Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Neisse Ria
Transféré par
Janelle Garcia0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues3 pagesaxsc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentaxsc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues3 pagesNeisse Ria
Transféré par
Janelle Garciaaxsc
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
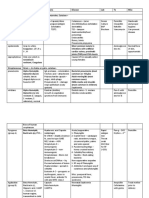
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS Symptoms may include
inflammation, redness, swelling,
Gram negative diplococci,
and dysuria (painful urination)
kidney shaped with adjacent
Also came conjunctivitis
sides flattened.
(ophthalmia neonatorum –
Most are encapsulated, non-
infants), pharyngitis, proctitis or
spore former.
urethritis, prostitis, rectal
Non – motile
involvement, cervico-vaginitis,
Oxidase and Catalase positive
PID and orchitis.
Anaerobe to facultative aerobes
Crede’s prophylaxis – 1% silver
Requires 2-10% CO2 for growth
nitrate in neonates eyes to
CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS prevent blindness (ophthalmia
neonatorum)
Fastidious organisms requiring
complex nutritional growth.
Translucent, grayish, convex, DGI – Disseminated Gonococcal
shiny colonies with entire margins Infectionb
that are non-hemolytic and non-
Most often present as arthritis –
pigmented.
aching and swelling in the joints
N. Gonorrhea also known as
but they can also cause skin
gonococcus/gonococci
lesions and infections of the
Also called the “clap” which is
heart, bones, and the sheaths
derived from the French word
that cover the nervous system
“clapier” meaning “brothel”.
(meninges).
Causes agent of gonorrhea a
In rare cases, disseminated
sexually transmitted disease.
gonorrheae can even be fatal.
Require nutrient supplementation
to grow in laboratory cultures. LABORATORY SPECIMENS
Specifically, they grow on CAP
Blood
with Co2.
CSF
Is able to prevent an immune
Synovial Fluid
response
Discharges
The host is also unable to develop
an immunological memory Culture Media
against N. gonorrhoeae – which
means that future re-infection is THAYER MARTIN MEDIUM
possible. Enriched cap with
supplement B or Isovitale X
MANIFESTATIONS and Antibiotics
Infection of the genitals can Vancomycin – inhibits gram +
result in a purulent (or pus like) Colistin – inhibits gram –
discharge from the genitals Nystatin – inhibits fungi
which may be foul smelling.
MODIFIED THAYER MARTIN
MEDIUM
Additional of hemoglobin meningococcemia, a life
solution and trimethophrim threatening sepsis.
lactate which inhibits the Also associated with
spreading of proteus. cerebrospinal lever or
Waterhouse Friderichsen
TRANSGROW MEDIUM syndrome
a Thayer martin medium with The gold standard of diagnosi is
glucose, 2% agar, isolation of N. meningitidis from
trimetophrim, lactate and sterile body fluid.
CO2 incorporated in a bottle.
N. meningitidis vs. N. gonorrhoeae
MARTIN LEWIS MEDIUM N. meningitidis
A modified Thayer martin - Glucose +
medium with the substitution - Maltose +
of anisomycin, an antifungal - Capsule +
agent with a longer half-life - Causes meningitis
for nystatin. - Oxidase +
New York city medium
Also modified Thayer martin N. gonorrhoeae
medium with substitution of - Glucose +
Amphoteracin B - Maltose –
- Capsule –
LABORATORY IDENTIFICATION - Causes gonorrhoeae
- Oxidase +
Oxidase test – presumptive test
FAT – fluorescent antibody MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS
tagging test - is a
Degradation of carbohydrate fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-
Cultivation in CTA (Cysteine negative, aerobic, oxidase-
Tellurite Agar) positive for glucose positive diplococcus that can
cause infections of the
respiratory system, middle ear,
Cultivation in TMM with eye, central nervous system,
vancomycin, colistin and nystatin septicemia, sinusistis,
Modified TM (with trimetroprim pneumonia and joints of
lactate to prevent swarming) humans.
Martin Lewis with anisomycin to - was previously placed in a
prevent growth of fungi separate genus
NYCA with amphotericin to named Branhamella. The
prevent growth of fungi rationale for this was that
CAP other members of the
genus Moraxella are rod-
N. meningitidis shaped and rarely caused
Often referred to as infections in humans.
meningococcus, is a bacterium However, results from DNA
that can use meningitis. hybridization studies
And other forms of and 16S rRNA sequence
meningococcal disease such as comparisons were used to
justify inclusion of the
species M. catarrhalis in the
genus Moraxella.
- As a consequence, the
name Moraxella catarrhalis is
currently preferred for these
bacteria. Nevertheless, some
in the medical field continue
to call these
bacteria Branhamella
catarrhalis.
- Resistant to penicillin ,
amoxicillin, and ampicillin.
- Cultured in BAP and CAP with
gray to white colonies and
waxy surface.
- Dnase +
- Hockey puck test in which a
wooden stick is used to try to
push the colonies across the
plate. The M.
catarrhalis colonies scored
positively on this test, which
means they could be slid
across the plate.
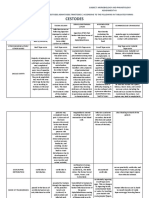
Veillonella are Gram-negative
anaerobic cocci. This bacterium
is well known for its lactate
fermenting abilities. They are a
normal bacterium in the
intestines and oral mucosa of
mammals. In humans they have
been rarely implicated in cases
of osteomyelitis and endocarditis
- V. parvula is the important
species
- Oxidase +
- Sugar degradation negative
- Dnase -
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Ideal Candida Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Alleviate Candida Symptoms And Restore Gut Health With Nutritious RecipesD'EverandThe Ideal Candida Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Alleviate Candida Symptoms And Restore Gut Health With Nutritious RecipesPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaDocument10 pagesBacteriology - Semifinals - Neisseria and MoraxellaUshuaia Ira Marie L. GallaronPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookD'EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (9)
- Gram Negative Cocci (Lecture Notes)Document5 pagesGram Negative Cocci (Lecture Notes)Dayledaniel Sorveto100% (1)
- Lameness, ShoatsDocument35 pagesLameness, Shoatskennyrogers kawooyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Candidiasis CryptococcosisDocument3 pagesCandidiasis CryptococcosisJuan Carlo CacaoPas encore d'évaluation
- James Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Document11 pagesJames Hupp, Head, Neck and Orofacial Infections. 2016-60-67Hukjvccx JjyfdxxvbPas encore d'évaluation
- Neisse RiaDocument9 pagesNeisse RiaNOEMI BARROGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Negative CocciDocument13 pagesGram Negative CocciZiaa MeryPas encore d'évaluation
- ECHINOCOCCUSDocument5 pagesECHINOCOCCUSGhina RizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Opportunistic MycosesDocument3 pagesOpportunistic MycosesMaryPas encore d'évaluation
- BacteriologyDocument20 pagesBacteriologyOj Alimbuyuguen100% (2)
- Staph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusDocument5 pagesStaph. Aureus Staph. Epidermidis Staph. SaprophyticusTom PedersonPas encore d'évaluation
- File 000Document48 pagesFile 000nasarcedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Actinomyces, Nocardia and Tropheryma: Actinomycosis Nocardiasis Whipple's DiseaseDocument4 pagesActinomyces, Nocardia and Tropheryma: Actinomycosis Nocardiasis Whipple's Diseasenour achkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Super Parasitology TableDocument11 pagesSuper Parasitology Tablesleepyhead archerPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Santo Tomas - Medical Technology Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas - Medical Technology Diagnostic Microbiologythedarkwing100% (1)
- MICRO2015 - Prelims To Finals Theo ReviewerDocument7 pagesMICRO2015 - Prelims To Finals Theo ReviewerAndrassy Twinkle AlineaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 36Document13 pagesLesson 36Abdelraouf ElmanamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraDocument26 pagesNeisseria: Family Neisseriaceae With Four GeneraAmit Mansukh MistryPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2 Gram Negative CocciDocument4 pages1.2 Gram Negative CocciJustine Mel Concepcion IlardePas encore d'évaluation
- Organism Description Drug of ChoiceDocument14 pagesOrganism Description Drug of ChoiceMary YongcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria.: MicrobiologyDocument10 pagesBacteria.: MicrobiologyHet KhokharPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology PinkDocument3 pagesMicrobiology PinkBenjamin GaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacte MnemonicsDocument10 pagesBacte MnemonicsIan Leo SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial Agents of Cardio-Vascular DiseasesDocument43 pagesBacterial Agents of Cardio-Vascular Diseasesfitrah fajrianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topnotch Parasitology Super Table by DR - Yns PereyraDocument50 pagesTopnotch Parasitology Super Table by DR - Yns PereyraRochelle Joyce AradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria PDFDocument13 pagesBacteria PDFJohn Christopher LucesPas encore d'évaluation
- Causative Agents of Yeast InfectionsDocument2 pagesCausative Agents of Yeast InfectionsDreyden HaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Quizlet-Com-871294Document40 pagesQuizlet-Com-871294minaantiochPas encore d'évaluation
- Caseous LymphadenitisDocument14 pagesCaseous LymphadenitismedinamargaretkellyPas encore d'évaluation
- Legion EllaDocument2 pagesLegion EllaJacklyn M. oPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 15 BacteriologyDocument3 pagesWeek 15 BacteriologyWansun MaglangitPas encore d'évaluation
- MicrofinalDocument7 pagesMicrofinaljwanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology - 19Document4 pagesMicrobiology - 19karmylle andradePas encore d'évaluation
- MB Yeasts PassDocument1 pageMB Yeasts PassJulia IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology - : University of Santo Tomas - Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic MicrobiologyDocument53 pagesBasic MicrobiologyJohn NirmalPas encore d'évaluation
- In Brief: MastoiditisDocument4 pagesIn Brief: Mastoiditismuthiadewi31Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Document6 pages2023.pedia - Trans24.-Bacterial-Infections - Gram Postitive (Part 1)Adrian CaballesPas encore d'évaluation
- GI Infections2Document8 pagesGI Infections2OM JHAPas encore d'évaluation
- 18 Non Fermentative Gram BacilliDocument7 pages18 Non Fermentative Gram BacilliAldren BeliberPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 3.01 Nervous System Study Guide 4Document3 pagesProblem 3.01 Nervous System Study Guide 4Monish NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathogenic BacteriaDocument6 pagesPathogenic BacteriaNit ZePas encore d'évaluation
- AntifungalagentsDocument57 pagesAntifungalagentsRafia Rayana btbcPas encore d'évaluation
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemDocument6 pagesStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoPas encore d'évaluation
- MICROBIO - FungiDocument4 pagesMICROBIO - FungiGleceree FilomenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Sheet - Capsule StainingDocument2 pagesLab Sheet - Capsule Stainingbliss polleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 5: Chapter 17: Erysipelothrix, Lactobacilllus, and Similar OrganismsDocument13 pagesSection 5: Chapter 17: Erysipelothrix, Lactobacilllus, and Similar OrganismsPatricia CabisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Reviewer paraDocument10 pagesLaboratory Reviewer paraDexcel concepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3 FinalDocument9 pagesAssignment 3 Finalcandido evanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Micro para Lec FinalsJohn Carl CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyogenic Cocci - GENUS NEISSERIA LGT11-12Document9 pagesPyogenic Cocci - GENUS NEISSERIA LGT11-12سجاد طالب رحمه حوشيPas encore d'évaluation
- VIRUSDocument7 pagesVIRUSHet KhokharPas encore d'évaluation
- Diplococci AerobicDocument6 pagesDiplococci Aerobichassanabbass208Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide To Salivary Gland DisordersDocument5 pagesA Guide To Salivary Gland Disordersdanny17phPas encore d'évaluation
- Infeksi Bakteri Muskuloskeletal: Oleh M.SabirDocument41 pagesInfeksi Bakteri Muskuloskeletal: Oleh M.Sabirmiftahul jannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteriology Edited 1Document65 pagesBacteriology Edited 1Ali AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracheostomy Site CancerDocument2 pagesTracheostomy Site CancerСварооп СатурнскыPas encore d'évaluation
- Morning ReportDocument31 pagesMorning Reports1882Pas encore d'évaluation
- Journals ListDocument15 pagesJournals ListVanshika JainPas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsJeff MarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Phool Vati BillDocument13 pagesPhool Vati BillVivek PaylaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutramine MenDocument2 pagesNutramine MenCh Ashish PawaskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1: Health and Skill Related FitnessDocument2 pagesLesson 1: Health and Skill Related FitnessCrhystal Joy ReginioPas encore d'évaluation
- Catheter Ablation For AFDocument12 pagesCatheter Ablation For AFPeny Ruth Jessica DamanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam Labor ProcessDocument4 pagesExam Labor ProcessAileen A. Monares0% (1)
- Strategic Intervention Materials PresentationDocument55 pagesStrategic Intervention Materials PresentationMary Athena Ibardaloza Adesna100% (15)
- Principles of Molecular Medicine - J. Larry Jamenson - Humana Press - 1998Document1 144 pagesPrinciples of Molecular Medicine - J. Larry Jamenson - Humana Press - 1998BOC100% (1)
- Humoral Imune Respon: SuhermanDocument62 pagesHumoral Imune Respon: SuhermansuhermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gordon's Functional Health PatternDocument8 pagesGordon's Functional Health PatternDanica NuevaexcijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Intrapartum DM Management: By: DRDocument38 pagesIntrapartum DM Management: By: DRYohannis AsefaPas encore d'évaluation
- K - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Document24 pagesK - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Ruthra Devi NarayanasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- American Board of Family Medicine: TTT SAMPLE TTTDocument148 pagesAmerican Board of Family Medicine: TTT SAMPLE TTTAbdulrhman AlruwiliPas encore d'évaluation
- PWAT (Panographic Wound Assesment Tool) RevisedDocument4 pagesPWAT (Panographic Wound Assesment Tool) RevisedYunie ArmyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Barium StudiesDocument89 pagesBarium StudiesManuel PoncianPas encore d'évaluation
- TransplantDocument30 pagesTransplantLoshi ChandrasekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology McqNEW 2Document7 pagesPharmacology McqNEW 2Ayman Ragab100% (2)
- Water Birth PPDocument5 pagesWater Birth PPAzi SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sas 20Document4 pagesSas 20Sistine Rose LabajoPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthodontic Pearls PDFDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Pearls PDFortho123Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Weight LossDocument41 pages5 Weight LossTasniiem KhmbataPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Description. Pathology of Musculosceletal SystemDocument52 pagesModule Description. Pathology of Musculosceletal SystemAlberto MayorgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Motor DevelopmentDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Motor DevelopmentRina Siason AbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Katzung QuestionsDocument29 pagesKatzung QuestionsToastie3100% (12)
- Notes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNotes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyRikki Mae Bueno100% (3)
- Judgment: in The High Court of The Republic of SingaporeDocument26 pagesJudgment: in The High Court of The Republic of SingaporeTerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Tara's Intro To Critical CareDocument6 pagesTara's Intro To Critical CareTara McNeillPas encore d'évaluation
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsD'EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (28)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (81)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionD'EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (42)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDD'EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (170)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (392)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningD'EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosD'Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (207)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryD'EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (328)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlD'EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (58)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)