Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Variation With Time T (Measured in Seconds) of The Current I (Measured in Amps) in The Resistor Is Given by The Expression I 9.9 Sin (380t)
Transféré par
OGBAGA ONOME JAMESDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Variation With Time T (Measured in Seconds) of The Current I (Measured in Amps) in The Resistor Is Given by The Expression I 9.9 Sin (380t)
Transféré par
OGBAGA ONOME JAMESDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
DOYEN ACADEMY, SCHOOL OF PRELIMININARY STUDIES
CAMBRIDGE ADVANCED LEVEL PROGRAMME
1ST PERIODIC EXAM (FEB, 2014) LEVEL: PRECAMBRIDGE
Subject: Physics TIME: 1 HOUR
PAPER 4 A2 STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
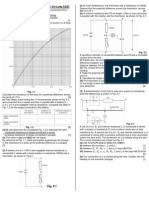
1. An alternating current supply is connected in series with a resistor R
The variation with time t (measured in seconds) of the current I (measured in amps) in the resistor is
given by the expression
I = 9.9 sin(380t).
(a) For the current in the resistor R, determine
(i) the frequency,
(ii) the r.m.s. current.
(b) To prevent over-heating, the mean power dissipated in resistor R must not exceed 400 W.
Calculate the minimum resistance of R.
2. A sinusoidal alternating voltage is to be rectified.
(a) Suggest one advantage of full-wave rectification as compared with half-wave rectification.
(b) The rectification is produced using the circuit of Fig. 2.1.
(c) (i) On Fig. 2.1, draw the symbol for a capacitor, connected into the circuit so as to provide
smoothing.
(ii) State how the amount of smoothing may be increased.
(d) Fig. 2.2 shows the variation with time t of the smoothed potential difference across
the resistor R in Fig. 2.1.
(i) On Fig. 2.2, draw the variation with time t of the potential difference across resistor R for
increased smoothing
(ii) State the interval of time during which the capacitor is being charged
(3) An ideal iron-cored transformer is illustrated in Fig. 3.1.
(a) Explain why
(i) the supply to the primary coil must be alternating current, not direct current,
(ii) for constant input power, the output current must decrease if the output voltage
increases.
(iii) Explain why the coils are wound on a core made of iron.
(iv) Suggest why thermal energy is generated in the core.
(b) A student is asked to design a circuit by which a direct voltage of peak value 9.0 V is obtained
from a 240 V alternating supply. The student uses a transformer that may be considered to be ideal
and a bridge rectifier incorporating four ideal diodes.
Calculate for the transformer used, the ratio of
(c) Electrical energy is usually transmitted using alternating current. Suggest why the transmission is
achieved using
(i) high voltages,
(ii) alternating current.
(4) A block diagram for an electronic sensor is shown in Fig. 4.1.
(a) Complete Fig. 4.1 by labelling the remaining boxes.
(b) State the name of an electrical sensing device that will respond to changes in
(i) length,
(ii) pressure.
(c) A potential divider circuit consists of two resistors of resistances P and Q, as shown in Fig. 4.2.
The battery has e.m.f. E and negligible internal resistance.
Deduce the potential difference V across the resistor of resistance P
(d) The resistances P and Q are 2000Ω and 5000Ω respectively. A voltmeter is connected in parallel
with the 2000Ω resistor and a thermistor is connected in parallel with the 5000Ω resistor, as shown
in Fig. 4.3.
The battery has e.m.f. 6.0 V. The voltmeter has infinite resistance.
(i) State and explain qualitatively the change in the reading of the voltmeter as the temperature of the
thermistor is raised.
(ii) The voltmeter reads 3.6 V when the temperature of the thermistor is 19 °C. Calculate the
resistance of the thermistor at 19 °C.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 3rd 2015 Physics PeriodicsDocument2 pages3rd 2015 Physics PeriodicsOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- Test On Electromagnetic Induction and ACDocument3 pagesTest On Electromagnetic Induction and ACUttam PathakPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Sc. (Aviation SC.) (I Sem.)Document3 pagesB.Sc. (Aviation SC.) (I Sem.)Vipan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN 221 Tutorial May 2024Document3 pagesGEN 221 Tutorial May 2024Charisse StevensPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Exam BDocument4 pagesModel Exam BsugunapriyaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circuits Analysis-I Question PaperDocument9 pagesElectrical Circuits Analysis-I Question Papershravani50% (2)
- Electricity 1 Nov01 4. Nov 02Document6 pagesElectricity 1 Nov01 4. Nov 02Coolman PoonPas encore d'évaluation
- May 2010 SupDocument8 pagesMay 2010 SupViswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- D.C Circuits Class TestDocument1 pageD.C Circuits Class TestShinde JayakrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Book 1 Complete Test 2024Document5 pagesBook 1 Complete Test 2024lukkuyadav050Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47Document134 pagesElectronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47dixitratan68Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHY2 June 2005Document2 pagesPHY2 June 2005api-3726022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Document147 pagesCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edc 3Document10 pagesEdc 329viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nov 2011 SupDocument8 pagesNov 2011 SupViswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Engg-IDocument6 pagesElectrical Engg-IXYZPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Serie Avaliacao EP2018 Ingles 18 SetDocument2 pages1 Serie Avaliacao EP2018 Ingles 18 SetmamellasPas encore d'évaluation
- Xii e - Current Electricity - Worksheet 2Document5 pagesXii e - Current Electricity - Worksheet 2zaharaaebrahim06Pas encore d'évaluation
- L2001a Lab ManualDocument13 pagesL2001a Lab ManualMuhammad Rais FawwaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision ElectricityDocument2 pagesRevision ElectricityLaura MkandlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nr320204-High Voltage EngineeringDocument8 pagesNr320204-High Voltage EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- DC Circuit WorkbookDocument52 pagesDC Circuit Workbookbrainx MagicPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Document8 pagesFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Kung ChinHanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Set No. 1: CEO CBODocument9 pagesSet No. 1: CEO CBO29viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd PeriodicDocument2 pages2nd PeriodicOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Sc. (H) Physics SEM IV (2020-21) DU Ques PaperDocument32 pagesB.Sc. (H) Physics SEM IV (2020-21) DU Ques PaperMerlin JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Scenario:: Internal Verification Form D1Document10 pagesScenario:: Internal Verification Form D1tanmoyr2001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basicelectronicdevicesandcircuits Jntu Model Paper (WWW - Studentyogi.com)Document7 pagesBasicelectronicdevicesandcircuits Jntu Model Paper (WWW - Studentyogi.com)sapabaplivePas encore d'évaluation
- Achievement Test Part - IiDocument3 pagesAchievement Test Part - Iiankit1754qPas encore d'évaluation
- Bt31r0521-p1 Power ElectronicsDocument34 pagesBt31r0521-p1 Power ElectronicsgtchsekharPas encore d'évaluation
- UEE504Document1 pageUEE504Rishab SinglaPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (181 Marks)Document36 pagesShort Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (181 Marks)Hiya ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02305 Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pages9A02305 Electrical CircuitssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Rr310204-Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageRr310204-Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- EDC Question-Papers Complete SetDocument13 pagesEDC Question-Papers Complete Setselvi04120% (1)
- RR 410207 High Voltage EngineeringDocument2 pagesRR 410207 High Voltage EngineeringsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc 4Document10 pagesEdc 429viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECE341 Lab3 FinalDocument6 pagesECE341 Lab3 FinalJhasper FLores0% (1)
- Questions On LCR CircuitDocument2 pagesQuestions On LCR CircuitKRISHNA PARIHARPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 3Document28 pagesCH 3terasaini77Pas encore d'évaluation
- PHYC10004 Examination 2015Document8 pagesPHYC10004 Examination 2015Bussemand12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 6 Arus Bolak Balik (AC)Document3 pagesModul 6 Arus Bolak Balik (AC)Sheila HuangPas encore d'évaluation
- EC101 BECE - Question BankDocument21 pagesEC101 BECE - Question Bankdarkhuntert9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity2 PDFDocument17 pagesElectricity2 PDFPraphul MalolPas encore d'évaluation
- Homwork - 1Document15 pagesHomwork - 1TimoPas encore d'évaluation
- Division Principle For Two Resistors in ParallelDocument12 pagesDivision Principle For Two Resistors in ParallelRaja pandiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 AC Tutorial (Student)Document10 pages2014 AC Tutorial (Student)محمد حازق بن رزوانPas encore d'évaluation
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocument4 pagesU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Classes: BY Vinit Saluja SirDocument3 pagesPhysics Classes: BY Vinit Saluja SirVinit SalujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 EE 2151 - Circuit TheoryDocument4 pages5 EE 2151 - Circuit TheoryBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankDocument9 pagesUnit 2: Current Electricity: Question BankNathanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsD'EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeD'EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)D'EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd 2015 Physics PeriodicsDocument7 pages3rd 2015 Physics PeriodicsOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Mechanics 2016 PeriodicsDocument2 pages2nd Mechanics 2016 PeriodicsOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 A Particle P Is Projected Vertically Upwards With Speed 11msDocument4 pages1 A Particle P Is Projected Vertically Upwards With Speed 11msOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st PeriodicDocument1 page1st PeriodicOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd PeriodicDocument2 pages2nd PeriodicOGBAGA ONOME JAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Status of E&M EquipmentDocument4 pagesManufacturing Status of E&M Equipmenttaimur ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
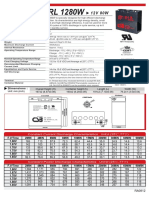
- CSB hrl-1280wDocument2 pagesCSB hrl-1280wGustavo BessonePas encore d'évaluation
- Bslbattlfp OF Performance: TheheightDocument3 pagesBslbattlfp OF Performance: TheheightCamilo PérezPas encore d'évaluation
- BA - Break Down TopicsDocument6 pagesBA - Break Down TopicsJin ZongPas encore d'évaluation
- Wiboonrat 2017Document6 pagesWiboonrat 2017Vetrivel PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Kilowatt Labs Sirius-Technical Data Sheet-1000-48-B-1C-TM-A-GDocument2 pagesKilowatt Labs Sirius-Technical Data Sheet-1000-48-B-1C-TM-A-GIvanPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Xtralis Internal Power Supply TDS A4 LoresDocument2 pages02 Xtralis Internal Power Supply TDS A4 Loreskmlowpg2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesElectric Potential EnergykruvanhPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Heating - Space For HeatDocument52 pagesCentral Heating - Space For HeatahmedaborashedPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Model ExamDocument2 pagesMe 2403 Power Plant Engineering - Model ExamBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- For Sustainable Energy: Our VisionDocument140 pagesFor Sustainable Energy: Our VisionSam ChanPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Oil and Gas IndustryDocument23 pagesGlobal Oil and Gas IndustryYash Agarwal100% (1)
- Nureg 1738Document369 pagesNureg 1738William IvansPas encore d'évaluation
- GTL Economics SPE-94380-MSDocument8 pagesGTL Economics SPE-94380-MSWayne MonneryPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Manual - Satellite MSP PDFDocument131 pagesTechnical Manual - Satellite MSP PDFhany hanafyPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Exam PDFDocument7 pagesBoiler Exam PDFJerick HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyDocument17 pagesUnit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyRut ChristinePas encore d'évaluation
- Lucy Ring MainDocument12 pagesLucy Ring MainfndprojectPas encore d'évaluation
- ASHRAE-90.1-Presentation - V6 - Website Tabla 6.5 Hydronic SystemDocument78 pagesASHRAE-90.1-Presentation - V6 - Website Tabla 6.5 Hydronic SystemAnonymous 8LOtly9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fire TechnologyDocument106 pagesFire TechnologyCJ LicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Report 2015-IESL SabaragamuwaDocument37 pagesAnnual Report 2015-IESL SabaragamuwaChaminda KumaraPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Leaflet Comem BR-En 2018-06-07Document2 pagesABB Leaflet Comem BR-En 2018-06-07Dave ChaudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajat Bhardwaj - DissertationDocument48 pagesRajat Bhardwaj - DissertationUPES IFMPMPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual Power System Protection by PaithankarDocument6 pagesSolution Manual Power System Protection by PaithankarHaseeb Nawaz64% (11)
- HVDC Jan SvenssonDocument13 pagesHVDC Jan SvenssonWilber William Moscoso ZamudioPas encore d'évaluation
- SolarCell Sunpower C60 PDFDocument2 pagesSolarCell Sunpower C60 PDFinginheroPas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Its Generation and Use 41st EdDocument1 119 pagesSteam Its Generation and Use 41st EdCarmine Saffioti100% (16)
- Calculating Free Energies Using Adaptive Biasing Force MethodDocument14 pagesCalculating Free Energies Using Adaptive Biasing Force MethodAmin SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- DS ACPowerBlock A4Document2 pagesDS ACPowerBlock A4edsonleviPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure HTD HTU HTX enDocument4 pagesBrochure HTD HTU HTX ensamiramixPas encore d'évaluation