Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Unit - Iv Flow Visualization: Part - A
Transféré par
EmmanuelJeevanandhan0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues2 pageswtt
Titre original
unit 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
RTF, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentwtt
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme RTF, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
18 vues2 pagesUnit - Iv Flow Visualization: Part - A
Transféré par
EmmanuelJeevanandhanwtt
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme RTF, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
UNIT – IV
FLOW VISUALIZATION
PART - A
·0 What are the optical methods of flow visualization?
·1 Schlieren system
·2 Shadowgraph technique
·3 Interferometer
·4
·5 What is an Interferometer?
The interferometer is an optical method most suited for qualitative
determination of the density field of high speed flows
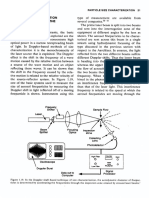
·6 What is Schlieren system?
Schlieren photography is similar to the shadowgraph technique and relies on the
the fact that light rays are bent whenever they encounter changes in density of a fluid.
Schlieren systems are used to visualize the flow away from the surface of an object. The
schlieren system shown in this figure uses two concave mirrors on either side of the test
section of the wind tunnel. A mercury vapor lamp or a spark gap system is used as a
bright source of light.
·7 How smoke visualization can be done?
Smoke is used to visualize the flow that is away from the surface of the model.
Smoke can be used to detect vortices and regions of separated flow.
·8 How Oils are used in flow visualization?
Colored oil flows are used on the silver internal surfaces to visualize the flow
down the duct. Surface oil is applied as small dabs of oil at some upstream location. The
oil is standard 40W treated with a flourescent dye or pigment. The thickness of the oil
can be modulated using naptha or 60-70W oil. As the air flows over the model, the oil is
carried downstream in long streaks. A variety of pigments aid in flow visualization.
·9 What is a spring gage?
A spring gage consists of a spring that is stretched by the application of a force,
and some kind of scale to determine the magnitude of the force. The spring gage is
based on the physical observation that the length L of a spring is linearly related to the
applied force F through a spring constant that itself depends on the material and
thickness of the spring. If the spring constant is specified by the letter K, then
L = (1/K) x F
F=KxL
·10 What do you mean by DPIV?
In a modern development, one can use laser sheets to not only visualize the
flow but also to determine the local velocity in the flow. Digital Particle Image
Velocimetry (DPIV) uses multiple laser sheet images and high speed computers to track
the motion of the seed particles and, from the particle motion, derive the local velocity.
DPIV is an attractive technique because it is non-invasive (the technique does not alter
or disturb the flow) and it quickly produces large amounts of data which would be
tedious to acquire using older flow mapping techniques like traversing probes.
·11 Explain Shadowgraph technique?
An optical method of rendering fluid flow patterns visible by using index-of-
refraction differences in the flow. The method relies on the fact that rays of light bend
toward regions of higher refractive index while passing through a transparent material.
The fluid is usually illuminated by a parallel beam of light.
·12 What are Tufts?
Tufts are another old visualization technique that is used in both flight test
and wind tunnel testing. Tufts are small lengths of string that are frayed on the
ends. Popular materials for tufts include monofilament nylon, and polyester or
cotton No. 60 sewing threads. Tufts may be coated with flourescant dyes to
increase visibility for photography. The tufts are attached to the surface of the
model using some adhesive such as tape or glue, and as the air flows over the
model, the tufts are blown and point downstream.
PART - B
·13 Explain in detail smoke and tuft grid generation techniques of flow visualization/?
·14 Write about the dye injection techniques?
·15 Explain Schlieren system of optical flow visualization?
·16 Explain Interferometer technique of flow visualization in detail?
·17 Explain shadowgraph technique in detail?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A132835183 - 19469 - 2 - 2020 - Lecture 2 April ATE304Document25 pagesA132835183 - 19469 - 2 - 2020 - Lecture 2 April ATE304sanjay poudelPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Visualization Techniques and Their use-RH5001A53 - Atish Kumar-CIV 208Document16 pagesFlow Visualization Techniques and Their use-RH5001A53 - Atish Kumar-CIV 208Atish Kumar100% (1)
- Particle Image VelocimetryDocument10 pagesParticle Image Velocimetrynewbie56Pas encore d'évaluation
- Particle Image VelocimetryDocument16 pagesParticle Image VelocimetrySiamakPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow VisualizationDocument6 pagesFlow VisualizationMuralikrishnan GMPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Refractive Index Measurements Using Rough SuDocument5 pagesFluid Refractive Index Measurements Using Rough Su11F10 RUCHITA MAARANPas encore d'évaluation
- Schlieren ImagingDocument10 pagesSchlieren ImagingPooja GounderPas encore d'évaluation
- The Shadowgraph Imaging Technique and Its Modern Application To Fluid Jets and DropsDocument10 pagesThe Shadowgraph Imaging Technique and Its Modern Application To Fluid Jets and Dropsnsa10124Pas encore d'évaluation
- UZB341E-Lecture8 IF HA OCY KBY4Document63 pagesUZB341E-Lecture8 IF HA OCY KBY4Okan BayarPas encore d'évaluation
- Schlieren Image Velocimetry of Swirl SpraysDocument25 pagesSchlieren Image Velocimetry of Swirl Sprayslokesh14Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sensors: Optical Feedback Interferometry For Velocity Measurement of Parallel Liquid-Liquid Flows in A MicrochannelDocument12 pagesSensors: Optical Feedback Interferometry For Velocity Measurement of Parallel Liquid-Liquid Flows in A MicrochannelyihibasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Safety Journal: Xiangyang Zhou, Stephen P. D'Aniello, Hong-Zeng YuDocument13 pagesFire Safety Journal: Xiangyang Zhou, Stephen P. D'Aniello, Hong-Zeng YuEvan SatyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Field MeasurementsDocument4 pagesFlow Field MeasurementsSurya prabha SPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids 06 00430Document12 pagesFluids 06 00430ranim najibPas encore d'évaluation
- Lda AssignmentDocument9 pagesLda AssignmentDee RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Flow Visualization: Shinju Joseph S6 Tde Roll No:47Document24 pagesFluid Flow Visualization: Shinju Joseph S6 Tde Roll No:47Modi EmPas encore d'évaluation
- A New Multiphase Holdup Tool For Horizontal WellsDocument4 pagesA New Multiphase Holdup Tool For Horizontal WellsAnre Thanh HungPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Visualisation TecniquesDocument15 pagesFlow Visualisation TecniquesPàresh JoshíPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow - Visualization - Wind - Tunnels - Ristic - 220831 Mod PDFDocument25 pagesFlow - Visualization - Wind - Tunnels - Ristic - 220831 Mod PDFELTON REGIS NASCIMENTO DA SILVAPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser Doppler VelocimetryDocument20 pagesLaser Doppler Velocimetryimsandy09Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measure - Refractive IndexDocument5 pagesMeasure - Refractive IndexHiệu LêPas encore d'évaluation
- Size Characterization Equipment Based On The Doppler EffectDocument14 pagesSize Characterization Equipment Based On The Doppler EffectpapsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Schlieren EffectDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Schlieren EffectDhana JayanPas encore d'évaluation
- 245739meet The Steve Jobs of The Lateral Ivd Rapid Test Manufacturer IndustryDocument3 pages245739meet The Steve Jobs of The Lateral Ivd Rapid Test Manufacturer IndustrycechinkfvsPas encore d'évaluation
- FOL Unit 4Document7 pagesFOL Unit 4Sudhar SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment About Gas DymanicsDocument6 pagesExperiment About Gas DymanicsMohamed KadhimPas encore d'évaluation
- PIV (Vortex Ring)Document13 pagesPIV (Vortex Ring)imryuk19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 To 3Document79 pagesChapter 1 To 3Shrikant ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Laser Torsional Vibrometer: A Step Forward in Rotating Machinery DiagnosticsDocument20 pagesThe Laser Torsional Vibrometer: A Step Forward in Rotating Machinery DiagnosticsNini CortesPas encore d'évaluation
- SPECTROPHOTOMETRYDocument4 pagesSPECTROPHOTOMETRYRhany HerianiPas encore d'évaluation
- JIISc-Rev 01Document16 pagesJIISc-Rev 01L VenkatakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Flow VisualizationDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Flow Visualizationnsa10124100% (1)
- An Intelligent Active Range Sensor For Vehicle Guidance: System OverviewDocument8 pagesAn Intelligent Active Range Sensor For Vehicle Guidance: System OverviewUtsav V ByndoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Tracki NG RadarDocument4 pagesTracki NG RadarSugunaPas encore d'évaluation
- ScannersDocument7 pagesScannersMehul JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Optical Correlation Techniques To Particle Imaging VelocimetryDocument24 pagesApplication of Optical Correlation Techniques To Particle Imaging VelocimetryEsmail AhouziPas encore d'évaluation
- Visualization of Flow Field Application of PLIFDocument6 pagesVisualization of Flow Field Application of PLIFRhys B. LockyerPas encore d'évaluation
- SdarticleDocument6 pagesSdarticlepedeefesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiber Optic Distributed Sensors For High-Resolution Temperature Field MappingDocument9 pagesFiber Optic Distributed Sensors For High-Resolution Temperature Field Mappingshashank guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drop Size Measurement Techniques For Sprays: Comparison of Image Analysis, Phase Doppler Particle Analysis, and Laser DiffractionDocument9 pagesDrop Size Measurement Techniques For Sprays: Comparison of Image Analysis, Phase Doppler Particle Analysis, and Laser DiffractionKhanh CungPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesPhysics Projectmadhurima100% (1)
- Q.4:-Elaborate With Diagram Working Principle, Salient Features, Solution:-Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Is A Non-ContactDocument4 pagesQ.4:-Elaborate With Diagram Working Principle, Salient Features, Solution:-Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Is A Non-ContactJay The PerfectPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Level MeasurementDocument15 pages1-Level MeasurementAhmed KamelPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysBased Interact Flow Vis Based On Schlieren and Interf Exp TechniquesDocument13 pagesPhysBased Interact Flow Vis Based On Schlieren and Interf Exp TechniquesRoxi InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Multi-Frame PivDocument13 pagesAdaptive Multi-Frame PivSantiago Cano ZapataPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4.4 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) : Using The Microscale Chromatography ColumnsDocument2 pages4.4.4 High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) : Using The Microscale Chromatography ColumnsJuanPas encore d'évaluation
- 153 341 1 SMDocument15 pages153 341 1 SMoktavPas encore d'évaluation
- MFHT PivDocument19 pagesMFHT PivFazal ChawlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Lens Focal Length Using Multi-Curvature Analysis of Shack-Hartmann Wavefront DataDocument13 pagesMeasurement of Lens Focal Length Using Multi-Curvature Analysis of Shack-Hartmann Wavefront DataZafar IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasonic Water Level Indicator and Controller Using AvrDocument22 pagesUltrasonic Water Level Indicator and Controller Using AvrAjmal Aju100% (1)
- Digital Image Correlation Applied To The Calculation of The Out-Of-Plane Deformation Induced by The Formation of Roll Waves in A Non-Newtonian FluidDocument9 pagesDigital Image Correlation Applied To The Calculation of The Out-Of-Plane Deformation Induced by The Formation of Roll Waves in A Non-Newtonian FluidVicente de Paulo Gonçalves JuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Laser InterferometeryDocument22 pagesLaser InterferometeryAndy ValleePas encore d'évaluation
- The Good, The Bad, and The Tiny: A Review of Microflow CytometryDocument14 pagesThe Good, The Bad, and The Tiny: A Review of Microflow CytometryMunir AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Schlieren Visualization of Ultrasonic Standing WavDocument6 pagesSchlieren Visualization of Ultrasonic Standing WavDiHuBar InnovationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Services Copy: Idaho State Police Forensic Laboratory Training Manual Infared SpectrophotometryDocument9 pagesServices Copy: Idaho State Police Forensic Laboratory Training Manual Infared SpectrophotometryMark ReinhardtPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 - Duocastella Et Al. - Sub-Wavelength Laser Nanopatterning Using Droplet Lenses - Scientific ReportsDocument9 pages2015 - Duocastella Et Al. - Sub-Wavelength Laser Nanopatterning Using Droplet Lenses - Scientific ReportsClaudio BiaginiPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Refractive Index and Optical RotationDocument16 pagesDetermination of Refractive Index and Optical RotationClaudia JunioPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iii Wind Tunnel Measurements: TransformerDocument2 pagesUnit - Iii Wind Tunnel Measurements: TransformerEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Ii High Speed Wind Tunnels: Part - ADocument3 pagesUnit - Ii High Speed Wind Tunnels: Part - AEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - I Wind Tunnels Part - ADocument8 pagesUnit - I Wind Tunnels Part - AEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I Layout of Open Circuit Wind TunnelsDocument17 pagesUnit I Layout of Open Circuit Wind TunnelsEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- WTT 2marksDocument4 pagesWTT 2marksEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Doo Dli NGDocument1 pageDoo Dli NGEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Resume FormatDocument3 pagesSample Resume FormatEmmanuelJeevanandhanPas encore d'évaluation
- ACV-12 Adjustable Choke Valves: For Wide Applications in Oil, Gas, and Water ServiceDocument2 pagesACV-12 Adjustable Choke Valves: For Wide Applications in Oil, Gas, and Water ServiceDeyokePas encore d'évaluation
- NFPA 329 - 2005 Handling Releases of Flammable and Combustible LiquidsDocument49 pagesNFPA 329 - 2005 Handling Releases of Flammable and Combustible LiquidsArnaldo J Brito Ñ100% (1)
- Chapter 8 (CHEM 104)Document76 pagesChapter 8 (CHEM 104)datPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Chemical Kinetics JH Sir-4309Document44 pagesAssignment Chemical Kinetics JH Sir-4309T sidharth100% (2)
- Chap 17 LectureDocument47 pagesChap 17 LecturesureshbabuPas encore d'évaluation
- (Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDocument5 pages(Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDanny Riel BarachinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strengthening MechanismsDocument17 pagesStrengthening Mechanismspkn_pnt9950Pas encore d'évaluation
- Local Anesthetics 2006Document22 pagesLocal Anesthetics 2006Shashikant DrShashikant BagadePas encore d'évaluation
- 3.5 Pressure Drop: ΔP = 8f (L/di)Document2 pages3.5 Pressure Drop: ΔP = 8f (L/di)fadi713Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lines Technical Document Admixtures For Concrete enDocument30 pagesLines Technical Document Admixtures For Concrete enJoseph ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Week No.2 - CLO-1 Size ReductionDocument18 pagesWeek No.2 - CLO-1 Size ReductionkhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Digestion and Absorption - A Closer Look - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument20 pagesChemical Digestion and Absorption - A Closer Look - Anatomy and PhysiologyMa Mayla Imelda LapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maks GTC 1000Document1 pageMaks GTC 1000Chiheb Eddine KourasPas encore d'évaluation
- FeC and TTT DiagramsDocument12 pagesFeC and TTT DiagramsMohamed El-WakilPas encore d'évaluation
- Senscient ELDS - Hydrogen Sulphide - Data Sheet Rev6Document2 pagesSenscient ELDS - Hydrogen Sulphide - Data Sheet Rev6Vincent GabrielPas encore d'évaluation
- Opt KnockDocument11 pagesOpt KnockanthazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Protect Rubber Goods To Prevent Failure: Tears ProtuberanceDocument2 pagesProtect Rubber Goods To Prevent Failure: Tears ProtuberancePedro SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm D5453 - 2004Document10 pagesAstm D5453 - 2004Teymur Regenmaister100% (1)
- Pears Pears Pears Pears Pears: Nitrogen (N)Document4 pagesPears Pears Pears Pears Pears: Nitrogen (N)Zineil BlackwoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument36 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAira Villarin100% (3)
- An Analytical Solution For Time-Dependent Displacements in A Circular TunnelDocument10 pagesAn Analytical Solution For Time-Dependent Displacements in A Circular TunnelEugenio DoglionePas encore d'évaluation
- Ger 3751a Understanding Diagnosing Repairing Leaks h20 Gen Stator WindingsDocument28 pagesGer 3751a Understanding Diagnosing Repairing Leaks h20 Gen Stator Windingsnareshvkkd100% (1)
- nbr002 1612 PDFDocument32 pagesnbr002 1612 PDFRanjith RPas encore d'évaluation
- VSI Week8 Lecture8 InstAnal 4th Stage Theory 2022Document30 pagesVSI Week8 Lecture8 InstAnal 4th Stage Theory 2022Sozdar ArgoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Table of Polyatomic Interferences in ICP-MSDocument6 pagesA Table of Polyatomic Interferences in ICP-MSDiana Buitrón OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparatory Problems SolutionsDocument38 pagesPreparatory Problems SolutionsĐạt Trần VănPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding PH MeasurementDocument10 pagesUnderstanding PH MeasurementAnnisa Novita Putri SiregarPas encore d'évaluation
- Elastic Vitrimers BeyondDocument32 pagesElastic Vitrimers BeyondMostafa AhmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Form Harga Bahan KimiaDocument1 pageForm Harga Bahan Kimiahasrat budimanPas encore d'évaluation
- POME ApplicationsDocument9 pagesPOME Applicationsaffeena100% (1)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldD'EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (597)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseD'EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessD'EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildD'EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (44)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorD'EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (137)
- The Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021D'EverandThe Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (8)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsD'EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (13)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutD'EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (142)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionD'EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (812)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldD'EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessD'EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (254)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsD'EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (65)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsD'EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (223)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeD'EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (19)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogD'EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (10)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsD'EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (1424)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignD'EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (19)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsD'EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (3)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldD'EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (397)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingD'EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (35)