Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure 3
Transféré par
Lisa Lu0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues3 pagesLysosomes are an organelle found in the nucleus of a cell. They are responsible for storing calcium ions in muscle cells. They also Control the activities of enzymes, and metabolize fatty acids.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentLysosomes are an organelle found in the nucleus of a cell. They are responsible for storing calcium ions in muscle cells. They also Control the activities of enzymes, and metabolize fatty acids.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
32 vues3 pagesCell Structure 3
Transféré par
Lisa LuLysosomes are an organelle found in the nucleus of a cell. They are responsible for storing calcium ions in muscle cells. They also Control the activities of enzymes, and metabolize fatty acids.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
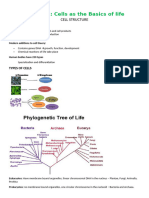
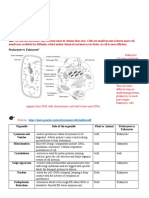
Cell
Function(s) Location in Cell Pro/Euk Kingdom(s) Unique Characteristics
Structure/Region
Where the DNA are Circular, double-stranded of DNA,
nucleoid region In middle Prokary. Monera
kept and multiple copies may exist
Separates the cell
from its surrounding
Monera, protist,
plasma membrane while allowing Surrounds the cytoplasm Both Selectively permeable
fungi, plant, animal
materials to pass
through
Outside the nucleus, Studded with protein-
rough endoplasmic Producing lysosomal Animal, plant,
connected to nuclear Eukary. manufacturing ribosomes giving it a
reticulum enzymes fungi, protist
envelope “rough” appearance
Help protect bacteria
capsule Outside the cell wall Prokary. Bacteria Exclude bacterial viruses and toxin
against phagocytosis
Metabolism of
smooth endoplasmic Connected to the nuclear Animal, plant, Known for its storage of calcium
carbohyd. and calci. Eukary.
reticulum envelope fungi, protist ions in muscle cells
concentration
Breaks down
Part of the secretory Malfunction of the lysosomes
lysosome macromolecules using Eukary. Animal, protist
pathway of a cell cause many illnesses
digestive enzymes
Control the activities Animal, plant,
nucleus In middle Eukary. First organelle discovered
of the cell fungi, protist
Production and
Monera, protist, Site where most of the ribosomal
nucleolus assembly of ribosome In the nucleus Both
fungi, plant, animal RNA is transcribed
components
Makes up
Monera, fungi,
chromatin chromosomes when In the nucleus Both Easily visualized by staining
plant, animal
cells aren’t dividing
Converts chemical of
foods, like sugar, to Animal, plant, Number in a cell varies widely by
mitochondria In the middle Eukary.
the chem. energy of a fungi, protist organism and tissue type
molecule called ATP
Process and package Part of the Animal, plant, Performs several functions in close
Golgi apparatus Eukary.
proteins and lipids endomembrane system fungi, protist with the ER
Participate in
metabolis of fatty Part of the secretory Animal, plant, They resemble lysosomes in being
peroxisome Eukary.
acids, ride the cell of pathway of a cell fungi filled with enzymes
toxic peroxides
Provide support for Three main cytoskeleton filaments:
Contained within the Protist, fungi,
cytoskeleton cell and maintains Both micro-, intermediate, and
cytoplasm plant, animal
shape, and protects microtubules
Regulates the
Protist, fungi, Mutant flies lacking centrioles can
centriole composition of In the centrosome Eukary.
animals, plants develop almost normally
cytoplasm
Allows bacteria to Projection from the cell Monera, protist, There are different type of flagella
flagellum Both
move body animal, plant depends on the cell
Simply move liquid Attached to cell’s Animal, plant, Make up undulipodia (with
cilium Eukary.
over their surface surface protist flagella)
Makes food by Contained by an envelope
chloroplast converting light into In middle Eukary. Plants consisting of an inner and outer
chemical phospholipids membrane
Bulk storage of starch, In roots and non-phot.
leucoplast Eukary. Plants
lipid or protein tissues of plants
Provides cell with Surrounds a cell outside Monera, fungi, Contructed from different
cell wall Both
structural support cell membrane plants materials, depending on species
Either “free” or
Synthesize proteins Monera, protist, Builds proteins form the
ribosome “membrane-bound” Both
using RNA animal, plant, fungi instructions within RNA
within a cell
Enables transport and Enable to direct regulate,
plasmodesmata communication In cell wall Eukary. Plants intercellular transport of substances
between cell walls between cells
Connects the
cytoplasm of cell, Between certain animal Make sure the molecules do not
gap junction Eukary. Animal
allowing some cell-types leak into the intercellular space
molecules to pass thru
Organized structures
Monera, protist, The DNA molecule may be
chromosome of DNA and proteins In the middle Both
fungi, plant, animal circular or linear
when cell is divided
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Structure and Organization of Genetic MaterialDocument2 pagesDomain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Structure and Organization of Genetic MaterialAaron AsnePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Cell - ANSDocument3 pagesAssignment Cell - ANSAj MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell TableDocument3 pagesCell TableJoshPas encore d'évaluation
- The Variety of Life TableDocument2 pagesThe Variety of Life TableSiraj EsscopriPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Samillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Document11 pagesSamillao Gen Bio Week 2 Q1Gem Kyla Mae SamillanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology QuicksheetsDocument11 pagesBiology QuicksheetsMaria Renee Lian NoblePas encore d'évaluation
- SCI-103 Lab8 FungiDocument4 pagesSCI-103 Lab8 FungiGrace Lilian CoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Eukaryotic Cells and Microorganisms ReviewerDocument12 pagesEukaryotic Cells and Microorganisms ReviewerMicalyn R. EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahPas encore d'évaluation
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (1)
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyPas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument21 pagesCellsEXTRA ACCOUNTPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument5 pagesCellGlenda ArajaPas encore d'évaluation
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Kingdom Scheme of ClassificationDocument6 pages6 Kingdom Scheme of Classificationabegail ballocanagPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microorganisms Growth PhasesDocument3 pagesMicroorganisms Growth PhasesRAYYAN ENIL ABDURAHAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology: Fundamentals of MycologyDocument3 pagesMicrobiology: Fundamentals of MycologyColleenPas encore d'évaluation
- Characterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesDocument4 pagesCharacterizing & Classifying ProkaryotesJennifer Davis CondimanPas encore d'évaluation
- cell compiledDocument7 pagescell compiledRizza Mae Telebrico CanterePas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 3. The Cells That Surround UsDocument6 pagesExercise 3. The Cells That Surround Usjunso2771Pas encore d'évaluation
- Living Organisms CellsDocument11 pagesLiving Organisms CellsShoag Al ArakzehPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure Locati ON Descripti ON FunctionDocument7 pagesCell Structure Locati ON Descripti ON Functionalvin christian pasteleroPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Kingdom Scheme of ClassificationDocument6 pages6 Kingdom Scheme of Classificationabegail ballocanagPas encore d'évaluation
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethPas encore d'évaluation
- Del Rosario Microbio Activity 1 Bacteria CellDocument6 pagesDel Rosario Microbio Activity 1 Bacteria CellNico LokoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesBiological Classificationsivarigil0610Pas encore d'évaluation
- Viruses: Lytic Cycle Lysogenic CycleDocument8 pagesViruses: Lytic Cycle Lysogenic CycleTài nguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument2 pagesCellJhon Rey LagosPas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument8 pagesCellsAnchal ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Diversity: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesMicrobial Diversity: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPonce Kristel Mae OPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4Document3 pagesLesson 4Samantha VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyESTHER NDUNGEPas encore d'évaluation
- ProtozoansDocument13 pagesProtozoansGabrielle ForgetPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cells: Cella - Small RoomDocument5 pagesThe Cells: Cella - Small RoomSarah Grace CajucomPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2ngelo.garolPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Document3 pagesCell Organelle and Parts Review Table - Chapter 6 Organelle/Cell Function Structure Plant/Animal/Proka Ryote?Lehman042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Cell Structure: Laura-Isidora-Matilde-Luciana 8BDocument15 pagesAnimal Cell Structure: Laura-Isidora-Matilde-Luciana 8Bbea regueraPas encore d'évaluation
- 2. Cell UltrastructureDocument5 pages2. Cell UltrastructureIrish Mae LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Only in Some Animal CellsDocument2 pagesOnly in Some Animal CellsAngela MahinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCDocument66 pagesPhle Reviewer Module 6 Qa QCMARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑOPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic MicroorganismsDocument16 pages3-Prokaryotic - Eukaryotic Microorganismsguestiam29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Structure and FunctionBrolyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter I - Characteristics & Classification of Living Organisms-MergedDocument13 pagesChapter I - Characteristics & Classification of Living Organisms-Mergedghostoast123Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Engineering NotesDocument13 pagesBiochemical Engineering NotesI am UnstoppablePas encore d'évaluation
- Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDocument14 pagesProkaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Distinguishing Their FeaturesDaniella Pasilbas SabacPas encore d'évaluation
- My Copy Cell Organelle Ws 1Document4 pagesMy Copy Cell Organelle Ws 1api-521781723Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4.2 Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument6 pages1.4.2 Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Celljumbergy01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology EOC Review Answers GuideDocument13 pagesBiology EOC Review Answers GuideIsaiah Knight Student - HeritageHSPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes 12&13 Phylum ApicomplexaDocument20 pagesLecture Notes 12&13 Phylum ApicomplexaAmirr4uddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure ComparisonDocument29 pagesCell Structure ComparisonChynna PornetePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PornetePas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Classification 2 anatomy the realDocument14 pagesBiological Classification 2 anatomy the realMukul YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideD'EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuidePas encore d'évaluation