Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Impact Test
Transféré par
Kimberly Anne0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesfd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentfd
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
30 vues2 pagesImpact Test
Transféré par
Kimberly Annefd
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
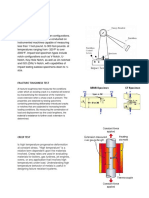
IMPACT TEST
most commonly consists
of Charpy and IZOD Specimen configurations.
The Charpy Impact Tests are conducted on
instrumented machines capable of measuring
less than 1 foot-pound. to 300 foot-pounds. at
temperatures ranging from -320°F to over
2000°F. Impact test specimen types include
notch configurations such as V-Notch, U-
Notch, Key-Hole Notch, as well as Un-notched
and ISO (DIN) V-Notch, with capabilities of
impact testing subsize specimens down to ¼
size.
FRACTURE TOUGHNESS TEST
A fracture toughness test measures the conditions
under which an existing crack in a material will extend
by characterizing the resistance of the material to
crack extension when a sharp crack is present. The
properties are obtained by testing specimens
containing preexisting deliberately introduced cracks
or notches that are subjected to increasing tensile
loading conditions. By measuring the combination of
load and displacement as the crack lengthens, the
material’s resistance to further crack extension is
determined.
CREEP TEST
Is high temperature progressive deformation
at constant stress. "High temperature" is a
relative term dependent upon the materials
involved. Creep rates are used in evaluating
materials for boilers, gas turbines, jet engines,
ovens, or any application that involves high
temperatures under load. Understanding high
temperature behavior of metals is useful in
designing failure resistant systems.
FATIGUE TEST
is defined as the process of progressive
localized permanent structural change
occurring in a material subjected to
conditions that produce fluctuating stresses
and strains at some point or points and that
may culminate in cracks or complete
fracture after a sufficient number of
fluctuations.
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY TEST
is a fundamental material property
associated with the ease with which heat
energy is conducted through a specific
material. Materials that conduct heat readily
with a small imposed temperature gradient
have a higher thermal conductivity than
materials that are more resistant (more
insulating) to the flow of heat. Accurate
knowledge of a material's thermal
conductivity is essential for predicting heat
transfer by conduction.
COEFFICIENT OF THERMAL EXPANSION TEST
Solid material test-samples are tested by
directly inserting them into the cylindrical
test chamber. They can be cylindrical or
polygonal with maximum cross sectional
dimension of 0.5 inches (12.5 mm) to fit
into the test chamber. The nominal
recommended sample length is 2 inches (50
mm) although this length is not critical and
shorter samples can be used.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Problem Cash FlowDocument3 pagesProblem Cash FlowKimberly AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grade: FOUR Date: - /day: - : E V A L U A T I O NDocument5 pagesGrade: FOUR Date: - /day: - : E V A L U A T I O NKimberly AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Lesson Plan ReyvenDocument6 pagesLesson Plan ReyvenKimberly AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Science QuestionsDocument4 pagesScience QuestionsKimberly Anne100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Impact TestDocument2 pagesImpact TestKimberly AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Column N Foundation DesignDocument26 pagesColumn N Foundation DesignSA023Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- ChairDocument7 pagesChairapi-487109487Pas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Activity Magnitude and IntensityDocument3 pagesActivity Magnitude and Intensityrobelyn valenzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Mechanical Report Square SectionDocument22 pagesMechanical Report Square SectiondrajkumarcePas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- Effect of Hydrogen Diffusion on Steel EmbrittlementDocument6 pagesEffect of Hydrogen Diffusion on Steel EmbrittlementmohammadpniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pile Cap of Abutment A1 & A2 (Takarma) - 1Document1 pagePile Cap of Abutment A1 & A2 (Takarma) - 1Nilay GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- BhujiDocument12 pagesBhujiVijey BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Column Design - As Per BS CodeDocument16 pagesColumn Design - As Per BS CodeFar AwayPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Rao 기계진동학 6판_Chapter 4Document146 pagesRao 기계진동학 6판_Chapter 4hbinnn29Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- RC II Hand Out Chapter 1 - ColumnsDocument30 pagesRC II Hand Out Chapter 1 - ColumnsNathnael JiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Euler Bernoulli PDFDocument2 pagesEuler Bernoulli PDFJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 8Document6 pagesLesson 8MIKE ARTHUR DAVIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Velloso - Piles Subjected To Horizontal Loads Due To Asymmetrical Surcharges On The SurfaceDocument5 pagesVelloso - Piles Subjected To Horizontal Loads Due To Asymmetrical Surcharges On The SurfaceMarcelaMarquesPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Materials Properties Laboratory Manual: BY: DR - Sabeeha A.J.Beden AhmedDocument66 pagesEngineering Materials Properties Laboratory Manual: BY: DR - Sabeeha A.J.Beden Ahmedb964 SpeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Stressed Modal Analysis Using FiniteDocument8 pagesPre Stressed Modal Analysis Using Finitegreat2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Transition From One-Way To Two-Way Shear PDFDocument14 pagesTransition From One-Way To Two-Way Shear PDFAdhi MukminPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- ES120 Spring 2018 - Section 1 Notes: Problem 1Document3 pagesES120 Spring 2018 - Section 1 Notes: Problem 1YI XUAN GOHPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Discovery Writing TopicsDocument6 pagesScience Discovery Writing TopicsMary Luz ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Macstars 2000 Reference Manual ENGDocument23 pagesMacstars 2000 Reference Manual ENGrycproyectistaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- BNBC 2020 Commentary on Soils and FoundationsDocument95 pagesBNBC 2020 Commentary on Soils and FoundationsTarif Aziz Maruf100% (1)
- Som MCQDocument14 pagesSom MCQVignesh Vicky0% (2)
- Composites Part B: M. Mohammadizadeh, A. Imeri, I. Fidan, M. ElkelanyDocument6 pagesComposites Part B: M. Mohammadizadeh, A. Imeri, I. Fidan, M. Elkelanysergio martinezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One: Introduction, Materials and Design ConceptsDocument12 pagesChapter One: Introduction, Materials and Design Conceptsdilnessa azanawPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Full Download Solution Manual For Mechanics of Materials Beer Johnston Dewolf Mazurek 6th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Mechanics of Materials Beer Johnston Dewolf Mazurek 6th Edition PDF Full Chaptermooneye.beeve.r572100% (19)
- Earthquake-Resistant Design of StructuresDocument36 pagesEarthquake-Resistant Design of Structures연민민Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gullapalli2020 Chapter EffectOfSoilStructureInteractiDocument10 pagesGullapalli2020 Chapter EffectOfSoilStructureInteractiManikanta SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthquake and Tsunami SimulationDocument2 pagesEarthquake and Tsunami SimulationKathleen DandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Review On Seismic Analysis of High Rise Building With Is-16700-2017Document3 pagesReview On Seismic Analysis of High Rise Building With Is-16700-2017Anonymous Qm0zbNkPas encore d'évaluation
- NSCP 2010 Seismic ProvisionsDocument67 pagesNSCP 2010 Seismic ProvisionsJule LobresPas encore d'évaluation
- Pushover Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structure Using SAP 2000Document8 pagesPushover Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structure Using SAP 2000Rishi RamakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)