Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 4 Parent Letter Unit 2
Transféré par
Niki Eskew TurcoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Grade 4 Parent Letter Unit 2
Transféré par
Niki Eskew TurcoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Grade 4 Unit 2
Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Volume 1 Issue 2
References Dear Parents,
Helpful Links: Your student’s math class is calling for students to be actively engaged in doing math in order
to learn math. In the classroom, students will frequently work on tasks and activities to
discover and apply mathematical thinking. Students will be expected to explain or justify their
http://www.learner.org/cou answers and to write clearly and properly. Your student will receive a consumable My Math
rses/learningmath/number/s textbook and online access from his or her teacher.
ession4/part_b/multiplicatio
n.html
http://www.adaptedmind.co Concepts Students will Use and Understand
m/Fourth-Grade-Math-
Worksheets-And-
Exercises.html ● Explain how a multiplication equation can be used to compare
● Multiply and divide to solve word problems that use multiplication to compare
http://resources.oswego.org ● Solve multistep word problems using the four operations
/games/mathmagician/maths ● Interpret the meanings of remainders
1.html
● Represent problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity
● Determine if answers make sense using mental math, estimation, and mental math
My Math Grade 4 ● Find factor pairs for whole numbers 1-100
Textbook Connection: ● Recognize a whole number as a multiple of each of its factors
● Decide whether a whole number (1-100) is a multiple of a given one-digit number
Ch. 3, Lessons 3.1- 3.8 ● Determine if a whole number (1-100) is prime or composite
Ch. 4, Lessons 4.1 – 4.5, 4.7 ● Create a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule
Ch. 5, Lessons 5.1 – 5.5
Ch. 6, Lessons 6.1 – 6.6, 6.8 ● Identify characteristics about a pattern that are not part of a rule
Ch. 7, Lessons 7.1 – 7.4 ● Multiply a four-digit whole number by a one-digit whole number using strategies and
properties of operations
Textbook Online: ● Multiply two, two-digit numbers using strategies and properties of operations
● Apply strategies to find whole number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit
http://connected.mcgraw- dividends and one-digit divisors
hill.com/connected/login.do ● Represent and explain multiplication and division using an equation, rectangular array,
and/or area models
Student User ID:
ccsd(student ID)
Password: cobbmath1
Vocabulary
area model: a model for multiplication and/or division problems, in which the length
and width of a rectangle represents the factors, or quotient and dividend
composite: a whole number that can be divided evenly by numbers other than one
and itself (0 and 1 are neither prime nor composite)
distributive property: allows you to multiply a sum by multiplying each addend
separately and then adding the products
dividend: the number to be divided
divisor: the number used to divide by
equation: mathematical expression where one part is equal to another part
expression: numbers and symbols with no equal sign
Grade 4 Unit 2 2015-2016
factors: numbers you multiply together to get another number
multiples: the result of multiplying a number by another number
place value: value of a digit according to its place in a number
prime: a whole number that can be divided evenly only by one or itself (0 and 1 are
neither prime nor composite)
product: the answer to a multiplication problem
quotient: the answer to a division problem
rectangular array: arrangement of objects into rows and columns that form a
rectangle
remainder: the amount left over after division
Symbols Example 1
A red scarf costs $18. A blue scarf costs $6. How many times as much does the red scarf
X multiplication
cost compared to the blue scarf?
÷ division
= equals
Example 2
There are 4 beans in a jar. Each day 3 beans are added. How many beans are in the jar for
each of the first 5 days?
Example 3
Your class is collecting bottled water for a service project. The goal is to collect 300 bottles of
water. On the first day, Max brings in 3 packs with 6 bottles in each container. Sarah wheels in
6 packs with 6 bottles in each container. About how many bottles of water still need to be
collected?
Student 1 Student 2
First, I multiplied 3 and 6 which First, I multiplied 3 and 6 which
equals 18. Then I multiplied 6 and equals 18. Then I multiplied 6 and
6 which is 36. I know 18 plus 36 is 6 which is 36. I know 18 is about
about 50. I’m trying to get to 300. 20 and 36 is about 40. 40 + 20 =
50 plus another 50 is 100. Then I 60. 300 – 60 = 240, so we need
need 2 more hundreds. So we still about 240 more bottles.
need 250 bottles.
Example 4
What would an array area model of 74 x 38 look like?
Grade 4 Unit 2 2015-2016
Example 5
There are 592 students participating in Field Day. They are put into teams of 8 for the
competition. How many teams are created?
Activities at Home
Create a list of 5 items that you plan to purchase while at the supermarket. Have your child estimate the total
amount.
Roll five number cubes. Use four cubes to make a four-digit dividend, and use the fifth cube as the one-digit
divisor. Repeat five times to make five different problems.
Write 3 story problems that involve multiplication and 3 story problems that involve division. Use pennies,
uncooked macaroni noodles, or other counters to represent each problem.
Place a deck of cards face down (remove the face cards). Flip over two cards to create a two-digit number. List
all of the factor pairs for the two-digit number. Repeat the activity 5 times.
Skip count by 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, etc. Discuss multiples of a number.
Try to incorporate “real world” word problems often.
Grade 4 Unit 2 2015-2016
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- ImmunologyDocument8 pagesImmunologyማላያላም ማላያላም89% (9)
- Put Call ParityDocument37 pagesPut Call ParityVaidyanathan Ravichandran100% (1)
- Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWDocument411 pagesProcessing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images - H. Maitre (Wiley, 2008) WWbehzad100% (4)
- UMTS Optimization GuidelineDocument84 pagesUMTS Optimization GuidelineEvelio Sotolongo100% (3)
- Hungr Et Al 2005 - Landslide Travel DistanceDocument30 pagesHungr Et Al 2005 - Landslide Travel DistanceJosé Ignacio RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Asm 10Document4 pagesAsm 10Tukaram ParabPas encore d'évaluation
- SOFARSOLAR ModBus-RTU Communication ProtocolDocument22 pagesSOFARSOLAR ModBus-RTU Communication ProtocolВячеслав ЛарионовPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.data Types Ver2Document56 pages2.data Types Ver2qwernasdPas encore d'évaluation
- Beginners Tutorial: Issue Status/Number - 1.0 Issue Date - 10 November, 2002Document17 pagesBeginners Tutorial: Issue Status/Number - 1.0 Issue Date - 10 November, 2002nathulalusaPas encore d'évaluation
- E5 - Geotextiles TDR - Rev00Document2 pagesE5 - Geotextiles TDR - Rev00Mohd Radzi MustaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Virgil Ionescu Eforie 2016Document99 pagesVirgil Ionescu Eforie 2016Andreea CimpoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sti260N6F6 Stp260N6F6: N-Channel 60 V, 0.0024 Ω, 120 A Stripfet™ Vi Deepgate™ Power Mosfet In To-220 And I²Pak PackagesDocument14 pagesSti260N6F6 Stp260N6F6: N-Channel 60 V, 0.0024 Ω, 120 A Stripfet™ Vi Deepgate™ Power Mosfet In To-220 And I²Pak PackagesRyn YahuFPas encore d'évaluation
- PET524 Saturation 1Document12 pagesPET524 Saturation 1Ronald NguelePas encore d'évaluation
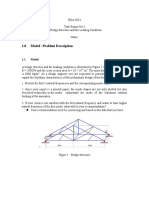
- Task 4 Finite Element MethodDocument7 pagesTask 4 Finite Element MethodMohd Azizee Bin SukorPas encore d'évaluation
- Triosonate in F (TWV 42-F7)Document17 pagesTriosonate in F (TWV 42-F7)EDMILSON BRUNO DO NASCIMENTOPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To PIC and Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To PIC and Embedded Systemsheno ahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Welding Equipment PowerpointDocument12 pagesGas Welding Equipment PowerpointChristian RexPas encore d'évaluation
- HST TrainingDocument11 pagesHST TrainingRamesh BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Linux NFS and Automounter Administration (Craig Hunt Linux Library)Document0 pageLinux NFS and Automounter Administration (Craig Hunt Linux Library)Bryan BowmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dawn C. Meredith, Meaning MakingDocument2 pagesDawn C. Meredith, Meaning MakingMrsriyansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualDocument54 pagesInstallation, Operation, and Maintenance ManualIsmael Berlanga ResPas encore d'évaluation
- Ruby On Rails 3 Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesRuby On Rails 3 Cheat SheetJarosław MedwidPas encore d'évaluation
- Demag KBK Alu Enclosed Track SystemDocument2 pagesDemag KBK Alu Enclosed Track SystemMAGSTPas encore d'évaluation
- Leading The Industry In: Solar Microinverter TechnologyDocument2 pagesLeading The Industry In: Solar Microinverter TechnologydukegaloPas encore d'évaluation
- NumaticsFRLFlexiblokR072010 EsDocument40 pagesNumaticsFRLFlexiblokR072010 EsGabriel San Martin RifoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation Eurocode 2Document4 pagesCalculation Eurocode 2rammirisPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryDocument23 pagesAssignment - 1 Introduction of Machines and Mechanisms: TheoryAman AmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Betriebsanleitung SM-RI-X - Q-75 Rev2Document65 pagesBetriebsanleitung SM-RI-X - Q-75 Rev2ABDULSALAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Real Time Operating SystemsDocument15 pagesReal Time Operating SystemsSaro VrsPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 ModularizationDocument5 pages03 ModularizationsumnatarajPas encore d'évaluation