Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pedagogy Map Edse12024
Transféré par
api-4108422560 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues5 pagesTitre original
pedagogy map edse12024
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
14 vues5 pagesPedagogy Map Edse12024
Transféré par
api-410842256Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 5
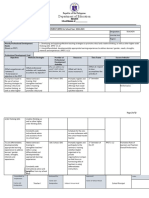
PEDAGOGY MAP
General Key Ideas Low-End High-End Authentic Learning ICT Connection
Capabilities Pedagogy Pedagogy Pedagogy
Literacy Teaching Challenging Deep Understanding: Students should use and
Students students to find Through evidence of experiment with vocabulary
vocabulary more powerful students work using high by typing responses into
through hand- and high modality modality vocabulary when Grammarly to show them
outs or alternatives to responding to questions and where sentences are
presentation low modality mathematical problems. fragmented, poor word
words such has choice or incorrect use of 3rd
because, person. Also, students
assuming or Knowledge as Problematic: should use note sharing
shown etc. Students will clique their programs to swap responses
own and peers use of and check for clear
vocabulary to suit the task. explanation of ideas and
cohesiveness.
In the general Capability for Literacy Background Knowledge:
this tie into Mathematics through the Students will have to dive
use of students learning and deep into past knowledge of
understanding the vocabulary higher modality vocabulary
associated with numbers, space, to select the correct
measurement, mathematical concepts, adjectives or verbs when
modality of vocabulary to use when communicating their
responding to questions and how to thoughts, opinions and
interpret and challenge a range of conclusions.
texts that are typical of mathematics.
This can include but is not limited to;
Calenders, maps and complex data
displays. (Australian Curriculum,
Assessment and Reporting Authority,
2018)
Numeracy Explicitly teach Teach students Problem Based Curriculum, Students can use
series of instructions to Active Citizenship & Cultural spreadsheets to convey data
instruction to basic problems Knowledges: Mathematical and calculate simple
solve problems and provide a problems may be created to variables of common data
range of challenge existing ideas graphs i.e. quartiles, mean,
problems that about cultural problems median and mode for
incorporate prior involving finance, land or statistics. Students will also
knowledge and leadership through statistics use blogging websites for
complex wording. and metric calculations. assessment purposes and
Problems may also act to blog their thoughts and
foster positive solutions to opinions as well as research
waste disposal, food pricing they undertook for the
and costs of commonly assessment.
“The Australian Curriculum: purchased items i.e. from
Mathematics plays an important role in Cars, furniture & houses to
ensuring the mathematics curriculum groceries, phones and
provides the opportunity to apply collectables through the use
mathematical understanding and skills of financing (compound
in context. A particularly important interest, fixed rate interest
context for the application of NUMBER and variable rate interest
AND ALGEBRA is financial calculations).
mathematics. In MEASUREMENT Knowledge Integration:
AND GEOMETRY, there is an Students must integrate
opportunity to apply understanding to knowledge of algebra into
design. The twenty-first-century world geometry calculations as
is information driven, and well as measurement
through STATISTICS AND conversions.
PROBABILITY students can interpret
data and make informed judgements Background Knowledge:
about events involving chance.” students must recall
(Australian Curriculum, Assessment background knowledge on
and Reporting Authority, 2018) simple algebra and
geometry to apply to more
complex mathematical
problems.
ICT Capability Students use Students use a Substantive Conversation: - Spreadsheets
Word to type range of note Students will engage in - Animated
notes and sharing programs conversation debating problems/solutions
assignments. to share notes for correct ICT tool/design or - AutoCAD for 3D
group the solution of solutions and
assessments and mathematical problems. designs
create advanced
digital
presentations to Student Direction: Students
convey will get to choose and
arguments of define the ICT tool they
assessments. utilise including the extent
Students will of its use. Including distance
receive copies of measuring apps on iPads.
any presentation,
In the Australian Curriculum: notes or quiz
Mathematics, students develop ICT through email or
capability when they investigate, online learning
create and communicate mathematical programs i.e.
ideas and concepts using fast, Class dojo,
automated, interactive and multimodal learning place etc
technologies. They use their ICT
capability to perform calculations; draw
graphs; collect, manage, analyse and
interpret data; share and exchange
information and ideas; and investigate
and model concepts and relationships.
Digital technologies, such as
spreadsheets, dynamic geometry
software and computer algebra
software, can engage students and
promote understanding of key
concepts. (Australian Curriculum,
Assessment and Reporting Authority,
2018)
Critical and Explain different students will be Deep Understanding: In
Creative ways to tackle tasked to search order for students to find
Thinking difficult for different ways more sophisticated ways to
mathematical to combat the tackle the mathematical
problems. problem to get problems they must have a
the correct deep understanding of the
solution. topic.
Problem-based curriculum:
Student are tasked with
problems that will be highly
likely to cross their paths in
the future and must think
up creative and effective
ways to tackle the problem
and find a solution.
“In the Australian Curriculum:
Mathematics, students develop critical
and creative thinking as they learn to
generate and evaluate knowledge,
ideas and possibilities, and use them
when seeking solutions. Engaging
students in reasoning and thinking
about solutions to problems and the
strategies needed to find these
solutions are core parts of the
Australian Curriculum: Mathematics.
Students are encouraged to be critical
thinkers when justifying their choice of
a calculation strategy or identifying
relevant questions during a statistical
investigation. They are encouraged to
look for alternative ways to approach
mathematical problems; for example,
identifying when a problem is similar to
a previous one, drawing diagrams or
simplifying a problem to control some
variables.” (Australian Curriculum,
Assessment and Reporting Authority,
2018)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Nepf Lesson Plan PrepDocument2 pagesNepf Lesson Plan Prepapi-460649413100% (1)
- Final Portfolio EssayDocument7 pagesFinal Portfolio Essayapi-340129196Pas encore d'évaluation
- Career AssessmentDocument13 pagesCareer Assessmentapi-3781744Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Day FDP BrochureDocument2 pages2 Day FDP BrochureBhargav ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Collaborative LearningDocument11 pagesCollaborative LearningChristopher PontejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Headmaster Info Packet 1Document9 pagesHeadmaster Info Packet 1api-355684961Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5117 Campoy Chapter 5 PDFDocument38 pages5117 Campoy Chapter 5 PDFIbrahim ShakirPas encore d'évaluation
- Malco Edited 10 QuestionDocument3 pagesMalco Edited 10 QuestionRizza Joy Sariego EsplanaPas encore d'évaluation
- District Reading Action PlanDocument4 pagesDistrict Reading Action PlanAnthony ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom Rules and ProceduresDocument13 pagesClassroom Rules and ProceduresTetzie SumayloPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay 4 Novel PDFDocument5 pagesEssay 4 Novel PDFhigdon_nickPas encore d'évaluation
- IPPDDocument2 pagesIPPDAriel Adriatico100% (1)
- Haridwar (Uttarakhand) : A Baseline Survey of Minority Concentration Districts of IndiaDocument50 pagesHaridwar (Uttarakhand) : A Baseline Survey of Minority Concentration Districts of IndiaurvashiakshayPas encore d'évaluation
- Greg Hardin CVDocument7 pagesGreg Hardin CVgreg hardinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pros and Cons of Assessment ToolsDocument19 pagesPros and Cons of Assessment Toolsapi-301639691Pas encore d'évaluation
- He AratohuDocument70 pagesHe Aratohuapi-244064781Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geo 201-01-World Cultural Geography: College of Arts and SciencesDocument5 pagesGeo 201-01-World Cultural Geography: College of Arts and SciencesKhaled SamaraPas encore d'évaluation
- T Tidwell Itec 7305 Structured Field Log Data SummaryDocument2 pagesT Tidwell Itec 7305 Structured Field Log Data Summaryapi-258167103Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aptitude Questions and Answers For FreshersDocument5 pagesAptitude Questions and Answers For Freshersmonving100% (1)
- SALAMERO-YUMO - Supervisory Program (SY 2022-2023)Document4 pagesSALAMERO-YUMO - Supervisory Program (SY 2022-2023)Abegael YumoPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Concepts in ELT: SchemasDocument1 pageKey Concepts in ELT: SchemasHanieh AkbarimehrPas encore d'évaluation
- MRF MT Sy 2023 2024Document8 pagesMRF MT Sy 2023 2024Ailyn OcomenPas encore d'évaluation
- Womens Studies in IndiaDocument16 pagesWomens Studies in IndiaAnil PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Finals in Research Ed 52...... FinalsDocument40 pagesFinals in Research Ed 52...... FinalsMitchang Valdeviezo100% (1)
- McDonough - 2007 - Motivation in ELT - ELT JournalDocument3 pagesMcDonough - 2007 - Motivation in ELT - ELT JournalBob Howes0% (1)
- Formal and Informal LanguageDocument10 pagesFormal and Informal LanguagePouyan Mobasher AminiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample CVDocument3 pagesSample CVGlendo Ray MaravePas encore d'évaluation
- Magoosh Essay Rubric For The GREDocument1 pageMagoosh Essay Rubric For The GRESasa MilosevicPas encore d'évaluation
- LP-Kinds of SentencesDocument3 pagesLP-Kinds of SentencesNorbert TomasPas encore d'évaluation