Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
B2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDF
Transféré par
Илларион ПанасенкоDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
B2 Electronic Fundamentals Syllabus PDF
Transféré par
Илларион ПанасенкоDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
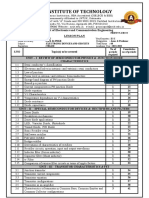
Cardiff and Vale College International Centre
for Aerospace Training
EASA Part-147
approved centre
Module 4
Electronic Fundamentals
Level
4.1 Semiconductors A B1 B2
Diodes
a) Symbols; Characteristics & properties; Diodes in series & parallel; Main characteristics & use - 2 2
of silicon controlled rectifiers (thyristors), light emitting diode, photo conductive diode, varistor,
rectifier diodes; Functional testing of diodes.
b) Materials, electron configuration, electrical properties; P & N type materials: effects of impurities - - 2
on conduction, majority & minority characters; PN junction in a semiconductor, development
of a potential across a PN junction in unbiased, forward biased and reverse biased conditions;
Diode parameters: peak inverse voltage, maximum forward current, temperature, frequency,
leakage current, power dissipation; Operation and function of diodes in the following circuits:
clippers, clampers, full and half wave rectifiers, bridge rectifiers, voltage doublers and triplers;
Detailed operation and characteristics of the following devices: silicon controlled rectifier(thyristor),
light emitting diode, Shottky diode, photocondiuctive diode, varactor diode, varistor, rectifier
diodes, Zener diode.
Transistors
a) symbols; Component description & orientation; characteristics & properties. - 1 2
b) Construction and operation of PNP & NPN transistors; Base, collector & emitter configurations: - - 2
Testing of transistors; Basic appreciation of other transistor types & their uses; Application of
transistors: classes of amplifier (A, B, C); Simple circuits including: bias, decoupling, feedback
and stabilisation; Multistage circuit principles: cascades, push-pull, oscillators, multivibrators,
flip-flop circuits.
Integrated Circuits
a) Description & operation of logic circuits & linear circuits / operational amplifiers. - 1 -
b) Description & operation of logic circuits & linear circ uits; Introduction to operation & function - - 2
of an operational amplifier used as: integrator, differentiator, voltage follower, comparator;
Operation & amplifier stages connecting methods: resistive capacitive, inductive (transformer),
inductive resistive (IR), direct; Advantages & disadvantages of positive & negative feedback.
4.2 Printed Circuit Boards A B1 B2
Description & use of printed circuit boards. - 1 2
4.3 Servomechanisms A B1 B2
a) Understanding of the following terms: Open & closed loop systems, feedback, follow up, - 1 -
analogue transducers; Principles of operation & use of the following synchro system components
/ features: resolvers, differential, control & torque, transformers, inductance & capacitance
transmitters.
b) Understanding of the following terms: Open & closed loop, follow up, servomechanism, - - 2
analogue, transducer, null, damping, feedback, deadband; Construction operation & use of the
following synchro system components: resolvers, differential, control & torque, E and I transformers,
inductance transmitters, capacitance transmitters, synchronous transmitters; Servomechanism
defects, reversal of synchro leads, hunting.
www.part66.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Part66 Module4Document2 pagesPart66 Module4K M Mosheur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 4&5 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMODULE 4&5 SyllabusSri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- EASA Module 4 SyllabusDocument2 pagesEASA Module 4 SyllabusPrabuddha ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- Official Journal of the European Union covers electronics education standardsDocument2 pagesOfficial Journal of the European Union covers electronics education standardsPRASADPas encore d'évaluation
- Document 2Document15 pagesDocument 2Sri Bhushan Prabhakar PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- EASA Part 66 Module 4 - Electronic FundamentalsDocument3 pagesEASA Part 66 Module 4 - Electronic FundamentalsAyyaj MujawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ael1037b-I Power Electronics Trainer v1.2014Document2 pagesAel1037b-I Power Electronics Trainer v1.2014Carbon Nano TubePas encore d'évaluation
- LICADocument2 pagesLICAYuvaraja KarunamurthiPas encore d'évaluation
- LDICA Digital NotesDocument263 pagesLDICA Digital NotesAbhishek Reddy Garlapati80% (5)
- II - II Linear Integrated Circuit Analysis Course Plan PDFDocument9 pagesII - II Linear Integrated Circuit Analysis Course Plan PDFshivgnitPas encore d'évaluation
- Nria20 Edc Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNria20 Edc Lesson PlanD. Ravi ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 Clippers and ClampersDocument6 pagesLab 4 Clippers and ClampersAlisha AasPas encore d'évaluation
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS COURSEDocument2 pagesLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS COURSEGaurav KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bamel Holder Syllabus b1Document5 pagesBamel Holder Syllabus b1Anonymous QqSHIKX6bDPas encore d'évaluation
- EDCunit 1Document55 pagesEDCunit 1Shiva NSPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE204 Analog Circuit DesignDocument2 pagesECE204 Analog Circuit DesignconnectvprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 04 Syllabus BreakdownDocument2 pagesModule 04 Syllabus Breakdownpraveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 04 Syllabus BreakdownDocument2 pagesModule 04 Syllabus BreakdownAngel RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- 18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFDocument125 pages18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFsuhas kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- E66 B2 04 SummaryDocument3 pagesE66 B2 04 SummarySteven J. SelcukPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear IC's & Applications GuideDocument146 pagesLinear IC's & Applications Guidecruger educorePas encore d'évaluation
- 2008-09 S.Y.B.sc ElectronicsDocument8 pages2008-09 S.Y.B.sc Electronicsvaibhavgc1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Shaping and Swiching CircuitsDocument3 pagesWave Shaping and Swiching Circuitskaran007_mPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity, Analog Electronics-2 (B.tech 4th Sem-Ece)Document1 pageAmity, Analog Electronics-2 (B.tech 4th Sem-Ece)deepak173Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Lic-2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Lic-2sangs_jayaPas encore d'évaluation
- MATRIX FOR ACQUIRING CATEGORY-B LICENSE FOR BAMEUBAMEEC HOLDERSDocument5 pagesMATRIX FOR ACQUIRING CATEGORY-B LICENSE FOR BAMEUBAMEEC HOLDERSrakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Relay Trip Circuit DesignDocument95 pagesRelay Trip Circuit Designykh92167100% (2)
- UG APE SyllabusDocument2 pagesUG APE Syllabusdivya k sPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus EC321Document2 pagesSyllabus EC321Sudheer KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics E-624Document3 pagesPower Electronics E-624etaPas encore d'évaluation
- 430 15EC73 Power Electronics Notes (Vtupro Com) 2Document100 pages430 15EC73 Power Electronics Notes (Vtupro Com) 2KN DEEPSHIPas encore d'évaluation
- 4031-Power Electronics Devices and Circuits SyllabusDocument5 pages4031-Power Electronics Devices and Circuits SyllabusAnshif KpPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear IC Syllabus GuideDocument270 pagesLinear IC Syllabus GuiderameshsmePas encore d'évaluation
- LIC SyllabusDocument1 pageLIC SyllabusECE - HOD, VECPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Savan KalalPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 Power Electronics - Lecture Plan - 2021-22Document1 page0 Power Electronics - Lecture Plan - 2021-22OmkarPas encore d'évaluation
- JNTUK Linear IC Applications GuideDocument1 pageJNTUK Linear IC Applications GuideAntony VishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Diploma Ii Year (Electrical Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsDocument28 pagesDiploma Ii Year (Electrical Engineering) : 2011-2012 SubjectsMeenu SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For Chargeman Certificates (April 2014) PVDocument2 pagesSyllabus For Chargeman Certificates (April 2014) PVMahasan Ahmad0% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Andhra Pradesh, IndiaDocument5 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Andhra Pradesh, Indiak jayaram kumar ACETPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus: Ufy12209Cdp Circuits and Devices Laboratory L T P CDocument75 pagesSyllabus: Ufy12209Cdp Circuits and Devices Laboratory L T P CvijayprasathmePas encore d'évaluation
- Polytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusDocument23 pagesPolytechnic 3rd Year SlaybusSudhakar MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec8453 Lic 2 MarksDocument28 pagesEc8453 Lic 2 Markskarthikamagesh100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics Course OverviewRojan PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsDocument41 pagesET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsChaitanya P V KPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Engineering SchemeDocument21 pagesElectronics Engineering SchemeDHANYASRI BOLLAPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Tech (ECE) Semester-IV: Amity School of Engineering & TechnologyDocument1 pageB.Tech (ECE) Semester-IV: Amity School of Engineering & TechnologyKaran MaanPas encore d'évaluation
- ES101Document3 pagesES101Sualé SualéPas encore d'évaluation
- KEC - 251 - Electronics - Lab AKTUDocument48 pagesKEC - 251 - Electronics - Lab AKTUimvuuser1Pas encore d'évaluation
- HshehDocument4 pagesHshehAsad TamamPas encore d'évaluation
- LICDocument5 pagesLICsaranyavinothkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERDocument5 pagesDgca Module Syllabus For BAMEL HOLDERJagbir SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- LDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFDocument143 pagesLDICA Lecture Notes by A.Mounika PDFTwinkle Ratna100% (1)
- Wave Shaping and Swiching CircuitsDocument5 pagesWave Shaping and Swiching Circuitskaran007_mPas encore d'évaluation
- Value Added CourseDocument4 pagesValue Added CourseSuresh VaruvelPas encore d'évaluation
- Rec SemiDocument20 pagesRec SeminadirPas encore d'évaluation
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFRishiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tradesman - Electronics TED - 1Document4 pagesTradesman - Electronics TED - 1sampreethpPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualD'EverandInstrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- En - LF18X401 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesEn - LF18X401 Spec SheetMarcioPas encore d'évaluation
- AUDISON Prima AP5 Tech Sheet PDFDocument1 pageAUDISON Prima AP5 Tech Sheet PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibrations inDocument7 pagesVibrations inИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Fusible CoringDocument2 pagesFusible CoringИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 08 Principles of FlighDocument87 pagesModule 08 Principles of FlighИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Systems Design PDFDocument16 pagesSystems Design PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017ole A9Document111 pages2017ole A9Илларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- AUDISON Prima AP5 Tech Sheet PDFDocument1 pageAUDISON Prima AP5 Tech Sheet PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Fundamentals Module-4 EASA Part-66Document90 pagesElectronic Fundamentals Module-4 EASA Part-66SK88% (58)
- 2017ole A9Document111 pages2017ole A9Илларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Support PDFDocument4 pagesSupport PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Airport Noise PDFDocument7 pagesAirport Noise PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Fanpac PDFDocument4 pagesFanpac PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine VibrationDocument3 pagesEngine VibrationИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Short PDFDocument16 pagesAdvanced Short PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- The European PDFDocument8 pagesThe European PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- The Application PDFDocument7 pagesThe Application PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- CO LaserDocument10 pagesCO LaserИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Technology PDFDocument3 pagesLaser Technology PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- New Developments PDFDocument5 pagesNew Developments PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- New Developments PDFDocument5 pagesNew Developments PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Industry PDFDocument4 pagesAircraft Industry PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Industry PDFDocument4 pagesAircraft Industry PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Short PDFDocument16 pagesAdvanced Short PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- The European PDFDocument8 pagesThe European PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 02 PhysicsDocument67 pagesModule 02 PhysicsИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- The Application PDFDocument7 pagesThe Application PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Technology PDFDocument3 pagesLaser Technology PDFИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- CO LaserDocument10 pagesCO LaserИлларион ПанасенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod 7.7 B1 Electrical CablesDocument127 pagesMod 7.7 B1 Electrical CablesИлларион Панасенко100% (1)
- AEIEDocument6 pagesAEIEarijit_ghosh_18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Travel Guide by Using AndroidDocument3 pagesMobile Travel Guide by Using AndroidLucasPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT G10 - Chapter 1Document17 pagesICT G10 - Chapter 1tonet enteaPas encore d'évaluation
- Peewee ORM Documentation: Quickstart GuideDocument142 pagesPeewee ORM Documentation: Quickstart GuidejohnnokiaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNCMag-201605 Issue24Document54 pagesDNCMag-201605 Issue24pjcdPas encore d'évaluation
- hd5650 HackintoshDocument7 pageshd5650 HackintoshAli PadaryamPas encore d'évaluation
- The Timepix3 Chip: C.Brezina, Y.Fu, M.De Gaspari, V.Gromov, X.Llopart, T.Poikela, F.Zappon and A.KruthDocument69 pagesThe Timepix3 Chip: C.Brezina, Y.Fu, M.De Gaspari, V.Gromov, X.Llopart, T.Poikela, F.Zappon and A.KruthVerena StreberPas encore d'évaluation
- IIB TutorialsDocument68 pagesIIB TutorialsDeepak Gupta100% (4)
- Sun Tracking System (Rahul Raj)Document22 pagesSun Tracking System (Rahul Raj)Rahul Raj88% (8)
- Truck Adblue Emulator For RENAULT INSTRUCTIONS PDFDocument4 pagesTruck Adblue Emulator For RENAULT INSTRUCTIONS PDFobd2works100% (3)
- Vxvm OverviewDocument8 pagesVxvm OverviewrsgsundarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 IT 35 Prototyping and Quality AssuranceDocument7 pages4 IT 35 Prototyping and Quality Assurancemichael pascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tle Ict Css 10 q2 Iccs Week 1 4 Iccs 2Document16 pagesTle Ict Css 10 q2 Iccs Week 1 4 Iccs 2nhoj eiram RodavlasPas encore d'évaluation
- Aci UpgradeDocument94 pagesAci Upgradesachin giriPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Report On E-FarmingDocument35 pagesReview Report On E-FarmingPriyanka Poshala80% (5)
- PCB GuideDocument1 pagePCB GuideMallappa PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- MAN-125-0003-C (Pegasus Quick Installation Guide (With Internal Transducers) )Document30 pagesMAN-125-0003-C (Pegasus Quick Installation Guide (With Internal Transducers) )Jorge Caicedo Frv LfuPas encore d'évaluation
- Z80 Instruction Set - ClrHomeDocument5 pagesZ80 Instruction Set - ClrHomesatriomochammadPas encore d'évaluation
- 25TRGEXT000054 Introduction To Interfaces v5Document25 pages25TRGEXT000054 Introduction To Interfaces v5Tim CCPas encore d'évaluation
- Documentation Practices in Agile Software DevelopmDocument9 pagesDocumentation Practices in Agile Software Developmyenix64460Pas encore d'évaluation
- How To Cli With NetappDocument2 pagesHow To Cli With NetappDennis DubePas encore d'évaluation
- FM1120 User Manual v5.2 - 47.07.XX - 47.08.XXDocument93 pagesFM1120 User Manual v5.2 - 47.07.XX - 47.08.XXJennsett SastrePas encore d'évaluation
- LG 22ld350-cb Chassis Lc01aDocument34 pagesLG 22ld350-cb Chassis Lc01aJuan Pablo Montoya CardenasPas encore d'évaluation
- ThinkPad T450s Platform SpecificationsDocument1 pageThinkPad T450s Platform SpecificationsisraelmpPas encore d'évaluation
- GFK1645JDocument704 pagesGFK1645JphuvtbuithuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap Error MessagesDocument7 pagesSap Error Messagesmarcoberg1964Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ikc2-Service Tips PDFDocument18 pagesIkc2-Service Tips PDFzoltan esteban Hrotko gonzalez100% (1)
- Carbide Series: Mid-Tower Gaming CaseDocument48 pagesCarbide Series: Mid-Tower Gaming CaseRoger SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Engineering The Discipline of SystemDocument30 pagesWeb Engineering The Discipline of Systemok januPas encore d'évaluation
- DX200 System SetupDocument260 pagesDX200 System SetupArno Botha100% (1)