Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Evaporators: in Evaporation Physical and Chemical Properties of The Solution Being Concentrated
Transféré par
digeca0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues19 pagesThis document discusses different types of evaporators used in evaporation processes. It describes open kettle evaporators, horizontal and vertical natural circulation evaporators, falling film evaporators, and forced circulation evaporators. It also covers the effects of material properties like concentration, solubility, temperature sensitivity, and foaming on evaporation. Multiple effect evaporator configurations like forward feed, backward feed, parallel feed, and mixed feed are summarized. Key processing variables like temperature, pressure, and steam pressure that affect evaporator size and cost are highlighted.
Description originale:
Evaporators
Titre original
Evaporators
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document discusses different types of evaporators used in evaporation processes. It describes open kettle evaporators, horizontal and vertical natural circulation evaporators, falling film evaporators, and forced circulation evaporators. It also covers the effects of material properties like concentration, solubility, temperature sensitivity, and foaming on evaporation. Multiple effect evaporator configurations like forward feed, backward feed, parallel feed, and mixed feed are summarized. Key processing variables like temperature, pressure, and steam pressure that affect evaporator size and cost are highlighted.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
22 vues19 pagesEvaporators: in Evaporation Physical and Chemical Properties of The Solution Being Concentrated
Transféré par
digecaThis document discusses different types of evaporators used in evaporation processes. It describes open kettle evaporators, horizontal and vertical natural circulation evaporators, falling film evaporators, and forced circulation evaporators. It also covers the effects of material properties like concentration, solubility, temperature sensitivity, and foaming on evaporation. Multiple effect evaporator configurations like forward feed, backward feed, parallel feed, and mixed feed are summarized. Key processing variables like temperature, pressure, and steam pressure that affect evaporator size and cost are highlighted.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 19
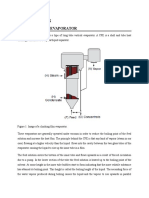
EVAPORATORS
IN EVAPORATION PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL
PROPERTIES OF THE SOLUTION BEING
CONCENTRATED
Properties on which the evaporation
greatly depends
Concentration of the liquid : by time liquid becomes concentrated .heat
transfer coefficient becomes adequately low so the circulation or the turbulence
must be there to prevent the coefficient becomes sufficiently low
Solubility: by the variation in temperature effects the solubility of the
solution either .condensation of the liquid from cold liquid causes
crystallisation of the substance .effects the evaporation
Temperature sensitivity of the material : some material degrade due to prolong
heating
Foaming and frothing: foam and froth forms during boiling accompanies the
vapour coming out of the evaporator due to which entrainment loss occurs
Pressure and temperature :B.P. of the solution is related to pressure of the
system. The higher the operating pressure of the evaporator the higher the
temp at boiling . By increase in the concentration temperature of boiling may
rise
Scale deposition and material of construction : by these factors heat transfer
coefficient decreases causes the decrease in heat transfer.
Types of evaporators
1. Open kettle or pan
2. Horizontal type natural circular evaporation
3. Vertical type natural circulation evaporation
4. Long tube vertical type evaporator
5. Falling film type evaporator
6. Forced circulation type evaporator
7. Agitated film evaporator
8. Open pan solar evaporator
Open kettle or pan evaporator
Cheap and simple
Heat economy is poor
Paddles and scrappers
are used for agitation
Heat is supplied by
condensation of stream
Horizontal type natural circulation
evaporator
Similar heating tubes such in
heat exchangers are used
Vapour leaves the liquid
surface often goes through de
entrainment device such as
baffles are used to prevent
carryover of liq. Droplets
relatively cheap then the other
higher evaporator devices
Used for non viscous liquid
with heat transfer coefficient
(since circulation is poor )
Liquids that do not deposit on
the surfaces
Stream enters inside the tube
Not used for foamy liquids
Vertical type natural circulation
evaporator
Types are basket type(liquid
inside ) and standard
type(liquid outside )
Velocity :1-3 fps
Boiling increases de
Boiling increases density
liquid rises in the tube by
natural circulation and flows
downward through a large
central open space or
downcomer
Natural circulation increases
heat transfer coefficient
Not for viscous liquid
Also called as short tube
evaporator
long tube vertical type evaporator or
kestner evaporator
Heat transfer on stream side is
very high as compare to
evaporating liquid side so high
liquid velocities are desirable
Liquid run inside the tube
Length of 12-20 ft.
3-10 mm tubes
Formation of vapours inside the
tube causing pumping action
which gives quite high liquid
velocities
Not re circulated (contact time is
low )
Can be adapt for foamy liquids
Not for scaling and not for
liquids of high viscosity
Falling film type evaporator
Liquid is fed from top and
flow down as a thin film
Vapour liquid separation
usually takes place at the
bottom
Used widely for
concentrating heat
sensitive materials such as
orange juice and other fruit
juice
Holdup time is very small
(5-10)
High heat transfer
coefficient (due to high
velocities )
Forced circulation type evaporator
We use pump in film type
evaporator
Increase heat transfer coefficient
Useful for viscous fluid
External heating provide more
ease to cleaning to tubes more
complicated piping is used
For viscous we use positive
pumps and for colloidal we use
low power pumps
Heating element is placed at the
lower level to avoid boiling on
heating surface .this reduces the
rate of deposition of solids
Agitated film evaporator
Main resistance of the heat
transfer is on evaporator side
Heat transfer coefficient and
turbulence is increased by
mechanical agitation of this
liquid film
Modifying falling film evaporator
with a single large jacketed tube
containing internal agitator
Used for viscous fluids ,high
sensitive materials like rubber,
latex, gelatine, antibiotics and
fruit
Heat transfer coefficient
increases
High cost
Small capacity
Open pan solar evaporator
Low scale evaporation
Takes longer time
Cheap
Solar energy is used to
evaporate the water from
the solution
Method of operation of evaporation
Single effect evaporator
Forward feed multiple effect evaporator
Backward feed multiple effect evaporator
Parallel feed multiple effect evaporator
Mixed feed multiple effect evaporator
Single effect evaporator
Required capacity of operation is relatively small
Forward feed multiple effect evaporator
Feed should be near the B.P. of
the solution at the pressure in the
1st effect
Previous unit vapour serves as a
heating medium for the next
effect
Here latent of the vapour can be
reused and recovered again
Uses when feed is hot or when
the concentration product might
be damaged at high temperature
B.P decreases from effect to effect
Pressure is 1 atm at 1st effect and
under vaccum in other effects
Backward feed multiple effect evaporator
Uses when fresh feed is
cold
Flows from low to high
pressure for this to happen
we apply pumps at certain
places
Temperature increases
from effect to effect
Used when concentrated
product is highly viscous
High temperature and low
viscosity gives high heat
transfer coefficient
Parallel multiple effect evaporator
Adding and withdrawal
of concentrated product
from each effect
Feed almost saturated
and solid crystals are the
product
Eg- evaporation of brine
to make salt
Mixed multiple effect evaporator
When feed moves
forward with fresh feed is
entering at the 2nd or 3rd
effect k/a mixed type
Used in solutions having
considerable change in
viscosity with
temperature over
concentration range
Effects of processing variables on
evaporator
Effect of temperature : feed must be at temp greater or
equal to the b.p of the solution . Preheating the feed can
reduce the size of evaporator heat transfer area
Effect of pressure : a pressure of 101.32 kpa is used in the
vapour space which gives the b.p of the feed .if the rise in
temperature increases .means large difference in
temperature is desirable heating surface area and the
cost of the evaporator decreases .if pressure decreases
under vaccum condenser and pump are used
Effect of stream pressure :with increase in pressure of
the saturated stream difference in b.p of increases giving
small size and hence cost decreases
Thank you
MADE BY: SHIKHA THAPA
COLLEGE NAME :INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
GURU GHASI DAS CENTRAL UNIVERSITY
STUDENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
S E M E S T E R : 5 TH
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Ethylene Quench Water Tower Rev WebDocument27 pagesENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Ethylene Quench Water Tower Rev WebaegosmithPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Assemblies TOCDocument9 pages2020 Assemblies TOCTobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesD'EverandProcess Engineering: Facts, Fiction and FablesÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Chapter 2 Evaporation PDFDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Evaporation PDFMaribel Moreno0% (2)
- Is 6533 Part-2 Design of Construction of Steel Chimney-CodDocument23 pagesIs 6533 Part-2 Design of Construction of Steel Chimney-CodRiaz M IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of EvaporatorsDocument12 pagesTypes of Evaporatorsapi-377437388% (8)
- 4KKKR3723 Part Iv-20200217084742 PDFDocument56 pages4KKKR3723 Part Iv-20200217084742 PDFPrince Yogadevan VijayanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Design Temperature of Flare SystemsDocument5 pagesThe Design Temperature of Flare Systemswiboonwi50% (2)
- Evaporation & Evaporators: Prepared By:-Kuldeep BhattDocument26 pagesEvaporation & Evaporators: Prepared By:-Kuldeep BhattKuldeep BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator SDocument23 pagesEvaporator SMehwish NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- NPT15 Medium & High VoltageDocument23 pagesNPT15 Medium & High VoltageElver Mesa100% (1)
- Climbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsDocument12 pagesClimbing Film Evaporation Data (2016) - All GroupsJuwon Jeremiah MakuPas encore d'évaluation
- AUTODYN - Chapter 5 - MM - Euler - Solver PDFDocument13 pagesAUTODYN - Chapter 5 - MM - Euler - Solver PDFFabiano OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- EvaporatorDocument7 pagesEvaporatormohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer Equipment EvaporatorDocument57 pagesHeat Transfer Equipment EvaporatorAsadulhaq Ali HamidiPas encore d'évaluation
- EvaporationDocument37 pagesEvaporationVimal KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Forced Circulation EvaporatorDocument8 pagesForced Circulation EvaporatorNIDHARSHANA S100% (2)
- PTT205 Heat and Mass Transfer: EvaporatorDocument43 pagesPTT205 Heat and Mass Transfer: Evaporatorkkk100% (1)
- VRF Air-Conditioner: Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument55 pagesVRF Air-Conditioner: Installation, Operation and Maintenance ManualArshad MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Enginnering WorkshopDocument6 pagesPlant Enginnering WorkshopdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect - 21 Evoporation Lecture 1 of 3Document56 pagesLect - 21 Evoporation Lecture 1 of 3Vivaan Sharma100% (1)
- Norsok ST 2001Document131 pagesNorsok ST 2001mamounsdPas encore d'évaluation
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument14 pagesPrestressed ConcretekomalPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Report: Design A Staggered Depressurization Sequence For Flare SystemsDocument4 pagesSpecial Report: Design A Staggered Depressurization Sequence For Flare Systemsdigeca100% (1)
- Double Effect EvaporatorDocument10 pagesDouble Effect Evaporatorgeek3112100% (7)
- Evaporator: How An Evaporator WorksDocument3 pagesEvaporator: How An Evaporator WorksJames VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator and Its TypesDocument22 pagesEvaporator and Its TypesIrfan ShafiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation and DehydrationDocument23 pagesEvaporation and DehydrationRogelyn JosolPas encore d'évaluation
- Energetics: Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft PulpingDocument6 pagesEnergetics: Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft Pulping박우진Pas encore d'évaluation
- Energetics: Coffee Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft PulpingDocument6 pagesEnergetics: Coffee Pharmaceutical Enzymes Kraft Pulping박우진Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation 2Document31 pagesEvaporation 2swatmujumdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Shina Gautam Associate Professor, Chemical Engineering, Shroff S. R. Rotary Institute of Chemical TechnologyDocument45 pagesDr. Shina Gautam Associate Professor, Chemical Engineering, Shroff S. R. Rotary Institute of Chemical TechnologyJITENDRA CARPENTERPas encore d'évaluation
- 8-Evaporation-Dr FakharDocument24 pages8-Evaporation-Dr Fakharawais khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21: Evaporation - Principles, Types of EvaporatorsDocument7 pagesChapter 21: Evaporation - Principles, Types of EvaporatorssdfaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation: DKK3433 Unit Operation Dr. Syed Mohd Saufi 2012/2013-IDocument43 pagesEvaporation: DKK3433 Unit Operation Dr. Syed Mohd Saufi 2012/2013-IAzmiHafifiPas encore d'évaluation
- EVAPORATORDocument8 pagesEVAPORATORyilma wendayehuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3. EvaporationDocument15 pagesUnit 3. EvaporationThabo ThaboPas encore d'évaluation
- KKKR3723 20182019 Utility Part 4 - EvaporationDocument56 pagesKKKR3723 20182019 Utility Part 4 - EvaporationPutriPas encore d'évaluation
- EvaporatorDocument20 pagesEvaporatorOscar Ballarta50% (2)
- UntitledDocument17 pagesUntitledSanjay v.r v.rPas encore d'évaluation
- Energetics: Solvents Desalination Zero Liquid Discharge Drinking WaterDocument6 pagesEnergetics: Solvents Desalination Zero Liquid Discharge Drinking Water박우진Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evapn NotesDocument12 pagesEvapn NotesShubham bangarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Objective of EvaporationDocument8 pages2.1 Objective of EvaporationwakPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared By: Hussein Maytham Saied: EvaporationDocument12 pagesPrepared By: Hussein Maytham Saied: Evaporationحسين ميثم سعيد مهديPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator HistoryDocument7 pagesEvaporator History박우진Pas encore d'évaluation
- Paper No.: 04 Paper Title: Unit Operations in Food Processing Module-14:EvaporationDocument9 pagesPaper No.: 04 Paper Title: Unit Operations in Food Processing Module-14:EvaporationNezlyn D'SouzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper No.: 04 Paper Title: Unit Operations in Food Processing Module-14:EvaporationDocument9 pagesPaper No.: 04 Paper Title: Unit Operations in Food Processing Module-14:EvaporationKanchanPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator AccessoriesDocument21 pagesEvaporator AccessoriesgrittyptPas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum Evaporators Mateo Torres.Document11 pagesVacuum Evaporators Mateo Torres.Jakson Mateo Torres GuerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator HistoryDocument7 pagesEvaporator History박우진Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sch1210 Heat Transfer Unit V Ii/Iv EvaporationDocument19 pagesSch1210 Heat Transfer Unit V Ii/Iv EvaporationLearning AspirationPas encore d'évaluation
- Keuntungan Dan Operasi EvaporatorDocument9 pagesKeuntungan Dan Operasi EvaporatorRavina Fatma Nazaretha100% (1)
- Evaporator: CH250 - Heat TransferDocument21 pagesEvaporator: CH250 - Heat TransferManas AkashPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Evaporation ToolsDocument41 pagesOperation Evaporation Toolsati atun chasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Stream FilterDocument5 pagesSide Stream FilterThạch ThayPas encore d'évaluation
- CPI Lab ReportDocument5 pagesCPI Lab ReportFurqan MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Evaporators: LTV Rising-Film LTV Falling-Film Forced-Circulation EvaporatorsDocument12 pagesTypes of Evaporators: LTV Rising-Film LTV Falling-Film Forced-Circulation EvaporatorsAldair Vergel RangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Is Used Over and Over Again and Getting The Evaporation in The Second and Subsequent Effects For NothingDocument25 pagesHeat Is Used Over and Over Again and Getting The Evaporation in The Second and Subsequent Effects For NothingSanjay v.r v.rPas encore d'évaluation
- FFEDocument8 pagesFFEsarthak vyavharePas encore d'évaluation
- EvaporationDocument36 pagesEvaporationPhương linh TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation 2021 22Document69 pagesEvaporation 2021 22xnzrjp55tsPas encore d'évaluation
- EvaporationDocument17 pagesEvaporationGingerQAPas encore d'évaluation
- FPE20306-2019 - Chapter 3 - Evaporation - TheoryDocument18 pagesFPE20306-2019 - Chapter 3 - Evaporation - TheoryAntonio MoncayoPas encore d'évaluation
- PERFORMANCE TEST ON VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATION SYSTEM USING R290 & R134a MIXTUREDocument7 pagesPERFORMANCE TEST ON VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATION SYSTEM USING R290 & R134a MIXTUREJASH MATHEWPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator: 4.2.2 Natural Circulation and Circulation RatioDocument1 pageEvaporator: 4.2.2 Natural Circulation and Circulation RatioRafika Erniza PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentSania SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System: Ubmited by Sourav Mondal B. E. Power Engg. Jadavpur UniversityDocument14 pagesReport On Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System: Ubmited by Sourav Mondal B. E. Power Engg. Jadavpur UniversitysouravPas encore d'évaluation
- White Blue Modern Geometric Annual ReportDocument7 pagesWhite Blue Modern Geometric Annual ReportZaynab JasimPas encore d'évaluation
- Evap BasicsDocument3 pagesEvap BasicsrahulbhavePas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporators PDFDocument25 pagesEvaporators PDFMunibah AhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporation and Other ProcessesDocument5 pagesEvaporation and Other Processeslaila khanPas encore d'évaluation
- EIA Country Analysis BriefsDocument7 pagesEIA Country Analysis BriefsdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation Techniques: ConferenceseriesDocument1 pageSeparation Techniques: ConferenceseriesdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- United States Patent (10) Patent N6. US 8,117,852 B2Document7 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent N6. US 8,117,852 B2digecaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pluto System: Initial Results From Its Exploration by New HorizonsDocument10 pagesThe Pluto System: Initial Results From Its Exploration by New HorizonsdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Obtain Free United States Published Engineering Documents PDFDocument1 pageHow To Obtain Free United States Published Engineering Documents PDFdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Settling Sludge in Crude TankDocument2 pagesSettling Sludge in Crude TankdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pluto System: Initial Results From Its Exploration by New HorizonsDocument10 pagesThe Pluto System: Initial Results From Its Exploration by New HorizonsdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- EIA Venezuela PDFDocument12 pagesEIA Venezuela PDFdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Limit Single-Source Peak Flaring Load With Staggered DepressurizationDocument6 pagesLimit Single-Source Peak Flaring Load With Staggered DepressurizationdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Remoción de Mercurio-HudsonDocument17 pagesRemoción de Mercurio-HudsondigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Obtain Free United States Published Engineering Documents PDFDocument1 pageHow To Obtain Free United States Published Engineering Documents PDFdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerants ClassificationDocument1 pageRefrigerants ClassificationdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Martin Towards Zero CO2Document18 pagesMartin Towards Zero CO2digecaPas encore d'évaluation
- FA5-Voith (Compatibility Mode)Document20 pagesFA5-Voith (Compatibility Mode)digecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Paper RECPDocument5 pagesFull Paper RECPSudhanshu67Pas encore d'évaluation
- SOFDocument5 pagesSOFdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulsation Design ReqsDocument2 pagesPulsation Design ReqsdigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulse Damper - Charging - Instructions - FlowguardDocument6 pagesPulse Damper - Charging - Instructions - FlowguarddigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- NotificationDocument14 pagesNotificationRoever Director officePas encore d'évaluation
- Sera CompressorsDocument37 pagesSera CompressorsJose SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Co-Gen BoilerAutomation Presentation EmailDocument39 pagesCo-Gen BoilerAutomation Presentation EmaildigecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Hot Box: Model E24Document2 pagesElectric Hot Box: Model E24digecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Polymer TechnologyDocument51 pagesPolymer Technologyanil kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- APC - U Oil & Gas - Refrigeration in Oil & Gas - tcm11-33983Document26 pagesAPC - U Oil & Gas - Refrigeration in Oil & Gas - tcm11-33983digecaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr410305 Refrigeration Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesRr410305 Refrigeration Air ConditioningSrinivasa Rao G100% (5)
- Mixing Non Viscous LiquidsDocument1 pageMixing Non Viscous LiquidsMohammed IrfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Exit SectionDocument1 pageFire Exit SectionrealcemackenziePas encore d'évaluation
- Maxtex PS-100Document1 pageMaxtex PS-100Hatem ElGabryPas encore d'évaluation
- AFBAD2A10971Document10 pagesAFBAD2A10971Samuel NkereuwemPas encore d'évaluation
- DX Evaporator Eng00013632 PDFDocument10 pagesDX Evaporator Eng00013632 PDFYaretiPas encore d'évaluation
- eRep-Performance Standards For Walk-In Refrigerator and Freezer Systems, AHRI 2012Document216 pageseRep-Performance Standards For Walk-In Refrigerator and Freezer Systems, AHRI 2012Moly69xPas encore d'évaluation
- Facts Type 455 - 456Document9 pagesFacts Type 455 - 456DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Tech. EXAMINATION, May 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 06 Roll No. ......................Document3 pagesB. Tech. EXAMINATION, May 2017: No. of Printed Pages: 06 Roll No. ......................ramphalPas encore d'évaluation
- B.tech 4th Sem MechanicalDocument8 pagesB.tech 4th Sem MechanicalRahul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Basement PDFDocument1 pageBasement PDFRonie MedelPas encore d'évaluation
- Sunanda PDFDocument3 pagesSunanda PDF9821694825100% (1)
- AntiferroelectricDocument6 pagesAntiferroelectricCristina ChirilaPas encore d'évaluation
- C532 PP M14 01 02Document27 pagesC532 PP M14 01 02kannanmech87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Works - SharingDocument37 pagesStructural Works - SharingEsvimy Deliquena CauilanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sabic Lldpe 118Wsj: Linear Low Density PolyethyleneDocument2 pagesSabic Lldpe 118Wsj: Linear Low Density PolyethyleneFahad MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Tehnički Opis SKYSTARDocument56 pagesTehnički Opis SKYSTARIgor SpasovicPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 1 3-01 08-Occ2-GbDocument2 pages3 1 3-01 08-Occ2-GbRa HulPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Plastic Concrete-TrainingDocument82 pagesSampling Plastic Concrete-TrainingAmir KhPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Various Heat Treatment On The Mechanical Properties of Steel Alloy EN31Document10 pagesEffect of Various Heat Treatment On The Mechanical Properties of Steel Alloy EN31IJIRSTPas encore d'évaluation
- Irc RecyclingDocument64 pagesIrc Recyclingkranthi13Pas encore d'évaluation
- E-01 Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesE-01 Electrical SymbolsPham Hoang TuanPas encore d'évaluation
- BPSC AE Paper 5 (Civil) 2022 (English)Document9 pagesBPSC AE Paper 5 (Civil) 2022 (English)धीरज कुमारPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Modular Construction For High-Rise Buildings: Building Structures-Arc 652Document6 pagesA Review On Modular Construction For High-Rise Buildings: Building Structures-Arc 652SUBHIKSHA D 1861738Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.chapter 2: Lateral Earth Pressures and Retaining WallsDocument20 pages1.chapter 2: Lateral Earth Pressures and Retaining Wallssalt2009Pas encore d'évaluation