Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mnre
Transféré par
Priya SaxenaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mnre
Transféré par
Priya SaxenaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RE FEATURE
WIND
POWER
DEVELOPMENT
IN INDIA An Overview
The utilization of wind energy in India
has been growing at a steady rate over
the past few years. In this article,
J K Jethani via detailed policy measures,
commercial viability, and wind power
infirmity management guidelines, traces the
trajectory of wind energy in the country and
the way forward.
»» Orange DND Wind Power Pvt Ltd- 22.5 MW
T
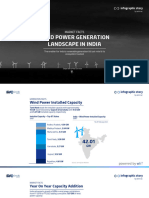
he wind power development projects in 1994. The present wind power As per the Global Wind 2016 Report,
in the country was initiated installed capacity in the country is over published by Global Wind Energy
in the early 1990s followed 32.7 GW and wind energy constitutes Council, at the end of 2016, globally India
by the introduction of 100% around 55% of the total renewable ranked fourth in terms of wind power
accelerated depreciation benefit for wind capacity in the country. installed capacity and the total wind
power installed capacity at the end of
2016 was around 487 GW.
In spite of the sharp increase in wind
power capacity in the country, only a
fraction of the country’s wind potential
has been tapped till date. As per the
recent assessment of National Institute
of Wind Energy (NIWE), the potential
for onshore wind at 100 m above ground
level is over 302 GW.
The vast untapped wind power
potential could be harnessed to meet
India’s policy goals, address energy
security challenges, and achieve low
»» Figure 1: Wind installed capacity (GW)
carbon growth, in a cost effective manner.
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 20
WIND POWER DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: AN OVERVIEW
In this endeavour, the Ministry of
New and Renewable Energy (MNRE),
Government of India, has adopted a
multidimensional approach, aiming at
large-scale commercialization of cost-
effective generation of grid-quality wind
power. The wind power programme
includes comprehensive wind resource
assessment programme, research
and development, implementation
of demonstration projects to create
awareness, development of infrastructural
capability, capacity to manufacture
along with installation, operation and
maintenance of wind turbines and
conducive policy formulation.
WIND POTENTIAL
Wind energy is intermittent and highly
site-specific and, therefore, an extensive
Wind Resource Assessment Programme »» 50.4 MW hybrid tower wind farm in Rajasthan
is essential for selecting the potential
sites. Therefore, MNRE, Government of The online wind atlas is available on the companies in India, through (i) joint
India, placed emphasis on Wind Resource NIWE website www.niwe.res.in. ventures under licensed production,
Assessment since the beginning and (ii) subsidiaries of foreign companies,
today, India has an abundance of data, COMMERCIAL and (iii) Indian companies with their
collected from over 800 wind monitoring DEVELOPMENT AND own technology. The current annual
stations installed all over India. GENERATION production capacity of domestic wind
The recent assessment conducted Technology development turbines is about 10,000 MW. The focus
by NIWE, with actual land availability and manufacturing base is to promote a technology suitable
estimation using NRSC Land Use Land The wind electric generator technology
for low wind regimes of India. Wind
Cover (LULC) data, indicates a gross has evolved very rapidly in the country.
turbines and wind turbine components
wind power potential of about 302 GW State-of-the-art technologies are now
available for manufacture of wind are exported to the US, Australia, Europe,
@ 100 m in the country. Most of this
turbines and all major global players in Brazil, and Asian countries. Due to a
potential exists in seven windy states. The
state-wise wind power potential at 100 m the field have made their presence in the stronger domestic manufacturing sector,
height is described in Table 1. country. The unit size of machines has around 70%–80% indigenization has been
Table 1: Wind power potential in India at gone up to 3.00 MW. Over 50 different achieved in the sector. Interestingly, the
100 m above ground level models of wind turbines are being cost of Indian wind turbines is one of the
S. State Wind Power manufactured by more than 20 different lowest in the world.
No. Potential at
100 m in GW
1 Andhra Pradesh 44.23
2 Gujarat 84.43
3 Karnataka 55.86
4 Madhya Pradesh 10.48
5 Maharashtra 45.39
6 Rajasthan 18.77
7 Tamil Nadu 33.80
Total (7 windy States) 292.97
8 Other States 9.28
All India Total 302.25 »» Figure 2: Year-wise cumulative wind power installed capacity in India (MW)
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 21
RE FEATURE
Generation achieve optimum generation of power
The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) in the most efficient and cost-effective
has begun compiling the renewable manner, MNRE issued revised guidelines
energy generation data since 2014/15. for wind power projects in 1996. These
The state-wise quantum of energy guidelines, relating to preparation
produced from wind energy during of Detailed Project Reports (DPRs),
2014/15, 2015/16, and 2016/17 is micro-siting, selection of wind turbine
described in Table 3. equipment, operation & maintenance,
Table 3: The state-wise quantum of energy produced from wind energy during 2014/15,
2015/16, and 2016/17
Sl. Wind Power Generation in MU
State
No. 2014/15 2015/16 2016/17 (Tentative)
1 Andhra Pradesh 1,675.82 2,013.04 3,187.85
2 Gujarat 5,660.09 6,446.58 7,720.01
3 Karnataka 4,658.1 4,797.95 6,058.65
4 Kerala 58.4 51.45 72.59
»» 90.3 MW hybrid tower wind farm in Madhya
Pradesh 5 Madhya Pradesh 592.25 1,558.43 3,256.38
6 Maharashtra 6,804.8 6,121.34 7,490.75
Deployment 7 Rajasthan 4,171.63 4,767.36 5,764.12
The annual growth picked up from 8 Tamil Nadu 10,147.1 7,273.23 11,935.26
the start of 2002. A total wind power 9 Telangana 0 0 211.93
capacity of around 32.3 GW was
Total 33,768.2 33,029.4 45,697.54
operational as on March 31, 2017. Year-
wise cumulative wind power installed The contribution of wind energy in performance evaluation, etc., have created
capacity is given in Figure 1. With an the total renewable generation during and raised the level of awareness among
installed capacity of over 7.86 GW, Tamil 2014/15, 2015/16, and 2016/17 was 55%, the State Electricity Boards, State Nodal
Nadu is the leader in wind. During 50%, and 56%, respectively. Agencies, manufacturers, developers, and
2016/17, capacity of 5502 MW, the investors about planned development and
highest ever in a single year, was added. GUIDELINES FOR implementation of wind power projects.
The state-wise wind power capacity added SETTING UP WIND However, due to the advancement in
during 2016/17 and cumulative wind POWER PROJECTS wind turbine technology and requirement
power capacity as on March 31, 2017, is To bring about healthy and organized to comply to various standards and
described in Table 2. regulations issued by CERC, CEA, and
growth of the wind energy sector and
other regulatory bodies, the need to issue
Table 2: State-wise wind power capacity
comprehensive guidelines for development
S. State Wind Power Capacity Cumulative Wind Power Installed of onshore wind power projects in the
No addition during FY Capacity operational at the end of country was felt. Accordingly, new
2017 (MW) FY 2017 (MW)
guidelines for development of onshore
1 Andhra Pradesh 2,187.45 3,618.85 wind power projects were issued
2 Gujarat 1,392.00 5,340.62 on October 22, 2016, incorporating
requirement of site feasibility, type
3 Karnataka 882.30 3,751.40
and quality certified wind turbines,
4 Kerala 8.00 51.50 micro-siting criteria, compliance of grid
5 Madhya Pradesh 356.70 2,497.79 regulations, real time monitoring, online
registry and performance reporting, health
6 Maharashtra 117.55 4,771.33
and safety provisions, decommissioning
7 Rajasthan 287.70 4,281.72 plan, etc. The key provisions of the new
8 Tamil Nadu 247.57 7,861.46 guidelines are as follows:
9 Telangana 23.10 100.80 ¾¾ NIWE mast data to be made available
online free of cost
10 Others - 4.30
¾¾ Wind site allocations to be developed
Total 5,502.37 32,279.77 within a maximum of four years
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 22
WIND POWER DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: AN OVERVIEW
¾¾ Micro-siting shall be based on an wind power.The Ministry of Power (MoP) Green Energy Corridors
optimized output rather a strict on September 30, 2016, issued an order The maximum wind power potential is
mandated minimum distance between for waiver of ISTS charges and losses concentrated in 7–8 wind resource-rich
wind turbines. for wind and solar power subject to the states wherefrom wind power is evacuated
¾¾ Safe distance prescribed for public following conditions: from the resource rich to the off-taker
roads, railway tracks, highways, I. The waiver is applicable for wind states. This requires strengthening of
buildings, public institutions, and power projects commissioned till transmission in intra-state as well as inter-
EHV (extra high voltage) lines. March 31, 2019, and for 25 years state transmission infrastructure.
¾¾ Wind turbines to comply with grid from the date of commissioning of The Green Energy Corridors Project,
regulations. It shall be mandatory the projects. Further, the waiver is instrumental in identification of
to install ABT (availability-based available for projects having power transmission requirement for renewable
tariff) meter with telecommunication purchase agreements (PPAs) with power capacity addition during the
facility. discoms for compliance of RPO. Twelfth Five Year Plan period, is currently
under implementation. Intra-state
¾¾ Online registry will be created II. For solar, the waiver was valid
transmission infrastructure projects of
followed by mandatory reporting of up to June 30, 2017, as per CERC
total cost over `10,000 crore, in eight
monthly performance. regulations.
states, have already been approved and
¾¾ Noise and shadow flicker to ensure III. The waiver is only applicable for solar the central government is providing 40%
health and safety of people working/ and wind projects awarded through a of the project cost as grant from National
residing near the wind farm will be competitive bidding process. Clean Energy Fund and another 40% of
prescribed. the project cost is available as soft loan
Forecasting and Scheduling through the German Bank KfW.
NEW INITIATIVES At this juncture, it is important to
The government, on its part, has been note that the infirm nature of wind Repowering Policy
instrumental in promoting the wind power, attributed to both natural wind Most of the wind turbines installed up to
energy sector in the country via a range of fluctuations as well as man-made designs the year 2000 are of capacity below 500
fiscal incentives and new schemes. of wind turbine, poses a challenge for grid kW and are at present located at sites
security and stability. The issue, however, replete with high wind energy potential. It
Amendment in Tariff Policy could be addressed through proper is estimated that over 3,000 MW capacity
Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) forecasting and scheduling of wind power. installations are produced by wind
was introduced through the Electricity The CERC has already notified a turbines of 500 kW capacity or below. In
Act, 2003, mandating the obligated mechanism for scheduling and forecasting order to optimally utilize the wind energy
entities to procure a minimum percentage in case of inter-state transmission of solar resources, repowering is imperative. The
of their total energy procurement from and wind power. The states of Gujarat, main features of the repowering policy are
renewables. The state regulators declared Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and Odisha, enumerated as follows:
the requisite RPO level, ranging from have already notified draft regulations for ¾¾ As part of the policy, wind turbine
3% to 12%, for the year 2016/17. The intra-state transmission of wind and solar generators of capacity 1 MW and
amended Tariff Policy notified in January power and the states of Andhra Pradesh, below will be eligible for repowering.
2016 provides for purchase of renewable Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Karnataka,
¾¾ IREDA will provide an additional
energy by different states in more or less and Rajasthan have already finalized
interest rate rebate of 0.25% for
the same proportion. The policy further these regulations. NIWE, Chennai, has
repowering projects.
provides for prescribing long-term growth undertaken the forecasting and scheduling
trajectory of RPO by Ministry of Power, exercise in Tamil Nadu which has resulted ¾¾ Benefits available to the new
Government of India, in consultation in better management of transmission wind projects, that is, accelerated
with MNRE.The MoP has issued RPO system for evacuation of wind power in depreciation or GBI as per applicable
trajectory up to 2019 notifying uniform the state and during 2016/17, over 12 BU conditions will also be available.
RPOs across the country. of wind power was evacuated compared ¾¾ In case augmentation of transmission
Since the wind power potential is to around 7 BU earlier. Similar initiatives system from pooling station onwards
concentrated in 7–8 windy states, to have been carried out in Rajasthan and is required, the same would be
facilitate the inter-state transmission of Gujarat as well. For proper forecasting carried out by the respective state
(wind) power from one windy state to and scheduling, it is necessary to put in transmission utility.
other states, the Tariff Policy provides place a metering and communication ¾¾ Additional generation could either be
for waiving of the interstate transmission infrastructure at all pooling stations for real purchased by discoms at feed-in-tariff
charges and losses for inter-state sale of time generation of data. applicable in the state at the time of
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 23
RE FEATURE
commissioning of the repowering
project or allowed for third party sale.
Draft Wind–Solar Hybrid
Policy
Research has revealed the
complementary nature of solar and wind
power and how hybridization of the two
technologies will aid in minimizing the
variability, apart from optimally utilizing
the infrastructure, including land and
transmission system. Accordingly, with
the objective of providing a framework
for promotion of large grid connected
wind-solar PV system for optimal and
efficient utilization of transmission
infrastructure and land, reducing
»» 90.3 MW hybrid tower wind farm in Madhya Pradesh
the variability in renewable power
generation, and achieving better grid through purchase of wind power at a of wind energy. The SECI issued letter
stability, MNRE issued the draft tariff determined by transparent bidding of allocation (LoA) to the selected five
Wind–Solar Hybrid Policy. process, a scheme for setting up of 1,000 bidders on April 5, 2017, and the projects
The goal of the policy, currently MW Inter-State Transmission System under the Scheme are likely to
pending approval, is to achieve wind– (ISTS) connected Wind Power Projects be commissioned by September 2018.
solar hybrid capacity of 10 GW by 2022 was sanctioned by MNRE on June 14, The wind tariff in India touched the
and to encourage new technologies, 2016. PTC India Ltd was selected as lowest level of `2.64 per kWh in the
methods, and way-outs involving trading company to sign PPAs with second wind auction (1,000 MW)
combined operation of wind and solar PV successful bidders and back-to-back conducted by SECI on October 4, 2017.
plants. The states of Andhra Pradesh and power sale agreements (PSAs) with Wind bidding guidelines under Section
Gujarat also issued draft hybrid policies. state utilities/bulk consumers under the 63 of Electricity Act, 2003, are likely to
Scheme. Solar Energy Corporation of be issued by the Ministry of Power,
Wind Bidding Scheme India (SECI), the implementing agency which will enable the states to bid for
Out of 302 GW wind power potential in of the Scheme, issued tender document wind power projects.
the country, over 297 GW is concentrated on October 28, 2016, and e-reverse
in the eight windy states in the country. auction was conducted on February 23,
To enable discoms of non-windy states
SMALL WIND ENERGY
2017. The first wind bid was concluded at
to fulfill their non-solar RPO obligation SYSTEMS
record low wind tariff of `3.46 per kWh
Besides, MNRE is also promoting a
scheme on ‘Small Wind Energy and
Hybrid systems (SWES)’, wherein both
the wind and solar energy are effectively
utilized for power generation by installing
a hybrid system consisting of both
aero-generator/small wind turbine and
solar photovoltaic technologies. Under
the scheme, CFA @`1.00 lakh per kw
is provided to the community users
for installation of small wind and solar
hybrid system. So far, a total of around
3,155 kW small wind energy systems
have been installed in 23 States/UTs. The
Scheme was operational till 31.3.17. An
evaluation of the scheme was undertaken
and it is proposed to redesign the scheme
»» 119.7 MW wind farm in Ellutla, Andhra Pradesh to increase its coverage.
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 24
WIND POWER DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: AN OVERVIEW
»» 119.7 MW wind farm in Ellutla, Andhra Pradesh
DEVELOPMENT OF the EEZ of the country and NIWE has of projects). Bidding has begun recently
OFFSHORE WIND been authorized as the nodal agency for and therefore no wind project being
ENERGY development of offshore wind energy as established through bidding process will
India has vast coastline of 7,600 km and well as to carry out allocation of offshore be commissioned during the current year,
considering the development of offshore wind energy blocks, coordination, and this will affect achievement of targets.
wind energy in the Indian Exclusive allied functions with related ministries The government has set a target of
Economic Zone (EEZ), the National and agencies. Initial studies carried out achieving 60,000 MW by 2022 which
Offshore Wind Energy Policy was by NIWE indicate offshore wind energy means a capacity addition of around
approved and notified in October 2015. potential on the coasts of Gujarat and 30,000 MW in the next 5 years (annual
MNRE has been authorized as the nodal Tamil Nadu. For assessment of offshore capacity addition of 6,000 MW). To
ministry for use of offshore areas within wind power potential, a LiDAR (Light achieve this ambitious target, conducive
Detection and Ranging) has been policy framework and long-term
installed at an identified offshore site near RPO trajectory prescribed by MoP is
The Ministry of New Gujarat. required to be adopted by the states. The
government has already taken positive
and Renewable Energy, steps by waiving inter-state transmission
ISSUES AND FUTURE
Government of India, PERSPECTIVE charges and losses for inter-state sale
placed emphasis Two major promotional incentives
of wind power, which will facilitate
non-windy states to fulfill their RPO
on Wind Resource curtailed—accelerated depreciation is
requirement by buying wind power
reduced from 80% to 40% and GBI not
Assessment since the extended after March 31, 2017. There are
from windy states. To further accelerate
the process, bidding has already been
beginning and today, apprehensions that cost of wind power
introduced in order to discover a suitable
will increase due to GST, which will be in
India has an abundance price discovery mechanism for interstate
force from July 2017.
of data, collected With successful auction of wind
sale of wind power. The focus area will
be on repowering and wind–solar hybrid
from over 800 wind power, all the wind capacity is likely to
projects that will require formulation of
be added through the bidding route.
monitoring stations The establishment of projects, through
promotional programmes and schemes
for demonstration.
installed all over bidding process, around 21 months’
Shri J K Jethani, Director, MNRE, Government of
India. time is required (3 months for bidding India, New Delhi.
process and 18 months for completion
August-October 2017 | Akshay Urja | 25
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GEC Alstom Relay Manual PDFDocument51 pagesGEC Alstom Relay Manual PDFPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Mechanics ExerciseDocument9 pagesPhysics Mechanics ExerciseblahPas encore d'évaluation
- Grid Connected Wind Power in ChinaDocument2 pagesGrid Connected Wind Power in ChinaRafael Torres GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Future and Scope of Wind Energy in India PDFDocument7 pagesFuture and Scope of Wind Energy in India PDFFazal PunewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Suzlonsustainabilityreportfy17 18Document88 pagesSuzlonsustainabilityreportfy17 18Aniruddh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Market OverviewDocument1 pageMarket OverviewRaghavendra SreeramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prospects of Wind Energy in Bangladesh PDFDocument7 pagesProspects of Wind Energy in Bangladesh PDFতানভীর আহমেদPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Energy in Pakistan: Department of Electrical Engineering Balochistan UET KhuzdarDocument23 pagesWind Energy in Pakistan: Department of Electrical Engineering Balochistan UET KhuzdarjarwarayazPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Resource Assessment and Energy Potential of Selected LocationsDocument19 pagesWind Resource Assessment and Energy Potential of Selected LocationsRaphael CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Power Potential in SAARC Country By: Safdar MehmoodDocument8 pagesWind Power Potential in SAARC Country By: Safdar MehmoodmehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Irjet V3i790 PDFDocument7 pagesIrjet V3i790 PDFShikha BhuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Energy Conversion System Using PMSG: R. A. GuptaDocument5 pagesWind Energy Conversion System Using PMSG: R. A. Guptaaman kathuriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Turbine Output Estimation Using Windographer SoftwareDocument6 pagesWind Turbine Output Estimation Using Windographer SoftwareAnonymous lPvvgiQjRPas encore d'évaluation
- Feasibility Study To Install Wind Farm in Bab Al-Hawa, Irbid, Northwest of JordanDocument19 pagesFeasibility Study To Install Wind Farm in Bab Al-Hawa, Irbid, Northwest of JordanFrederik MitevPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy From Wind: A Study On A Captive Windmill Installation in TamilnaduDocument10 pagesEnergy From Wind: A Study On A Captive Windmill Installation in TamilnaduSumundra RathPas encore d'évaluation
- 5C 1 GIZ17 019 Paper Joydeb BandyopadhyayDocument9 pages5C 1 GIZ17 019 Paper Joydeb BandyopadhyayPower PlantPas encore d'évaluation
- NigeriaDocument16 pagesNigeriaJean AvalosPas encore d'évaluation
- 13.ISCA IRJEvS 2014 52Document6 pages13.ISCA IRJEvS 2014 52Akshat SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Wind Speed Data and Wind Energy in KSADocument26 pagesAnalysis of Wind Speed Data and Wind Energy in KSAYSMHXSTS SYTMXSPas encore d'évaluation
- February 2023 in DepthDocument31 pagesFebruary 2023 in DepthHari KisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Power System Scenario Modified-1Document4 pagesIndian Power System Scenario Modified-1Tanvi Ravindra MahatmePas encore d'évaluation
- SuzlonDocument7 pagesSuzlonAbhishek RastogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy Grand Plan For India: Given byDocument17 pagesRenewable Energy Grand Plan For India: Given byAbhishek SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Power Sector in IndiaDocument139 pagesWind Power Sector in IndiaVijay Chander Reddy KeesaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Sector IBEFDocument42 pagesPower Sector IBEFHaardik GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Article: Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2020, 7 (7) :109-121Document13 pagesResearch Article: Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2020, 7 (7) :109-121Chidi DiyokePas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Power Development India by Dr. Dilip NigamDocument27 pagesWind Power Development India by Dr. Dilip NigamRahul JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prateek IJPES Actapress 2020Document5 pagesPrateek IJPES Actapress 2020Nimisha PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Extract WindDocument4 pagesExtract WindMubarak YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy in India: Status and Future ProspectsDocument34 pagesRenewable Energy in India: Status and Future ProspectsTushar AjitsariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Science and Technology, An International JournalDocument6 pagesEngineering Science and Technology, An International JournalKamil IbraPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Reports: Ephraim Bonah Agyekum, Michael Nii Sanka Ansah, Kwame Bright AfornuDocument9 pagesEnergy Reports: Ephraim Bonah Agyekum, Michael Nii Sanka Ansah, Kwame Bright AfornuYohanes AnggoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Potential and Economic Feasibility of Wind Energy in South West Region ofDocument8 pagesPotential and Economic Feasibility of Wind Energy in South West Region ofJorgePas encore d'évaluation
- India's Wind SectorDocument5 pagesIndia's Wind Sectorakhil86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Conversion and Management: Fazia Baghdadi, Kamal Mohammedi, Said Diaf, Omar BeharDocument9 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Fazia Baghdadi, Kamal Mohammedi, Said Diaf, Omar Beharollata kalanoPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Performance in Wind Power DevelopmentDocument25 pagesIndia's Performance in Wind Power DevelopmentAnand ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertical Access Wind TrubineDocument6 pagesVertical Access Wind TrubineTejeshwiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Power Economics IndiaDocument8 pagesSolar Power Economics IndiaSMPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Energy SourceDocument23 pagesWind Energy SourceKurk EstremaduraPas encore d'évaluation
- Present and Future Energy Scenario in IndiaDocument8 pagesPresent and Future Energy Scenario in IndiaRomario OinamPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Wind Power Feasibility at Various Locations of Coastal Regions of Andhra PradeshDocument27 pagesA Review On Wind Power Feasibility at Various Locations of Coastal Regions of Andhra PradeshkiranjiPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Utility-Scale Solar Parks A Global Success StoryDocument14 pagesIndia's Utility-Scale Solar Parks A Global Success StoryAbhishek VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind EnergyDocument1 pageWind EnergyShehab AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator Top Ologies With ConvertersDocument7 pagesGenerator Top Ologies With ConvertersEsperance KAMPIREPas encore d'évaluation
- IBEF Power June 2022Document39 pagesIBEF Power June 2022Sumiran BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Sizing of Microgrids For Indian Systems Using HOMER: Prema V.I and Vma Rao K.2Document5 pagesSizing of Microgrids For Indian Systems Using HOMER: Prema V.I and Vma Rao K.2ftahPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Wind Energy Potential Across Varying Topographical Features of Tamil Nadu, IndiaDocument26 pagesAssessment of Wind Energy Potential Across Varying Topographical Features of Tamil Nadu, IndiaGeorge FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks For Tehran, IranDocument14 pagesShort-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks For Tehran, IranblehPas encore d'évaluation
- ReferenceDocument22 pagesReferenceSakina ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Elec System Scenario Development 2030 - W Import DependenceDocument13 pagesElec System Scenario Development 2030 - W Import DependenceNikhil ThejeshPas encore d'évaluation
- 0035 PDFDocument8 pages0035 PDFBalan PalaniappanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sector Report - Solar Energy 1Document13 pagesSector Report - Solar Energy 1anand62002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Wind Power Program 2011 2Document337 pagesIndian Wind Power Program 2011 2kalaieee28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy in IndiaDocument40 pagesRenewable Energy in IndiaSAEL SOLARPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Wind Energy Development and Policy in IndiaDocument12 pagesReview of Wind Energy Development and Policy in IndiaPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- ICIRD - May 2018 - Comparison of PnO and ICDocument6 pagesICIRD - May 2018 - Comparison of PnO and ICAndri PradiptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project FinalDocument76 pagesProject FinalVish SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- Magazine PDFDocument64 pagesMagazine PDFDawn UnderwoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable Energy SourcesDocument35 pagesRenewable Energy Sourcespraveen100% (1)
- Wind Energy Unit 3Document72 pagesWind Energy Unit 3R TharunishPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable energy market analysis: GCC 2019D'EverandRenewable energy market analysis: GCC 2019Pas encore d'évaluation
- 13.3.2018 Energy Consumtion and Economic GrowthDocument3 pages13.3.2018 Energy Consumtion and Economic GrowthPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Wind Energy Development and Policy in IndiaDocument12 pagesReview of Wind Energy Development and Policy in IndiaPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Protection NotesDocument78 pagesProtection NotesPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Companies in IndiaDocument3 pagesDistribution Companies in IndiaPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- This Indian State Produces More Wind Power Than Sweden or Denmark - World Economic ForumDocument8 pagesThis Indian State Produces More Wind Power Than Sweden or Denmark - World Economic ForumPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- APRS Notes - 4.8.18Document1 pageAPRS Notes - 4.8.18Priya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- KIET Contact List - 10 July'18Document41 pagesKIET Contact List - 10 July'18Priya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Electricity Generation in Three States of India: Policies and StatusDocument8 pagesWind Electricity Generation in Three States of India: Policies and StatusPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part II BookDocument285 pagesPart II BookPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part I BookDocument205 pagesPart I BookPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nirma University Institute of Technology Electrical Engineering Department M.Tech in Electrical Engineering (Eps) Sem.I, July - 2017 3EE2102: Advanced Protective Relaying & Switchgear IndexDocument1 pageNirma University Institute of Technology Electrical Engineering Department M.Tech in Electrical Engineering (Eps) Sem.I, July - 2017 3EE2102: Advanced Protective Relaying & Switchgear IndexPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSP Lab ManualDocument35 pagesPSP Lab ManualPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques: Disadvantages of Dams:: Features of Bamboo Drip Irrigation SystemDocument1 pageQues: Disadvantages of Dams:: Features of Bamboo Drip Irrigation SystemPriya SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- NPSH - An Introduction For Pump Users: 1. General FormulationDocument4 pagesNPSH - An Introduction For Pump Users: 1. General FormulationTravis SkinnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Lithospheric PlatesDocument5 pagesMajor Lithospheric PlatesBRILLIANT MARK BALABAGPas encore d'évaluation
- Doe Organizational Chart 10152019 PDFDocument1 pageDoe Organizational Chart 10152019 PDFJenny VillegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Desalination and Water TreatmentDocument9 pagesDesalination and Water TreatmentRavi PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North ACADEMIC SESSION 2021-2022 Ut2 Revision Work Sheet TOPIC: Sorting Materials Into Group Answer KeyDocument6 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore North ACADEMIC SESSION 2021-2022 Ut2 Revision Work Sheet TOPIC: Sorting Materials Into Group Answer KeySumukh MullangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Ageing in Amorphous Polymers and Other MaterialsDocument249 pagesPhysical Ageing in Amorphous Polymers and Other Materialswc_11111Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Adonis, 2004) Uji Kuat Tekan Beton Batu Apung Dan Batu PalimananDocument24 pages(Adonis, 2004) Uji Kuat Tekan Beton Batu Apung Dan Batu Palimananagam teoPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring Pendulum LabDocument2 pagesSpring Pendulum Labspd bahrilPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 BDocument8 pagesChapter 6 BAurang Zeb SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Vernacular Architecture Structure On Urba 2018 Frontiers of ArchiDocument14 pagesEffects of Vernacular Architecture Structure On Urba 2018 Frontiers of ArchiSofia FigueredoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 4 - Analysis of Closed SystemDocument3 pagesExercise 4 - Analysis of Closed SystemPuviin VarmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 Spring 2018-19Document3 pagesTutorial 2 Spring 2018-19ANMOLPas encore d'évaluation
- Sf6 Circuit BreakerDocument18 pagesSf6 Circuit BreakerAbhinaw RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAssignment /quiz 1:: 1 - Dalton Atomic TheoryRuffa Mae PortugalPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Amphibious HomesDocument5 pagesDesign of Amphibious HomesVIVA-TECH IJRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Useful Phrases Describing WeatherDocument3 pagesUseful Phrases Describing WeatherLHHPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar PV Systems - Theory, Planning and Design With Calculations in Accordance With NECDocument23 pagesSolar PV Systems - Theory, Planning and Design With Calculations in Accordance With NECasifkhokherPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heat Formation: OF OF DioxideDocument24 pagesThe Heat Formation: OF OF Dioxidevela vanPas encore d'évaluation
- (Science 6 WK 4 L7) - Separating Mixture Through EvaporationDocument18 pages(Science 6 WK 4 L7) - Separating Mixture Through EvaporationRhea OcitePas encore d'évaluation
- Reduction of Water Vapour by Using Shade PDFDocument4 pagesReduction of Water Vapour by Using Shade PDFPrashant SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument26 pagesGce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 Solutionsjan12th2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5054 w08 Ms 2Document6 pages5054 w08 Ms 2mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial No 1Document2 pagesTutorial No 1Zainal AbidhynPas encore d'évaluation
- PlasticDocument3 pagesPlasticVinayraj PoojaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Grain-Water Suspensions in TubeDocument15 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling of Grain-Water Suspensions in TubebhuniakanishkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Descent With Modification: A Darwinian View of Life: BIOLOGY, Eighth Edition Neil Campbell & Jane ReeceDocument11 pagesDescent With Modification: A Darwinian View of Life: BIOLOGY, Eighth Edition Neil Campbell & Jane Reecemayching207Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metals 164 Tata Steel Jamshedpur 0 PDFDocument41 pagesMetals 164 Tata Steel Jamshedpur 0 PDFkalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M0019 COHEN 2014 - Exploration GeochemistryDocument28 pagesM0019 COHEN 2014 - Exploration GeochemistryEduardoPas encore d'évaluation