Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Comparing Compound and Simple Interest
Transféré par
waseem555Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Comparing Compound and Simple Interest
Transféré par
waseem555Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The University of Trinidad and Tobago
Centre for Education Programmes
Lesson Plan- Mathematics Specialization (Secondary)
DATE: 1st Februray,2018.
CLASS: Form 3
SUBJECT: Mathematics
AGE RANGE: 14-15
NO. PRESENT:
TOPIC: Compound Interest and Simple Interest
DURATION: 35 minutes
OBJECTIVES: CLASSIFICATION
At the end of the lesson, students will be able to:
1) Identify the differences between simple and
compound interest . Cognitive (Understand)
2) Determine the better investment based on the
type of interest offered. Cognitive (Apply)
3) Cooperate with classmates to solve problems. Affective
PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE, SKILLS AND EXPERIENCES:
The students have previously been exposed to percentages, profit and loss, and discounts. The
students have shown a moderate level of proficiency when doing calculations involving
percentages. The students have studied both compound and simple interest as individual topics
but have not done the comparison between the two.
THE LEARNING ENVIRONMENT:
The classroom’s physical arrangement is ideal for group work. The students are seated in pairs
at a table with individual chairs. There is a large whiteboard at the front of the classroom.
However, there is only natural ventilation through the windows in the classroom. Once the
windows are open, the glare on the whiteboard becomes a problem and the teacher must be
mindful of where work is placed. The classroom is located on the second floor of a three-story
building.
RESOURCES: Sentence fragments, Question cards, Question sheets
SET INDUCTION:
The teacher will ask students to recall their knowledge of simple and compound interest.
CONTENT:
TEACHING POINTS TEACHING STRATEGIES LEARNING ACTIVITIES
1) Compound interest Discussion/ Group Students will form groups of 4 and discuss
differs from simple Activity the similarities and differences between
compound and simple interest.
interest in that each year The teacher will ask students to
the interest is added to examine the steps discussed in
the set induction, and to
the principal thus,
determine similarities and
accumulating more differences between simple and
interest. compound interest.
2) To determine which Guided Discovery Students will analyse the question
offer is better between presented.
The teacher will present a
compound and simple comparison question to the
students and will guide the Students will suggest ways to solve.
interest, mathematical students through the steps to
calculations can be determine which investment is Students will follow the steps of the
better. solution.
done.
CLOSURE: Questioning techniques used to engage students in recapping of basic investment
comparison between simple and compound interest.
ASSESSMENT: Formative Assessment- observe as students answer question and perform
group work.
LESSON APPRAISAL: The lesson went well. Unfortunately, some students mixed up simple
interest and compound interest. When I emphasized the difference between the two (simple
interest and compound interest) the students become clearer on the calculations involved. It
was motivating to me as prospective teacher to see how my students understood which was the
better investment, this knowledge will help them in their future investment as young adults.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Draft Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDraft Lesson PlanAyu Alfina Pratiwi AmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Updated Lesson PlansDocument25 pagesUpdated Lesson Plansapi-455080964100% (1)
- Adult LearnersDocument8 pagesAdult LearnersSalaheddine Rahmani100% (1)
- Math Lesson Plan EportfolioDocument7 pagesMath Lesson Plan Eportfolioapi-302731084Pas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Teaching Assignment 2Document16 pagesDesigning Teaching Assignment 2api-357686594Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Activities, Instructional Materials and Tools, and Evaluation InstrumentsDocument3 pagesLearning Activities, Instructional Materials and Tools, and Evaluation InstrumentsAlona MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2api-459019139Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ooo-Graduate School: Skills (Lots) Involve Memorization, While Higher-Order Thinking RequiresDocument2 pagesOoo-Graduate School: Skills (Lots) Involve Memorization, While Higher-Order Thinking RequiresXerries Kaye JumalonPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of TeachingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of TeachingCrystal RedublaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooperative Learning Lesson Plan 542Document6 pagesCooperative Learning Lesson Plan 542api-347023972Pas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional StrategiesDocument6 pagesInstructional StrategiesJeanette MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiated Instruction in The Mixed Ability ClassroomDocument23 pagesDifferentiated Instruction in The Mixed Ability Classroomapi-207112029100% (1)
- Section 03Document136 pagesSection 03Ali razaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10-28-2022 Formal ObservationDocument6 pages10-28-2022 Formal Observationapi-723456721Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ued496 Ashley Speelman Student-Centered Differentiated Instruction Competency ReflectionDocument7 pagesUed496 Ashley Speelman Student-Centered Differentiated Instruction Competency Reflectionapi-440291829Pas encore d'évaluation
- Obe LP Final NaniDocument17 pagesObe LP Final NaniKert IbañezPas encore d'évaluation
- Assgnment Didatics OriginalDocument17 pagesAssgnment Didatics OriginalNooruddin RozbullyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jane Lee Li Cheng 0361547Document14 pagesJane Lee Li Cheng 03615470361547Pas encore d'évaluation
- Orina Episode9 FS1Document5 pagesOrina Episode9 FS1Jiziel OrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pec 7 Week 2Document6 pagesPec 7 Week 2Jason Binondo0% (1)
- Integrative Teaching StrategyDocument4 pagesIntegrative Teaching StrategyJuliet Ardales100% (1)
- Lipio Educ1Document4 pagesLipio Educ1Apple MosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1 - PCK8Document8 pagesTask 1 - PCK8Andrea SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Fs 3Document45 pagesFs 3Joy VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- FS-Eps 10Document3 pagesFS-Eps 10Jhoana LiradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Edtech1 Topic2 Handouts Technologies For LearningDocument7 pagesEdtech1 Topic2 Handouts Technologies For LearningRiena Jane AdriagaPas encore d'évaluation
- SUMLMSDocument7 pagesSUMLMSJAN MARK CHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrected Field Study Observation SheetDocument7 pagesCorrected Field Study Observation SheetEllen Grace Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- INTEGRATIVE TEACHING STRATEGY-special TopicsDocument4 pagesINTEGRATIVE TEACHING STRATEGY-special TopicsJuliet Ardales100% (1)
- Finals FS 2 Reig JastDocument8 pagesFinals FS 2 Reig JastJhastrine ReigPas encore d'évaluation
- FS2 Le5Document2 pagesFS2 Le5Jorebell W. QuiminoPas encore d'évaluation
- GM Ii 2 DLPDocument3 pagesGM Ii 2 DLPMA. CHRISTINA ANDALESPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3Document3 pagesLesson 3api-459019139Pas encore d'évaluation
- FS 2 Experiemcing The Teaching - LearninDocument18 pagesFS 2 Experiemcing The Teaching - LearninJonnah LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Session2 - Differentiation Session 2Document54 pagesSession2 - Differentiation Session 2Demee ResulgaPas encore d'évaluation
- M2 Ep1 Activity Sheet 4Document6 pagesM2 Ep1 Activity Sheet 4RIAMAY APIADOPas encore d'évaluation
- Week10 Research Proposal IlysbDocument26 pagesWeek10 Research Proposal IlysbGeorgina AITRPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Planning Template SNR-FET Mathematics February 2023-1-3Document6 pagesLesson Planning Template SNR-FET Mathematics February 2023-1-3tf9wgz2ysdPas encore d'évaluation
- IIED: ICT in Education Lesson Plan Form: Name of The LessonDocument4 pagesIIED: ICT in Education Lesson Plan Form: Name of The LessonTeachers Without Borders100% (1)
- Spring2022 Field Observation Edu201 Edu202 Packet Word 1Document7 pagesSpring2022 Field Observation Edu201 Edu202 Packet Word 1api-635562745Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flex Time 1Document3 pagesFlex Time 1api-434488792Pas encore d'évaluation
- English For Academic Purposes: Reading & WritingDocument25 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes: Reading & WritingLily ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Remote Field Log Educ 376-78Document12 pagesRemote Field Log Educ 376-78api-534924709Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Meaning of Cooperative Learning ? What Are The Cooperative Learning Techniques ? What Are The Elements of Cooperative Learning?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of Cooperative Learning ? What Are The Cooperative Learning Techniques ? What Are The Elements of Cooperative Learning?safnitaambaritaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Topic 2Document3 pagesMath Topic 2KAETH LAURENCE ORILLA NOTARIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom Modeling - PhippsDocument8 pagesClassroom Modeling - Phippsapi-399906068Pas encore d'évaluation
- I. Essay: Directions: Explain The Following Briefly. Provide Another Sheet For Your Answers. 10 Point Each ItemDocument3 pagesI. Essay: Directions: Explain The Following Briefly. Provide Another Sheet For Your Answers. 10 Point Each ItemLiza Mae JamindenPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Study 1: Learning Episode FS1 9Document9 pagesField Study 1: Learning Episode FS1 9Mikee GallaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 - Accele1 - 2.2.2 RMDocument3 pages2020 - Accele1 - 2.2.2 RMMila MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Field Study 6 Lesson 3Document7 pagesField Study 6 Lesson 3TegebPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Plan 1-5Document21 pagesUnit Plan 1-5api-326620154Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 Decision MakingDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 Decision Makingbabalwamoyake32Pas encore d'évaluation
- FS1. Ep9 Ep16Document52 pagesFS1. Ep9 Ep16Marites Deliarte DipadPas encore d'évaluation
- LP CombinationDocument7 pagesLP CombinationSandy Manligro NainguePas encore d'évaluation
- FS1 Ep10Document8 pagesFS1 Ep10Millet CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Inquiry Based Learning Ilt 4Document13 pagesInquiry Based Learning Ilt 4api-657595957Pas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Centered Teaching: Foundation and CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesLearning Centered Teaching: Foundation and CharacteristicsMaria Cristina Importante100% (1)
- Assignment No: 1: NAME: Hafiz Naveed Shahzad ROLLNO: cb661612 PROGRAM: Bed (1.5year)Document10 pagesAssignment No: 1: NAME: Hafiz Naveed Shahzad ROLLNO: cb661612 PROGRAM: Bed (1.5year)Naveed MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugade, A. - Lesson Plan, TTL2Document4 pagesTugade, A. - Lesson Plan, TTL2Angelbert TugadePas encore d'évaluation
- The Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesD'EverandThe Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Home Work and ExamplesDocument13 pagesForm 4 Home Work and Exampleswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5 Assessment 1.5Document2 pagesForm 5 Assessment 1.5waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 1 InstructionsDocument2 pagesAssessment 1 Instructionswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3-2: Solving Systems of Equations Using EliminationDocument18 pages3-2: Solving Systems of Equations Using Eliminationwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
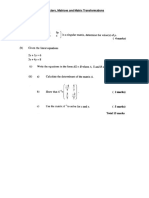
- Matrices Question 1: Form 5: Assessment 1 Vectors, Matrices and Matrix TransformationsDocument5 pagesMatrices Question 1: Form 5: Assessment 1 Vectors, Matrices and Matrix Transformationswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preparing For: RamadanDocument28 pagesPreparing For: Ramadanwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ramadan Ks3 III Y91Document26 pagesRamadan Ks3 III Y91waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civ 2Document5 pagesCiv 2waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- SamplrDocument2 pagesSamplrwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Specification Final Exam StudentDocument1 pageTable of Specification Final Exam Studentwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- FRM One123Document3 pagesFRM One123waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- F4-Revision On Functions and Co-Ordinate GeometryDocument2 pagesF4-Revision On Functions and Co-Ordinate Geometrywaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- AsdsadDocument2 pagesAsdsadwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Case Fatality Rate: Total Confirmed Deaths Due To COVID-19 Per Million PeopleDocument3 pagesCase Fatality Rate: Total Confirmed Deaths Due To COVID-19 Per Million Peoplewaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civ 5Document3 pagesCiv 5waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Canada: Province Compulsory TradesDocument2 pagesCanada: Province Compulsory Tradeswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Signs and Symptoms: Coronavirus Disease 2019Document2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Coronavirus Disease 2019waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apprenticeship After General EducationDocument4 pagesApprenticeship After General Educationwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civ 1Document5 pagesCiv 1waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apprenticeship Systems Worldwide: AustraliaDocument3 pagesApprenticeship Systems Worldwide: Australiawaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apprenticeship: "Apprentice" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument4 pagesApprenticeship: "Apprentice" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, Seewaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Early Life: Mechanical Engineer Inventor Hydraulics Fire HydrantDocument3 pagesEarly Life: Mechanical Engineer Inventor Hydraulics Fire Hydrantwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stuntmen: Fire Extinguishers in A Museum Storeroom, Cut To Display Their Inner WorkingsDocument4 pagesStuntmen: Fire Extinguishers in A Museum Storeroom, Cut To Display Their Inner Workingswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- United Kingdom: Bsen3 RAL 3000 Color Coded Fire ClassesDocument5 pagesUnited Kingdom: Bsen3 RAL 3000 Color Coded Fire Classeswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 FireDocument3 pages2 Firewaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Extinguisher: "Extinguisher" Redirects Here. Extinguisher May Also Refer To ADocument4 pagesFire Extinguisher: "Extinguisher" Redirects Here. Extinguisher May Also Refer To Awaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Protection: Classifying FiresDocument3 pagesFire Protection: Classifying Fireswaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Hydrant: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument7 pagesFire Hydrant: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchwaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Sprinkler: HistoryDocument5 pagesFire Sprinkler: Historywaseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire 5Document6 pagesFire 5waseem555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Half Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsDocument7 pagesHalf Yearly Examination, 2017-18: MathematicsSusanket DuttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng03 Module Co4Document14 pagesEng03 Module Co4Karl Gabriel ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Hackerearth Online Judge: Prepared By: Mohamed AymanDocument21 pagesHackerearth Online Judge: Prepared By: Mohamed AymanPawan NaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 22301 2019 en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 22301 2019 en PDFImam Saleh100% (3)
- RS2 Stress Analysis Verification Manual - Part 1Document166 pagesRS2 Stress Analysis Verification Manual - Part 1Jordana Furman100% (1)
- Writing About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsDocument68 pagesWriting About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsLangers BastasaPas encore d'évaluation
- DOT RequirementsDocument372 pagesDOT RequirementsMuhammadShabbirPas encore d'évaluation
- Panera Bread Case StudyDocument28 pagesPanera Bread Case Studyapi-459978037Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDocument11 pagesSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- P6 - TT2 - Revision Test 2021-2022 Page 1 of 11Document11 pagesP6 - TT2 - Revision Test 2021-2022 Page 1 of 11Nilkanth DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Effective TeachingDocument94 pagesEffective Teaching小曼Pas encore d'évaluation
- C103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratoriesDocument19 pagesC103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratorieshuidhyiuodghPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAditya ShanbhagPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Performance of Senior High School Students 4Ps Beneficiaries in VNHSDocument19 pagesAcademic Performance of Senior High School Students 4Ps Beneficiaries in VNHSkathlen mae marollanoPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1 Viscous Fluid Flow Part 1Document29 pagesCH 1 Viscous Fluid Flow Part 1Ammar WahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Swiss Army Triplet 1Document2 pagesSwiss Army Triplet 1johnpwayPas encore d'évaluation
- All Nobel Prizes in LiteratureDocument16 pagesAll Nobel Prizes in LiteratureMohsin IftikharPas encore d'évaluation
- Dress Code19sepDocument36 pagesDress Code19sepapi-100323454Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesFinal Lesson Planapi-510713019Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson PlanIsaac-elmar Agtarap74% (23)
- ENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014Document12 pagesENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014TheColonel999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Document12 pagesDesign of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Pamela Joanne Falo AndradePas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianDocument6 pagesTechnical Rockwell Automation FactoryTalk HistorianAmit MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ishrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19Document4 pagesIshrana Studenata I Nastavnika Visoke Škole U Subotici Tokom Pandemije COVID-19DejanPas encore d'évaluation
- Periodic Table Lab AnswersDocument3 pagesPeriodic Table Lab AnswersIdan LevyPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoshana Bulka PragmaticaDocument17 pagesShoshana Bulka PragmaticaJessica JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chain: SRB Series (With Insulation Grip)Document1 pageChain: SRB Series (With Insulation Grip)shankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Behavior Intervention MenuDocument56 pagesBehavior Intervention Menuapi-479527084100% (4)
- Chapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Document27 pagesChapter 6 Strategy Analysis and Choice: Strategic Management: A Competitive Advantage Approach, 16e (David)Masum ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- GST RATE LIST - pdf-3Document6 pagesGST RATE LIST - pdf-3Niteesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation