Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ABET, Inc., Is The Recognized Accreditor For College and University Programs in Applied Science
Transféré par
Ghazi Bahroz JumaaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ABET, Inc., Is The Recognized Accreditor For College and University Programs in Applied Science
Transféré par
Ghazi Bahroz JumaaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ABET, Inc.
, is the recognized accreditor for college and university programs in applied science,
computing, engineering, and technology. Among the most respected accreditation organizations
in
the U.S., ABET has provided leadership and quality assurance in higher education for over 75
years.
ABET accredits over 3,100 programs at more than 600 colleges and universities worldwide.
What Is ABET Accreditation?
ABET accreditation is assurance that a college or university program meets the quality standards
established by the profession for which it prepares its students. For example, an accredited
engineering program must meet the quality standards set by the engineering profession. An
accredited computer science program must meet the quality standards set by the computing
profession.
Who Sets the ABET Quality Standards?
The quality standards programs must meet to be ABET-accredited are set by the ABET
professions themselves. This is made possible by the collaborative efforts of many different
professional and technical societies. These societies and their members work together through
ABET to develop the standards, and they provide the professionals who evaluate the programs to
make sure they meet those standards.
Why Is ABET Accreditation Important?
Accreditation helps students and their parents choose quality college programs.
Accreditation enables employers to recruit graduates they know are well-prepared.
Accreditation is used by registration, licensure, and certification boards to screen
applicants.
Accreditation gives colleges and universities a structured mechanism to assess,
evaluate and improve the quality of their programs.
Further details on ABET accreditation is available at : http://www.abet.org
What Are the ABET Objectives?
IE Possible ABET Description
Outcomes Objective
A 3a Apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering principles
in solving industrial problems.
B 3b Design, develop, and conduct engineering experiments and analyze
outcome data.
C 3c Design and realize products and services that meet market needs.
Design and develop production and management systems that assure
quality and maintain efficiency.
D 3d Participate effectively in teams, and apply project and time management
skills.
E 3e Formulate engineering problems using mathematical and computer
models and deploy solutions and design controls to maintain
performance. Troubleshoot industry problems and prescribe solutions
for continuous improvement.
F 3f Recognize and practice engineering ethics and professional conduct.
G 3g Write technical reports and deliver professional presentations using
latest technologies. Practice industry-communication and interaction
skills and communicate effectively.
H 3h Recognize the impact of engineering solutions on industry, society, and
the environment.
I 3i Demonstrate the ability to seek knowledge, stay updated, and pursue
further learning and training.
J 3j Stay aware of latest technologies and advances in disciplines related to
Industrial Engineering and engineering in general utilizing latest
resources of knowledge.
K 3k Apply learned techniques, tools, and skills to solve engineering
problems.
L 3l Develop and apply safety rules and ergonomic standards in the work
environment.
What Is Accreditation?
Accreditation is a review process to determine if educational programs meet defined standards
of quality. Once achieved, accreditation is not permanent—it is renewed periodically to ensure
that the quality of the educational program is maintained.
In the United States, academic accreditation is voluntary, decentralized, and carried out by
many non-governmental, non-profit organizations. The process of academic accreditation
typically culminates in an external quality review by a team of professional experts from
academe or industry. These experts volunteer their time, professional knowledge, and
experience to this process of quality assurance and ongoing improvement to education in their
disciplines.
In other countries, accreditation may be required or governmental. The United Nations
Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) provides information about
accreditation and quality assurance in countries outside of the United States.
What Distinguishes ABET Accreditation?
ABET accreditation is not a ranking system. It is a form of quality assurance for programs in
the areas of applied and natural science, computing, engineering, and engineering technology.
Our accreditation is recognized globally as evidence that a program meets the standards set by
its technical profession.
We offer accreditation to programs only, not to degrees, departments, colleges, institutions,
or individuals.
ABET is a federation of member professional and technical societies. These societies and their
individual members collaborate through ABET to develop standards of quality, known as
ABET Criteria, on which our review teams base their evaluations of programs under
consideration for accreditation.
ABET Civil Engineering
Accreditation
The University of Missouri program in Civil Engineering is accredited
by the Engineering Accreditation Commission of ABET, www.abet.org.
CE Program Educational Objectives
The current educational objectives of the Civil Engineering (CE) program are:
Graduates will meet the expectations of employers of Civil Engineers, including acquiring the
professional experience necessary to qualify them for professional licensure;
Qualified graduates will pursue advanced study, if they so desire and/or use their technical
backgrounds to advance in other professions/roles, such as law, business, or government
service;
Graduates will actively engage with their profession and/or communities.
CE Student Outcomes
Students from the CE program will attain (by the time of graduation):
a. An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
b. An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data
c. An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic
constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety,
manufacturability, and sustainability
d. An ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams
e. An ability to identify, formulate and solve engineering problems
f. An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility
g. An ability to communicate effectively
h. The broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global,
economic, environmental, and societal context
i. A recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in, life-long learning
j. A knowledge of contemporary issues
k. An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for
engineering practice
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Programme Accreditation Models and Quality CodeDocument23 pagesProgramme Accreditation Models and Quality CodeKarthikeyan PurusothamanPas encore d'évaluation
- TraducciónDocument23 pagesTraducciónVictor AscuePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Engineering Education and ABET AccreditationDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Engineering Education and ABET AccreditationAli SabbahPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Programme SpecificationDocument78 pagesEngineering Programme SpecificationKhaLed El ArabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering ABET Status - ReviewDocument28 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering ABET Status - Reviewkhaleel_anwar2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- ABET Accreditation EssentialsDocument51 pagesABET Accreditation EssentialshameeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Engineering Course WorkDocument4 pagesComputer Engineering Course Workvup0nemyj1n3100% (2)
- Iswa GecgDocument38 pagesIswa GecgMunavvar PopatiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Engineering (New)Document10 pagesSoftware Engineering (New)Tamiru Dereje100% (1)
- Business Level 3 Btec Extended Diploma CourseworkDocument7 pagesBusiness Level 3 Btec Extended Diploma Courseworkemlwymjbf100% (1)
- ABET Accreditation OverviewDocument20 pagesABET Accreditation OverviewNgovancuong NgoPas encore d'évaluation
- ABET Criteria For Accrediting Engineering ProgramsDocument5 pagesABET Criteria For Accrediting Engineering ProgramsawakenatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Boollet Pasific Plant-Palm PhilmDocument48 pagesBoollet Pasific Plant-Palm PhilmlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Program ObjectivesDocument5 pagesProgram ObjectivesAlvinPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Accreditation SummaryDocument3 pagesIT Accreditation Summarykhaleel_anwar2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Electronics Engineering Program Self-Assessment ReportDocument14 pagesMedical Electronics Engineering Program Self-Assessment ReportPrashant SunagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance For IEng or CEng Applicants Who Work in AcademiaDocument4 pagesGuidance For IEng or CEng Applicants Who Work in AcademiaMohd Helmy HakimiePas encore d'évaluation
- Abet Eac Criteria 2011 2012Document26 pagesAbet Eac Criteria 2011 2012Acreditacion Fic UniPas encore d'évaluation
- AI 1131[1] (1)Document65 pagesAI 1131[1] (1)pratikdholariya97255Pas encore d'évaluation
- 7-22-22 II K CTE Standards - Attachment 43 - Principles Engineering TechnolDocument5 pages7-22-22 II K CTE Standards - Attachment 43 - Principles Engineering TechnolCliff Holice MakunganyaPas encore d'évaluation
- ATMAE AccreditationDocument4 pagesATMAE AccreditationKrista LawrencePas encore d'évaluation
- Csi 2911 Module 1 Professionalism and RegulationDocument58 pagesCsi 2911 Module 1 Professionalism and RegulationBruce YinPas encore d'évaluation
- OOP Lab Manual for Core Java ConceptsDocument91 pagesOOP Lab Manual for Core Java ConceptsKavish Panchal0% (1)
- Accreditation Workshop: Mechanical Engineering Preparation For The Accreditation ProcessDocument25 pagesAccreditation Workshop: Mechanical Engineering Preparation For The Accreditation ProcessKrishna MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Admissioncompetenciesverification MothesDocument5 pagesPre Admissioncompetenciesverification Mothesapi-282645567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Programme Specification: Mcomp Information TechnologyDocument10 pagesProgramme Specification: Mcomp Information TechnologyViraat SewrajPas encore d'évaluation
- 2021 Beng Software Engineering 4465Document10 pages2021 Beng Software Engineering 4465FrankPas encore d'évaluation
- Software EngineeringDocument12 pagesSoftware EngineeringAbishu GemedoPas encore d'évaluation
- An Example of Course and Program Outcome AssessmentDocument20 pagesAn Example of Course and Program Outcome AssessmentmdazrienPas encore d'évaluation
- 18.10.23 ABOUT THE DEPARTMENT - Gojan EceDocument4 pages18.10.23 ABOUT THE DEPARTMENT - Gojan EceJ edward paulrajPas encore d'évaluation
- AbetDocument3 pagesAbetsaidhaggagPas encore d'évaluation
- CDIO Optional Standards 3.0Document6 pagesCDIO Optional Standards 3.0Ricardo ChegwinPas encore d'évaluation
- 3140702 Operating System and Rjp Vgec GecmDocument72 pages3140702 Operating System and Rjp Vgec Gecmkunalkhairanar007Pas encore d'évaluation
- PEO PO and PSC 17-5-13Document5 pagesPEO PO and PSC 17-5-13DrPrakash G ChithappaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3161608-Ai GecmDocument45 pages3161608-Ai Gecmchimanjithakor79148Pas encore d'évaluation
- Only EngineeringDocument6 pagesOnly EngineeringLiliane AlameddinePas encore d'évaluation
- MAD LabManual - SSECDocument171 pagesMAD LabManual - SSECcoloringcraft318Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp4 Os(Deep)Document71 pagesExp4 Os(Deep)kunalkhairanar007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cdio Standards 3Document14 pagesCdio Standards 3Ricardo ChegwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Uwl4623 PGP Computer-Tech VawDocument4 pagesUwl4623 PGP Computer-Tech VawalikhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Leadership Development Program: Electronic SystemsDocument11 pagesEngineering Leadership Development Program: Electronic Systemslexluther234234Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2.1. Describe The Programme Educational Objectives (Peos)Document3 pages1.2.1. Describe The Programme Educational Objectives (Peos)Sandeep ManePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is AbetDocument38 pagesWhat Is AbetDr_M_SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- AbetDocument4 pagesAbetamare ayelePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Engineering PracticeDocument17 pagesWhat Is Engineering PracticeIzijesuTosanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mission, Vision, Program Objectives, Program OutcomesDocument2 pagesMission, Vision, Program Objectives, Program OutcomesAlvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Related Coursework For Industrial EngineeringDocument7 pagesRelated Coursework For Industrial Engineeringguj0zukyven2100% (1)
- Enhancing Engineering Problem Solving Skills in A Mechatronics CourseDocument8 pagesEnhancing Engineering Problem Solving Skills in A Mechatronics CourseMehdi ArroubPas encore d'évaluation
- BSCE Document Upd 24-5-10Document32 pagesBSCE Document Upd 24-5-10Faisal SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- PEO and SO of B.S. in Computer EngineeringDocument2 pagesPEO and SO of B.S. in Computer EngineeringKristineBinadayEstiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Aiml Bee Lab Manual i Yr II Sem 2023-24 (1)Document102 pagesAiml Bee Lab Manual i Yr II Sem 2023-24 (1)holagoogolPas encore d'évaluation
- ACT Prospectus: Associate in Computer Technology Degree ProgramDocument15 pagesACT Prospectus: Associate in Computer Technology Degree Programjohnny abellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Descriptions: MsmotDocument15 pagesCourse Descriptions: MsmotNani NRajPas encore d'évaluation
- Rushitha 007Document27 pagesRushitha 007Yohan Tharish WarnakulasooriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Manager JDDocument3 pagesProject Manager JDAspirejobsPas encore d'évaluation
- Routes to Membership (MICE) SummaryDocument4 pagesRoutes to Membership (MICE) SummaryMatthew DPas encore d'évaluation
- Outcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesDocument42 pagesOutcome Based Education Curriculum in Polytechnic Diploma ProgrammesSanthosh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Education Standards SummaryDocument98 pagesIT Education Standards SummaryJulie Ann PiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Seismic Design Manual and Application of The 2010 AISC Seismic ProvisionsDocument2 pagesSeismic Design Manual and Application of The 2010 AISC Seismic ProvisionsGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridge Inspection Report: Thornton 247/079Document6 pagesBridge Inspection Report: Thornton 247/079Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Ce 382 Fall 38 39Document17 pagesIntroduction Ce 382 Fall 38 39Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- HistoryDocument21 pagesHistoryGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
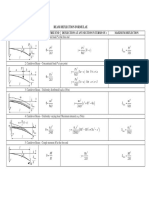
- Beam Deflection FormulaDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection FormulaYogiAndrésDíazGómez100% (1)
- Introduction To EngineeringDocument33 pagesIntroduction To EngineeringTine ArevaloPas encore d'évaluation
- 99 - Viscometer Sayboldt Type - Asphalt Content Binder Ignition FurnaceDocument1 page99 - Viscometer Sayboldt Type - Asphalt Content Binder Ignition FurnaceGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- dm519 - dm195 - Makmal JalanrayaDocument1 pagedm519 - dm195 - Makmal JalanrayaGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam Deflection FormulaDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection FormulaYogiAndrésDíazGómez100% (1)
- 101 - Film OvensDocument1 page101 - Film OvensGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Civil EngineeringDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Civil EngineeringManish Shashikant DharekPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Civil Engineering PDFDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Civil Engineering PDFBarun SarangthemPas encore d'évaluation
- CivilDocument34 pagesCivilDarshit DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1 Structures WU MASE101Document58 pagesLecture1 Structures WU MASE101CarylJaneVeriña100% (1)
- Astm c67 BrickDocument12 pagesAstm c67 BrickGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1666Document8 pages1666Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Test Procedures for Determining Dimensions and Properties of BricksDocument8 pagesStandard Test Procedures for Determining Dimensions and Properties of BricksAltaf HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- 14-Irrigularity Asce 7-16Document23 pages14-Irrigularity Asce 7-16Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- ch.8 Part 2Document10 pagesch.8 Part 2Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- ETABS 2015 (Extended 3D Analysis of Building Systems) : Tutorial 1Document12 pagesETABS 2015 (Extended 3D Analysis of Building Systems) : Tutorial 1Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - NN Elchabib2005Document12 pages1 - NN Elchabib2005Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- A - Academic DebateDocument4 pagesA - Academic DebateGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On The Influence of Curing On The Strength of A Standard Grade Concrete MixDocument12 pagesA Study On The Influence of Curing On The Strength of A Standard Grade Concrete MixAyo OshoPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning ObjectivesDocument43 pagesLearning ObjectivesKashiPrakash DambalPas encore d'évaluation
- 0354 46051001023KDocument80 pages0354 46051001023KGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ars Lan 2007Document10 pagesArs Lan 2007Ghazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ects enDocument64 pagesEcts enTaoTherapyPas encore d'évaluation
- Early carbonation curing of concrete masonry units with PLCDocument11 pagesEarly carbonation curing of concrete masonry units with PLCGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of wastewater curing on concrete strength and water absorptionDocument8 pagesEffect of wastewater curing on concrete strength and water absorptionGhazi Bahroz JumaaPas encore d'évaluation
- EADK Architecture GuideDocument31 pagesEADK Architecture GuideUltrazikingPas encore d'évaluation
- EC20 HMI Connection GuideDocument3 pagesEC20 HMI Connection GuideGabriel Villa HómezPas encore d'évaluation
- GPU Fundamentals ExplainedDocument20 pagesGPU Fundamentals ExplainedJyotirmay SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- LearnTube Project ReportDocument14 pagesLearnTube Project ReportManogya Pratap SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Igad Policy Youth 2022 - Document 1aDocument112 pagesIgad Policy Youth 2022 - Document 1aRICHARD BONYOPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Year Project TopicsDocument112 pagesFinal Year Project TopicsJyothi BurlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesCharlon Mamacos100% (9)
- Presentation of Dairy Management SystemDocument35 pagesPresentation of Dairy Management SystemEnola Syawla100% (1)
- Unit 1 - IMEDDocument37 pagesUnit 1 - IMEDAlishka RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- UAV-based Multispectral Remote Sensing For Precision Agriculture: A T Comparison Between Different CamerasDocument13 pagesUAV-based Multispectral Remote Sensing For Precision Agriculture: A T Comparison Between Different CamerasSantiago BedoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter Iqbal100% (1)
- Accounting 12 Course OutlineDocument3 pagesAccounting 12 Course OutlineKenrose LaguyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ssp393 - Audi A5 - Convenience Electronics and Driver Assist SystemsDocument56 pagesSsp393 - Audi A5 - Convenience Electronics and Driver Assist SystemsCyberemulePas encore d'évaluation
- ZJ 5780s Instruction BookDocument102 pagesZJ 5780s Instruction BookRATSITOHARA EricPas encore d'évaluation
- CIS Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Benchmark v1.0.0Document66 pagesCIS Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 Benchmark v1.0.0Elisha MushaijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic College Bell REPORTDocument61 pagesAutomatic College Bell REPORTDebashishParida100% (1)
- Jabra Android SDK Developers GuideDocument12 pagesJabra Android SDK Developers GuideEmilio AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- MikroTik Wireless Wire nRAYDocument3 pagesMikroTik Wireless Wire nRAYddddPas encore d'évaluation
- Transportation Model Optimization With MODI MethodDocument2 pagesTransportation Model Optimization With MODI Methodhello_khayPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDocument27 pagesAdvanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant PublishersPas encore d'évaluation
- Positioning & ErrorsDocument3 pagesPositioning & ErrorsAhsan Hussain100% (4)
- KPT ShapeShifterDocument28 pagesKPT ShapeShifterLuis TovarPas encore d'évaluation
- C Pointers Questions PDFDocument30 pagesC Pointers Questions PDFRoshni Khurana0% (2)
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusBhavana NagarajPas encore d'évaluation
- MOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesDocument3 pagesMOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesJyoti PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring CoreDocument480 pagesSpring CoreANUSHA S GPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument1 903 pagesUntitledTu Vieja A casa petePas encore d'évaluation
- 1654286-1 - Connectors For Circular Contact SystemsDocument68 pages1654286-1 - Connectors For Circular Contact Systemswww.erwer9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Easychair Preprint: Adnene Noughreche, Sabri Boulouma and Mohammed BenbaghdadDocument8 pagesEasychair Preprint: Adnene Noughreche, Sabri Boulouma and Mohammed BenbaghdadTran Quang Thai B1708908Pas encore d'évaluation
- WSN Monitoring System For BillboardsDocument11 pagesWSN Monitoring System For BillboardsRaja RKPas encore d'évaluation
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionD'EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: The Infographics EditionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2475)
- The 30 Day MBA: Your Fast Track Guide to Business SuccessD'EverandThe 30 Day MBA: Your Fast Track Guide to Business SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (19)
- The Proximity Principle: The Proven Strategy That Will Lead to the Career You LoveD'EverandThe Proximity Principle: The Proven Strategy That Will Lead to the Career You LoveÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (93)
- Designing Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeD'EverandDesigning Your Life by Bill Burnett, Dave Evans - Book Summary: How to Build a Well-Lived, Joyful LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (61)
- Steal the Show: From Speeches to Job Interviews to Deal-Closing Pitches, How to Guarantee a Standing Ovation for All the Performances in Your LifeD'EverandSteal the Show: From Speeches to Job Interviews to Deal-Closing Pitches, How to Guarantee a Standing Ovation for All the Performances in Your LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (39)
- From Paycheck to Purpose: The Clear Path to Doing Work You LoveD'EverandFrom Paycheck to Purpose: The Clear Path to Doing Work You LoveÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (39)
- The Confidence Code: The Science and Art of Self-Assurance--What Women Should KnowD'EverandThe Confidence Code: The Science and Art of Self-Assurance--What Women Should KnowÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (175)
- The 12 Week Year: Get More Done in 12 Weeks than Others Do in 12 MonthsD'EverandThe 12 Week Year: Get More Done in 12 Weeks than Others Do in 12 MonthsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (90)
- Work Stronger: Habits for More Energy, Less Stress, and Higher Performance at WorkD'EverandWork Stronger: Habits for More Energy, Less Stress, and Higher Performance at WorkÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Company Of One: Why Staying Small Is the Next Big Thing for BusinessD'EverandCompany Of One: Why Staying Small Is the Next Big Thing for BusinessÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (14)
- The Dictionary of Body Language: A Field Guide to Human BehaviorD'EverandThe Dictionary of Body Language: A Field Guide to Human BehaviorÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (95)
- Start.: Punch Fear in the Face, Escape Average, and Do Work That MattersD'EverandStart.: Punch Fear in the Face, Escape Average, and Do Work That MattersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (56)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindD'EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindPas encore d'évaluation
- The Search for Self-Respect: Psycho-CyberneticsD'EverandThe Search for Self-Respect: Psycho-CyberneticsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (10)
- Ultralearning: Master Hard Skills, Outsmart the Competition, and Accelerate Your CareerD'EverandUltralearning: Master Hard Skills, Outsmart the Competition, and Accelerate Your CareerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (359)
- Radiographic Testing: Theory, Formulas, Terminology, and Interviews Q&AD'EverandRadiographic Testing: Theory, Formulas, Terminology, and Interviews Q&APas encore d'évaluation
- The First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterD'EverandThe First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (122)
- When to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantD'EverandWhen to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (18)
- Real Artists Don't Starve: Timeless Strategies for Thriving in the New Creative AgeD'EverandReal Artists Don't Starve: Timeless Strategies for Thriving in the New Creative AgeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (197)
- The Power of Body Language: An Ex-FBI Agent's System for Speed-Reading PeopleD'EverandThe Power of Body Language: An Ex-FBI Agent's System for Speed-Reading PeopleÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (9)
- When to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantD'EverandWhen to Jump: If the Job You Have Isn't the Life You WantÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (16)
- How to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpD'EverandHow to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Ultimate Sales Letter, 4th Edition: Attract New Customers, Boost Your SalesD'EverandThe Ultimate Sales Letter, 4th Edition: Attract New Customers, Boost Your SalesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (98)
- Write It Down, Make It Happen: Knowing What You Want And Getting It!D'EverandWrite It Down, Make It Happen: Knowing What You Want And Getting It!Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (103)




















![AI 1131[1] (1)](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/721723158/149x198/15ed82559e/1712739647?v=1)