Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy MCB 247 Diseases
Transféré par
Jeremy Vivit0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues12 pagesdiseases 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentdiseases 2
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
13 vues12 pagesAnatomy MCB 247 Diseases
Transféré par
Jeremy Vivitdiseases 2
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
Anatomy MCB 247 3/3/13 10:52 PM
definition and cause of disease are not always the same
Gigantism- Pituitary Gigantism. Excess growth and height that is
significantly above average. Cause- Overproduction in growth hormone is
childhood before growth plates have closed or a tumor on the pituitary
gland. Symptoms- delayed puberty, increased sweating, larger hands and
feet, possibly enlarged internal organs. Treatment- tumor=surgery, growth
hormone levels= dopamine agonists, radiation therapy.
Acromegaly- Cause- excessive growth hormone after the growth plates
have closed or a benign (usually) tumor. Symptoms- Face, hands and feet
are enlarged. Swelling in bony areas around the joints. Treatments- surgery
if tumor, radiation or medication if change in HGH.
Dwarfism- Pituitary dwarfism. Very short stature significantly below
average height. Cause- decrease in growth hormone signaling pathway.
(mutation or deletion in growth hormone receptors so therefore unable to
reach the target tissue). Usually a genetic reason. Symptoms- very slow
growth rate, delayed puberty, face appears younger than actual age, chubby
body build. Treatment- growth hormone injections.
Cretinism- Congenital hypothyroidism. Neonatal hypothyroidism. Congenital
means either present before birth or during birth. Severely stunted growth
both physically and mentally. Causes- congenital deficiency of thyroid
hormone. Born with a missing or poorly structured thyroid gland. Iodine
deficiency in diet. Symptoms- Neurological and cognitive impairment,
puberty can be severely delayed, protruding abdomens. Treatment-
thyroxine medication (t4).
Hyperthyroidism- Overactive thyroid. overactive thyroid yielding more
thyroid hormone. Cause- most common cause is Graves’ disease, too much
iodine in the diet, benign growth on the thyroid gland. Symptoms- goiter
(swelling of the thyroid gland), heat intolerance, polyuria (excessive
urinations), polydipsia (excessive thirst). Treatment- anti-thyroid
medication, radioactive iodine and surgery is tumor is the cause.
Hypothyroidism- underactive thyroid yielding less thyroid hormone. Cause-
main= thyroiditis (inflammation and swelling of thyroid), iodine deficiency.
Symptoms- goiter, cold intolerance, strong sensitivity to the cold.
Treatment- thyroid replacement therapy taken every day.
Graves Disease- hyperthyroidism. Auto-immune disease which is the
difference. Internal rather than diet-related. Causes overproduction of
thyroid gland. Cause- thyroid auto-antibodies (anti-body produced by your
own immune system but attacks your own proteins) which activate TSH
receptors which cause excessive growth hormone. Symptoms- eyeballs that
stick out, lid-lag, excessive tear production, excessive lacrimation, muscle
weakness, increased heart rate, sweating. Treatment- anti-thyroid
medications, radioactive iodine, beta-blockers (block heart rate increase).
Hashimoto’s Disease- Chronic Lymphocytic Thyroiditis. Auto-immune
disease (immune system attacking the thyroid gland of the same structure).
Causes- antibodies against the thyroid meaning that when its attacking the
thyroid, the follicles get denatured. Symptoms- sensitivity to both heat and
cold, muscle weakness, fatigue. Treatment- replacement hormone therapy.
Cushing’s Disease- Hypercortisolism. Increase levels of cortisol in the
blood. Cause- tumor on the pituitary gland -> tumor causes pituitary gland
to secrete ATCH and an increase in ATCH causes increased levels of cortisol.
Symptoms- Moon face- very round filled out reddish face, buffalo hump-
excess fat around the back of the neck, central obesity- rapid weight gain
situated around face and trunk. Treatments- surgery to remove tumor,
radiation, hydro-cortisone replacement therapy.
Addison’s Disease- Hypo-cortisolism. Chronic Adrenocortical Insufficiency.
Adrenal glands don’t produce the correct amount of steroid hormones.
Cause- “primary adrenal insufficiency”, immune system is attacking its own
tissues, specifically damaging the adrenal cortex. Symptoms- fatigue,
muscle weakness, light-headedness. Treatments- replacement corticoid
steroids.
Adrenalgenital Disease- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Inherited disease
of the adrenal gland. Cause- gene mutation that tampers with transition
from cholesterol to cortisol production and results in over excessive amounts
of androgens during the prenatal period. Symptoms- more apparent in baby
girls, enlarged clitoris and lack of menstruation, not present in baby boys
usually. Treatment- medication of cortisol and for girls, reconstructive
surgery.
Type 1 diabetes- diabetes myelitis. Bodies failure to produce insulin.
Cause- genetic, auto-immune destruction of the beta cells which are insulin
producing cells of the pancreas. Symptoms- polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia
(excessive hunger), weight loss. Treatment- insulin injections, healthy diet
and exercise
Type 2 diabetes- diabetes myelitis. Insulin resistance, response doesn’t
occur. More common diabetic occurrence. Symptoms- Early Symptoms are
same as Type 1, long term are increased risk of heart attack and stroke,
more vulnerable to kidney failure. Treatment- proper exercise and diet.
Gynocomastia- abnormal development in mammory glands. Causes (not
definite)- changes in levels of sex hormones, changes in how the body
responds to levels of hormones. Symptom- enlargement of the male breasts.
Treatment- testosterone replacement medication, surgery for breast
reduction.
Androgen insensitivity (deficiency)- hypogonadism. Androgen hormones
fall below specific levels required yielding the sex glands not procucing
enough hormones that are necessary. Causes- primary- ovaries or testes are
not functioning properly, central cause- hypothalamus/pituitary gland aren’t
functioning properly. (could be from an accident or infection or many other
causes). Symptoms- females- menstruation stops, low sex drive, hot
flashes. Males- breast development, sex drive deficiency, muscle loss.
Treatment-hormone based medications.
Precocious Puberty- Pubertas Praecox. Early puberty. Physically and
sexually mature at an unusually early age. Causes- genetic problems,
changes in the brain, certain tumors that can induce earlier release of
hormones. Symptoms- all puberty related symptoms just earlier. Treatment-
removal of tumors if that’s the cause, hormone based medications,
counseling
MCB 247 3/3/13 10:52 PM
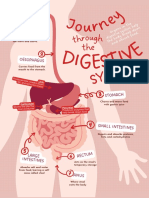
Stomach Ulcers- Peptic Ulcer Syndrome
• Definition- Painful sores or ulcers in the lining of the stomach or
duodenum
• Cause- No single cause. Ulcers are the end result of an imbalance
between digestive fluids in the stomach and the duodenum. Can be
caused by an infection with a type of bacteria- Helicobacter Pylori.
Can be caused by painkillers such as aspirin, ibuprofen, aleve. Or
from excess acid production from gastrinomas (tumors on the acid
producing cells of the stomach causing imbalance and leading to
ulceration).
• Symptoms- bloating, heartburn, nausea, gnawing or burning pain in
the stomach between meals, weight loss, vomiting blood, vomiting
• Treatment- Limiting dairy, alcohol and tobacco. Taking antibiotics if
the bacteria is the cause. Take proton pump inhibitors (ex- prilosec)
to reduce acid levels. Upper endoscopy. Surgery if the ulcer has
created a hole in the wall of the stomach.
Acid Reflux/GERD- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
• Definition- A condition in which the stomach contents leak
backwards from the stomach into the esophagus. Irritates
esophagus.
• Cause- The lower esophageal sphincter doesn’t close well due to
weakness or inappropriate relaxation and the stomachs contents go
back up into the esophagus. No known cause of the weakness of
the LES but it can be caused by obesity, pregnancy, alcohol/caffeine
consumption, eating before bed, acidic foods.
• Symptoms- Heartburn, bitter/sour taste in mouth, trouble
swallowing, chronic cough, wheezing
• Treatment- Lifestyle changes and OTC medications. Eat small,
frequent meals, lose weight, avoid wearing tight clothes around the
midsection. Take antacids to help neutralize stomach contents, and
H2 blockers which prevent production of stomach acid. Take proton
pump inhibitors (prescription) to block stomach acid production
more effectively than H2 blockers.
Colonoscopy-
• Definition- Endoscopic examination of large bowl and the distal part
of the small bowel with a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube
passed through the anus. Begin at age 50 and then repeated every
10 years if no precancerous polyps are found.
Celiac Disease- Sprue/Gluten intolerance
• Definition- Disease that damages the lining of the small intestine
and prevents it from absorbing parts of food that are important for
staying healthy. Due to eating gluten
• Cause- Villi help absorb nutrients in the intestines and when gluten
in ingested, the immune system reacts by attacking the villi.
• Symptoms- Malnutrition, constipation, abdominal pain, lactose
intolerance, diarrhea, decreased appetite, bruising easily, hair loss
• Treatment- no cure. Gluten-free diet will make symptoms go away
Irritable Bowel Syndrome- Spastic colon/Mucous colitis
• Definition- Common disorder that affects your large intestine- no
permanent damage to colon and doesn’t cause inflammation or
changes in bowel tissue like ulcerative colitis and crohn’s.
• Cause- no known cause
• Symptoms- abdominal pain, fullness, gas, bloating
• Treatment- more of a relief treatment. Lifestyle changes-increase
fiber, avoid large meals, avoid stimulating foods. Some medications
to be taken for the specific symptoms ( anticholinergic medications
for internal muscle spasms, bisacodyl to treat constipation etc)
Ulcerative colitis- Inflammatory bowel disease
• Definition- Chronic. Inflammation of large intestine and rectum
• Cause- Abnormal response in immune system which causes
food/acid/whatever passes through to agitate tissue and develop
ulcers
• Symptoms- Abdominal pain, blood and pus in the stools, diarrhea,
fever, tenesmus, weight loss, joint pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting
• Treatment- avoid fatty/fried/high in fiber foods. Eat small amounts
of food throughout the day. Medications to decrease the number of
attacks such as immunosuppressant’s and corticosteroids during a
flare. Surgery to remove the colon and rectum will cure it and
removes the threat of colon cancer.
Diverticulitis-
• Definition- small bulging sacs or pouches on the inner lining of the
intestine that becomes inflamed or infected. Most often in the large
intestine
• Cause- No specific cause known for the formation of the sacs-
Eating a low-fiber diet is a likely cause. Diverticulitis is caused by
small pieces of feces that get trapped in the sacs, causing infection
or inflammation.
• Symptoms- Tenderness in the lower left side of abdomen, bloating
or gas, fever and chills, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite
• Treatment- Some need to be hospitalized. Otherwise, rest and use
a heating pad on stomach, take pain medications, drink only fluids
for a day or two to clear out intestines. Afterwards, increase fiber in
diet to decrease chances of constipation and sac formation.
Pancreatic Cancer- Pancreatic carcinoma
• Definition- Cancer of the pancreas. The tumor can block the
common bile duct and bile cannot pass into the digestive system.
• Cause- Cause is unknown, most common in people with diabetes,
smokers, or people with long-term inflammation of the pancreas.
• Symptoms- No symptoms at first which is why it often goes
unfound at first. Dark urine and clay colored stools, fatigue,
weakness, jaundice, loss of appetite and weight loss,
nausea/vomiting, blood clots, indigestion and diarrhea
• Treatment- because pancreatic cancer is found in an advanced
state, very few tumors can be removed through surgery. When
tumor is concentrated in pancreas alone but removal is not an
option- radiation, therapy and chemotherapy together are
recommended. If tumor has spread to other organs, chemotherapy
alone. If tumor cannot be removed but there is an obstruction to
the bile ducts, surgery and/or a biliary stent can be applied. IF
pancreatic cancer is caught early enough, the Whipple procedure is
the surgery that removes a tumor.
Barrett’s esophagus-
• Definition- disorder in which the lining of the esophagus is damaged
by stomach acid and changed to a lining similar to that of the
stomach. Serious disorder of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
• Cause- Cardiac sphincter does not close properly and stomach acid
leaks back into the esophagus causing the lining of the esophagus
to change to the tissue of the lining of the stomach. GERD does not
always lead to Barrett’s esophagus
• Symptoms- Barrett’s esophagus doesn’t have symptoms, but acid
reflux that causes this disease leads to heartburn, a sour/burning
sensation in the back of the throat, chronic cough, nausea
• Treatment- is cells are likely to lead to cancer, surgery may be
recommended to remove. To remove harmful tissue before cancer
develops- Photodynamic therapy along with the drug Photofrin,
other procedures use high types of energy to destroy precancerous
tissue, surgery to remove abnormal lining
Crohn’s Disease- Regional enteritis/Ileitis
• Definition- Inflammatory bowel disease. Usually affects the
intestines but can occur anywhere from the mouth to the rectum.
Causes inflammation of the lining of your digestive tract.
• Cause- Unknown. It occurs when your body’s immune system
mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue (autoimmune
disorder)
• Symptoms- Abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, severe malnutrition,
fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, constipation, rectal bleeding
• Treatment- Eat a well-balanced, healthy diet with enough protein
and nutrients from a variety of food groups. Avoid stress. Take fiber
supplements and over the counter drugs for the abdominal pain,
inflamed tissue, and diarrhea. Some people need surgery to remove
a damaged part of the intestine, sometimes the whole large
intestine is removed.
Pancreatitis-
• Definition- a disease in which the pancreas becomes inflamed. Can
be chronic or can be acute.
• Cause- Pancreatic damage being when the digestive enzymes are
activated before they are secreted into the duodenum and begin
attacking the pancreas. Caused by gallstones and alcohol abuse.
• Symptoms- upper abdominal pain radiating into the back, swollen
and tender abdomen, nausea and vomiting, fever, increased heart
rate, headache, lethargy, irritability
•Treatment- Stop alcohol consumption, liquid diet and OTC pain
medications for pain relief. Most admitted to hospital, an IV to
replace water lost, antibiotics given if an infection is suspected. If
attack lasts longer than expected, nutritional supplements are
administered through IV. Diet changes
Appendicitis-
• Definition- Inflammation of the appendix (small pouch at beginning
of the appendix)
• Cause- appendix becomes blocked by feces, a foreign object or
(rarely) a tumor. Can also be caused by infection, since the
appendix swells in response to any infection in the body. Appendix
can burst if not treated immediately
• Symptoms- pain around your belly button, reduced appetite,
nausea, vomiting, low fever- pain will shift towards right lower
abdomen, abdominal swelling. Constipation, fever, nausea, shaking
• Treatment- Appendectomy- surgery to remove appendix. If an
abscess has also formed, you also need a procedure to drain it
Gastroenteritis- stomach flu
• Definition- condition that causes irritation and inflammation of the
stomach and intestines.
• Cause- viral infections are most common cause, but bacteria,
parasites, and food-borne illnesses can do it too. Severity of
infection depends on the immune system’s ability to resist the
infection.
• Symptoms- diarrhea, nausea, crampy abdominal pain, vomiting,
dehydration, low grade fever
• Treatment- self-care remedies to keep patients hydrated. If not
able to take fluids, an IV will be inserted in order to prevent serious
dehydration. Antibiotics not commonly given because if the wrong
one is used, it can worsen symptoms.
Hemorrhoids- piles
• Definition- swollen and inflamed veins in your anus and lower
rectum
• Cause- increased pressure in the veins of the anus. Pressure causes
the veins to swell and make them painful. Causes include straining
during bowel movements, constipation, liver cirrhosis, anal
infections, sitting for long periods of time
• Symptoms- anal itching, bright red blood in stool, pain during bowel
movement, tender lumps near anus, leakage of feces.
• Treatment- Home treatments usually clear up hemorrhoids- OTC
corticosteroid creams to reduce pain, sitz baths, stool softeners. If
these don’t work, need infared coagulation (heat treatment) to
shrink them. Surgery can be done- rubber band litigation, or
removal.
Cirrhosis of the Liver-
• Definition- scarring of the liver and abnormal structure/function of
the liver
• Cause- End result of chronic liver damage caused by chronic liver
disease. Also caused by autoimmune inflammation of the liver,
hepatitis B, metabolic disorders of iron and copper
• Symptoms- jaundice, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, itchy,
easy bruising, nosebleeds, edema, impotence
• Treatment- if cirrhosis progresses to end-stage liver disease- liver
transplant. Otherwise, lifestyle changes such as limited salt, no
alcohol, nutritious diet, antibiotics, vitamin K
Acetaminophen Toxicity- Tylenol Poisoning
• Definition- overdose on acetaminophen
• Cause- Caused primarily by liver damage. Acetaminophen is
metabolized by the liver and can overwhelm the liver is not healthy.
• Symptoms- nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, abdominal pain
• Treatment- call poison control, emptying of the stomach, N-
acetylcysteine is the antidote for toxicity, activated charcoal can be
given by mouth to bind any drug remaining in the GI tract
Fibrosis of the Liver-
• Definition- Fibrosis is excessive accumulation of scar tissue that
results from ongoing inflammation and liver cell death that occurs
in most types of chronic liver diseases.
• Cause- Fibrosis occurs when excessive scar tissue builds up faster
than it can be broken down and removed from the liver. Chronic
infection with hepatitis C or hepatitis B virus (HCV or HBV), heavy
alcohol consumption, toxins, trauma or other factors can all lead to
liver fibrosis
• Symptoms- abdominal pain, fatigue, nausea, dark urine, loss of
appetite, weight loss, vomiting of blood, muscle loss, gallstones
• Treatment- irreversible so treatment focuses on stopping
progression and further complications. Proper diet, avoiding toxins,
use of vitamin supplements.
Hepatitis A- Viral Hepatitis
• Definition- Inflammation/disease of the liver from Hepatitis A virus
• Cause- Eating or drinking something that has been contaminated by
stools containing the hepatitis A virus.
• Symptoms- feeling tired, muscle soreness, upset stomach, fever,
loss of appetite, diarrhea, stomach pain, jaundice, pale stools
• Treatment- Will get better in a few weeks without treatment- avoid
things that are toxic to the liver.
Hepatitis B-
• Definition- Inflammation/disease of the liver from Hepatitis B virus
• Cause- coming into contact with the Hepatitis B virus through
blood, semen, vaginal fluids or any other fluids from someone else
• Symptoms- appetite loss, fatigue, fever, muscle and joint aches,
nausea, vomiting, jaundice, chronic liver damage, cirrhosis
• Treatment- Not treated unless it becomes chronic. Chronic is
treated with medicines that slow or stop damage to the liver. If
damage is severe enough, a liver transplant will be necessary
Hepatitis C- Non-A(B) hepatitis
• Definition- Viral disease that leads to swelling of liver
• Cause- Hepatitis C virus. People at risk are those on long-term
kidney dialysis, have regular contact with blood, sharing needles
• Symptoms- jaundice (not too common), abdominal pain, dark
urine, fatigue, fever, itching, nausea, vomiting
• Treatment- goal is to remove the virus from the blood and reduce
the risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer. Some benefit by medication
(24-48 weeks of it). If cirrhosis or liver cancer develops, liver
transplant is necessary.
Jaundice-
• Definition- Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus
membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a
byproduct of old red blood cells.
• Cause- The liver removes dead blood cells, forming bilirubin. The
liver helps break down bilirubin so that it can be removed by the
body in the stool. When too much bilirubin builds up in the body,
jaundice may result. When liver is overloaded or damaged, or too
many RBC’s are dying.
• Symptoms- yellow skin, yellow color inside of mouth, pale stools
• Treatment- depends on cause
3/3/13 10:52 PM
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 10: Infection: Awarded 1.0 Points Out of 1.0 Possible PointsDocument3 pagesChapter 10: Infection: Awarded 1.0 Points Out of 1.0 Possible PointsJeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Affecting Blood PressureDocument54 pagesDrugs Affecting Blood PressureJeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- TB 57Document3 pagesTB 57Jeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Management of Diabetes: Presence Health: Lakeview Internal MedicineDocument2 pagesSelf-Management of Diabetes: Presence Health: Lakeview Internal MedicineJeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- Soc 100 SyllabusDocument5 pagesSoc 100 SyllabusJeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical TherapyDocument2 pagesPhysical TherapyJeremy VivitPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- AphasiaDocument4 pagesAphasiaSusan KPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System NotesDocument43 pagesCardiovascular System Notestruefriends0809Pas encore d'évaluation
- Major Herbs of AyurvedaDocument2 pagesMajor Herbs of AyurvedaAleeza SarfrazPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System ResonanceDocument72 pagesNervous System ResonanceEkta ManglaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides To Draw and StudyDocument21 pagesSlides To Draw and StudyAndrea Galang CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Anomalies of Kidney and Ureter 2161 0940 1000190Document10 pagesCongenital Anomalies of Kidney and Ureter 2161 0940 1000190Indra JayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sorenson Atlas of Human Histology Chapter 1 PDFDocument32 pagesSorenson Atlas of Human Histology Chapter 1 PDFMiruna Portocală100% (2)
- Auditory Pathway PDFDocument3 pagesAuditory Pathway PDFShruthi DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- 15.the Anatomy of The Ear 2017 NewDocument109 pages15.the Anatomy of The Ear 2017 NewMuhammed100% (1)
- Curs Engleza Partea 2 Corectat - LariDocument205 pagesCurs Engleza Partea 2 Corectat - LariVili Robert VoichițoiuPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodyDocument5 pages3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodySabrina PorcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperthyroidism in Children and Adolescents: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document3 pagesHyperthyroidism in Children and Adolescents: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Neha ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruminant Digestive SystemDocument37 pagesRuminant Digestive SystemEnJe Thea100% (1)
- 2d) Patofisiologi Sesak Napas by Dr. AminuddinDocument39 pages2d) Patofisiologi Sesak Napas by Dr. AminuddinMUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument42 pagesPsychological and Physiological Changes of PregnancyAustine James Sabenicio PantiloPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectroneurogramDocument10 pagesElectroneurogramIrina Luciana DumitriuPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensory Evaluation and AnalysisDocument83 pagesSensory Evaluation and Analysisampoloquiozachary4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthPas encore d'évaluation
- Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Stadium V Akibat Nefrolitiasis: Case ReportDocument5 pagesPenyakit Ginjal Kronik Stadium V Akibat Nefrolitiasis: Case ReportAmanah UtamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Amiey SehokPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 - Breast Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument50 pagesUnit 1 - Breast Anatomy and PhysiologyClyde R.OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothyroidism in PregnancyDocument29 pagesHypothyroidism in PregnancyhanaddulPas encore d'évaluation
- B - SC Nursing I Year SyllabusDocument159 pagesB - SC Nursing I Year SyllabusSusheelabaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diploma in Occupational TherapyDocument47 pagesDiploma in Occupational TherapyAzmi Plus100% (2)
- Permanent PacemakerDocument24 pagesPermanent PacemakerAwais PanhwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts of The EarDocument5 pagesParts of The EarThons Nacu LisingPas encore d'évaluation
- Poster BIODocument4 pagesPoster BIONureen ZuhairahPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System Gizmos LabDocument5 pagesCirculatory System Gizmos LabLast FazePas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Care ClassDocument16 pagesSkin Care ClassMuhammad Aliff Abdul RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Ginjal Dan Vesika Urinaria PADA MUSANG LUWAK (Paradoxurus Hermaphroditus) DI PULAU TIMORDocument11 pagesGambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Ginjal Dan Vesika Urinaria PADA MUSANG LUWAK (Paradoxurus Hermaphroditus) DI PULAU TIMORSaadatulPas encore d'évaluation