Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Infinitives and Gerunds
Transféré par
Hernán Ignacio Rojas Contreras0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues12 pagesinfinitivos y gerundios en inglés
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentinfinitivos y gerundios en inglés
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
34 vues12 pagesInfinitives and Gerunds
Transféré par
Hernán Ignacio Rojas Contrerasinfinitivos y gerundios en inglés
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
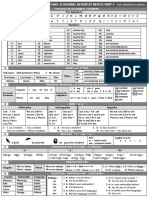
Words used with the Infinitive
Infinitive as the Subject of a Clause (followed by the verbs below)
Example: To follow his advice seemed logical.
be
seem
appear
Infinitive after certain Expressions (without 'to')
Example: I would rather stay at home.
had better
would rather
would sooner
why not
why should I/you/… [not]
Infinitive after certain Verbs (without to)
Example: We must stay at home.
can
dare (also with to)
do
help (also with to)
let
may
must
need (also with to)
shall
should
will
Infinitive after certain Verbs (with to)
Example: He refused to pay the bill.
afford
agree
aim
appear
arrange
attempt
be determined
beg
care
choose
claim
condescend
consent
dare (also without to)
decide
demand
deserve
determine
endeavour
expect
fail
guarantee
happen
have
help (also without to)
hesitate
hope
learn
long
manage
mean
need (also without to)
neglect
offer
ought
plan
prepare
pretend
proceed
promise
refuse
resolve
seem
stop
swear
tend
threaten
trouble
undertake
used
volunteer
vow
want
wish
would hate
would like
would love
would prefer
Infinitive after certain Verbs with Interrogative (how, if, what, where, whether)
Example: We didn't remember where to meet.
ask
advise + Objekt
consider
decide
explain
find out
forget
know
learn
remember
see
show
teach
tell + object
understand
wonder
Infinitive after certain Verbs with an Object (without 'to')
Example: We heard him scream.
let
make
Infinitive after certain Verbs with an Object (with 'to')
Example: She got me to wash the dishes.
advise
allow
ask
beg
cause
enable
encourage
expect
forbid
force
get
help
invite
mean
order
permit
persuade
recommend
remind
teach
tell
want
warn
would hate
would like
would love
would prefer
Infinitive after certain Adjectives
Example: It was impossible to go back.
amazed
amazing
angry
astonished
astonishing
awkward
brave
careless
clever
cowardly
crazy
delighted
difficult
disappointed
disgusted
easy
extraordinary
funny
generous
glad
happy
hard
honest
horrified
impossible
kind
nice
odd
pointless
relieved
ridiculous
rude
sad
selfish
silly
sorry
strange
stupid
surprised
wicked
wise
Infinitive after certain Nouns
Example: There was no need to get angry.
effort
agreement
aim
appearance
arrangement
attempt
choice
claim
decision
determination
expectation
failure
guarantee
hesitation
hope
longing
need
neglect
offer
plan
preparation
procedure
promise
refusal
resolution
tendency
threat
trouble
try
Adjectives (with Prepositions) followed by the Gerund
Example: I am interested in visiting the museum.
afraid of
angry about / at
bad at
busy
clever at
crazy about
disappointed about
excited about
famous for
fond of
glad about
good at
impressed by
interested in
keen on
like
near
proud of
sick of
sorry about
tired of
worried about
worth
Prepositions followed by the Gerund
Example: Instead of studying for her exams, she went out every night.
about (in 'how/what about')
after
apart from
because of
before
by
in
in spite of
instead of
on
without
Verbs followed by the Gerund
Example: I enjoy enjoy cooking.
admit
advise
allow
appreciate
avoid
can't help
can't stand
consider
delay
deny
dislike
enjoy
escape
fancy
finish
go (in go swimming)
imagine
involve
keep
mention
mind
miss
permit
postpone
practise
reject
resist
risk
stop
suggest
understand
waste time / money
Verbs with Prepositions followed by the Gerund
Example: I'm looking forward to seeing you again soon.
accuse of
adjust to
agree with
apologize for
approve of
ask about
ask for
begin by
believe in
be used to
blame for
care for
carry on
complain about
concentrate on
congratulate on
consist of
cope with
decide against
decide for
depend on
die of
dream about / of
escape from
feel like
forgive for
give up
insist on
keep on
look forward to
object to
pay for
prevent sb. from
protect from
put off
rely on
spend money on
spend time on
succeed in
suspect of
take part in
talk about / of
thank for
think of
use for
warn against
worry about
Nouns / Nouns with Prepositions followed by the Gerund
Example: There's no point in waiting any longer.
advantage of
alternative of
chance of
choice between
danger of
difficulty in
doubt about
experience in
fun
hope of
idea of
interest in
opportunity of
place for
pleasure in
point in
possibility of
problem
reason for
trouble
trouble in
use
way of
waste of money
waste of time
Words with the same meaning
Example: I started to read. / I started reading.
attempt
begin
bother
cannot bear
cease
continue
hate
intend
love
prefer
start
Words with the same meaning but different use
WordInfinitive - with an objectGerund – without an objectadviseI advise you to go by bus.I advise
going by bus.allow / permitHe allowed her to take the car.He allowed taking the car.forbidShe forbids
us to smoke.She forbids smoking.
Words with a different meaning
WordInfinitive meaningGerund meaningforget / rememberwith regard to the future
Remember to switch off the lights.with regard to the past
Do you remember switching off the lights?go onstart something new
Go on to read.continue with the same action
Go on reading.regretwith regard to the future
I regret to say that.with regard to the past
I regret saying that.stopinterrupt another action
I stopped to smoke.terminate
I stopped smoking.trydo something complicated
Try to solve this riddle.do it and see what happens
Try talking to him.
Infinitive or Present Participle
Gerund and present participle are not exactly the same. As this chapter is about when to use the
infinitive and when to use the ing-form, however, we have also listed words here that can be used either
with the infinitive or the present participle. (for more information on the present participle see
participles)
WordsInfinitive meaningGerund meaningfeel
hear
seeEmphasises that the action is completed.
Example: I saw him go up the stairs. Action can be completed, but not necessarily.
Example: I saw him going up the stairs. go
comeexpresses a purpose
Example: She is coming to show us the pictures.in connection with activities
Example: Let’s go shopping / dancing.
Gerunds and Infinitives Part 1
1. A gerund is a noun made from a verb by adding "-ing." The gerund form of the verb "read" is
"reading." You can use a gerund as the subject, the complement, or the object of a sentence.
Examples:
Reading helps you learn English. subject of sentence
Her favorite hobby is reading. complement of sentence
I enjoy reading. object of sentence
Gerunds can be made negative by adding "not."
Examples:
He enjoys not working.
The best thing for your health is not smoking.
2. Infinitives are the "to" form of the verb. The infinitive form of "learn" is "to learn." You can also use
an infinitive as the subject, the complement, or the object of a sentence.
Examples:
To learn is important. subject of sentence
The most important thing is to learn. complement of sentence
He wants to learn. object of sentence
Infinitives can be made negative by adding "not."
Examples:
I decided not to go.
The most important thing is not to give up.
3. Both gerunds and infinitives can be used as the subject or the complement of a sentence. However, as
subjects or complements, gerunds usually sound more like normal, spoken English, whereas infinitives
sound more abstract. In the following sentences, gerunds sound more natural and would be more
common in everyday English. Infinitives emphasize the possibility or potential for something and
sound more philosophical. If this sounds confusing, just remember that 90% of the time, you will use a
gerund as the subject or complement of a sentence.
Examples:
Learning is important. normal subject
To learn is important. abstract subject - less common
The most important thing is learning. normal complement
The most important thing is to learn. abstract complement - less common
4. As the object of a sentence, it is more difficult to choose between a gerund or an infinitive. In such
situations, gerunds and infinitives are not normally interchangeable. Usually, the main verb in the
sentence determines whether you use a gerund or an infinitive.
Examples:
He enjoys swimming. "Enjoy" requires a gerund.
He wants to swim. "Want" requires an infinitive.
5. Some verbs are followed by gerunds as objects. List of Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Examples:
She suggested going to a movie.
Mary keeps talking about her problems.
6. Some verbs are followed by infinitives. List of Verbs Followed by Infinitives
Examples:
She wants to go to a movie.
Mary needs to talk about her problems.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- List Verbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitive Lower Intermediate PDFDocument1 pageList Verbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitive Lower Intermediate PDFAngel BermudezPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerunds and InfinitivesPraery PraePas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitive PDFDocument4 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitive PDFfranklincxPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise For Adverbs and AdjectivesDocument5 pagesExercise For Adverbs and AdjectivesTheaayaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerund & InfinitiveDocument23 pagesGerund & InfinitiveGemma Castillo100% (1)
- Forming Nouns and Adjectives Derived From VerbsDocument6 pagesForming Nouns and Adjectives Derived From VerbsBeri DarioPas encore d'évaluation
- PET Phrasal VerbsDocument1 pagePET Phrasal Verbslolita digiacomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Reference: Unit 1Document17 pagesGrammar Reference: Unit 1PK10620 Aisyah Nadhirah Binti ZainuziPas encore d'évaluation
- 154 Verb Preposition CombosDocument2 pages154 Verb Preposition CombosTuấn Anh Phan NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Humour Vocabulary LessonDocument2 pagesHumour Vocabulary Lessonyouness100% (1)
- Eng Irregular VerbsDocument24 pagesEng Irregular Verbsbubac7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inverted Word OrderDocument6 pagesInverted Word OrderMuffin175Pas encore d'évaluation
- Collocations Delexical Verbs Make, Do, Have and TakeDocument1 pageCollocations Delexical Verbs Make, Do, Have and Takesam kadadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phrasal Verb HOLDDocument3 pagesPhrasal Verb HOLDAmpy Varela Ríos100% (1)
- Forms of The InfinitiveDocument3 pagesForms of The InfinitiverepidonPas encore d'évaluation
- Preposition (Phrasal Verbs & Prepositional Verbs)Document18 pagesPreposition (Phrasal Verbs & Prepositional Verbs)Ali JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Making ArrangementsDocument2 pagesMaking ArrangementsNicole ModigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cutting Edge Advanced Module 3 - 2018-2019Document3 pagesCutting Edge Advanced Module 3 - 2018-2019v. Adesh BhageloePas encore d'évaluation
- Phrases For Online MeetingDocument3 pagesPhrases For Online MeetingSUNIL TV100% (1)
- Present Perfect ContinuousDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect ContinuousFelipe R CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Preposition Combinations With Adjectives and VerbsDocument13 pagesPreposition Combinations With Adjectives and VerbsVoichita-iuliana Pernes100% (1)
- Do and Make - Difference !!!Document3 pagesDo and Make - Difference !!!Juan Martines100% (1)
- Intermediate Reading Comprehension Test 02Document3 pagesIntermediate Reading Comprehension Test 02Diosmari Santos100% (1)
- Active - Passive VoiceDocument1 pageActive - Passive Voicepranavwest12100% (1)
- Ast Simple Tense: Marjorie Mujica Salame Noviembre 2012Document10 pagesAst Simple Tense: Marjorie Mujica Salame Noviembre 2012De Alonso AlaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indefinite PronounsDocument5 pagesIndefinite PronounsnikitetPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher's Activity Student's ActivityDocument8 pagesTeacher's Activity Student's ActivityMa. Irish Joy CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- 88 Verb-Collocations US Student 0Document6 pages88 Verb-Collocations US Student 0Daniela Mercuri AlessioPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument8 pagesGerund or InfinitiveHằng NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- 88 Gerunds and Infinitives CanDocument19 pages88 Gerunds and Infinitives CanCindyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharsal VerbDocument169 pagesPharsal VerbHarshit SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- General EnglishDocument169 pagesGeneral EnglishSanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Outcomes Adv Workbook Unit10Document6 pagesOutcomes Adv Workbook Unit10Vi NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Simple and ContinuousDocument26 pagesPast Simple and ContinuousBalonash Q SclipiciPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb and Preposition: SO Somebody ST SomethingDocument17 pagesVerb and Preposition: SO Somebody ST SomethingDelia CatrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument4 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesThais22 EstudosPas encore d'évaluation
- Relaxed Pronunciation ReferenceDocument5 pagesRelaxed Pronunciation ReferencevlkwolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Infinitive and Gerund in EnglishDocument3 pagesInfinitive and Gerund in EnglishRaul Wal SchPas encore d'évaluation
- GI B1 Irregular VerbsDocument2 pagesGI B1 Irregular VerbsLucia Guadalupe PetrichPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions "On," "At," and "In"Document3 pagesPrepositions "On," "At," and "In"eylulozgePas encore d'évaluation
- Easy English VocabularyDocument23 pagesEasy English VocabularyAbanoub AdelPas encore d'évaluation
- I2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDocument15 pagesI2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDanielSánchezMartínezPas encore d'évaluation
- Infinitives Vs Gerunds ListDocument2 pagesInfinitives Vs Gerunds ListClaudia RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Collocation 2Document14 pagesCollocation 2Jessica ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading Tasks by @teachingteacupDocument7 pagesReading Tasks by @teachingteacupÁngela Naranjo GómezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Focus: Difference Between "Enough" and "Too Much"Document15 pagesGrammar Focus: Difference Between "Enough" and "Too Much"Angel CaPas encore d'évaluation
- Separable Phrasal VerbsDocument7 pagesSeparable Phrasal VerbsImposedPas encore d'évaluation
- AdjectivesDocument3 pagesAdjectivesErynaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Relative Clauses - ActivitiesDocument26 pagesThe Relative Clauses - ActivitiesBondfriendsPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs Followed by Gerund or InfinitiveDocument7 pagesVerbs Followed by Gerund or Infinitivemjesusra50% (2)
- Infinitive and Gerund (To - Ing)Document19 pagesInfinitive and Gerund (To - Ing)Luiz Henrique MendesPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Core - A General Review of BasicsDocument4 pagesCommon Core - A General Review of BasicsEnglish With Simo100% (1)
- TAG QUESTION PresentationDocument6 pagesTAG QUESTION PresentationSergio SuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- 16) ALL 12 Verb Tenses in English EXPLAINED!Document5 pages16) ALL 12 Verb Tenses in English EXPLAINED!Laura Pujol100% (1)
- Adjective or Adverb: How To Use The AdverbDocument4 pagesAdjective or Adverb: How To Use The AdverbManjit DhaliwalPas encore d'évaluation
- English Tenses:: V1: Be + V-Ing: V2 Future: Will + V-Inf: Have + V3Document2 pagesEnglish Tenses:: V1: Be + V-Ing: V2 Future: Will + V-Inf: Have + V3kebonarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Giving OpinionsDocument12 pagesGiving OpinionsCuong Huy NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Document12 pagesGerundijus Arba Bendratis Infinitive)Lukas PavardisPas encore d'évaluation
- Review Topic 6 and Topic 7Document15 pagesReview Topic 6 and Topic 7Linh ChuPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar 1 (Sweet H.)Document2 pagesSeminar 1 (Sweet H.)Ekaterina Rudaya0% (1)
- PSAT Identifying Sentences PracticeDocument3 pagesPSAT Identifying Sentences PracticeEdward AlmazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecce 8 - Grammar PracticeDocument4 pagesEcce 8 - Grammar PracticemileslegionisPas encore d'évaluation
- English Scheme of Work For Year 5Document42 pagesEnglish Scheme of Work For Year 5Mohamad Tarmidzi0% (1)
- Lesson Plan Active and Passive VoiceDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Active and Passive VoiceGary Osiba100% (1)
- Vulcan GuideDocument10 pagesVulcan GuideDaisuke IshidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adjectives: Add Exceptions Word AdjectiveDocument4 pagesAdjectives: Add Exceptions Word Adjectivewitria oktavianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Act 7 English III B1 Writing ForumDocument5 pagesAct 7 English III B1 Writing ForumFrank Blandon GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios Del Present Perfect y Del Present Perfect ContinuousDocument6 pagesEjercicios Del Present Perfect y Del Present Perfect ContinuousFernanda JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Eastern Armenian TextbookDocument338 pagesEastern Armenian TextbookToddus Aurelius67% (3)
- Verbal Inflection and Clause Structure in SwahiliDocument150 pagesVerbal Inflection and Clause Structure in SwahiliCarolyn Harford100% (1)
- Competencia Comprendr Resultados 7 - 11Document19 pagesCompetencia Comprendr Resultados 7 - 11Cristian MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary EnglishDocument159 pagesElementary Englishmajaema100% (2)
- Parts of Speech ExerciseDocument1 pageParts of Speech ExerciseAprillia Chrisani100% (1)
- English 7Document3 pagesEnglish 7gcu974Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reflexive Verbs PDFDocument27 pagesReflexive Verbs PDFSergioPas encore d'évaluation
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument4 pagesGerund or InfinitiveHachim RidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Dan JawabanDocument6 pagesContoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Dan JawabanShintaWijaya100% (2)
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument7 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechJasmin Binauhan Niegos-TrongcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Worksheets So SoDocument347 pagesGrammar Worksheets So SoJoanna SmithsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Activities Ielts and TipsDocument12 pagesWriting Activities Ielts and TipsBeymar Leonardo Solórzano AlvizPas encore d'évaluation
- Present PerfectDocument20 pagesPresent PerfectAna PaguPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas PronounsDocument20 pagesTugas PronounsNurIzzaHerraniPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Most Common Esl Irregular Verbs ListDocument3 pages100 Most Common Esl Irregular Verbs ListIvana Sarcevic Ex BrkovicPas encore d'évaluation
- English-Training-Material Direct Indirect 2016 NMDocument42 pagesEnglish-Training-Material Direct Indirect 2016 NMUmer AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Academic English Workshop 0910S4 FragmentsDocument21 pagesAcademic English Workshop 0910S4 Fragmentstwy113Pas encore d'évaluation
- The InfinitiveDocument10 pagesThe InfinitiveAman GodaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Q-The Levels of Meaning. 1-Expression Meaning 2 - Utterance Meaning 3 - Communicative MeaningDocument9 pagesQ-The Levels of Meaning. 1-Expression Meaning 2 - Utterance Meaning 3 - Communicative MeaningOmar H. Almahdawi100% (1)
- The Simple Past Tense: Meaning & Use Form (Structure) ExerciseDocument16 pagesThe Simple Past Tense: Meaning & Use Form (Structure) ExerciseElizabethCarrionPas encore d'évaluation
- Sentence PatternsDocument25 pagesSentence PatternsNoorhasliza HalimPas encore d'évaluation