pagesApplied Epidemiology and Data N7002 Syllabus Fall 2019gabiPas encore d'évaluation
- VA Information Security Rules of Behavior for Non-Organizational UsersDocument5 pagesVA Information Security Rules of Behavior for Non-Organizational UsersgabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cornell Notes TemplateDocument1 pageCornell Notes TemplategabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Form-ExampleDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Form-ExamplegabiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3770 Course SyllabusDocument5 pages3770 Course SyllabusgabiPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTES PersonalityDO2013Document15 pagesNOTES PersonalityDO2013gabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Risk Factors Activity Student 8-14-15Document1 pageEvaluation of Risk Factors Activity Student 8-14-15gabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsDocument4 pagesEvolutionary Reclassification of Protozoa and Chromista KingdomsWormInchPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz ReviewerDocument8 pagesQuiz ReviewerCai PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Kurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsDocument12 pagesKurukshetra University Date-Sheets for BA/BSc Part ExamsabhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Pro To Zoology 1954 KudoDocument988 pagesPro To Zoology 1954 KudoClaau GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Performed Structural DesignDocument93 pagesPerformed Structural DesignSaiful IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- MARA TRIAL 2013 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 ANSWER KEYDocument43 pagesMARA TRIAL 2013 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 ANSWER KEYAhmad Imran Idzqandar100% (2)
- ACE Biology O'level Book@2021Document213 pagesACE Biology O'level Book@2021DuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration in Plants: Key Terms and ProcessesDocument12 pagesRespiration in Plants: Key Terms and ProcessesNalla Raghuram ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Precocity PDFDocument5 pagesSexual Precocity PDFmist73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Potassium Persulfate InformationDocument3 pagesPotassium Persulfate InformationmeimeiliuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 UrinaryDocument24 pagesChapter 15 Urinary3amabelle arevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitality Fitness Assessment Form: 1. DetailsDocument2 pagesVitality Fitness Assessment Form: 1. DetailsmusturPas encore d'évaluation
- Behaviourist TheoriesDocument16 pagesBehaviourist Theoriesjnandre100% (1)
- Optimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004Document5 pagesOptimizing Ba and Iba Concentrations For Micro Propagation of Spineless Yucca Yucca Elephantipes IJERTV8IS010004SHUBHAM JIBHAKATEPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajeev Kumar Talakayala CVDocument37 pagesRajeev Kumar Talakayala CVSanjeev KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- CK-MB production method reportDocument1 pageCK-MB production method reportOkura JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Conduction System of HeartDocument2 pagesConduction System of HeartEINSTEIN2DPas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Arteries PDFDocument18 pagesRenal Arteries PDFServo LedPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Meningitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument49 pagesUnderstanding Meningitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDrAbhilash RMPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Motivation Edited2Document23 pagesHuman Motivation Edited2jingoPas encore d'évaluation
- BugSpeaks Sample ReportDocument27 pagesBugSpeaks Sample ReportAnonymous 76wOMTpPas encore d'évaluation