Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Stainless Steel PDF
Transféré par
Giri DharanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Structural Stainless Steel PDF
Transféré par
Giri DharanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Structural stainless steel
Decorative stainless steel panels are widely used in façades, roofs and elevators because they are attractive
and long-lasting. Increasingly, engineers now use stainless steel for load-bearing structures in challenging
environments. In many cases stainless steel is cost-effective if the whole life cycle of the installation is considered.
More than half of the annual production and maintenance are impossible or very Designing with structural stainless
of steel worldwide is used in construction. costly. steel
Typically I-beams, plates and reinforcing
bars in buildings and bridges are made This is true even though stainless steel Design codes and specifications for
of affordable carbon or low-alloy structural is significantly more expensive than conventional structural carbon steel
steel. Unfortunately, these grades of carbon steel. There are ways to reduce cannot be used with stainless steel,
steel rust easily. This has an enormous the gap in material costs, however. because the mechanical properties
economic and environmental impact on Eliminating coatings decreases installed (specifically the stress-strain behavior)
the world’s infrastructure, affecting roads, cost, and when using the higher-strength of the two materials are fundamentally
bridges, buildings and systems that duplex stainless steel, it may be possible different. Stainless steel therefore needs
distribute oil, gas, water and waste water. to trim section sizes (and weight) to its own set of design rules.
further lower the initial investment.
The annual cost of corrosion to In Europe, Part 1.4 of Eurocode 3,
industrialized countries is 3 to 4% of their When it comes to maintenance cost over EN 1993-1-4 Design of steel structures,
GDP according to numerous studies. an installation’s life, the use of stainless Supplementary rules for stainless steels,
This figure includes only the direct cost steel eliminates coating maintenance was published in 2006 1. It is based on
of replacing damaged material and costs and component replacement due many years of research carried out
components. Indirect costs, such as loss to corrosion. Stainless steel construction around the world and covers hot-rolled,
of production, environmental impact, may also provide a more sustainable welded and cold-formed structural
transportation disruptions, injuries and solution, reducing emissions, resource sections. ›
fatalities are estimated to be just as high. depletion and waste.
Standard structural steels must be Minimum specified values of design strength fy for structural stainless steel hot-rolled plate
painted or covered with metallic coatings
to minimize corrosion. In addition to US Specification European Specification
the initial cost of such protection,
Grade Design Grade Design
coated steels require costly inspection, Type of
strength a strength b
maintenance, and sometimes replace- stainless
ment over a structure’s life. The indirect steel fy fy
Common UNS EN
cost of maintenance such as loss of
name designation MPa designation MPa
production and revenue can also be high.
Sometimes it is simply impossible to
Austenitic, 304 S30400 205 1.4301 210
access components of a structure to
without Mo
carry out inspection and maintenance. 304L S30403 170 1.4307 200
Comparing life-cycle costs Austenitic, 316 S31600 205 1.4401 220
2% Mo
316L S31603 170 1.4404 220
Designers increasingly take into account
the costs of a structure throughout its whole Duplex, <0.5% Mo 2101 S32101 450 1.4162 450
life, not only its initial cost. When life-cycle
costs are considered, stainless steel Duplex, <0.5% Mo 2304 S32304 400 1.4362 400
becomes viable, particularly for structures
Duplex, 3% Mo 2205 S32205 450 1.4462 460
requiring durability or where inspection
a ASTM 240 and A276 b EN 10088
1 EN 1993-1-4:2006 Eurocode 3 Design of steel structures Part 1-4: General rules. Supplementary rules for stainless steels
Excerpt from MolyReview 1/2014 1
In the US, guidance on design with As always with stainless steels, grade
lighter gauge stainless steel sections has selection is crucial. Molybdenum provides
been available for years 2, but there was the improved corrosion resistance of
no design specification covering hot- grades like Type 316 (2% Mo, austenitic)
rolled and welded stainless steel structural or 2205 (3% Mo, duplex). These grades
sections. This required designers to work are, therefore, often specified in corrosive
from first principles or use rules for environments such as coastal regions, or
carbon steel with additional safety factors, where there is exposure to de-icing salts,
a significant obstacle. Moreover, the lack heavy pollution or chemicals. Duplex
of a design standard required building stainless steels like 2205 are twice as
enforcement officials to approve each strong as most austenitics, giving them
application individually. an additional advantage in load-bearing
applications.
IMOA, in cooperation with stainless
steel producers and other industry Structural stainless steel
associations, initiated a project in 2009 to applications
develop design rules for heavier stainless The Design Guide is a comprehensive
steel structural sections. The effort document covering design rules for The key advantages of stainless steel for
resulted in the publication of AISC Design structural members and connections at load-bearing applications include corrosion
Guide 27: Structural Stainless Steel, ambient temperatures and in fire. It resistance and hence durability even in
authored by Nancy Baddoo of the Steel discusses material properties, grade corrosive environments, better retention of
Construction Institute in September selection and durability, and gives strength in fires compared to carbon steel,
2013 3. The guide can be downloaded guidance on fatigue, fabrication and high impact resistance, good cleanability
from AISC’s website at www.aisc.org/dg. erection. and a pleasing appearance.
The Passerelle Mobile footbridge in Lyon-Confluence, designed by PCCP and ALTO, has 2205 duplex stainless steel structural members.
Their strength allowed a considerable reduction of the size and thickness of the sections and the weight of the bridge. © ALTO and PCCP
2 American Society of Civil Engineers (2003) Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Stainless Steel Structural Members,
SEI/ASCE 8-02, Reston, VA
3 Baddoo, N R, AISC Design Guide 27: Structural Stainless Steel, AISC, September 2013
Excerpt from MolyReview 1/2014 2
2205 duplex stainless steel escape
tunnel on a floating production, storage
and offloading (FPSO) vessel. © BP p.l.c.
Among the most iconic structural
applications are monuments such as
Arlington’s Air Force Memorial, Dublin’s
Spire or St. Louis’ Gateway Arch, and
sculptures like the Cloud Gate (known
as “The Bean”) in Chicago. Pedestrian
bridges like The Helix in Singapore and
San Diego’s Harbor Drive Bridge, both
previously covered in MolyReview, also
have high visibility.
Stainless steel structural components
are often used in commercial buildings to
support glass curtain walls. For example,
the smallest connections in New York’s
5th Avenue Apple Cube are almost
invisible, allowing nearly unobstructed
views. Like stainless steel canopies,
handrails and street furniture, connectors
require little maintenance. Fasteners,
anchoring systems and support angles
for wood, stone and masonry are often
inaccessible or difficult to replace and
benefit from structural stainless steel’s
good corrosion resistance. Wood and
masonry can themselves be corrosive to
other metals and are likely to absorb
moisture and corrosive chemicals over
time.
Road tunnels are harsh environments for
materials. Maintenance costs are high
and a structural failure or fire can have
Tunnel ceiling suspended from a duplex stainless steel system,
severe consequences. Stainless steel is North-South Bypass Tunnel, Brisbane, Australia. © Ancon
therefore deployed in tunnel construction
for linings and their support frames,
maintenance walkways, fixings and
fasteners, lighting and signage supports barriers and bollards. It can absorb The water treatment, pulp and paper,
and ground-support rock anchors. The considerable impact without fracturing nuclear, biomass, chemical, pharmaceu-
CLEM7 Tunnel under the Brisbane River, due to its excellent ductility and strain- tical, and food and beverage industries
the longest road tunnel in Australia, hardening characteristics. make extensive use of stainless steel in
has many advanced safety features. In platforms, barriers, gates, ladders, stairs,
the event of a fire or explosion, a On offshore structures, escape routes cable trays and equipment supports.
high-tech ventilation system comprising are required for personnel in the event
100 jet fans will rapidly extract smoke to of explosion and fire. They can vary from Engineers are increasingly selecting
a longitudinal duct high above the road semi-open walkways to fully enclosed stainless steel for load-bearing applications
deck. A duplex 2205 stainless steel high-integrity fire- and blast-rated tunnels, that benefit from its durability, attractive
system suspends the massive concrete an example of which is the escape tunnel appearance, strength, ductility, toughness
slabs, which form the duct in the highly suspended on the side of the Skarv and formability. The broader availability
corrosive environment. FPSO (Floating production, storage and of design guides makes it easier to
offloading) vessel. The tunnel is over specify stainless steel for applications that
Stainless steel is also used for explosion- 200 meters long and comprises an inner require durable, resilient and sustainable
and impact-resistant structures such carbon steel truss and an outer 2205 structures and go beyond decorative
as blast and security walls, gates, security duplex stainless steel envelope. panels. (Nancy Baddoo)
Excerpt from MolyReview 1/2014 4
Structural stainless steel case study: UK’s first desalination plant
London is a surprising location for a
desalination plant considering its cool,
wet climate. Predictions based on climate
change and population expansion,
however, indicated that London water
demand could outstrip existing freshwater
supply in the next few years. Therefore,
the UK’s first desalination plant, the
Thames Gateway Water Treatment
Works in East London, was opened in
2010. The plant treats brackish Thames
River water to produce up to 150 million
liters of clean drinking water each day,
enough to supply up to one million
Londoners. It will be used to supplement
supplies during extended periods of low
rainfall, maintain supplies in the event
of incidents at other water facilities and
support future demand growth.
Plant design with carbon steel – The
Gateway plant utilizes the world’s first
high-efficiency four-step, rather than
the more common two-step, reverse
osmosis desalination process. Brackish
A framework of duplex stainless steel beams support the lamella clarifiers. © Interserve
river water passes four times through
semipermeable membranes to achieve a
high level of salt removal.
They also must be highly corrosion water without coating, thanks to the
The water first passes through lamella resistant, not to be compromised addition of 3% molybdenum. This grade
clarifiers, containing a coarse filter throughout the 60-year design life of the is also approved for contact with drinking
medium, to remove solid particles. The plant. The beams were initially specified water by the Drinking Water Inspectorate
clarifiers are large open tanks, supported as epoxy-coated carbon steel, but (DWI), the independent regulator of
by a framework of 78 I-beams. These it was recognized that there would be a drinking water in England and Wales.
beams need good strength and stiffness. high risk of damage to the coating during
installation and maintenance. This would Minimizing costs – Simply replicating
have resulted in rusting of the carbon the carbon steel beams in stainless steel
steel beams and subsequent damage to would have led to a 74% cost increase,
the £7 million desalination membranes. so several measures were undertaken to
reduce cost. Firstly, the superior strength
Using molybdenum-containing properties of duplex stainless steel were
stainless steel instead – Unlike carbon exploited. A web depth of 500 mm was
steel, the surface of stainless steel is selected for the fabricated beams, to be
protected from corrosion by an adherent cut from 2-meter wide plate, reducing
layer of chromium-rich oxide that offcut wastage. The flange dimensions
reforms immediately if damaged, self- were sized to optimize bending strength,
healing the surface. Thus, the engineers, while keeping beam deflection within
concerned about the durability of the acceptable limits. As a result, the total
epoxy-coated beams, specified 2205 weight of the stainless steel beams was
duplex stainless steel instead. This reduced from 140 tonnes to 75 tonnes,
Desalination Plant at Thames Gateway Water grade has high strength, requires little allowing considerable cost savings.
Treatment Works, East London. © Interserve maintenance and is durable in brackish (Nancy Baddoo)
Excerpt from MolyReview 1/2014 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Duplex Stainless Steel 2d Edition PracticalDocument64 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 2d Edition Practicalmahmoud_allam3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Duplex Stainless Steel 3rd EditionDocument68 pagesDuplex Stainless Steel 3rd EditionPhani Sridhar Ch100% (3)
- Your Guide To Shaker Furniture: 3 Classic ProjectsDocument25 pagesYour Guide To Shaker Furniture: 3 Classic Projectsjpl.guedes6842100% (1)
- Knife Maintenance and SharpeningDocument44 pagesKnife Maintenance and SharpeningDanie-ElsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cladding & Overlay - Ni InstituteDocument24 pagesCladding & Overlay - Ni Institutesajid aslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Stainless SteelDocument13 pagesApplication of Stainless Steelsweety1188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Testing of Austenitic Stainless SteelsDocument64 pagesTesting of Austenitic Stainless SteelsmirelamanteamirelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailing of Reinforcement in Concrete Structures-17Document328 pagesDetailing of Reinforcement in Concrete Structures-17Ahmed Refaey76% (17)
- Static Calculation CWDocument64 pagesStatic Calculation CWlayaljamal2100% (1)
- Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument7 pagesDuplex Stainless SteelsRizalzi BachtiarPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Shotcrete ConcreteDocument8 pagesDesign of Shotcrete ConcreteDevinder SokhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Frame ConstructionDocument47 pagesSteel Frame Constructionapi-386384775Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gardner2005 TheuseofstainlesssteelinstructuresDocument39 pagesGardner2005 Theuseofstainlesssteelinstructuresherdi sutanto adigunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm A743 PDFDocument6 pagesAstm A743 PDFzafarbadal100% (2)
- DSR 2012 Excel FormatDocument141 pagesDSR 2012 Excel FormatAkash Goyal50% (2)
- Brochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingDocument36 pagesBrochure - Joint Sealants For Building Envelope WaterproofingBudi Max100% (1)
- STANDARD ComparisonDocument10 pagesSTANDARD Comparisonsarath6725Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astm B633-19Document3 pagesAstm B633-19Cj Elamparo100% (1)
- Design of Fillet Weld (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, CL 4.5.3) : KN M KN KN M KN KN MMDocument2 pagesDesign of Fillet Weld (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, CL 4.5.3) : KN M KN KN M KN KN MMGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Strength of Screw AAMA TIR-A9Document1 pageDesign Strength of Screw AAMA TIR-A9Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 Steel Design Batch 4Document197 pagesModule 3 Steel Design Batch 4Aileen PornelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Survey FlooringDocument12 pagesMarket Survey FlooringJhanviPas encore d'évaluation
- SFA Framing Guide 07 PDFDocument12 pagesSFA Framing Guide 07 PDFalattar98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion and its Consequences for Reinforced Concrete StructuresD'EverandCorrosion and its Consequences for Reinforced Concrete StructuresPas encore d'évaluation
- CETEST Notes FinalsDocument33 pagesCETEST Notes FinalsKrischanSayloGelasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thep Khong GiDocument9 pagesThep Khong GiQuân BùiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Stainless Steel: in The Construction IndustryDocument12 pagesThe Use of Stainless Steel: in The Construction IndustrywitwatersrandPas encore d'évaluation
- Bake Hardening SteelDocument15 pagesBake Hardening SteelAnoop KizhakathPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Fabrication in Architectural Stainless Steel: ISBN 2-87997-062-8Document10 pagesGood Fabrication in Architectural Stainless Steel: ISBN 2-87997-062-8pavi32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Fact Sheet No 02 Selection of Stainless Steels For Use in The Water IndustryDocument6 pagesMaterials Fact Sheet No 02 Selection of Stainless Steels For Use in The Water IndustrydipankarbasakPas encore d'évaluation
- TRM255 Use of Stainless Steel ReinforcementDocument3 pagesTRM255 Use of Stainless Steel ReinforcementTuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Steel FramingDocument8 pagesChapter 8 - Steel Framingleowongck0119Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02-Duplex Stainless Steel For Indian Construction and Architecture Application-YpsuriDocument10 pages02-Duplex Stainless Steel For Indian Construction and Architecture Application-YpsuriPrashant PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Reiforced Concrete Ce-Ment & Steel Structure: Group 2Document51 pagesReiforced Concrete Ce-Ment & Steel Structure: Group 2Caesar DagaasPas encore d'évaluation
- Stainless Steel 6Document10 pagesStainless Steel 6YKAGARWALPas encore d'évaluation
- New Generation Stainless Steel Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresDocument28 pagesNew Generation Stainless Steel Reinforcing Bars For Concrete StructuresAshfaq SaudagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Metallurgy and Processing of Ultralow Carbon Bake Hardening SteelsDocument14 pagesMetallurgy and Processing of Ultralow Carbon Bake Hardening SteelsvictorPas encore d'évaluation
- NiDi Rpt. - McGurn - Schaffhausen Bridge LCCDocument15 pagesNiDi Rpt. - McGurn - Schaffhausen Bridge LCCBabu SundararamanPas encore d'évaluation
- IJETR021817Document3 pagesIJETR021817erpublicationPas encore d'évaluation
- Choice of Specifications and Design Codes For Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument12 pagesChoice of Specifications and Design Codes For Duplex Stainless SteelsRonald Leyva GiraldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Austenitic Stainless SteelsDocument10 pagesAustenitic Stainless SteelsbramPas encore d'évaluation
- SteelDocument28 pagesSteelAshfaq SaudagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Duplex Stainless Steels - A Simple Guide: How The Austenite/Ferrite Balance Is AchievedDocument4 pagesDuplex Stainless Steels - A Simple Guide: How The Austenite/Ferrite Balance Is AchievedAndy PhoenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials ProjectDocument4 pagesMaterials Projectxtopherus124Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Use of Stainless Steel in Structures: Progress in Structural Engineering and Materials April 2005Document39 pagesThe Use of Stainless Steel in Structures: Progress in Structural Engineering and Materials April 2005RatanRatuPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion Properties of UNS S32101 Reinforcement Bar 2005 2Document15 pagesCorrosion Properties of UNS S32101 Reinforcement Bar 2005 2Kuldeep BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Gardner2005 TheuseofstainlesssteelinstructuresDocument39 pagesGardner2005 TheuseofstainlesssteelinstructuresthisaintwapPas encore d'évaluation
- SFA Framing Guide Final 2Document12 pagesSFA Framing Guide Final 2SevrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Products To Be Hot-Dip Galvanized After FabricationDocument28 pagesDesign of Products To Be Hot-Dip Galvanized After FabricationArlet BibriescaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel in Stadium EgineeringDocument4 pagesSteel in Stadium EgineeringFrans HeidelooPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding and Post Fabrication Cleaning For Construction and Architectural Applicatio-Pag2Document1 pageWelding and Post Fabrication Cleaning For Construction and Architectural Applicatio-Pag2eugenio.gutenbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion Protection: Arcelormittal Europe - Long Products Sections and Merchant BarsDocument48 pagesCorrosion Protection: Arcelormittal Europe - Long Products Sections and Merchant BarstecnidibujosPas encore d'évaluation
- Arminox SSReinforce Report Arminox WebDocument29 pagesArminox SSReinforce Report Arminox WebSuraj PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aming Members Sept 04Document16 pagesAming Members Sept 04Edison BecerraPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Introduction To Structural Steel ConstructionDocument20 pages5 Introduction To Structural Steel ConstructionKosygin LeishangthemPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0924013616301480 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0924013616301480 MaintarnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- CMT - Module 7 (STEEL)Document7 pagesCMT - Module 7 (STEEL)John Fred Marzan CativoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFDocument13 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of Modern High Strenght Steel Sheets PDFJose Merced Martinez VazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Stainless Steel As ReinforcementDocument21 pagesReport On Stainless Steel As ReinforcementAnket PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document35 pagesPresentation 1S RPas encore d'évaluation
- By - Shaik ShahidDocument22 pagesBy - Shaik ShahidAnonymous q6SfMddJDoPas encore d'évaluation
- And Steel Framing: Pressure Treated WoodDocument2 pagesAnd Steel Framing: Pressure Treated WoodGopi KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- D153 PSSC2010RWhiteDocument17 pagesD153 PSSC2010RWhiteJamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel: Construction's Material TechnologyDocument26 pagesSteel: Construction's Material TechnologyUtamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm B633-19Document8 pagesAstm B633-19sharma.sumeet2290Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 ReinforcementDocument6 pages2 ReinforcementymanfasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013v12 New Guide PDFDocument4 pages2013v12 New Guide PDFlucianolimapgecivPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Structures Design Based on Eurocode 3D'EverandSteel Structures Design Based on Eurocode 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
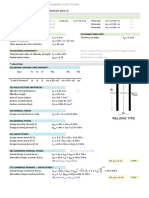
- KN KN KN MM MM KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Document1 pageKN KN KN MM MM KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - Curtain Wall Systems DesignDocument5 pagesPaper - Curtain Wall Systems DesignGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - Anchoring To Concrete Tensile Loadings CriteriaDocument6 pagesPaper - Anchoring To Concrete Tensile Loadings CriteriaGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - A Cladding Designers PerspectiveDocument2 pagesPaper - A Cladding Designers PerspectiveGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Weld Connection Hooking Plate and SHSDocument1 pageWeld Connection Hooking Plate and SHSGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - Anchoring To Concrete Shear Loadings CriteriaDocument5 pagesPaper - Anchoring To Concrete Shear Loadings CriteriaGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper - A New Design Model Based On Actual Behaviour of Glass PanelsDocument4 pagesPaper - A New Design Model Based On Actual Behaviour of Glass PanelsGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- STEEL BASE PLATE Verfication BS EN 1993 1 & 8Document1 pageSTEEL BASE PLATE Verfication BS EN 1993 1 & 8Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
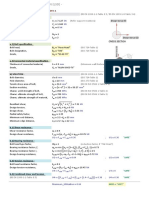
- Design As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: - Verification of Flat Plate, InputDocument2 pagesDesign As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: - Verification of Flat Plate, InputGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: Max Max Max Ed Ed EdDocument2 pagesDesign As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: Max Max Max Ed Ed EdGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Weld Connection Betweeen SHSDocument1 pageWeld Connection Betweeen SHSGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Document1 pageKN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Bolt (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, Table 3.4) : KN MM MM KN KN KN KNDocument1 pageDesign of Bolt (As Per Bs en 1993 1 8, Table 3.4) : KN MM MM KN KN KN KNGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- WELD Check - STEEL BS 1993 1 8 - Horizontal (2 Lines) (8to8mm)Document1 pageWELD Check - STEEL BS 1993 1 8 - Horizontal (2 Lines) (8to8mm)Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mullion Transom Connector BS-EN-1991-1-1 V2.0Document2 pagesMullion Transom Connector BS-EN-1991-1-1 V2.0Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Glass - Bottom Row: MM KNM MM MM KNDocument1 pageFixed Glass - Bottom Row: MM KNM MM MM KNGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- WELD Check - STEEL BS 1993 1 8 - Horizontal (2 Lines) (8to8mm)Document1 pageWELD Check - STEEL BS 1993 1 8 - Horizontal (2 Lines) (8to8mm)Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Document1 pageKN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KN KN: Design of Bolt & NutDocument1 pageKN KN KN: Design of Bolt & NutGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KN KN: Design of Bolt & NutDocument1 pageKN KN KN: Design of Bolt & NutGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt CalcDocument1 pageBolt CalcGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Document1 pageKN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Design As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: Ed Ed Max Max Max EdDocument2 pagesDesign As Per Bs en 1993 1 1: Ed Ed Max Max Max EdGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Document1 pageKN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt CalcDocument1 pageBolt CalcGiri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Document1 pageKN KN KN: Design As Per Bs en 1999 1 1Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- KN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Document1 pageKN KNM KN MM KNM KN KNM: (Shear, H) (-) (-) (Shear, V) (Normal) (-)Giri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensitization of AISI 304 and Reversing of Corrosion 2012Document13 pagesSensitization of AISI 304 and Reversing of Corrosion 2012Adnan SaadiPas encore d'évaluation
- UK Smoothbore 16.12.21 Rev 46Document13 pagesUK Smoothbore 16.12.21 Rev 46stevensilvasaPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 - Underpinning Piles of Segmental Precast ConcreteDocument2 pages08 - Underpinning Piles of Segmental Precast ConcreteaggibudimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Taper Taps CatalogDocument2 pagesTaper Taps Catalogandreas kriswantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kennedy Valve c515 Gate ValveDocument21 pagesKennedy Valve c515 Gate ValveHani SaadePas encore d'évaluation
- Resilient Seat Gate ValveDocument2 pagesResilient Seat Gate Valvekhai rulePas encore d'évaluation
- FTM HFV HiltiDocument5 pagesFTM HFV HiltiPrabartak Das100% (1)
- (DIN 28050 - 2009-09) - Behà Lter Und Apparate - Maximal Zulã Ssiger Druck - 1, 0 Bar Bis +0, 5 Bar - Technische Lieferbedingungen - 0001.de - enDocument8 pages(DIN 28050 - 2009-09) - Behà Lter Und Apparate - Maximal Zulã Ssiger Druck - 1, 0 Bar Bis +0, 5 Bar - Technische Lieferbedingungen - 0001.de - enNaveen Suresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dow Corning 983Document3 pagesDow Corning 983antoinePas encore d'évaluation
- BONT Level GaugeDocument13 pagesBONT Level Gaugeabdul azzam Al BanjariPas encore d'évaluation
- Galvanic Corrosion ChartDocument2 pagesGalvanic Corrosion Chartrmartinson8Pas encore d'évaluation
- CAB Solar Tube Hangers SalesSheet5 AUG2022ADocument2 pagesCAB Solar Tube Hangers SalesSheet5 AUG2022AtammamshPas encore d'évaluation
- Din 6330Document1 pageDin 6330PatriciaeRafael AlmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewal of Product Approval MS Sika India PVT LTDDocument4 pagesRenewal of Product Approval MS Sika India PVT LTDsandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- On BondsDocument18 pagesOn BondsMahesh Ramteke100% (1)
- SBS Basalt 101Document4 pagesSBS Basalt 101kelvinyeohPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Grinding & Other Abrasive ProcessesDocument82 pages6 Grinding & Other Abrasive Processessakali ali100% (1)
- Unitherm Cat 2210 Pre Insulated TubingDocument2 pagesUnitherm Cat 2210 Pre Insulated TubingSebas FaustoPas encore d'évaluation
- Uni MechDocument2 pagesUni MechSAMPATHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanitaryware AER (Offline)Document11 pagesSanitaryware AER (Offline)Tri Setia BudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Globe Valves: Bronze Globe Valve - Series B PN32Document1 pageGlobe Valves: Bronze Globe Valve - Series B PN32Juan ZapataPas encore d'évaluation
- M-Jet 60 Basic ManualDocument5 pagesM-Jet 60 Basic ManualJordi Ferrer0% (1)