Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)
Transféré par
Pangangan NHSTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)
Transféré par
Pangangan NHSDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
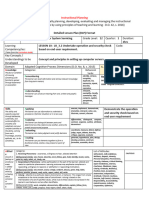
Instructional Plan [iPlan]
[With inclusion of the provision of DepEd Order No. 8, s. 2015]
Learning Area: TLE Computer Systems Servicing (CHS) NCII Grade Level: 10
iPlan No.: 9 Quarter: 2 Duration:
Learning Demonstrate an understanding of concepts and underlying Code:
Competency principles in applying standard in computer systems TLE_IACSS9-
/ies: servicing 12AQS-Ia-1
[Taken from Demonstrates skills in configuring computer systems and
the
networks as prescribed by TESDA Training Regulations.
Curriculum
Guide]
Key Apply quality standards in computer systems servicing
Concepts/
Understandi
ngs to be
Developed
Learning Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions
Objectives
Knowledg Rememberin The learner can Obtain work instruction in
g recall information
e and retrieve relevant accordance with standard
The factor or knowledge from operating procedures;
condition of long-term memory:
knowing identify, retrieve,
Identify the received
something with recognize, duplicate, materials against workplace
familiarity list, memorize, standards and specifications
gained through repeat, describe,
experience or reproduce and isolate faulty materials
association related to work
Understandi The learner can
ng construct meaning
from oral, written
and graphic
messages: interpret,
exemplify, classify,
summarize, infer,
compare, explain,
paraphrase, discuss
Skills Applying The learner can use
The ability and information to
capacity undertake a
acquired procedure in familiar
through situations or in a
deliberate, way: execute,
systematic, and implement,
sustained effort demonstrate,
to smoothly and dramatize, interpret,
adaptively carry solve, use, illustrate,
out complex convert, discover
activities or..
the ability, Analyzing The learner can
coming from distinguish between
one’s parts and determine
knowledge, how they relate to
practice, one another, and the
aptitude, etc., to overall structure and
purpose:
do something differentiate,
distinguish,
compare, contrast,
organize, outline,
attribute,
deconstruct
Evaluating The learner can Detect any identified causes
make judgments
and justify decisions: to the supervisor concerned
coordinate, in accordance with workplace
measure, detect,
defend, judge,
procedures.
argue, debate,
describe, critique,
appraise, evaluate
Creating The learner can put Create report and replace
elements together to
form a functional faulty materials in
whole, create a new accordance with workplace
product or point of procedures.
view: generate,
hypothesize, plan,
design, develop,
produce, construct,
formulate,
assemble, devise
Attitude A settled way of thinking or feeling Impart ideas on how to check
about someone or something, received materials against
typically one that is reflected in a
person’s behavior: workplace standards.
Values [RA 849]
· A learner Maka-Diyos
principles or
standards of
behavior; Maka-tao
one’s
judgment of Makakalikasan
what is
important in
life. Makabansa
· Go beyond
learner’s life
on earth,
include more
than wealth
and fame and
would affect
the eternal
destiny of
millions
Resources Listing of all Book, computer system unit, projector, laptop, internet,
resources
Needed needed photocopy etc.
METHODOLOGY
Introductory Activity True or False. Write True or False. Refer on page 11
This part introduces the lesson 1. Working while the computer is on is safe.
content. Although at times optional, it
is usually included to serve as a 2. Do not work alone so that there is someone to help you.
warm-up activity to give the learners 3. Leaving your tools after working is fine.
zest for the incoming lesson and an
idea about what it to follow. One
4. Use excessive force while in installing hardware parts is
principle in learning is that learning always advisable.
occurs when it is conducted in a
pleasurable and comfortable 5. Holding the components on the edges is okay.
atmosphere.
Activity Identify and Isolate Errors.
This is an interactive strategy to elicit A. Quantity of work (untimely completion, limited production)
learner’s prior learning experience. It
serves as springboard for new B. Quality of work (failure to meet quality standards)
learning. It illustrates the principle C. Inappropriate behavior
that learning starts where the
learners are. Carefully structured
D. Resistance to change
activities such as individual or group E. Inappropriate interpersonal relations
assessment, dyadic or triadic F. Inappropriate physical behavior
interactions, puzzles, simulations or
role-play, cybernetics exercise,
gallery walk and the like may be
created. Clear instructions should be
considered in this part of the lesson.
Analysis Group Activity. Analyze safe working procedures:
Essential questions are included to · Teacher and students’ tasks to undertake
serve as a guide for the teacher in
clarifying key understandings about · Tasks that undertake risks
the topic at hand. Critical points are · Equipment to be used in the tasks
organized to structure the discussion · Control measures formulated
allowing the learners to maximize
instructions and sharing of ideas and · Training or qualification needed to undertake the tasks
opinions about expected issues. · Personal protective equipment to be worn
Affective questions are included to
elicit the feelings of the learners · Action to be undertaken to address safety issues
about the activity or the topic. The
last questions or points taken should
lead the learners to understand the
new concepts or skills that are to be
presented in the next part of the
lesson.
Abstraction Sum-up Discussion. Apply quality standards
This outlines the key concepts,
important skills that should be
enhanced, and the proper attitude
Quality Improvement can be distinguished from Quality Control in
that should be emphasized. This is that Quality Improvement is the purposeful change of a process
organized as a lecturette that to improve the reliability of achieving an outcome.
summarizes the learning emphasized
from the activity, analysis and new
inputs in this part of the lesson.
Application Flow Chart. Cause and Effect Diagrams
This part is structured to ensure the Create a cause and effect diagram. Please refer on page 27.
commitment of the learners to do
something to apply their new learning
in their own environment.
Assessment Group Performance. Please refer to Performance
For the Teacher to:
1. Assesses whether learning
Sheet for Research and Investigate. Please read
objectives have been met for a directions in page 41
specified duration
2. Remediate and/or enrich with
appropriate strategies as needed
3. Evaluate whether learning
intentions and success criteria
have been met
[Reminder: Formative Assessment
may be given before, during or after
the lesson.]
Assignment Reinforcin
Note: Fill-in any of g/
the four purposes strengthen
ing the
day’s
lesson
Enhancing
/ inspiring
the day’
lesson
Preparing Make a research on Computer Operations on page 43
for the
new
lesson
Concluding Closing Quote: The teacher reads this quote.
Activity
This is usually a § “The point is that being able to demonstrate ‘due diligence’ is not
brief but effective
closing activity
about having a thing (a policy or a system or a heap of procedures
such as a strong and checklists) it is about doing a thing” – Max Geyer
quotation, a short http://www.safetyrisk.net/famous-safety-quotes/
song, an anecdote,
parable or a letter
that inspires the
learners to do
something to
practice their new
learning.
Prepared by:
School: DALAGUETE NATIONAL
Name: GEORGE P. LUMAYAG HIGH SCHOOL
Position/Designation: SST-3, TM level 1 Division: CEBU PROVINCE
Contact Number: 09213964825 Address: Poblacion, Dalaguete, Cebu
Email Address: Phone Number: 4848486
george.lumayag@deped.gov.ph
Website: www.georgelumayag.com Department Website: www.dnhs-
eclassroom.weebly.com
Bibliography
Appendices: [attach all materials that will be used]
1. Activity Sheet…
2. Formative Assessment…
3. Answer key…
4. Handouts…
5. PowerPoint Presentation…
6. Others…
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasD'EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasPas encore d'évaluation
- CSS Lesson Plan Q1Document6 pagesCSS Lesson Plan Q1Kuyawan kulbaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeDocument9 pagesLearning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeJuvyGonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015jayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015jayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts and Principles in Performing Computer OperationsDocument4 pagesConcepts and Principles in Performing Computer Operationsjayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts and Principles in Performing Computer OperationsDocument3 pagesConcepts and Principles in Performing Computer Operationsjayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.1 Establish Information Requirements For Internet SearchDocument3 pages2.5.1 Establish Information Requirements For Internet Searchjayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 15Document3 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 15Måřïä Ļà ĞŕëàthaPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP FBS 4Document3 pagesDLP FBS 4Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq2 LC7Document3 pagesMilq2 LC7Michael PantaleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 13Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 13Glycelle Urlanda MapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP FBS 5Document3 pagesDLP FBS 5Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq4 LC7Document2 pagesMilq4 LC7Maribel MarmitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document4 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Anne Atienza GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : Computer Systems Servicing NC Ii 8 I 2 HrsDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : Computer Systems Servicing NC Ii 8 I 2 HrsSarah Canillo RomaratePas encore d'évaluation
- EN1112RWS IVhj 13.1Document12 pagesEN1112RWS IVhj 13.1Muzika Hamlette MalonPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS - DLP-Q3-Week-1-Day-3Document4 pagesGRADE 9 MATHEMATICS - DLP-Q3-Week-1-Day-3macgigaonlinestorePas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan)Document6 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan)Earl Cris RiggsPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusionof The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document3 pagesWith Inclusionof The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Gerald E BaculnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq1 LC2Document4 pagesMilq1 LC2Paron MarPas encore d'évaluation
- Perform Testing DocumentationDocument5 pagesPerform Testing DocumentationGerald E Baculna100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Plan CSS 2Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan CSS 2kenneth llorentePas encore d'évaluation
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 12Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 12Glycelle Urlanda MapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts CodeDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts Codejayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts CodeDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts Codejayson reyes100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan: (Taken From The Curriculum Guide)Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan: (Taken From The Curriculum Guide)raziel yuragPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq2 LC7Document3 pagesMilq2 LC7renzmarion.penalesPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS - DLP-Q3-Week-1-Day-1Document3 pagesGRADE 9 MATHEMATICS - DLP-Q3-Week-1-Day-1macgigaonlinestorePas encore d'évaluation
- Milq2 LC9Document5 pagesMilq2 LC9renzmarion.penalesPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Wil-Ly de la CernaPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document3 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)raziel yuragPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan BlankDocument4 pagesInstructional Plan BlankRene L. LofrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq1 LC2Document4 pagesMilq1 LC2Jennifer AlbaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts CodeDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts Codejayson reyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Media and Literacy DLP Q1 Week1 Day 2Document3 pagesMedia and Literacy DLP Q1 Week1 Day 2macgigaonlinestorePas encore d'évaluation
- OC 4 Distinguishes The Unique Features of One Communication Process From The OtherDocument3 pagesOC 4 Distinguishes The Unique Features of One Communication Process From The OtherZeen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.3.2 DLP BenitezDocument5 pages10.3.2 DLP BenitezGlad Norman LimoconPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015marjunampoPas encore d'évaluation
- With Inclusionof The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document3 pagesWith Inclusionof The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- DLP FBS 2Document3 pagesDLP FBS 2Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Understanding SDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Understanding SAnalie Imbing CabanlitPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 08Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 08Glycelle Urlanda MapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- (With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, 2016) Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument5 pages(With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015 and D.O. 42, 2016) Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatJoong SeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Media and Literacy DLP Q1 Week2 Day 3Document3 pagesMedia and Literacy DLP Q1 Week2 Day 3macgigaonlinestorePas encore d'évaluation
- DLP Nutri Mascot #30 Q1Document3 pagesDLP Nutri Mascot #30 Q1Christine Rose Villanueva VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- IP of Subtraction of IntegersDocument4 pagesIP of Subtraction of IntegersAnonymous 45yUH2ONcTPas encore d'évaluation
- Milq1 LC2Document4 pagesMilq1 LC2DANNAH FAYE ARDIENTEPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document3 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Suzette AnubPas encore d'évaluation
- Science8 Q1 W4 D3 WhenIsWorkDoneDocument3 pagesScience8 Q1 W4 D3 WhenIsWorkDoneLenlen NamocPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 83Document1 pageActivity Sheet 83Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 85bDocument2 pagesActivity Sheet 85bPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Reaction Rates: ExercisesDocument1 pageFactors Affecting Reaction Rates: ExercisesPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 85cDocument2 pagesActivity Sheet 85cPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Notes: Carbohydrates: Dextrose) and FructoseDocument3 pagesConcept Notes: Carbohydrates: Dextrose) and FructosePangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 84Document1 pageActivity Sheet 84Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 10Document13 pagesApEcon Module 10Mary Ann PaladPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 79Document1 pageActivity Sheet 79Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- What's in A Reaction: Pangangan National High School Talisay, Calape, BoholDocument2 pagesWhat's in A Reaction: Pangangan National High School Talisay, Calape, BoholPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing Act: Steps in Balancing EquationsDocument1 pageBalancing Act: Steps in Balancing EquationsPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Sheet 81Document1 pageActivity Sheet 81Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Business Environment 666Document12 pagesApplied Economics: Business Environment 666RUBEN LEYBA100% (2)
- Activity Sheet 78Document1 pageActivity Sheet 78Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Cost-Effective AnalysisDocument11 pagesApplied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Cost-Effective AnalysisPangangan NHS100% (1)
- ApEcon Module 13Document12 pagesApEcon Module 13Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Application of Cost-Benefit AnalysisDocument12 pagesApplied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Application of Cost-Benefit AnalysisPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 11Document13 pagesApEcon Module 11Pangangan NHS100% (1)
- ApEcon Module 12Document13 pagesApEcon Module 12Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 14Document12 pagesApEcon Module 14Pangangan NHS100% (1)
- Applied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Cost-Benefit AnalysisDocument12 pagesApplied Economics: Minimizing and Maximizing Business's Impact: Cost-Benefit AnalysisPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 7Document13 pagesApEcon Module 7Mary Ann PaladPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 8Document12 pagesApEcon Module 8Mary Ann PaladPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 4Document12 pagesApEcon Module 4Yen SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- ApEcon Module 9Document12 pagesApEcon Module 9Pangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Impact of Business On The Community: ExternalitiesDocument13 pagesApplied Economics: Impact of Business On The Community: ExternalitiesPangangan NHS100% (1)
- Applied Economics: Porter's Five Forces AnalysisDocument12 pagesApplied Economics: Porter's Five Forces AnalysisPangangan NHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Economics: Retail Trade IndustryDocument12 pagesApplied Economics: Retail Trade IndustryMary Ann Palad100% (1)
- Summative Test 1Document3 pagesSummative Test 1Pangangan NHS100% (2)
- ApEcon Module 6Document11 pagesApEcon Module 6Mary Ann Palad100% (1)
- Applied Economics: SWOT Analysis 666Document12 pagesApplied Economics: SWOT Analysis 666Yen SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan GameDocument2 pagesLesson Plan GameReynaldo CuestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Who We Are LKG PlannerDocument25 pagesWho We Are LKG PlannerSushmita100% (1)
- Madayag Laarni Grace F. Worksheet No. 1Document1 pageMadayag Laarni Grace F. Worksheet No. 1Laarni Grace MadayagPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson Planapi-289845800Pas encore d'évaluation
- Five Major Philosophies of EducationDocument2 pagesFive Major Philosophies of Educationeunice nikki tavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing The Guidance ProgramDocument18 pagesDesigning The Guidance ProgramjessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Lesson Planning: Guidance Notes For ITE Trainers/mentors Lesson PlanningDocument5 pagesGeography Lesson Planning: Guidance Notes For ITE Trainers/mentors Lesson PlanningJACOB CHAMBALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Education ReflectionDocument3 pagesSpecial Education Reflectionapi-304926018100% (1)
- Learning Disorders 101: Jennifer Coloma, PHD Licensed Psychologist Ann Lyke, Med Educational SpecialistDocument26 pagesLearning Disorders 101: Jennifer Coloma, PHD Licensed Psychologist Ann Lyke, Med Educational SpecialistDrNihilismPas encore d'évaluation
- Deadline of Submission Will Be On FRIDAY, September 18,: ETHICS 101 Who Chose The OFFLINE ModalityDocument4 pagesDeadline of Submission Will Be On FRIDAY, September 18,: ETHICS 101 Who Chose The OFFLINE ModalityJonalyn OmerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Adapting Basketball Instruction: Including Students With Disabilities in Physical EducationDocument4 pagesAdapting Basketball Instruction: Including Students With Disabilities in Physical EducationfirdiniePas encore d'évaluation
- VE021 Personal Goal Setting WorksheetDocument3 pagesVE021 Personal Goal Setting WorksheetJoy Danielle LlandinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview For Teachers ApplicantDocument5 pagesInterview For Teachers ApplicantGail MagPas encore d'évaluation
- There Are 5 Questions. Answer All QuestionsDocument4 pagesThere Are 5 Questions. Answer All QuestionsBrian GnorldanPas encore d'évaluation
- Excellence in Coaching The Industry Guide PDFDocument2 pagesExcellence in Coaching The Industry Guide PDFSarah0% (1)
- Health 4 Quarter 3Document8 pagesHealth 4 Quarter 3Lobmosgam HaileyhanaelainePas encore d'évaluation
- Coping Skills ToolkitDocument75 pagesCoping Skills ToolkitintanlqPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd QUARTER TOS RWSDocument2 pages3rd QUARTER TOS RWSAngelica OrbizoPas encore d'évaluation
- Passion Based LearningDocument4 pagesPassion Based LearningFor SocialPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5Document2 pagesLesson 5api-537946229Pas encore d'évaluation
- FULLTEXT01Document37 pagesFULLTEXT01Ömür BilginPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio Spreadsheet Aitsl StandardsDocument3 pagesPortfolio Spreadsheet Aitsl Standardsapi-653318448Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement: Itand Ang Gitas-On Sa Mga KahoyDocument4 pagesMeasurement: Itand Ang Gitas-On Sa Mga KahoyJoevelyn Krisma Cubian0% (1)
- Input Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearDocument21 pagesInput Data Sheet For E-Class Record: Region Division School Name School Id School YearBenedict LumaguePas encore d'évaluation
- Apakah Penyelesiaan Kepada Kenaikan Harga Minyak?Dalam Konteks Kehidupan Seharian...Document18 pagesApakah Penyelesiaan Kepada Kenaikan Harga Minyak?Dalam Konteks Kehidupan Seharian...Beman EasyPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Relationship Between SAT Scores and Family Income of The Test Takers Around The World?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Relationship Between SAT Scores and Family Income of The Test Takers Around The World?ajaywadhwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Background of The StudyDocument12 pagesBackground of The StudyChloe Mae BelvegarPas encore d'évaluation
- Project 2Document100 pagesProject 2Ne'am Mohamed AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Strong Interest InventoryDocument14 pagesStrong Interest Inventoryapi-298977804Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre - Service Teacher Practicum Grading SheetDocument2 pagesPre - Service Teacher Practicum Grading SheetMelchor E. BalteroPas encore d'évaluation