Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
001 Scat
Transféré par
Sergio CabralTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
001 Scat
Transféré par
Sergio CabralDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
7 7
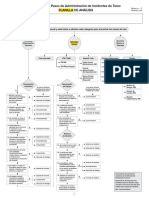
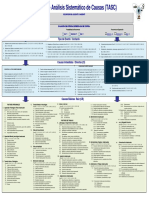
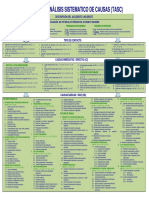
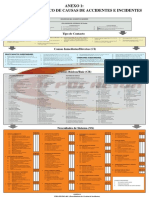
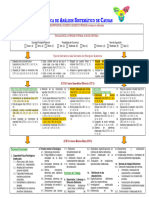
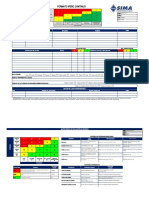
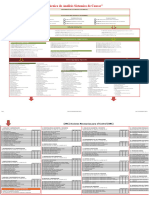
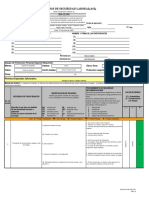
DNV SYSTEMATIC CAUSE ANALYSIS TECHNIQUE FOR isrs (SCAT-isrs )
DESCRIPTION OF EVENT
Type of Loss: ¨ People ¨ Health
¨ Property ¨ Safety
¨ Process/Business ¨ Environment
¨ Reputation ¨ Quality
EVALUATION OF LOSS POTENTIAL IF NOT CONTROLLED
Loss Severity Potential Likelihood of Event Recurring
¨ Major ¨ Serious ¨ Minor ¨ Unlikely (e.g. < 1 in 50 years) ¨ Likely (e.g. 1 in 10 years) ¨ Very likely (e.g. > 1 in 1 year)
Type of Event
1. Struck Against (Running or Bumping Into) 4. Fall on Same Level (Slip and Fall, Trip Over) 8. Contact With (Electricity, Heat, Cold, Radiation, Caustics, Toxics, 10. Product, Process Nonconformities 13. Environmental Release
(See ICs: 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 12, 13, 14, 21, 22, 23, 24, 27, 29, 30, 37) (See ICs: 4, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, 23, 28, 29, 30) Biological and Noise) (See ICs: 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 23, (See ICs: 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 23, 27,
2. Struck By (Hit By Moving Object) 5. Caught In (Pinch and Nip) (See ICs: 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 21, 22, 24, 27, 29, 30, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 39, 41) 28, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 36, 38, 40, 41)
(See ICs: 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, 18, 21, (See ICs: 5, 6, 9, 13, 14, 15, 17, 21, 22, 23, 32) 23, 24, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 37) 11. Overstress, Overpressure, Overexertion, Ergonomic 14. Customers/Stakeholders Complaints
22, 23, 24, 27, 30, 37) 6. Caught On (Snagged, Hung) 9. Abnormal Operations (See ICs: 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 24, 27, (See ICs: 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22,
3. Fall from Elevation to Lower Level (See ICs: 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 21, 23, 33) (See ICs: 1, 2, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 23, 24, 27, 33, 35, 37, 39, 40, 41) 23, 25, 26, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 38, 40, 41)
(See ICs: 2, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 21, 22, 23, 29, 31, 7. Caught Between or Under (Crushed or Amputated) 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36) 12. Equipment Failure
34, 37) (See ICs: 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 24, 27, 32, (See ICs: 1, 4, 6, 8, 14, 16, 20, 23, 27, 30, 31, 32, 33, 35, 36, 37,
34, 35) 41)
Immediate/Direct Causes
SUBSTANDARD ACTS 10. Servicing Equipment and Operation 19. Failure to Identify Customer and Stakeholder Expectations 26. Failure to Reach Business Goals and/or Objectives 35. Inadequate Support/Assistance/Resources
(See BCs: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 14, 16, 17) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18) (See BCs: 7, 9, 11, 12, 16)
1. Operating Equipment Without Authority
11. Improper Employee/Management Behavior 20. Failure to Identify and Dispose Nonconforming Parts/Materials 27. Inadequate Warning System 36. Inadequate Communications Hardware/Software/Process
(See BCs: 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 13, 14, 16)
(See BCs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 14) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17) (See BCs: 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16) (See BCs: 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15, 16)
2. Failure to Warn/Secure
12. Under the Influence of Alcohol and Other Drugs 28. Fire & Explosion Hazards 37. Road and Weather Conditions
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 17)
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 14) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15) (See BCs: 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16)
3. Failure to Allocate Resources
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18)
13. Using Equipment Improperly SUBSTANDARD CONDITIONS 29. Poor Housekeeping/Disorder 38. Inadequate Identification of Regulations/Industry Codes and
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18) 21. Inadequate Guards or Barriers (See BCs: 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 16) Permits to Operate
4. Operating at Improper Speed
14. Failure to Follow Procedure/Policy/Practice/Values and Working (See BCs: 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15) 30. Inadequate Quality/Safety/Health and Environmental Exposures (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 14, 17 ,18)
(See BCs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14)
Permits 22. Inadequate or Improper Protective Equipment
5. Making Safety Devices Inoperative (See BCs: 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) 39. Inadequate Design Preparation/Planning
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 14, 17) (See BCs: 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15)
(See BCs: 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 18) 31. Presence of Harmful Materials (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18)
15. Failure to Identify Hazard/Risks (E, Q, S, H, Process and
6. Using Defective Equipment 23. Defective Tools, Equipment or Materials (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) 40. Failure to Comply with Customers and Stakeholders
Business)
(See BCs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18) (See BCs: 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15) 32. Inadequate Instructions/Procedures Requirements/Complaints
(See BCs: 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 14, 17, 18)
7. Failure to Use PPE Properly 24. Congestion or Restricted Action (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 14, 16) (See BCs: 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17)
16. Failure to Check/Monitor
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16) (See BCs: 9, 10, 11, 14) 33. Inadequate Information Data/Indicators 41. Inadequate EQSH System
(See BCs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18)
8. Improper Loading/Placement/Lifting 25. Inadequate Communication with Employees, Customers or (See BCs: 5, 6, 9, 10, 11, 12, 16) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18)
17. Failure to Analyze React/Correct
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14) Stakeholders 34. Inadequate Preparation/Planning
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18)
9. Improper Position for Task (See BCs: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18) (See BCs: 5, 6, 7, 9, 14, 16)
18. Failure to Communicate/Coordinate
(See BCs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 13, 14, 16)
(See BCs: 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 16, 17)
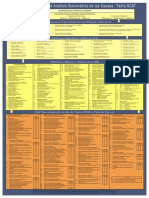
Basic/Root Causes
PERSONAL FACTORS 5.2. Inadequate orientation 9.9. Inadequate identification and evaluation of loss 12.3.2. Inadequate pre-use inspection system 15.3. Inadequate inspection and/or monitoring
5.3. Inadequate initial training exposures 12.3.3. Inadequate E, Q, S special equipment 15.4. Improper loading or rate of use
5.4. Inadequate update training 9.10. Lack of supervisory/management job knowledge inspection system 15.5. Inadequate maintenance
1. Inadequate Physical/Physiological Capability 5.5. Misunderstood directions 9.11. Inadequate matching of individual qualifications and 12.3.4. Inadequate measuring and test equipment 15.6. Use by unqualified or untrained people
(See ACs: 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15) 5.6. Lack of situational awareness job/task requirements system 15.7. Use for wrong purpose
1.1. Inappropriate height, weight, size, strength, reach, etc. 6. Inadequate Skill 9.12. Inadequate performance measurement and evaluation 12.3.5. Inadequate control of risk identification for (E, 16. Inadequate Communications
1.2. Restricted range of body movement (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15) 9.13. Inadequate or incorrect performance feedback Q, S, H, process and business) (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15)
1.3. Limited ability to sustain body positions 6.1. Inadequate initial instruction 9.14. Inadequate system of monitoring E, S, H & Q 12.3.6. Inadequate behavior and task observations 16.1. Inadequate horizontal communication between peers
1.4. Substance sensitivities or allergies 6.2. Inadequate practice management controls 13. Inadequate Product, Tools and Equipment 16.2. Inadequate vertical communication between
1.5. Sensitivities to sensory extremes (temperature, sound, 6.3. Infrequent performance 9.14.1. Inadequate audits (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15) supervisor and person
etc.) 6.4. Lack of coaching 9.14.2. Inadequate monitoring of customer 13.1. Inadequate assessment of needs and risks 16.3. Inadequate communication between different
1.6. Vision deficiency 6.5. Inadequate review instruction satisfaction 13.2. Inadequate human factors/ergonomics considerations organizations
1.7. Hearing deficiency 6.6. Improper instructor qualification 9.14.3. Inadequate perception survey 13.3. Inadequate standards or specifications 16.4. Inadequate communication between work groups
1.8. Other sensory deficiency (touch, taste, smell, balance) 6.7. Inadequate training systems 10. Inadequate Project Management and Engineering 13.4. Inadequate availability 16.5. Inadequate communication between shifts
1.9. Respiratory incapacity 7. Improper Motivation/Hiring & Placement (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 13.5. Inadequate adjustment/repair/maintenance 16.6. Inadequate communication methods
1.10. Other permanent physical capabilities (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15) 10.1. Inadequate assessment of loss exposures 13.6. Inadequate salvage and reclamation 16.7. No communication method available
1.11. Temporary disabilities 7.1. Improper performance is rewarded (tolerated) 10.2. Inadequate consideration of human factors/ergonomics 13.7. Inadequate removal and replacement of unsuitable 16.8. Incorrect instructions
2. Inadequate Mental/Psychological Capability 7.2. Proper performance is punished 10.3. Inadequate standards, specifications and/or design items 16.9. Inadequate communication due to job turnover
(See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 7.3. Lack of incentives criteria 13.8. Inadequate health/safety and environmental hazard 16.10. Inadequate communication of safety and health data,
2.1. Fears and phobias 7.4. Excessive frustration 10.4. Inadequate monitoring of construction monitoring regulations or guidelines inside or outside the
2.2. Emotional disturbance 7.5. Inappropriate aggression 10.5. Inadequate assessment of operational readiness 13.9. Inadequate stewardship organization
2.3. Mental illness 7.6. Improper attempt to save time or effort 10.6. Inadequate or improper controls 14. Inadequate Work Standards/Compliance Requirements 16.11. Standard terminology not used
2.4. Intelligence level 7.7. Improper attempt to avoid discomfort 10.7. Inadequate monitoring of initial operation (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 16.12. Verification/repeat feedback techniques not used
2.5. Inability to comprehend 7.8. Improper attempt to gain attention 10.8. Inadequate evaluation of changes 14.1. Inadequate development of standards 16.13. Messages too long
2.6. Poor coordination 7.9. Inadequate discipline 10.9. Inadequate project coordination/planning/execution/ 14.1.1. Inventory and evaluation of exposures and 16.14. Speech interference
2.7. Slow reaction time 7.10. Inappropriate peer pressure control and closeout needs 16.15. Inadequate management meeting and meeting
2.8. Low mechanical aptitude 7.11. Improper supervisory example 11. Inadequate Purchasing and Contractor Management 14.1.2. Coordination with process design coordination
2.9. Low learning aptitude 7.12. Inadequate performance feedback (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 14.1.3. Employee involvement 16.16. Improper recognition system
2.10. Memory failure 7.13. Inadequate reinforcement of proper behavior 11.1. Inadequate specifications on requisitions 14.1.4. Procedures/practices/rules 16.17. Inadequate promotion system
3. Physical or Physiological Stress 7.14. Improper production incentives 11.2. Inadequate research on materials/equipment 14.2. Inadequate communication of standards 17. Inadequate Business Planning
(See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14) 7.15. Inadequate recruitment 11.3. Inadequate specifications to vendors 14.2.1. Publication (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15)
3.1. Injury or illness 7.16. Inadequate recognition program 11.4. Inadequate mode or route of shipment 14.2.2. Distribution 17.1. Inadequate purpose/values
3.2. Fatigue due to task load or duration 7.17. Failure to capture knowledge of existing employees 11.5. Inadequate receiving inspection and acceptance 14.2.3. Translation of appropriate languages 17.2. Inadequate business goals
3.3. Fatigue due to lack of rest 7.18. Inadequate process of organizational change 11.6. Inadequate communication of safety and health 14.2.4. Training 17.3. Inadequate business strategy
3.4. Fatigue due to sensory overload 8. Abuse or Misuse data 14.2.5. Reinforcing with signs, color codes and job 17.4. Inadequate stakeholder identification and
3.5. Exposure to health hazards (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 11.7. Improper handling of materials aids involvement
3.6. Exposure to temperature extremes 8.1. Intentional non-intentional improper use/condition 11.8. Improper storage of materials 14.3. Inadequate maintenance of standards 17.5. Inadequate identification and control of business
3.7. Oxygen deficiency 8.1.1. Intentional 11.9. Improper transporting of materials 14.3.1. Tracking of work flow risks
3.8. Atmospheric pressure variation 8.1.2. Unintentional 11.10. Inadequate identification of hazardous materials 14.3.2. Updating 17.6. Inadequate leadership commitment
3.9. Constrained movement 8.2. Improper conduct that is not condoned 11.11. Improper salvage and/or waste disposal 14.3.3. Monitoring use of procedures/practices/rules 17.7. Inadequate short/long term strategic plan
3.10. Blood sugar insufficiency 8.2.1. Intentional 11.12. Inadequate contractor selection/administration/ 14.4. Inadequate monitoring of compliance 17.8. Inadequate business work planning
3.11. Drugs 8.2.2. Unintentional termination 14.5. Inadequate formal system to address identification of 17.9. Inadequate action tracking for goals, objectives,
4. Mental or Psychological Stress 12. Inadequate Maintenance Inspection and Controls regulatory and industry codes and permits to operate strategy, short/long term strategic plan
(See ACs: 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15) (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15) 14.5.1. Inadequate reporting to authorities 17.10. Inadequate definition/analysis of business indicators
4.1. Emotional overload JOB/SYSTEM FACTORS 12.1. Inadequate preventive 14.5.2. Inadequate monitoring of regulations, permits 17.11. Inadequate management meetings to review all
4.2. Fatigue due to mental task load or speed 12.1.1. Assessment of needs and industry codes business activities
4.3. Extreme judgment/decision demands 9. Inadequate Leadership and/or Supervision 12.1.2. Lubrication and servicing 14.6. Inadequate investigation of events (incidents & 17.12. Failure to identify customer expectations
4.4. Routine, monotony, demand for uneventful vigilance (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15) 12.1.3. Adjustment/assembly nonconformities) 18. Inadequate Emergency Systems
4.5. Extreme concentration/perception demands 9.1. Unclear or conflicting reporting relationships 12.1.4. Cleaning or resurfacing 14.6.1. Inadequate investigation training (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13, 15)
4.6. “Meaningless” or “degrading” activities 9.2. Unclear or conflicting assignment of responsibility 12.1.5. Planning and scheduling 14.6.2. Inadequate investigation system 18.1. Inadequate identification of all probable emergencies
4.7. Confusing directions/demands 9.3. Improper or insufficient delegation 12.2. Inadequate reparative 14.6.3. Inadequate management participation 18.2. Inadequate emergency internal/external plan
4.8. Conflicting demands/directions 9.4. Giving inadequate policy, procedure, practices or 12.2.1. Communication of needs 14.6.4. Inadequate management of internal/external 18.3. Inadequate identification and operation of response
4.9. Preoccupation with problems guidelines 12.2.2. Scheduling of work customer complaints team
4.10. Frustration 9.5. Giving objectives, goals or standards that conflict 12.2.3. Examination of units 14.6.5. Inadequate corrective action system 18.4. Inadequate mutual aid and medical support
4.11. Mental illness 9.6. Inadequate work planning or programming 12.2.4. Part substitution 15. Excessive Wear and Tear
5. Inadequate Knowledge 9.7. Inadequate instructions, orientation and/or training 12.3. Inadequate inspections (See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15)
(See ACs: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14) 9.8. Providing inadequate reference documents, directives 12.3.1. Inadequate general planned inspection 15.1. Inadequate planning of use
5.1. Lack of experience and guidance publications system 15.2. Improper extension of service life
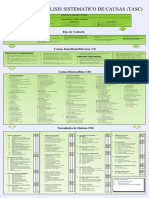
Actions for Improvement
S PS C S PS C PROCESS 10 - ASSET MANAGEMENT S PS C S PS C
PROCESS 1 - LEADERSHIP PROCESS 6 - PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROCESS 13 - LEARNING FROM EVENTS
1.1. Purpose and Values 6.1. Project Co-ordination 10.1. Maintenance Program 13.1. Learning from Events System
1.2. Goals 6.2. Project Planning 10.2. Maintenance Planning and Scheduling 13.2. Learning from Success
1.3. Policy 6.3. Project Execution 10.3. Execution of Maintenance 13.3. Participation in Investigations
1.4. Strategy 6.4. Project Control 10.4. Maintenance Review 13.4. Near-Miss and Substandard Conditions
1.5. Stakeholder Engagement 6.5. Project Close Out 10.5. General Conditions Inspections 13.5. Complaints Management
1.6. Business Processes 10.6. Physical Conditions Tour 13.6. Event Announcements
1.7. Business Risks 10.7. Special Equipment Inspections 13.7. Away-from-Work Accidents
1.8. Accountabilities S PS C 10.8. Pre-Use Equipment Inspections 13.8. Action Follow-Up
PROCESS 7 - TRAINING AND COMPLIANCE
1.9. Management Commitment 10.9. Engineering Change Management 13.9. LFE Reporting Verification
7.1. Training System
10.10. Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment 13.10. Event Analysis
S PS C
7.2. Training Needs Analysis
PROCESS 2 - PLANNING AND ADMINISTRATION 10.11. Acquisition and Sale 13.11. Improvement Teams
7.3. Instructor Competence
2.1. Business Planning 7.4. Delivery of Training
2.2. Work Planning and Control 7.5. Leadership Orientation/Induction
2.3. Action Tracking 7.6. General Orientation/Induction PROCESS 14 - RISK MONITORING S PS C
2.4. Management System Documentation 7.7. Job Orientation/Induction PROCESS 11 - CONTRACTOR MANAGEMENT 14.1. Health Hazard Monitoring
2.5. Records S PS C
7.8. Training Systems Evaluation AND PURCHASING 14.2. Safety Hazard Monitoring
11.1. Contractor/Supplier Selection 14.3. Security Hazard Monitoring
S PS C
PROCESS 3 - RISK EVALUATION 11.2. Contractor Operations 14.4. Environmental Hazard Monitoring
3.1. Health Hazard Identification and Evaluation 11.3. Contractor/Supplier Assurance 14.5. Customer Satisfaction
PROCESS 8 - COMMUNICATIONS AND
3.2. Safety Hazard Identification and Evaluation S PS C 11.4. Supply Chain and Purchasing 14.6. Effectiveness of Monitoring
PROMOTION
3.3. Security Hazard Identification and Evaluation 11.5. Logistics 14.7. Perception Surveys
8.1. Communication System
3.4. Environmental Hazards Identification and Evaluation 14.8. Behavioral Observation
8.2. Meeting Co-ordination
3.5. Customer Expectations Identification and Evaluation 14.9. Task Observations
8.3. Management Meetings
3.6. Process Risk Identification and Evaluation 14.10. Audits
8.4. Group Meetings
8.5. Joint Committee/Council S PS C
S PS C PROCESS 12 - EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS
PROCESS 4 - HUMAN RESOURCES 8.6. Coaching 12.1. Emergency Needs Assessment
4.1. Human Resources System S PS C
8.7. Recognition 12.2. Site Emergency Plan PROCESS 15 - RESULTS AND REVIEW
4.2. Recruitment 8.8. Promotion Campaigns 12.3. Off-Site Emergency Plan 15.1. Business Results
4.3. Managing Individual Performance 8.9. Away from Work Safety Information 12.4. Crisis Plan 15.2. Management Review
4.4. Recognition and Discipline 12.5. Business Continuity Plan 15.3. Reporting to Stakeholders
4.5. Leaving the Organization 12.6. Emergency Plan Review
4.6. Management of Organizational Change S PS C 12.7. Emergency Communications
PROCESS 9 - RISK CONTROL
9.1. Health Hazards Controls 12.8. Emergency Protection Systems
S PS C
PROCESS 5 - COMPLIANCE ASSURANCE 9.2. Safety Hazards Controls 12.9. Energy Controls
LEGEND
5.1. Regulations 9.3. Security Controls 12.10. Emergency Teams
5.2. External Authorizations to Operate 12.11. Drills and Exercises S - System Inadequate. Action required to fill the gap in our
9.4. Environmental Hazard Controls
5.3. Industry Codes and Standards 12.12. First Aid management system e.g., improvement team to develop a new
9.5. Quality Control of Materials and Products
5.4. Reporting to Authorities 12.13. Medical Support
system, process or procedure.
9.6. Process Control and Operating Procedures
5.5. Information Security 12.14. Organized Outside Help and Mutual Aid PS - Performance Standard Inadequate. Action required to define
9.7. Rules
5.6. Product Stewardship better WHO does WHAT and WHEN e.g., change the
9.8. Work Permits
5.7. Compliance Assessment procedure, instruction or rule.
9.9. Warning Signs and Notices
9.10. Personal Protective Equipment C - Compliance with Performance Standard Inadequate. Action
required to improve compliance e.g., implement a program of
training, coaching or promotion.
© Copyright 2006. Det Norske Veritas (U.S.A.), Inc., 3805 Crestwood Parkway, Suite 200, Duluth, GA 30096. All rights reserved. This item may not be reproduced in whole or part by any method without the express permission of the publisher. Our toll-free number is 1-800-486-4524 or visit our website at www.dnvtraining.com.
(NOTE: SCAT Rev1.2 is aligned with isrs7 Rev1.2.) INTERNAL VERSION. DNV PROPERTY FOR THE USE OF DNV PERSONNEL ONLY.
SCAT-isrs7_Rev1.2 Internal.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Accidente IAP EE - CC. SIMACERDocument41 pagesAccidente IAP EE - CC. SIMACERFelipe Ahumada100% (1)
- Anexo 20 - GNLQ-SOS-PR-003 Sistema de Permisos de TrabajoDocument18 pagesAnexo 20 - GNLQ-SOS-PR-003 Sistema de Permisos de TrabajoSergio Saez GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Estandar de SeguridadDocument11 pagesEstandar de Seguridadenimartinez92Pas encore d'évaluation
- 41 - Control de Energía Peligrosa Candado y Tarjeta de BloqueoDocument29 pages41 - Control de Energía Peligrosa Candado y Tarjeta de BloqueoBryan Kenneth Villar SandovalPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparación para Emergencias (Estándar)Document4 pagesPreparación para Emergencias (Estándar)Genaro RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ficha Educacion04 Caída en EscaleraDocument1 pageFicha Educacion04 Caída en EscaleraMelissa MiddletonPas encore d'évaluation
- Interpretacion Tabla SCAT Rev DNV GL Rev2 FinalDocument7 pagesInterpretacion Tabla SCAT Rev DNV GL Rev2 FinalLS GinezPas encore d'évaluation
- PR-GI-02 - Proced. Identificación y Evaluación Aspectos AmbientalesDocument14 pagesPR-GI-02 - Proced. Identificación y Evaluación Aspectos AmbientalesJosé Luis BonelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiper Seguridad Ocupacional SsoDocument1 pageHiper Seguridad Ocupacional SsoDiego MillaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.09.precourse assignment-ISO 45001 EspaDocument10 pages1.09.precourse assignment-ISO 45001 EspajaimeduH.Pas encore d'évaluation
- GhsDocument2 pagesGhsJorge Herrera GuitarreroPas encore d'évaluation
- Plan Anual de Capacitaciones y Actividades en SSTDocument3 pagesPlan Anual de Capacitaciones y Actividades en SSTMiguel Angel DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- PC - 2 PSSRDocument9 pagesPC - 2 PSSRJimmy RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- FR020A Hoja de Bloqueo y Aislamiento (Final)Document1 pageFR020A Hoja de Bloqueo y Aislamiento (Final)Roxana López De la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- TAP ROOT Incident Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesTAP ROOT Incident Analysis Worksheetnoe100% (1)
- Riesgos Con ExplosivosDocument23 pagesRiesgos Con ExplosivosCecilia Lopez ValenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lot 600542 2102 Turb550-IRDocument2 pagesLot 600542 2102 Turb550-IRFERNANDO ANDRADAPas encore d'évaluation
- Metodo-Bow-Tie-4551661236Document24 pagesMetodo-Bow-Tie-4551661236Jhoswa Medina CurePas encore d'évaluation
- Formato Toma 5Document4 pagesFormato Toma 5angelica castiblancoPas encore d'évaluation
- DC-021 Identificación y Evaluación de Aspectos AmbientalesDocument20 pagesDC-021 Identificación y Evaluación de Aspectos AmbientalesChristian Castro LozanoPas encore d'évaluation
- IPERC-EXP-14 Aumento de Tubería A La Columna de Perforación Con Rod Feeder v01Document11 pagesIPERC-EXP-14 Aumento de Tubería A La Columna de Perforación Con Rod Feeder v01Ana MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 PET - CONT - PR - 002 Trazado y Nivelacion (Control Topográfico)Document5 pages03 PET - CONT - PR - 002 Trazado y Nivelacion (Control Topográfico)Alexander Alex VPPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis Accidentes Ishikawa EjmDocument2 pagesAnalisis Accidentes Ishikawa Ejmferlaboxy100% (1)
- Bloqueo y EtiquetadoDocument13 pagesBloqueo y EtiquetadoAnonymous DEj0WIVPas encore d'évaluation
- Cronograma PrexorDocument5 pagesCronograma PrexorCristy Bravo UribePas encore d'évaluation
- Tasc DNV Rev 1Document2 pagesTasc DNV Rev 1KALATUS100% (1)
- Modelo TASCDocument2 pagesModelo TASCyesica mora0% (1)
- Tasc DNV Rev-AvanceDocument2 pagesTasc DNV Rev-AvanceCesar PumaPas encore d'évaluation
- TASCDocument1 pageTASCWILFREDO CALISAYAPas encore d'évaluation
- TASCDocument1 pageTASCCily UsseglioPas encore d'évaluation
- TASCDocument1 pageTASCChristian AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz TascDocument1 pageMatriz Tascbrigitte molinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla ScatDocument1 pageTabla ScatCarlos Alcca PuchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla SCATDocument1 pageTabla SCATMarcoPas encore d'évaluation
- ScatDocument1 pageScatkarina Jorge MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz TASCDocument1 pageMatriz TASCAnthony Raskolnikov Fierro QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Tasc para Analisis de Investigaciones de IncidentesDocument1 pageTasc para Analisis de Investigaciones de IncidentesMafer RdPas encore d'évaluation
- Tabla TASC - DNVDocument2 pagesTabla TASC - DNVLisbeth GaribayPas encore d'évaluation
- DNV Tabla de Analisis Sistematico de CausasDocument2 pagesDNV Tabla de Analisis Sistematico de CausasCristian TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- TASCDocument1 pageTASCHiran Richard Pizarro100% (1)
- Tabla SCATDocument3 pagesTabla SCATCarlos AyamamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- SIG-PR-009-02 METODOLOGIA DE TABLA SCAT - ImprimirDocument2 pagesSIG-PR-009-02 METODOLOGIA DE TABLA SCAT - ImprimirLUCEROPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedimiento para Adquisiciones y Compras de SSTDocument23 pagesProcedimiento para Adquisiciones y Compras de SSTR. S.Pas encore d'évaluation
- TASC - Tecnicas de Analisis Sistematico de Cauzas PDFDocument1 pageTASC - Tecnicas de Analisis Sistematico de Cauzas PDFPAULOPas encore d'évaluation
- Anexo 1. Tabla SCATDocument1 pageAnexo 1. Tabla SCATMijailPas encore d'évaluation
- R.M. #050-2013-TR, Anexo #3 Guía Básica Sobre Sistema de Gestión de Seguridad y Salud en El TrabajoDocument13 pagesR.M. #050-2013-TR, Anexo #3 Guía Básica Sobre Sistema de Gestión de Seguridad y Salud en El TrabajoCarla GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablero TASCDocument1 pageTablero TASCArmando RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Técnica Investigación Accidentes DNVDocument2 pagesTécnica Investigación Accidentes DNVanibalmora653Pas encore d'évaluation
- VolcanDocument49 pagesVolcanMaycol Alvarez100% (1)
- Anexo 01. SST-FT-01 - Iper ContinuoDocument2 pagesAnexo 01. SST-FT-01 - Iper ContinuoJuan SheenPas encore d'évaluation
- Iperc - Mantenimiento de Electrobombas Sumergibles de Camara de RebombeoDocument17 pagesIperc - Mantenimiento de Electrobombas Sumergibles de Camara de RebombeoPatricio RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Iperc Metodo 3 ElectricidadDocument5 pagesIperc Metodo 3 ElectricidadSandra AlemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz, CrissDocument5 pagesMatriz, CrissCristhian CañazacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz de Riesgos PRO-RT-WEDocument3 pagesMatriz de Riesgos PRO-RT-WEDiem UrquetaPas encore d'évaluation
- TASCDocument3 pagesTASCmariano seguraPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA-22-181 CORTE TALUD BOG COMPRESSOR, Rev.1 - ECALDocument5 pagesJSA-22-181 CORTE TALUD BOG COMPRESSOR, Rev.1 - ECALFabian DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- JSA-22-181 CORTE TALUD BOG COMPRESSOR, Rev.2 - ECALDocument6 pagesJSA-22-181 CORTE TALUD BOG COMPRESSOR, Rev.2 - ECALFabian DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- IpercDocument17 pagesIpercSan BPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarea 2 - 104561 - 69Document98 pagesTarea 2 - 104561 - 69carlos miguel cardona carrilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Fo-Sst - 42 - TascDocument3 pagesFo-Sst - 42 - TascJean Pierre De Los RiosPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotipologia CriminalDocument5 pagesBiotipologia CriminalAnny Rodas100% (1)
- Desarrollo de Habilidades Directivas Unidad 3 Actividad 2Document4 pagesDesarrollo de Habilidades Directivas Unidad 3 Actividad 2carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Diario Pedagogico No. 2Document3 pagesDiario Pedagogico No. 2Clara Isabel RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad Quinto La Entrevista Martes 27-09Document2 pagesActividad Quinto La Entrevista Martes 27-09Romina Robles SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- El Kata Como Conocimiento - Pablo Pereda González (Con Pagine Del Manoscr - Pereda)Document28 pagesEl Kata Como Conocimiento - Pablo Pereda González (Con Pagine Del Manoscr - Pereda)rgonellaPas encore d'évaluation
- El Problema de La Interpretación FilológicaDocument41 pagesEl Problema de La Interpretación FilológicaManuelCrespillo100% (1)
- Consolidado 1 Nota1Document3 pagesConsolidado 1 Nota1Dennis Niko PV50% (4)
- Tipos de Conocimiento 1Document9 pagesTipos de Conocimiento 1Fallo Re DoPas encore d'évaluation
- Análisis TransaccionalDocument25 pagesAnálisis TransaccionalJordan RChPas encore d'évaluation
- 1303 Ejercicios de Creacion LiterariaDocument262 pages1303 Ejercicios de Creacion LiterariaMay Montoya82% (17)
- Comunicacin Public It Aria Inca Kola Reporte Escrito 1230474328175176 1Document30 pagesComunicacin Public It Aria Inca Kola Reporte Escrito 1230474328175176 1ChoFa Chang100% (1)
- Tesina Trabajo de InvestigacionDocument17 pagesTesina Trabajo de InvestigacionRaulFigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- GUIA HABILIDADES BLANDAS No 2Document7 pagesGUIA HABILIDADES BLANDAS No 2patricia gomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepto: La EducaciónDocument2 pagesConcepto: La EducaciónCastañeda Vázquez Yareli AnaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Valores Agustinianos en La Sociedad Venezolana PDFDocument21 pagesValores Agustinianos en La Sociedad Venezolana PDFdocumentoseducacionenvaloresPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Consejos para Ser Mas InteligenteDocument8 pages5 Consejos para Ser Mas InteligenteWilson Infa Mamani0% (1)
- Consultoria GestaltDocument25 pagesConsultoria GestaltEnriqueAndreini0% (1)
- Capitulo 1 - Mente y Fe PDFDocument60 pagesCapitulo 1 - Mente y Fe PDFjcmesiasjPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1-Reporte de TrabajoDocument3 pages1.1-Reporte de TrabajoRodrigo CollazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Comunicacion InternaDocument7 pagesComunicacion InternaDorisDoritaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muñoz Burgos Marquiri Descripción de Un ProblemaDocument3 pagesMuñoz Burgos Marquiri Descripción de Un Problemamarquiri munozPas encore d'évaluation
- George Morrisey 1996Document12 pagesGeorge Morrisey 1996Orlando J Fernandes RPas encore d'évaluation
- Ensayo ProduccionDocument4 pagesEnsayo ProduccionByron YossimarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía para El Docente - Introducción A Las Ciencias Sociales (Piña)Document40 pagesGuía para El Docente - Introducción A Las Ciencias Sociales (Piña)PaquitosonrisasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ae 309Document135 pagesAe 309HermithSantaCruzMeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Let 012 Unidad II Ejerc. Juana Orlanny NúñezDocument7 pagesLet 012 Unidad II Ejerc. Juana Orlanny NúñezPedro Luis SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexismo y Juguetes InfantilesDocument4 pagesSexismo y Juguetes InfantilesLaura GuzmánPas encore d'évaluation
- Entrevista Semiestructurada A Un Adolescente 2019-FinalisimaDocument6 pagesEntrevista Semiestructurada A Un Adolescente 2019-FinalisimaBeta DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Robert Darnton La Gran Matanza de GatosDocument30 pagesRobert Darnton La Gran Matanza de GatosJuan Andrés Freire100% (5)
- 4 Cuarto PasoDocument1 page4 Cuarto PasoEduardo Espinosa100% (3)