Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Matter and Energy
Transféré par
CharlieCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Matter and Energy
Transféré par
CharlieDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Matter and Energy
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
The mass of an object measures how much matter is in the object. Mass is
directly proportional to weight at any given place in the universe. If we leave
the surface of the Earth, our mass remains the same, but our weight changes.
Energy is the capacity to do work.
CLASSIFICATIONS OF MATTER
Let's begin our study of chemistry by examining some fundamental ways in
which matter is classified and described. Two principal ways of classifying
matter are according to its physical state (as a gas, liquid, or solid) and according
to its composition (as an element, compound, or mixture).
States of Matter
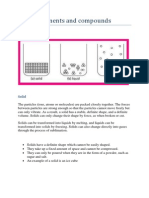
A sample of matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. These three forms of matter
are called the states of matter.
The states of matter differ in some of their simple observable properties. A gas
(also known as vapor) has no fixed volume or shape; rather, it conforms to the
volume and shape of its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller
volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one. A liquid has a distinct volume
independent of its container but has no specific shape. A liquid assumes the shape
of the portion of the container that it occupies. A solid has both a definite shape
and a definite volume. Neither liquids nor solids can be compressed to any
appreciable extent.
A pure substance (usually referred to simply as a substance) is matter that has
distinct properties and a composition that does not vary from sample to sample.
Elements are the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down chemically
into simpler, stable substances.
A compound is a chemical combination of elements that has its own set of properties and a
definite composition.
Mixtures are physical combinations of substances that have properties related to those of their
components but that do not have definite compositions.
They can be either heterogeneous or homogeneous mixtures.
In heterogeneous mixtures, two or more different types of matter can be seen to be present with
the naked eye or a good optical microscope. Homogeneous mixtures, also called solutions, look
alike throughout, even under a microscope.
Usar ejercicios pag 17 y 18 Goldberg
1.11 Classify each of the following as a pure substance or a mixture. If a mixture,
indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: (a) rice pudding, (b)
seawater, (c) magnesium, (d) gasoline.
1.12 Classify each of the following as a pure substance or amixture. lf a mixture,
indicate whether it is homogeneous or heterogeneous: (a) air, (b) tomato juice, (c)
iodine crystals, (d) sand.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Matter: Tiny, Fundamental Particles Called AtomsDocument6 pagesMatter: Tiny, Fundamental Particles Called AtomsSittie Annia CAIRODINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading 1 CLASSIFICATION OF MATTERDocument1 pageReading 1 CLASSIFICATION OF MATTERThu Ngân TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Is Matter Arounds As Pure: S.GowrilakshmiDocument8 pagesIs Matter Arounds As Pure: S.GowrilakshmiSomasundariPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of MatterDocument3 pagesClassification of MatterJosefina TabatPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-Iii. Matter and EnergyDocument9 pagesChapter-Iii. Matter and EnergyNIEL RYAN HIZOLEPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Article Theory of MatterDocument19 pagesChemistry: Article Theory of MatterLizzy XeryuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of AggregationDocument6 pagesStages of AggregationgrandayaizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document257 pagesChapter 1Ebin JoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Park JeydsskiiPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-1-2-for-CHEM-1-FINAL-copyDocument17 pagesUNIT-1-2-for-CHEM-1-FINAL-copySherlynMaeBasalatanPas encore d'évaluation
- BiochemisDocument38 pagesBiochemismaxwell amponsahPas encore d'évaluation
- Classify Matter and Its StatesDocument10 pagesClassify Matter and Its Statesshem Louise caladoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Lecture Quiz General ChemistryDocument33 pages1st Lecture Quiz General Chemistrykkpop3931Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 113E Module 1Document11 pagesChem 113E Module 1Christopher Lirasan Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st LectureDocument33 pages1st Lectureaminqasm111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Chemistry Phases and Phase ChangesDocument50 pagesIntroduction to Chemistry Phases and Phase ChangesMicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Basic Concepts in ScienceDocument51 pagesModule 3 Basic Concepts in Sciencehs4fptm82gPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterNicole VictorinoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry FundamentalsDocument33 pagesGeneral Chemistry FundamentalsrenataPas encore d'évaluation
- Module in Science 8 Third Quarter Week 1 Most Essential Learning CompetencyDocument2 pagesModule in Science 8 Third Quarter Week 1 Most Essential Learning CompetencyJR PellejeraPas encore d'évaluation
- All About MatterDocument9 pagesAll About MatterJC UNGRIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 ScienceDocument18 pagesModule 1 ScienceLuisa SevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesThe Properties of MatterShobie Marie AntequisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1Q SCI 7 2Document22 pagesModule 1Q SCI 7 2PeterClomaJr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Instructed Module in Science 6Document21 pagesSelf-Instructed Module in Science 6NikkiBoy Reyes BernabePas encore d'évaluation
- Chem01 - General and InorganicDocument15 pagesChem01 - General and InorganicJetz Hontimara RegioPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryDocument4 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - Chapter SummaryAnirudhPas encore d'évaluation
- Homogeneous and Heterogeneous MixturesDocument2 pagesHomogeneous and Heterogeneous MixturesReyven Computer ShopPas encore d'évaluation
- Fu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Document58 pagesFu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Nermeen ElmelegaePas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter ClassificationDocument19 pagesStates of Matter ClassificationJoshua KulotPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics An Chemistry 3rd ESO - Unit3Document22 pagesPhysics An Chemistry 3rd ESO - Unit3humanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 101 MatterDocument3 pagesChemistry 101 MatterTroy SaguinPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry: Chapter Description Review and Add-OnsDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Chapter Description Review and Add-OnsJesieBoyLlanesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Document9 pagesChapter1 (Matter and Its Properties)Anyanna MunderPas encore d'évaluation
- The 5 Main Branches of ChemistryDocument18 pagesThe 5 Main Branches of ChemistryMohammad khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry BasicsDocument12 pagesChemistry BasicsJanna EchavezPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemistryDocument29 pagesChemistryWith SophPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of MatterDocument4 pagesClassification of MatterDum Spiro SperoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 Introd'n & 2.0 Gaseous State NotesDocument36 pages1.0 Introd'n & 2.0 Gaseous State Notesparkinsondilys7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DPas encore d'évaluation
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument45 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesLu NaPas encore d'évaluation
- Written IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteDocument54 pagesWritten IN General Chemistry: Maharlika Highway, Brgy. Campetic, Palo, LeyteJireh Mae CorderoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 STDocument2 pages1 STPatricia Jane CabangPas encore d'évaluation
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds: The Properties of Solids, Liquids and GasesDocument4 pagesAtoms, Elements and Compounds: The Properties of Solids, Liquids and GaseskimmlisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical and Chemical Changes in MatterDocument2 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes in MatterMaria BachilleratoPas encore d'évaluation
- LAS Week 1 GenChem1 Q3Document6 pagesLAS Week 1 GenChem1 Q3Leonor LlavanesPas encore d'évaluation
- PrentationDocument12 pagesPrentationapi-275785241Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 6 Elements. Compounds, and MixturesDocument4 pagesActivity 6 Elements. Compounds, and MixturesAriane DionisioPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers - For Questions 1 To 12Document3 pagesAnswers - For Questions 1 To 12jokish0% (1)
- Unit 1: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument13 pagesUnit 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistryjahir golandajPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Lecture Outline on MatterDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Lecture Outline on MatterSelene VerhofstadPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Elements KeyDocument4 pagesProperties of Elements KeyDaniel HodgesPas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerJohn Nicolo P. GurangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerodynamics - Basic and Fundamental Concepts-02Document1 pageAerodynamics - Basic and Fundamental Concepts-02ae00505Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Worksheet Packet KEY Name Period Worksheet 1 (Goals 1 - 6) SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES of MATTER (Pages 34 - 37)Document11 pagesUnit 1 Worksheet Packet KEY Name Period Worksheet 1 (Goals 1 - 6) SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES of MATTER (Pages 34 - 37)wendzPas encore d'évaluation
- XI ChemistryDocument86 pagesXI Chemistryadvietiya.fiverrPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ChemistryDocument15 pagesBasic ChemistryNurharis MunandarPas encore d'évaluation
- MatterDocument15 pagesMatterapi-450826118Pas encore d'évaluation
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeD'EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Fund Phy LosDocument1 pageFund Phy LosCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Classical Mechanics Newton's LawsDocument1 pageClassical Mechanics Newton's LawsCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Diffequa 4Document1 pageDiffequa 4CharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Estructuras Quimicas OrganicasDocument2 pagesEstructuras Quimicas OrganicasCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Expr IngDocument1 pageExpr IngCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- EnglishDocument2 pagesEnglishCharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Consistent Units - LS-DYNA SupportDocument1 pageConsistent Units - LS-DYNA SupportpajadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys12 c06 6 1Document9 pagesPhys12 c06 6 1Ruby Angel MannPas encore d'évaluation
- Delegate Angel Salazar Jr. Memorial SchoolDocument4 pagesDelegate Angel Salazar Jr. Memorial Schoolcharis m. alejoPas encore d'évaluation
- NUDocument182 pagesNUHermann Dejero LozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectile Motion LectureDocument30 pagesProjectile Motion LectureherawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- IOAA 2009, Iran (Problems & Solutions)Document57 pagesIOAA 2009, Iran (Problems & Solutions)Science Olympiad Blog60% (5)
- PH2100 Final Exam InstructionsDocument13 pagesPH2100 Final Exam InstructionsAnonymous L21MIUqAPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 1, Solutions PDFDocument2 pagesHomework 1, Solutions PDFYing YaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sacs Sacs: User Training Course Notes User Training Course Notes SEPT 2011 SEPT 2011 Ho Chi Minh City Ho Chi Minh CityDocument68 pagesSacs Sacs: User Training Course Notes User Training Course Notes SEPT 2011 SEPT 2011 Ho Chi Minh City Ho Chi Minh CityphuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws LessonDocument24 pagesNewton's Laws LessonArgel Panganiban DalwampoPas encore d'évaluation
- 07.09. Schauberger - Repulsine - Redesign - Rotor PDFDocument7 pages07.09. Schauberger - Repulsine - Redesign - Rotor PDFTomislav JovanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- KeplarDocument10 pagesKeplarprashant94Pas encore d'évaluation
- G9 PhysicsDocument1 pageG9 PhysicsjanithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Year 7: 9.1 Seeing ForcesDocument25 pagesPhysics Year 7: 9.1 Seeing ForcesNurulAinMatAron100% (1)
- FIITJEE PUNE PRACTICE SET ON UNITS & DIMENSIONSDocument1 pageFIITJEE PUNE PRACTICE SET ON UNITS & DIMENSIONSAmeya KanunjePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 12 Study GuideDocument2 pagesCH 12 Study Guidetownsenr94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shake User ManualDocument94 pagesShake User Manualanita_ygyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Examples & Exercises MCQs (XII - Physics)Document92 pagesNCERT Examples & Exercises MCQs (XII - Physics)Sana SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity For Warp Speed: by John Frederick SweeneyDocument34 pagesGravity For Warp Speed: by John Frederick Sweeneysandeepkshatriy5709Pas encore d'évaluation
- Free Fall and Equations of MotionDocument1 pageFree Fall and Equations of MotionWeteachPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamic Analysis of Slider Crank MechanismsDocument14 pagesDynamic Analysis of Slider Crank MechanismssenthilPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure Moment of Inertia FlywheelDocument8 pagesMeasure Moment of Inertia FlywheelSanil Khinchi100% (1)
- Tutorial Chapter 2 Problems SolvedDocument4 pagesTutorial Chapter 2 Problems SolvedFareez SedakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Weston Fundner - Research Paper 2020Document4 pagesWeston Fundner - Research Paper 2020api-499416081Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mid. Ex. Calculus-Based PhysicsDocument26 pagesMid. Ex. Calculus-Based Physicsarvie montemayorPas encore d'évaluation
- Relativity Conceptual Problems ExplainedDocument50 pagesRelativity Conceptual Problems ExplainedElisabetePas encore d'évaluation
- Cape Physics 2012 U1 p1Document12 pagesCape Physics 2012 U1 p1jason derulo100% (1)
- 9709 w15 QP 53Document4 pages9709 w15 QP 53yuke kristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 FCI Examen SpanishDocument18 pages15 FCI Examen SpanishCésar DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Midterm Exam Questions ExplainedDocument8 pagesPhysics Midterm Exam Questions ExplainedJovan PetkoskiPas encore d'évaluation