Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lipids: Functions, Including Storage of Metabolic Energy, Protection Against Dehydration and Pathogens, The
Transféré par
ulanrain311Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lipids: Functions, Including Storage of Metabolic Energy, Protection Against Dehydration and Pathogens, The
Transféré par
ulanrain311Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lipids: functions, including storage of metabolic energy, protection against dehydration and pathogens, the
carrying of electrons, and the absorption of light. Lipids also contribute to the structure of membranes.
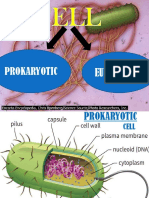
Ribosomes: Ribosomes are smallest and the most abundant cell organelle. It comprises of RNA and protein.
Ribosomes are sites for protein synthesis. They are found in all cells because protein are necessary for the
survival of the cell. The ribososomes are known as the protein factories of the cell.
Endoplasmic reticulum: Endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane bound compartment, which look like flattened
sacs lined side by side. It is a large network of interconnecting membrane tunnels. It is composed of both rough
endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
They are responsible for protein translation, and protein transport to be used in the cell membrane. They also aid
in sequestration of calcium, and production and storage of glycogen and other macromolecules.
Cytoplasm: It helps to move materials around the cell and also dissolves cellular waste.
Cell membrane: It is the outer boundary of the cell, it encloses the cytoplasm and the organelles of the cells. In
plants cells it is inside the cell wall. The cell membrane is semi permeable, allowing only specific substances to
pass through and blocking others.
Cell Nucleus: It controls the activity of the cell by regulating protein synthesis within the cell.
Vacuoles are the temporary storage center of the cell.
Golgi body is the unit where proteins are sorted and packed.
Mitochondria carries out cellular respiration and provides energy to the cells.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument21 pagesCellsouravPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport MechanismssdfkgjkDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - Cells Structure and Transport Mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology ProjectBemnet TayePas encore d'évaluation
- Cell OrganellesDocument42 pagesCell OrganellesTrisha OxalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Biohem NotesDocument118 pagesBiohem Notesdalweravikumar69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaePas encore d'évaluation
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Last-Cell Organelles.Document3 pagesLecture Last-Cell Organelles.OnSolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15Pas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument8 pagesCellvjaPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument8 pagesCellWhyL NificentPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Bio VivaDocument49 pagesFinal Bio Vivamanuel ortegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell OrgenellesDocument10 pagesCell OrgenellesShruti TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- بايو م 2Document7 pagesبايو م 2alidoctor678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles JigsawDocument10 pagesCell Organelles JigsawSusan VictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical Engineering: SCH1209 Biochemical Engineering Unit 1 Prepared By: DR - Annam Renita.ADocument14 pagesBiochemical Engineering: SCH1209 Biochemical Engineering Unit 1 Prepared By: DR - Annam Renita.ARamyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument43 pagesStructure and Function of The CellElvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Gen BioDocument3 pagesGen BioKeneth Parohinog ABM 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell Unit of LifeNavaneeth KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument10 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesHARKIRIT KAUR100% (1)
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 CIE Biology A-LeveloqypooPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathPas encore d'évaluation
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- The Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Document10 pagesThe Plant Cell Pharma With Bot&tax Week 4-6Katrina CarolasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell PartsDocument1 pageCell PartsamandadepaPas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMDocument40 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMnomysalihPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesMembrane-Bound Organelles Which Are Found in Animal Cells. Enzymes Digestive SystemFarah Jaye Verde CayayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarDocument61 pagesSeminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarKomal MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics 101Document4 pagesGenetics 101Jhon Ric BajePas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes - Cell The Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesRevision Notes - Cell The Unit of LifetPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Document30 pagesCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944Pas encore d'évaluation
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AliDocument20 pagesHuman Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AlikmoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesCell The Unit of LifeSREE GANESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- RibosomesDocument1 pageRibosomesatanu mitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForAlix AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForDocument12 pagesCells: Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol) - This Is The Solution Within The Cell Membrane. It Contains Enzymes ForShakera ReidPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellJayPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Crop PhysiologyDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Crop PhysiologyRsPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoPas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsAmabelle DorothyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles 2Document10 pagesCell Organelles 2Hardik tyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- By Muhammad SalmanDocument37 pagesBy Muhammad SalmanAmber ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument37 pagesCellAmber ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 8 Cell The Unit of Lifeaatishsubash9b35832Pas encore d'évaluation
- Models of Organizational BehaviorDocument11 pagesModels of Organizational Behaviorulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Senators of The Philippines 17 Congress: Paolo "Bam" Benigno Aquirre Aquino IVDocument1 pageSenators of The Philippines 17 Congress: Paolo "Bam" Benigno Aquirre Aquino IVulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Main Propositions Reinforcement TheoryDocument1 pageMain Propositions Reinforcement Theoryulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Bigay Lunas: Mercury Drug FoundationDocument2 pagesOperation Bigay Lunas: Mercury Drug Foundationulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Agriculture Is The Basis of All CivilizationDocument1 pageAgriculture Is The Basis of All Civilizationulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Agri 32 Exer 6Document3 pagesAgri 32 Exer 6ulanrain311100% (1)
- Agri 32 Study Questions Exer 2Document3 pagesAgri 32 Study Questions Exer 2ulanrain311100% (1)
- Instrument of VisayasDocument2 pagesInstrument of Visayasulanrain31175% (4)
- Horizontal Flower Arrangement Crescent Flower ArrangementDocument1 pageHorizontal Flower Arrangement Crescent Flower Arrangementulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Agri 41 Plant Path ReviewerDocument3 pagesAgri 41 Plant Path Reviewerulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Baguio BrochureDocument1 pageBaguio Brochureulanrain31159% (17)
- FoodDocument1 pageFoodulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Separating MixturesDocument4 pagesSeparating Mixturesulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Afro - Asian Culture: Dragon Dance - China Origami - JapanDocument4 pagesAfro - Asian Culture: Dragon Dance - China Origami - Japanulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is EnergyDocument2 pagesWhat Is Energyulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Art Forms in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesArt Forms in The Philippinesulanrain31179% (29)
- The Story of Mars RaveloDocument5 pagesThe Story of Mars Raveloulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Microscope: Decompose TDocument3 pagesMicroscope: Decompose Tulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diamon D: Earing S Kite RingDocument1 pageDiamon D: Earing S Kite Ringulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Parable of DivisionDocument3 pagesThe Parable of Divisionulanrain31185% (20)
- Teacher'S Guide: Exploratory Course On Commercial CookingDocument16 pagesTeacher'S Guide: Exploratory Course On Commercial Cookingulanrain311100% (1)
- Bahay Kubo With NotesDocument1 pageBahay Kubo With Notesulanrain311Pas encore d'évaluation