Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Verbs PDF
Transféré par
Tko ToolTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Verbs PDF
Transféré par
Tko ToolDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Verb Forms and Tenses
Adapted from The Little, Brown Handbook, 11th Edition, Contributors Dayne Sherman,
Jayetta Slawson, Natasha Whitton, and Jeff Wiemelt, 2010, 272-289. Prepared by the Southeastern
Writing Center. Last updated July, 2011.
A verb expresses action or a state of being and tells (in active voice) what the subject of the clause is or does. A verb is necessary to make
a complete statement.
All verbs are constructed from three basic forms known as the principal parts of a verb:
• Infinitive (or present) is the base form of a verb, preceded by to: to run, to go, to laugh.
• Past is the simplest form of a verb. Past is used to show action that has already taken place: ran, gone, laughed.
• Past participle is the form a verb takes when it is accompanied by an auxiliary verb (helping verbs using forms of be, have, or
do) to show a more complex past tense form: had gone, will have gone, would have laughed.
Active and Passive Verbs
Active verbs (active voice) tell what the subject (a person, place, thing, or concept) does.
Example: The boy kicked the ball.
Passive verbs (passive voice) tell what is done to the subject.
Example: The ball was kicked by the boy.
Verb Forms
Regular Verbs
A regular verb is used to form the past tense by adding a suffix –d or -ed.
Example: hope, hoped laugh, laughed
Irregular Verbs
An irregular verb does not take the –d or –ed ending. The past tense for irregular verbs is formed by changing the verb
internally. Refer to the Southeastern Writing Center’s handout Irregular Verbs for a list of the most commonly used irregular
verb forms.
Example: run, ran catch, caught
Verb Tenses
Verb tenses are used to show time. Verb tenses tell when events happen, happened, or will happen.
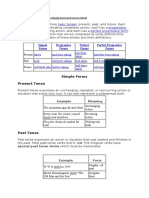
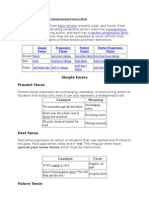
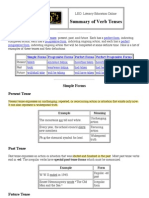
Simple Tense
Present
The present tense may express an action that is repeated or ongoing. It can also express an action that is happening at
this moment or a situation that is always true.
Example: Jane and Sarah jog every morning.
Past
The past tense expresses an action that has already happened. In regular verbs, the past tense is formed by adding –ed
or –d to the base form. In irregular verbs, the past tense takes a variety of forms.
Example: John and Sara hiked to the top of the mountain.
Future
The future tense expresses an action that will take place in the future. The future tense is formed by adding will to the
base form.
Example: I will fly to Atlanta Friday evening.
Southeastern Writing Center
Celebrating the Writer’s Voice
383 D. Vickers Hall
(985) 549-2076 ~ writing@selu.edu
http://www.selu.edu/acad_research/programs/writing_center
Perfect Tense
Present perfect
The present perfect tense is used to express an action that took place at some unspecified time in the past. The present
perfect tense can also be used to express an action that began in the past and continues in the present. The present
perfect tense is formed with the past tense of the verb and the helping verbs has or have.
Example: Sarah has watched the movie.
Past perfect
The past perfect tense is used to show that one action in the past began and ended before another action in the past
started. The past perfect tense is formed with the past participle of the verb and the helping verb had.
Example: Sarah had seen the movie before I watched it.
Future perfect
The future perfect tense is used to show that one action or condition in the future will begin and end before another
event in the future starts. The future perfect tense is formed with the past participle of the verb and the construction will
have.
Example: By the time I finish this semester, I will have read ten novels.
Progressive Tense
Present progressive
The present progressive tense is used to show an ongoing event that is happening at the moment of speaking or
writing. The present progressive tense is formed by using am, is, or are with the verb form ending in –ing.
Example: The children are sleeping.
Past progressive
The past progressive tense is used to show a past event that was happening when another event occurred. The past
progressive tense is formed by using was or were with the verb form ending in –ing.
Example: The children were sleeping when we arrived.
Future progressive
The future progressive tense is used to show an ongoing or continuous event that will take place in the future. The
future progressive tense is formed by using will be or shall be with the verb form ending in –ing.
Example: The children will be sleeping when we arrive.
Present perfect progressive
The present perfect progressive tense is used to show an event that began in the past, continues in the present, and
may continue in the future. The present perfect progressive tense is form by using has been or have been with the
present participle verb form ending in –ing.
Example: The children have been sleeping.
Past perfect progressive
The past perfect progressive tense is used to show a past, ongoing event that was completed before another past event.
The past perfect progressive tense is formed by using had been with the present perfect verb form ending in -ing.
Example: The children had been sleeping when we arrived.
Future perfect progressive
The future perfect progressive tense is used to show a future, ongoing event that will happen before a specified future
time. The future perfect progressive tense is formed by using will have been and the present participle verb form ending
in –ing.
Example: The children will have been sleeping.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Aspects of The VerbsDocument2 pagesAspects of The VerbsKathy MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- English TensesDocument29 pagesEnglish TensesRadheShyam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument29 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormRadheShyam SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Functional Grammar: Patterns and Usage: VoicesDocument29 pagesFunctional Grammar: Patterns and Usage: VoicesAarishti SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesMayur RawoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFDocument85 pagesGrammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFKarma Kuenzang WangdiPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Basic Tenses and Verb TensesDocument9 pages12 Basic Tenses and Verb TensesniensjvrPas encore d'évaluation
- Have SatDocument4 pagesHave SatLim SenglyPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Verb TenseDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Verb TenseDavie Jane PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses and AspectDocument17 pagesVerb Tenses and AspectJosh BhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Objectives:: The Tense of A Verb Tells You When A Person Did Something or When Something Existed or Happened.Document7 pagesObjectives:: The Tense of A Verb Tells You When A Person Did Something or When Something Existed or Happened.deidreanne patawePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesTrinh100% (1)
- ProgressiveDocument5 pagesProgressiveDaisylineCaleonCruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Dbdistin 531Document2 pagesDbdistin 531malintha999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningDocument16 pagesSimple Forms Present Tense: Example MeaningyanieggPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSummary of Verb TensesRamir Y. LiamusPas encore d'évaluation
- English TensesDocument30 pagesEnglish TensesMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (65)
- Verb Tenses Present Future PastDocument7 pagesVerb Tenses Present Future PasthansikasulanjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- TensesDocument16 pagesTensesMisham GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSC GrammarDocument5 pagesCSC Grammarsandra seguientePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument4 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect Form Progressive Form Perfect Progressive FormsumitPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument4 pagesSimple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive Formshardy annawayPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs: Prepared By: Mr. Leeroi Christian Q. Rubio School of Education, Arts and Sciences St. Anne College Lucena, IncDocument17 pagesVerbs: Prepared By: Mr. Leeroi Christian Q. Rubio School of Education, Arts and Sciences St. Anne College Lucena, IncLeeroi Christian Q RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Perfect TenseDocument8 pagesPresent Perfect TenseMustafa AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Abad - 1 & 2Document27 pagesAbad - 1 & 2Jeff LacasandilePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Verb TensesDocument24 pages4 - Verb TensesJemie CortilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Auxiliary Verbs - Definition and ExamplesDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Verbs - Definition and ExamplesDard TongPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses of Verb Pre-DemoDocument31 pagesTenses of Verb Pre-DemoMaridel DiamsayPas encore d'évaluation
- Progressive Form Basic Tenses Perfect Form Perfect Progressive FormDocument10 pagesProgressive Form Basic Tenses Perfect Form Perfect Progressive FormLilibeth Magbanua PasicaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Progressive Tense - Hand-OutDocument2 pagesProgressive Tense - Hand-OutAlthea Kate PagdilaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument4 pagesVerb TensesRishabh GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouisePas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses of The VerbDocument22 pagesTenses of The VerbLouisePas encore d'évaluation
- PERFECT PROGRESSIVE - NewwDocument3 pagesPERFECT PROGRESSIVE - NewwSandrina ZalliantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tense Describes Events That Have Already Happened and Are Completely FinishedDocument7 pagesTense Describes Events That Have Already Happened and Are Completely FinishedShela MaePas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs: State-Of-Being Verbs/ Verbs of BeingDocument4 pagesVerbs: State-Of-Being Verbs/ Verbs of BeingYesha ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 SV Understanding Verb Tense and MoodDocument62 pages6 SV Understanding Verb Tense and MoodkamalshahPas encore d'évaluation
- Conditionals PPT KoDocument60 pagesConditionals PPT KoRicky SoleroPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Verb TensesDocument3 pagesSummary of Verb TensesWan Hazlina A TajudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pertemuan 2 Verbs PDFDocument8 pagesPertemuan 2 Verbs PDFriko cmenoxPas encore d'évaluation
- EnglishDocument31 pagesEnglishJerreca DasasPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument6 pagesVerb TensesnornPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Verb Tenses-3Document4 pagesOverview of Verb Tenses-3Afrim TonuziPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Forms Present Tense: Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument8 pagesSimple Forms Present Tense: Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsJp Karl Gonzales UliganPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb TensesDocument4 pagesVerb TenseshendyahmarPas encore d'évaluation
- English LessonDocument8 pagesEnglish LessonRalf LlenaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Overview of Verb TensesDocument5 pages1 Overview of Verb TensesedithPas encore d'évaluation
- The Tenses IntanDocument25 pagesThe Tenses IntansonnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 78 VerbsDocument42 pages78 VerbsDiandra NovitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment in LinguisticsDocument11 pagesAssignment in LinguisticsAmeurfina MiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Progressive Verb Tense - Definition, Examples of The Continuous Tense - Writing ExplainedDocument31 pagesWhat Is The Progressive Verb Tense - Definition, Examples of The Continuous Tense - Writing ExplainedAroom AffandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Verb Tenses: Academic Achievement CenterDocument2 pagesVerb Tenses: Academic Achievement CenterGerwilmotPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Verb Tenses: CCCCC CCCCC CCC CC C CCCC CC C CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCCCCCC CC CCCCCDocument5 pagesSummary of Verb Tenses: CCCCC CCCCC CCC CC C CCCC CC C CC CCC CC C CCCC CC CCCCCCC CC CCCCCMark Christian BagsicPas encore d'évaluation
- CCS PPT!Document25 pagesCCS PPT!Dhien KinilitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture - (Tenses)Document35 pagesLecture - (Tenses)Waqas HafeezPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsDocument4 pagesSimple Forms Progressive Forms Perfect Forms Perfect Progressive FormsYolanda RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- TenseDocument2 pagesTenseRBT10621 Noorain Maisarah Binti ZainalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pot HG1Document1 pagePot HG1Tko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- POT HG - pdf1Document1 pagePOT HG - pdf1Tko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- All Tenses Form CheatsheetDocument1 pageAll Tenses Form Cheatsheetapi-271296545Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tenses TableDocument5 pagesTenses Tableapi-314670535Pas encore d'évaluation
- Path DefDocument1 pagePath DefTko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercice1 (Contole 1994)Document2 pagesExercice1 (Contole 1994)Tko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Figures SDocument1 pageFigures STko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Le SucreDocument1 pageLe SucreTko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques de Commande Des Machines Electriques - Cours Et Problèmes..Document2 pagesTechniques de Commande Des Machines Electriques - Cours Et Problèmes..Tko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- HttpsDocument1 pageHttpsTko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration Internet de Nexttel Cameroun - Paramètres APN PDFDocument3 pagesConfiguration Internet de Nexttel Cameroun - Paramètres APN PDFTko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- Configuration Internet de Nexttel Cameroun - Paraamètres APNDocument3 pagesConfiguration Internet de Nexttel Cameroun - Paraamètres APNTko ToolPas encore d'évaluation
- LM125 ExocorrectionDocument2 pagesLM125 Exocorrectionفريد محمد حسنPas encore d'évaluation