Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Voltage Regulator AVC63-7 Manual PDF
Transféré par
Eduardo A. CottaniTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Voltage Regulator AVC63-7 Manual PDF
Transféré par
Eduardo A. CottaniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
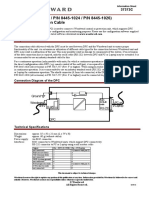
INSTRUCTIONS
FOR
Basler Electric VOLTAGE REGULATOR Power Systems Group
Phone 618 654-2341 Fax 618 654-2351
MODEL: AVC63-7
Route 143 Box 269 http://www.basler.com
9 3028 00 100
Highland IL 62249 USA info@basler.com
INTRODUCTION Storage Temperature Reactive Droop Compensation
For reactive droop compensation, connect the CT
The Basler AVC 63-7 Voltage Regulator is an -65 C (-85 F) to +85 C (+185 F). to its respective regulator as shown on Figures 4
encapsulated unit contained in a plastic case. Vibration and 5.
The regulator controls the dc exciter field power of Withstands 1.2 Gs at 5 to 26 Hz; 0.036" double
conventional, 50 or 60 Hz brushless generators amplitude at 27 to 53 Hz; 5 Gs at 53 to 1000 Hz. A unit-parallel switch shorts the parallel CT
that have a 63 Vdc exciter field to regulate the secondary to prevent any droop signal from being
Shock injected into the regulating system during single
generator output voltage.
Withstands up to 15 Gs in each of three mutually unit operation. The switch may not be required on
Regulation is provided by sensing the generator perpendicular axes. parallel droop compensation applications where a
output voltage, converting it to a dc signal and voltage drop is not objectionable.
Weight
comparing the signal to a reference voltage signal.
1.1 lb (0.5 kg) net.
An error signal is developed and used to control Reactive Differential Compensation
the dc field power in order to maintain a constant INSTALLATION On parallel reactive differential compensation
generator output. applications a contact should be used to short out
Mounting
the paralleling CT secondary when that generator
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS The regulator may be mounted in any position.
is not paralleled to the bus. If the switch is not
Refer to the outline drawing (Figure 2). The
Dc Output Power used, a voltage droop will be introduced into the
regulator may be mounted directly on the
7 Adc at 63 Vdc maximum continuous with a 240 system. This is due to the unloaded generator
generator set using 1/4" hardware. Select the
Vac input. parallel CT not supplying its compensating signal,
proper hardware to withstand any expected
but allowing a voltage drop to occur across it.
Exciter Field DC Resistance shipping/transportation and operating conditions.
Lack of this shorting contact will also cause the
9.0 ohms minimum.
Interconnection voltage of the incoming generator to fluctuate prior
Ac Power Input Refer to Figures 3 and 4. to paralleling. Ideally, this contact is an auxiliary
170 to 305 Vac, single-phase, 50/60 Hertz. a. Connect a jumper from COM to the 50 Hz on the circuit breaker contactor that opens when
Burden: 900 VA maximum at 240 Vac power. terminal for 50 Hz operation, or leave the two the circuit breaker is closed.
Ac Sensing Voltage terminals unconnected for 60 Hz operation.
For reactive differential compensation, connect
170 to 264 Vac, single-phase, 50/60 Hertz. b. If an external voltage adjust control is being
each CT to its respective regulator. Then connect
Burden: 5 VA. used, connect the potentiometer to terminals
the finish of the first CT to the start of the second
6 and 7 as shown. If not, connect a jumper
Voltage Adjust Range CT, the finish of the second CT to the start of the
between terminals 6 and 7.
170 to 264 Vac using the internal voltage adjust. c. Connect the exciter field to terminals F+ and third CT, etc. Continue until all CT’s are
The external voltage adjust provides a ±10% connected in series. The final step will be to
F-. Be sure to observe polarity. connect the finish of the last CT to the start of the
adjustment of the nominal value determined by the d. Connect the input power to the generator
internal voltage adjust. first CT. (See Figure 5).
stator to provide power to terminals 3 and
Regulation Accuracy E3/4. Fuse both leads. Install the optional Reactive differential compensation cannot be used
Plus/minus 0.25%. shutdown switch, if desired. when paralleled with the utility or any infinite bus.
e. Connect the sensing input to E1 and E3/4. If this compensation system is used, a switching
Voltage Drift circuit must be used to convert the system to a
<±1% voltage variation for a 50°C (90°F) change. The sensing should be connected "line-to-
line". reactive droop compensation system. Contact the
Response Time factory for additional information.
<16mSec. Parallel Compensation
When it is required to operate the regulator in OPERATION
Frequency Compensation parallel with an isolated or utility bus, in addition to
Refer to Figure 1. General
the regulator provisions, a 10 VA current
The below procedures provide instructions for
Voltage Build-Up transformer (CT) is required (See Figures 3 and 4.)
setting up, starting, operating, and adjusting the
Internal provisions for automatic build-up from This CT is connected in a generator line and AVC 63-7 Voltage Regulator. Symptoms of
generator residual voltages as low as 6 Vac at 25 should deliver from 3 to 5 amperes secondary problems occurring during start-up that result from
hertz. current at rated load.
incorrect regulator adjustment and certain
Power Dissipation The phase relationship of CT signal to the generator system problems that resemble faulty
35 W maximum. regulator sensing voltage must be correct or the regulation, are included together with possible
system will not parallel properly. The CT must be solutions.
Paralleling Provisions
installed in the line of the three-phase generator
CT input for customer supplied 5 Amp nominal CT. Preliminary Set-Up
that does not supply sensing to the regulator.
Adjustable droop from 0 to 6% with 5 Amps input To prevent damage to the regulator, complete the
at 0.8 power factor. Figures 4 and 5 show the correct CT polarity for A- following steps before proceeding with system
B-C phase rotation sequence. If the phase rotation start-up.
PHYSICAL SPECIFICATIONS
sequence is A-C-B, the CT’s secondary leads
a. Verify that the voltage regulator specifications
Operating Temperature must be interchanged.
conform with the generator system re-
-40 C (-40 F) to +60 C (+140 F). quirements.
Publication: Rev First Printing 06/96 Copyright
9 3028 00 990 B Revised - 12/2001 1996 - 2001
b. Ensure that the regulator has been installed (negative) in series with a limiting resistor. Use adjustment to vary the generator nominal voltage
and connected in accordance with the one ohm of resistance for each volt from the dc over the range shown in the Specifications.
paragraphs on installation. power source with a power rating of least one watt b. A 1500 ohm, 2 watt rheostat may be
Operation At Reduced Speeds per ohm. EXAMPLE: If using a 24 Vdc source, connected to terminals 6 and 7. This will allow
During periods of prime mover idling, use the use a 24 ohm, 24 watt resistor. approximately +10% adjustment via the
shutdown switch to remove power from the regu- b. Allow the field to be flashed for approximately remote, 1500 ohm rheostat.
lator. ten seconds before removing the dc source.
Droop Adjustment. The droop adjustment allows
c. If voltage build-up does not occur after for adjustment of the amount of droop which will
System Start-Up performing steps a and b, verify the polarity of
a. Perform preliminary set-up as described in the occur in the generator output voltage for a given
the dc source used in steps a and b and amount of reactive load current. A CT should be
above paragraphs. perform again.
b. Start the prime mover and bring up to rated selected which will supply the AVC with 3 to 5
speed. Frequency Roll-Off Adjustment. The AVC 63-7 amperes of current with rated load and power
Result: Voltage should build up. If not, underfrequency adjust is factory preset to cause factor on the generator. With 5 amperes of current
perform field flashing. an average 1 volt drop in the generator's line input supplied by the CT, at 0.8 power factor, the
voltage to the regulator when the frequency is amount of droop can be adjusted from 0 to 6% of
c. Slowly adjust VOLT adjustment or external between 54.5 and 55.5 Hz (for 60 Hz applications). nominal generator voltage.
voltage adjust rheostat until the generator For 50 Hz applications, the frequency roll-off is a. Determine the amount of droop desired; 3% to
output voltage reaches the nominal value. factory preset to between 44 and 46 Hz. To reset 5% is common. Adjust the droop potentio-
d. Apply and remove load to check stability. the frequency roll-off, proceed as follows:. meter fully CCW.
a. Adjust the prime mover RPM to the desired b. Bring the generator up to rated speed and
e. Check the regulator under normal operating
frequency compensation (corner frequency rated voltage. Apply full load at rated power
conditions.
roll-off) point. factor.
Result: If regulation is not within range,
b. Adjust the front panel FREQ control CW until c. Adjust the droop potentiometer until the
verify the prime mover is at rated speed.
the output voltage starts to drop off. desired amount of droop is achieved.
f. Reduce generator frequency to approxi- c. Bring the prime mover up to rated speed. The
mately 5 Hz below nominal. output voltage should return to normal. OPERATIONAL TEST
Result: Generator output voltage should To operationally test any AVC 63-7, refer to Figure
Stability Adjustment. An oscilloscope or other 6 and perform the following steps.
decrease at desired frequency.
voltage recording device should be used if a a. Connect the voltage regulator as shown in
Adjustments stability setting is desired that will provide the Figure 6 and apply 240 Vac.
Field Flashing. When the regulator is operated fastest possible voltage response with good gen- b. Adjust the front panel VOLT control fully
with the generator for the first time, the polarity of erator stability. counter-clockwise (CCW).
the residual magnetism may not be correct or of a. Rotation of the front panel STAB control in the RESULT: Observe that the lamp does not
sufficient magnitude. If the residual voltage at clockwise (CW) direction will slow response light.
terminals 3 and 4 is greater than 6 Vac, replace time. c. Adjust the front panel VOLT control fully
the regulator. If generator residual voltage is less b. Rotation of the front panel STAB control in the clockwise (CW).
than 6 Vac at terminals 3 and 4, shut down the counter-clockwise (CCW) direction will speed RESULT: Observe that the lamp is now lit.
prime mover and proceed with the following steps. response time. If rotated too far CCW, the d. Adjust the front panel VOLT control until the
generator voltage may oscillate (hunt). lamp just goes out.
CAUTION c. Rotate the front panel STAB control CCW until
Do not flash the field with the generator in the system starts oscillating and then rotate Regulator operation is satisfactory if the above
motion. The regulator may be damaged. CW just past the point where oscillation results are obtained. Stability, however, must be
occurred. tested with the generator and regulator operating.
a. With the prime mover at rest, apply a dc
Voltage Adjustment..
source (ungrounded), of not more than 48
a. Installation of a jumper across terminals 6 and
Vdc, to terminals F+ (positive) and F-
7 allows the internal (front panel) VOLT
120
Corner Frequency
GENERATOR OUTPUT VOLTAGE
100
50 Hz
(% OF NOMINAL)
80
60 Hz
60
40
20
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
P0004-19.vsd
FREQUENCY (HZ) 10-26-00
Figure 1. Typical AVC 63-7 Frequency Compensation Curves
5.517 .228 DIA. 2.983
4 PLCS
(137.9)
(5.7) (MAX.)
(74.5)
DROOP
U/F
4.917 3.928
(122.9) 1 (98.2)
STAB +
VOLT
.70
(17.5)
.492
2 .35 TYP. (12.3)
2
(8.7)
.51 (10 PLCS)
(12.7)
4.528 .492
(113.2) (12.3)
TERM., QC, MALE NOTES:
.032 X .250 1.) DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES (MILLIMETERS).
(.8 X 6.25) 2 DIMENSIONS TO TERMINALS ARE APPROXIMATE.
3.) NET WEIGHT = 1 LB. 1 OZ.
4.) WATTS DISSIPATED = 35 MAX.
1.10
P0004-20.vsd
1 2 7 6 50 COM E1 E3/4 3 F+ F- (27.5)
10/31/00
Figure 2. AVC 63-7 Outline Drawing
1 A
PARALLELING CT
GENERATOR 1 2 5A SEC NOMINAL TO LOAD
B OR
200 - 240 VAC CIRCUIT
50/60 HZ BREAKER
C
EXCITER
2 2
FIELD
UNIT/PARALLEL SWITCH
CLOSE FOR SINGLE UNIT REMOTE 3
OPEN TO PARALLEL VOLT. ADJ.
RHEOSTAT
1.5K
2W
4
E3 CW
F- F+ E1 3 4 1 2 50 COM 6 7
AVC63-7 P0004-21.vsd
11-02-00
1 Phase rotation A-B-C.
2 Item not supplied by Basler Electric Co.
3
If remote voltage adjust is not used, short terminals 6 and 7 together.
4 Short terminals 50 and COM together for 50 Hz operation. Leave unconnected for 60 Hz operation.
Figure 3. Typical Shunt-Powered Interconnection Diagram
1 A
Regulator 1
PARALLELING CT
GENERATOR 1 2 5A SEC NOMINAL TO LOAD
B OR E3
200 - 240 VAC CIRCUIT
E1 1 2
4
50/60 HZ BREAKER
C
EXCITER A
2 2
FIELD AUXILIARY
WINDING UNIT/PARALLEL SWITCH
CLOSE FOR SINGLE UNIT REMOTE 3
OPEN TO PARALLEL VOLT. ADJ.
RHEOSTAT GENERATOR B
1
CT
1.5K C
2W
F- F+ E1 3
E3
4 1 2 50 COM 6 7 CW Regulator 2
E1 E3 1 2
AVC63-7 P0004-22.vsd
4
11-02-00
1 Phase rotation A-B-C.
2 Item not supplied by Basler Electric Co. A
3
If remote voltage adjust is not used, short terminals 6 and 7 together.
4 Short terminals 50 and COM together for 50 Hz operation. Leave unconnected for 60 Hz operation.
GENERATOR B
1
Figure 4. Typical Auxiliary Winding Powered CT
Interconnection Diagram C
Regulator 3
E1 E3 1 2
4
120 V
LIGHT BULB 240 VAC A
GENERATOR B
10 OHM
10 WATT 1
CT
E3 C
F- F+ E1 3 4 6 7
NOTES:
1) When more than 3 generators are to be paralled,
AVC63-7 P0004-24.vsd continue connections as shown.
11-02-00 2) Paralleling CT polarities are shown A-B-C 11-02-00
phase rotation. P0004-23.vsd
Figure 6. Operational Test
Figure 5. Reactive Differential (Cross Current)
Compensation CT Interconnection
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- AVC63-7F Voltage Regulator - Instructions - 9302800994-D - March 2012 - BASLER ELECTRIC PDFDocument4 pagesAVC63-7F Voltage Regulator - Instructions - 9302800994-D - March 2012 - BASLER ELECTRIC PDFpevarePas encore d'évaluation
- EA05A ManualDocument4 pagesEA05A ManualAnonymous vqsuRyPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation and Maintenance: This Manual Is To Be Given To The End UserDocument12 pagesInstallation and Maintenance: This Manual Is To Be Given To The End UserHoang GiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Controls: Powerwizard 2.0 - Digital Control PanelDocument2 pagesControls: Powerwizard 2.0 - Digital Control PanelEduardo DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- SG2D Governador de VelocidadeDocument4 pagesSG2D Governador de VelocidadealbertooliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Eaam052209en PDFDocument249 pagesEaam052209en PDFMaicon ZagonelPas encore d'évaluation
- Dse 704-4120Document3 pagesDse 704-4120Jose Daniel Garcia RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- As440 Automatic Voltage Regulator (Avr) : Specification Installation and AdjustmentsDocument4 pagesAs440 Automatic Voltage Regulator (Avr) : Specification Installation and AdjustmentsMeriem ZAGRIRIPas encore d'évaluation
- PC3.3 Parallel-ApplicationDocument39 pagesPC3.3 Parallel-ApplicationVivek AwasthiPas encore d'évaluation
- CDocument2 pagesCincore1976100% (1)
- Safety: Operation and Maintenance Manual ExcerptDocument30 pagesSafety: Operation and Maintenance Manual ExcerptIuri BragaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual de Ligaçao SX 460Document6 pagesManual de Ligaçao SX 460RobertoSoaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec5000 6-09 PDFDocument5 pagesEc5000 6-09 PDFHusi NihaPas encore d'évaluation
- User'S Manual: Lift ApplicationDocument63 pagesUser'S Manual: Lift ApplicationyounesPas encore d'évaluation
- MANUAL Conexiones ATI FG WilsonDocument9 pagesMANUAL Conexiones ATI FG WilsonreacerxPas encore d'évaluation
- Linz - New Product - AlumenDocument4 pagesLinz - New Product - AlumenTTIBCCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Be23 Genset Controller ManualDocument26 pagesBe23 Genset Controller Manualناجى ابوعورة100% (2)
- KP-C500P (KTA19-G3A) Generating Set Technical Data SheetDocument5 pagesKP-C500P (KTA19-G3A) Generating Set Technical Data SheetMario CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrelec Single Function Timers PDFDocument105 pagesEntrelec Single Function Timers PDFembasianPas encore d'évaluation
- WEG Regulador de Tensao Grt7 Th4 10040217 Manual Portugues BRDocument50 pagesWEG Regulador de Tensao Grt7 Th4 10040217 Manual Portugues BRJuan I. Meza Lozano100% (1)
- 056-013 Load Demand Scheme PDFDocument2 pages056-013 Load Demand Scheme PDFahamed jabirPas encore d'évaluation
- GTEC EspecificacionesDocument7 pagesGTEC Especificacionescarlosj_echeverriaPas encore d'évaluation
- ADVR-16: Universal Hybrid Analog-Digital Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument6 pagesADVR-16: Universal Hybrid Analog-Digital Voltage Regulator Operation ManualMahendraLiyanage0% (1)
- Datakom-Dkg 517Document39 pagesDatakom-Dkg 517Hernan100% (2)
- GEP62SP-3 (Single Phase)Document5 pagesGEP62SP-3 (Single Phase)Jose PirulliPas encore d'évaluation
- GU620ADocument62 pagesGU620AEric JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- DYN110794 Technical BulletinDocument4 pagesDYN110794 Technical BulletinGolbert GolbiPas encore d'évaluation
- EA08A 2000 ManualDocument3 pagesEA08A 2000 ManualFaeistenYwePas encore d'évaluation
- InteliCharger 65 - 24 AF DatasheetDocument3 pagesInteliCharger 65 - 24 AF Datasheetjean sanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual EA20S CaterpillarDocument3 pagesManual EA20S CaterpillarHernán Peñafiel ReaPas encore d'évaluation
- PCC1301 Modbus Register Map - Cph031105Document8 pagesPCC1301 Modbus Register Map - Cph031105Gabriel CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Panel Relay Remoto PDFDocument12 pagesPanel Relay Remoto PDFroberto sanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Avrcf12a PDFDocument2 pagesAvrcf12a PDFduaPas encore d'évaluation
- GOB EG1065x Manual en PDFDocument8 pagesGOB EG1065x Manual en PDFRonaldCarrasquelPas encore d'évaluation
- Eabm031004za - HT Gc310 350 500 User ManualDocument100 pagesEabm031004za - HT Gc310 350 500 User ManualBayanaka Tehnik100% (2)
- S287 Fozmula Capacitance Coolant Level Switch Data JP 24 Nov 15 3.2 Rev 2Document1 pageS287 Fozmula Capacitance Coolant Level Switch Data JP 24 Nov 15 3.2 Rev 2Parinya0% (1)
- Stamford AVR SX460 PDFDocument4 pagesStamford AVR SX460 PDFNasredine AlainPas encore d'évaluation
- A400 PDFDocument25 pagesA400 PDFArturo FuentesPas encore d'évaluation
- Gac Esd5500Document7 pagesGac Esd5500christramPas encore d'évaluation
- General Information: Drilling Template (MM)Document4 pagesGeneral Information: Drilling Template (MM)Bruno MarianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Micrologic 2.0A PDFDocument154 pagesMicrologic 2.0A PDFGabriel ZorattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sx460 Automatic Voltage Regulator (Avr)Document4 pagesSx460 Automatic Voltage Regulator (Avr)rajan_2002eee100% (1)
- Output Ratings: Designed For The Rental MarketDocument4 pagesOutput Ratings: Designed For The Rental MarketRui Ferreira100% (1)
- DKG 705 User ManualDocument58 pagesDKG 705 User ManualMarioEnriqueAlcocerÁvila100% (1)
- Manual Regulador AVR7 PDFDocument3 pagesManual Regulador AVR7 PDFOmarColonPas encore d'évaluation
- Conzerv 6438Document10 pagesConzerv 6438Pur WantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans-Auto Eng Man v16Document77 pagesTrans-Auto Eng Man v16asif MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Zenith ZTG SeriesDocument8 pagesZenith ZTG SeriesFlo MircaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fault Code 429 Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low SourceDocument12 pagesFault Code 429 Water-in-Fuel Indicator Sensor Circuit - Voltage Below Normal or Shorted To Low SourceAhmedmahPas encore d'évaluation
- 5855292-Avr Users Manual Ea63-5 CDocument8 pages5855292-Avr Users Manual Ea63-5 CAbhoe StankPas encore d'évaluation
- KohlerDocument5 pagesKohlerRajesh S BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- IR470LYDocument3 pagesIR470LYHusejin MehmedovićPas encore d'évaluation
- DG SPEC C110D5 With 6BT5.9G2Document4 pagesDG SPEC C110D5 With 6BT5.9G2Anonymous tXzjQAJttH100% (1)
- Intelilite4 Amf8 Global GuideDocument573 pagesIntelilite4 Amf8 Global GuideJaime Igor100% (1)
- Instructions: AVC63-7F Voltage RegulatorDocument4 pagesInstructions: AVC63-7F Voltage RegulatorFady HazzouryPas encore d'évaluation
- AVC63 7 ManualDocument4 pagesAVC63 7 ManualLuciano PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Instructions: Automatic Voltage Regulator AVC63-12 AVC125-10Document4 pagesInstructions: Automatic Voltage Regulator AVC63-12 AVC125-10yao nestorPas encore d'évaluation
- SX440 Manual enDocument4 pagesSX440 Manual enAnsoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction Manual FOR Voltage Regulator Model: AVC63-4A: Part Number: 9 2858 00 100Document3 pagesInstruction Manual FOR Voltage Regulator Model: AVC63-4A: Part Number: 9 2858 00 100Guilherme ChiminelliPas encore d'évaluation
- SX440 Manual enDocument4 pagesSX440 Manual enMuhammad Sajjad ShadPas encore d'évaluation
- 637 - 2024 Lab-5 Synchronous MachinesDocument13 pages637 - 2024 Lab-5 Synchronous Machineseren.alliPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnets Think Big QuestionDocument15 pagesElectromagnets Think Big QuestionBen MasonPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Bab 2Document14 pagesSoal Bab 2royPas encore d'évaluation
- Grafik Humidity Robert TraybalDocument27 pagesGrafik Humidity Robert Traybalbila cantikPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 24 - Capacitance and DielectricsDocument16 pagesChapter 24 - Capacitance and DielectricsAlexis OrganisPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Fluid MechanicsDocument27 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanicsdodoy kangkongPas encore d'évaluation
- Diccionario CientíficoDocument440 pagesDiccionario CientíficoCamb LysPas encore d'évaluation
- 10ROTATIONAL Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium (P211) Rev2.2Document7 pages10ROTATIONAL Equilibrium and Non-Equilibrium (P211) Rev2.2Shriya SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Berkeley Review MCAT Physics Part 1 (PDFDrive)Document284 pagesThe Berkeley Review MCAT Physics Part 1 (PDFDrive)Chonpanut WonjirapaphatPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2Malindu WickramasinghePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Revision ChecklistDocument36 pagesPhysics Revision Checklistapi-3723991100% (5)
- GQ 2.2 - Divisible and Indivisible Obligations To Obligations With A Penal ClauseDocument5 pagesGQ 2.2 - Divisible and Indivisible Obligations To Obligations With A Penal ClauseAlvin ValerioPas encore d'évaluation
- Relay MY2NDocument16 pagesRelay MY2NSofyan AndikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface Area and Volume Imp Questions Paper 1Document1 pageSurface Area and Volume Imp Questions Paper 1vmehrotra301045Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch. 02 - Kinematics in One DimensionDocument42 pagesCh. 02 - Kinematics in One Dimensionsthembisosthera992Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Resistance: Ammeter - Voltmeter Methods: Date Course Name Instructor Name Student(s) NameDocument5 pagesMeasurement of Resistance: Ammeter - Voltmeter Methods: Date Course Name Instructor Name Student(s) NamerimonPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument8 pages10 Mechanical Properties of FluidsMokshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One: Fluid Properties by Ahmed YASHARDocument37 pagesChapter One: Fluid Properties by Ahmed YASHARSogolPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Unknown ResistanceDocument12 pagesDetermination of Unknown Resistancesparkle-A TenchPas encore d'évaluation
- Assertion and ReasoningDocument4 pagesAssertion and Reasoningnavyaa sambharPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectile Motion Newton'S Laws of Motion Law of InertiaDocument2 pagesProjectile Motion Newton'S Laws of Motion Law of Inertianing ningPas encore d'évaluation
- Follow Instructions Safely Take Careful Measurements.: Investigating Force, Mass and AccelerationDocument14 pagesFollow Instructions Safely Take Careful Measurements.: Investigating Force, Mass and AccelerationSamuel KalemboPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample MCQ Questions For EMDocument18 pagesSample MCQ Questions For EMNilesh Tanna TannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week3 AssignmentDocument2 pagesWeek3 AssignmentJainil PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Entry #4Document67 pagesChem Entry #4Vivialyn YumulPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Form3 - Question PaperDocument12 pagesPhysics Form3 - Question PaperBalgo BalgobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 6 (1) : Title: Free FallDocument6 pagesExperiment 6 (1) : Title: Free FallKizito UkwuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fanuc AC Spindle Servo Unit Maintenance ManualDocument113 pagesFanuc AC Spindle Servo Unit Maintenance Manualdv groupPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Guide #1Document16 pagesLearning Guide #1Willy D. CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- 4a.18, 4a.19Document3 pages4a.18, 4a.19Nicolás KozakPas encore d'évaluation