Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
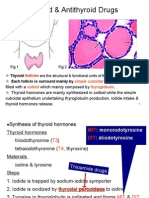
Anti-Thyroid Drugs Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side Effects
Transféré par
Thulasi tootsieTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anti-Thyroid Drugs Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side Effects
Transféré par
Thulasi tootsieDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
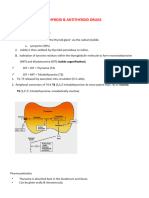
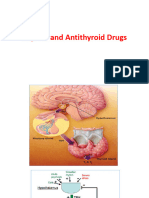
ANTI-THYROID DRUGS
Rx for HYPOthyroidism
CLASS EXAMPLES INDICATION M.O.A SIDE EFFECTS
T4 L- thyroxine -Hypothyroidism -Absorption of oral T4 is Rapid increase of dose
(Tetraiodo-L- (levothyroxine sodium) incomplete and variable. /high dose therapy:
thyronine) thyroxine deficiency -It is 99.9% bound to plasma
T4 is the less active from any cause. proteins; -> angina, heart failure,
precursor of T3 “Replacement - mainly to thyroxine-binding tachycardia, atrial
therapy” globulin (TBG) fibrillation
-T4 passes in to the -T4 is converted to the active
cells of target organ IMPORTANT: form; T3 in tissues. Especially in the elderly
and combines with Treatment must be -T4 is deiodinated and conjugated and in ischaemic heart
specific nuclear life-long in the liver and excreted in bile disease
receptors. and urine.
Main Causes: t 1/2, depends on the thyroid -start with a low dose;
These receptors are Autoimmune status of the person 12.5-25
found in most (Hashimoto) micrograms/day
tissues. thyroiditis, 1o thyroid *7 days in euthyroid subjects,
failure *14 days in hypothyroism Over dose of thyroxine
-They induce protein Symptoms: Reversible *3 days in hyperthyroidism -> features similar to
synthesis (growth slowing of body thyrotoxicosis
retardation and short functions, lethargy, -With regular dosing, the steady (finger tremors,
stature in children tiredness, BMR, state plasma concentration is tachycardia)
with untreated appetite, CO, dry achieved only after 4-5
hypothyroidism) skin, cold intolerance, weeks.(t1/2x 5) Certain drugs interfere
wt, constipation with absorption –
-Increase the basal *Dosage form; T4 sodium tablets *sucralfate,
metabolic rate and -Cretinism (neonatal *strength of tablets; in *cholestyramine resin
O2 consumption. hypothyroidism) micrograms(50ug, 100ug/tablet) *iron/calcium/ mineral
-hypo at any age *Store tablets <250C; preferably supplements
-T4 causes -Myxoedema in the refrigerator *aluminium hydroxide
proliferation of beta -Autoimmune *Once a day therapy in the *Some soy products
adrenergic receptors thyroiditis morning. Before breakfast; for *Phenytoin/
particularly in the -Subclinical (no better absorption and better carbamazepine/
CVS. features) bioavailability. rifampicin enhances
- therefore there is hypothyroidism excretion through
increased sensitivity *Elderly and in patients with IHD effect on liver enzymes
to catecholamines Dx: Low free thyroxin + start with 12.5-25ug/day.
(epinephrine and TSH **Increase the dose gradually ->This may necessitate
norepinephrine) every 2- 4 weeks an increase in the dose
T3 Liothyronine sodium -Hypothyroidism -Is about 5 times as biologically associated with more
(Triiodo- L- (Na salt of T3) -Severe active as T4 adverse effect
thyronine) hypothyroidism -Its binding to plasma proteins is (hence, uses is
Less protein bound (hypothyroid coma) weaker than T4 uncommon)
faster action than -T ½ is 2 days in euthyroid subjects
T4 Used only when a -It is mainly used to manage
quicker onset of action severe hypothyroidism;
T3 is the major is needed e.g. impending coma or coma;
mediator of myxodema coma administered IV or through a
physiological effects nasogastric tube (a high dose).
-Used (together with
hydrocortisone)
Liotrix Constituent of many Expensive with no Mimics ratio of normal thyroid
commercial thyroid special advantage secretion
hormone in fixed
ratio of 4:1 (T4:T3)
Rx of HYPERthyroidism
CLASS EXAMPLES INDICATION M.O.A SIDE EFFECTS
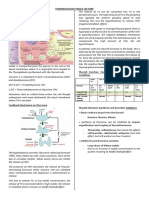
1. Inhibitors of Propylthiouracil 1. Management of *Inhibit iodine organification -Nausea
hormone “Graves” disease: an -> blocking thyroxine peroxidase -Taste disturbance
synthesis *Inhibits peripheral autoimmunedisorder which promotes coupling of I- -Pruritic rash
(Thionamides) deiodination of T4 to T3 characterized by with Tyrosine MIT and with -vasculitis
*Reserved for pts
Inhibits: remissions and MIT DIT) -arthralgia
->oxidation of intolerant of carbimazole
exacerbations. *Immunosupressive -cholestatic jaundice
iodide (1/10th activity of
2. Hyperthyroidism Hepatitis
->Iodination of methimazole)
*High agranulocytosis due to toxic multi *accumulate in the thyroid -lymphadenopathy
tyrosine
(report any fever/ sore nodular goitre: proir to Onset of effect ~ 3-4 wks (time - hypo
(organification)
->Coupling of throat which tend to surgery for depletion of preformed prothrombinaemia
iodotyrosines precede this) 3. Management of hormone) - Agranulocytosis +
thyroid crisis (severe ->Although t 1/2 is short; 2-4 hrs, Neutropenia
Methimazole hyperthyroidism/ ->High intrathyroidal (most dangerous
thyroid storm) concentration of all thionamides -> sore throat+fever)
*not bound to plasma 4. Adjuvant therapy for 30-40 hrs prolong their
proteins and is with radio iodine duration of action Cross sensitivity b/wn
metabolised in the liver therapy ->Hence a single daily dose is propylthiouracil and
and excreted in urine methimazole ~ 50%
adequate (once a day therapy).
Carbimazole ->Do not block the release of
*All are given p.o. stored thyroid hormones
*Drug of choice in
*Rapidly absorbed ->Hence clinical effects are seen
Grave’s
*Converted in vivo to
from the gut only after7-10days (when
methimazole-1st pass met preformed T4 is depleted)
(rapidly and completely)
2. Inhibitors of Perchlorates Anion Inhibitors: Competitively inhibits the uptake Causes aplastic
iodide trapping (Thiocyanates/ Nitrates) Potassium perchlorate of iodine anaemia (rarely used)
3. Inhibitors of Iodine, iodides of K & *Short term Rx only -Action not clear -Adverse reactions to
hormone Na, organic iodides (antithyroid effect -Inhibits organification and iodide (iodism) is rare
release drops) hormone release and reversed by
*Inhibit all aspects of T4 *Quick (2-7 days) -Decreases size and vascularity of withdrawal
formation + release effect useful in gland (smaller) ->rash, swollen salivary
thyroid storm -useful pre-thyroidectomy (10 glands, conjunctivitis,
days prior) rhinorhoea, drug fever,
-Reduces conversion of T4 to T3 metalic taste
Inhibit thyrotropin action
4. Agent that I131, I 125, I 123 1.Relapse of Graves Concentrated by thyroid ->Eventual
destroy thyroid disease following Emits beta rays which destroy hypothyroidism:
tissue thionamide therapy thryoid tissue within few weeks -> identify early and
2.In patients who *cytotoxic effect is restricted to treat with thyroxine
develop cells of thyroid follicles ->c/i: pregnancy and in
agranulocytosis *Does not damage the breast feeding
following thionamide parathyroid
therapy *Given p.o (syrup)
3.To treat some types *single dose (8wks for full effect)
of thyroid carcinoma * Stabilise Pt first with
with metastasis Carbimazole before 131I
*Stop Carbimazole 3-4/7 b4 131I
Rx
5. β blockers Propanolol (non- 3. Before and after radio 1. In newly diagnosed, until thyroid c/i: asthma
only as short selective) iodine therapy function test results are available for
term adjuvant 4. To treat thyroid crisis confirmation.
therapy (“thyroid storm”) 2. Concurrently with the
commencement of thionamides until
their action is well established
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- APA - DSM 5 Depression Bereavement Exclusion PDFDocument2 pagesAPA - DSM 5 Depression Bereavement Exclusion PDFDaniel NgPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Nodules, and CancerDocument77 pagesHypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism, Thyroid Nodules, and CancerDann San AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Stimulation Motor Points GuideDocument33 pagesElectrical Stimulation Motor Points GuideSreeraj S R100% (5)
- Thyroid and Antithyroid Agent-VDocument60 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid Agent-VVine100% (1)
- Pharmacology Tyroid and Antitiroid HormonDocument21 pagesPharmacology Tyroid and Antitiroid HormonPuterinugraha Wanca ApatyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anamnesis & PemfisDocument81 pagesAnamnesis & PemfisFikriYTPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrinology Board Review: Thyroid DisordersDocument46 pagesEndocrinology Board Review: Thyroid DisordersDemuel Dee L. BertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Diabetes Prevention ProgramDocument19 pagesPhilippine Diabetes Prevention Programkoala100% (1)
- Clinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmDocument73 pagesClinical Approach of Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidsm and HyperthyroidsmdiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesRespiratory SystemThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Week 3 Pharmaco Part 2Document34 pagesWeek 3 Pharmaco Part 2Tiko JomidavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuro OSCE - Student Guide PDFDocument9 pagesNeuro OSCE - Student Guide PDFDAVE RYAN DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Case Study Acute PancreatitisDocument62 pagesCase Study Acute PancreatitisAilyne A. CleofePas encore d'évaluation
- Canadian Framework For Teamwork and Communications Lit ReviewDocument68 pagesCanadian Framework For Teamwork and Communications Lit ReviewanxxxanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid DisordersDocument34 pagesThyroid DisordersAbdulhameed Mohamed100% (1)
- Therapeutics: Thyroid DisordersDocument24 pagesTherapeutics: Thyroid DisordersSharas FarhadPas encore d'évaluation
- Cues/ Data Cues/ Data: Family Nursing Problem Family Nursing ProblemDocument14 pagesCues/ Data Cues/ Data: Family Nursing Problem Family Nursing ProblemAriane Rose Saria CedronPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid ReportDocument105 pagesThyroid ReportAARVPas encore d'évaluation
- The Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021Document9 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021abcde990075Pas encore d'évaluation
- PCOL - Thyroid DrugsDocument4 pagesPCOL - Thyroid DrugsTerepe CrimsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs: Thyroglobulin, Hormone SynthesisDocument13 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid Drugs: Thyroglobulin, Hormone SynthesisLatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsDocument7 pagesThyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsPrincess Noreen SavellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of ThyroidDocument32 pagesPharmacology of Thyroidbrigita charvioPas encore d'évaluation
- Management and Medications in Thyroid Strom and Myxoedema ComaDocument41 pagesManagement and Medications in Thyroid Strom and Myxoedema ComaBhavesh kunvarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersDocument11 pagesPharmacology Finals Lecture Thyroid DisordersJuliann100% (1)
- Pharmacology of the Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPharmacology of the Thyroid GlandRhena Fitria KhairunnisaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Lecture 10 Anti-Thyroid Drugs (DR Thatcher Pod Pharm 2022)Document36 pages02 Lecture 10 Anti-Thyroid Drugs (DR Thatcher Pod Pharm 2022)sahilaminPas encore d'évaluation
- CombinedDocument40 pagesCombinedshortsmotivation87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hormones, Antagonists, and Other Agents Affecting Endocrine FunctionDocument36 pagesHormones, Antagonists, and Other Agents Affecting Endocrine Functionapi-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020Document7 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020irenePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2Document51 pages11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2nica velanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs... HaftomDocument40 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid Drugs... Haftomkaleab AlemayehuPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 TSHDocument7 pages2 TSHNashat SaadiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3ES-2 Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs 1436Document46 pages3ES-2 Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs 1436Muath AlqarniPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid DisorderDocument10 pagesThyroid DisorderDr-Mohammed ElsawyPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid & Anti-thyroid Drugs: An Overview of Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism TreatmentDocument59 pagesThyroid & Anti-thyroid Drugs: An Overview of Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism TreatmentNiranjanPas encore d'évaluation
- THYROIDDocument24 pagesTHYROIDanaya khan StudentPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Disorders - 2023Document82 pagesThyroid Disorders - 2023JEPHTHAH KWASI DANSOPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothyroidism - Types: Type Primary Secondary Origin ThyroidDocument7 pagesHypothyroidism - Types: Type Primary Secondary Origin Thyroidboinklets100% (1)
- Im-Thyroid DisordersDocument9 pagesIm-Thyroid DisordersRyan F. BernalPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Thyroid Disorders and Their TreatmentDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Thyroid Disorders and Their TreatmentPrincess Krenzelle BañagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Thyroid Disorders and Their TreatmentDocument15 pagesUnderstanding Thyroid Disorders and Their TreatmentPrincess Krenzelle BañagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System Chapter on Thyroid Hormones and Antithyroid DrugsDocument40 pagesEndocrine System Chapter on Thyroid Hormones and Antithyroid DrugsMSKCPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Disorders ExplainedDocument28 pagesThyroid Disorders ExplainedMina RoxasPas encore d'évaluation
- OS 215: Anti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid Hormone RegulationDocument7 pagesOS 215: Anti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid Hormone Regulationmicheal1960100% (1)
- Lesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument28 pagesLesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugstheintrovPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesEndocrine Cheat Sheetsdarlington D. y ayimPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid and Antithyroid PharmaDocument31 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid PharmaxaviermargaridaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in HypothyroidismDocument24 pagesDrugs Used in Hypothyroidismsigit_riyantonoPas encore d'évaluation
- CC 3-Lab FKM 17Document4 pagesCC 3-Lab FKM 17mayabangkurtipotPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrinology Part 2Document4 pagesEndocrinology Part 2Alondra SagarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid and Antityr DrugsDocument23 pagesThyroid and Antityr Drugsmsmobile shPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenDocument29 pagesThyroid Gland Diseases in ChildrenadinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid HormonesDocument6 pagesThyroid Hormonesحوراء عارف الموسويPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3Document10 pagesEndocrine Drug: T4 Is Secreted in Excess To T3emmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- 1656070457849442Document161 pages1656070457849442aldeeray01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Storm TreatmentDocument1 pageThyroid Storm TreatmentIlham NiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti - Thyroid Drugs: Renju.S.RaviDocument27 pagesAnti - Thyroid Drugs: Renju.S.RavidrfatimarizPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyrotoxicosis & Hypothyroidism by Prof DR NK ChopraDocument52 pagesThyrotoxicosis & Hypothyroidism by Prof DR NK ChopraAbdulsalam DostPas encore d'évaluation
- THYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIDocument4 pagesTHYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIAnonymous HH3c17osPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacological Properties of PTUDocument21 pagesPharmacological Properties of PTUHanif JundanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Effecting On Thyroid Gland: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdDocument22 pagesDrugs Effecting On Thyroid Gland: Abdullaev Dzhumadil, PharmdRtxGaming Zone 73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of The Thyroid GandDocument167 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid GandWendy Figueroa MijaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Hormones & Antithyroid Drugs: Mechanisms, Uses & Side EffectsDocument27 pagesThyroid Hormones & Antithyroid Drugs: Mechanisms, Uses & Side EffectsjabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument38 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsbrkbsnPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Hyperthyroidism (Graves) Vs Thyrotoxicosis (Thyroiditis) ? RAIU To Differentiate Causes of Hyperthyroidism? Thyroid ScanDocument4 pagesPrimary Hyperthyroidism (Graves) Vs Thyrotoxicosis (Thyroiditis) ? RAIU To Differentiate Causes of Hyperthyroidism? Thyroid ScanmbdzPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid Hormones & DrugsDocument51 pagesThyroid Hormones & DrugsSUTHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Hearts PDFDocument30 pagesHearts PDFLaura RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative IV M207Document2 pagesSummative IV M207Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Patho QuizDocument5 pagesRenal Patho QuizThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Past Year RespiDocument5 pagesPast Year RespiThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Past Year QuestionsDocument3 pagesRenal Past Year QuestionsThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Summative m108Document2 pagesSummative m108Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Summative m107 Endo, Repro, RenalDocument6 pagesSummative m107 Endo, Repro, RenalThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- RENAL and Reproductive Systems - Q & ADocument13 pagesRENAL and Reproductive Systems - Q & AThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of The Cranial Nerves. Cranial Information. Patient - Patient - CoDocument7 pagesExamination of The Cranial Nerves. Cranial Information. Patient - Patient - CoThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Mskcns Sum m107Document2 pagesMskcns Sum m107Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Past Year ReproDocument4 pagesPast Year ReproThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Ovary PathologyDocument2 pagesOvary PathologyThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Pass Year CVSDocument6 pagesPass Year CVSThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- MSK Formative 2012Document13 pagesMSK Formative 2012Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- MalariaDocument1 pageMalariaThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Past Year Me110Document2 pagesPast Year Me110Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- MEQ AnswerDocument9 pagesMEQ AnswerThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- M208 MSK+CNS Summative (12 Nov 2010)Document11 pagesM208 MSK+CNS Summative (12 Nov 2010)Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Male Genital TractDocument4 pagesMale Genital TractThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- By WehloongDocument5 pagesBy WehloongThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- HematologyDocument39 pagesHematologyThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Female Genital TractDocument2 pagesFemale Genital TractThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- MEQDocument1 pageMEQThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- M208 Sum 5Document3 pagesM208 Sum 5Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- ME110 Summative Sem 5Document17 pagesME110 Summative Sem 5Thulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- M109 MSKCNSSummativeDocument5 pagesM109 MSKCNSSummativeThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- GI+hemato Past YearDocument9 pagesGI+hemato Past YearThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- Important MechanismDocument2 pagesImportant MechanismThulasi tootsiePas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Formative 2012Document17 pagesCNS Formative 2012Ho Yong WaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1.A: First Aid for Common Outdoor EmergenciesDocument30 pagesLesson 1.A: First Aid for Common Outdoor EmergenciesAnonymous LToOBqDPas encore d'évaluation
- Peplau's Theory of Interpersonal Relations: An Alternate Factor Structure For Patient Experience Data?Document9 pagesPeplau's Theory of Interpersonal Relations: An Alternate Factor Structure For Patient Experience Data?Rila LuaduPas encore d'évaluation
- GlossectomyDocument68 pagesGlossectomyRohan GroverPas encore d'évaluation
- English Meeting 2Document10 pagesEnglish Meeting 2Tya DwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedDocument19 pagesOsteosarcoma DR: Gehan MohamedNico DougaPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Issues in Spinal AnesthesiaDocument19 pagesCurrent Issues in Spinal AnesthesiaNadhifah RahmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dehydration PPDocument17 pagesDehydration PPApol PenPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation of Hypoglycemia: & Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome (Hirata Disease)Document15 pagesEvaluation of Hypoglycemia: & Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome (Hirata Disease)Anonymous B3J9sWPas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment Plan AssignmentDocument2 pagesTreatment Plan AssignmentyourzxtrulyPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument136 pagesPrinciples of Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Arrow Flex Sheath - Brochure - EN PDFDocument3 pagesSuper Arrow Flex Sheath - Brochure - EN PDFbiomedical_com_brPas encore d'évaluation
- GNMK IMC 20152 A EPlex BrochureDocument4 pagesGNMK IMC 20152 A EPlex BrochureBilgi KurumsalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dall Miles Surgical ProtocolDocument16 pagesDall Miles Surgical Protocolfarnaz_2647334Pas encore d'évaluation
- History Taking GuideDocument2 pagesHistory Taking GuideKristel Anne G. CatabayPas encore d'évaluation
- SAMPLE Common Medical AbbreviationsDocument10 pagesSAMPLE Common Medical AbbreviationsReina AzaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Adrenergic Drugs Classification and UsesDocument2 pagesAdrenergic Drugs Classification and UsesSunshine_Bacla_4275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKyla CalzadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Child Psychiatric DisordersDocument30 pagesCommon Child Psychiatric DisordersabrihamPas encore d'évaluation
- Explanation of BenefitsDocument1 pageExplanation of Benefitsmohamed hamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastritis Treatment PlanDocument2 pagesGastritis Treatment PlanSuresh ThanneruPas encore d'évaluation
- A Clinical Decision Support Framework ForDocument5 pagesA Clinical Decision Support Framework FordineshshaPas encore d'évaluation