Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers: Engineering Data
Transféré par
sebaversaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers: Engineering Data
Transféré par
sebaversaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers
achieve the corresponding guaranteed efficiency as published, the boiler manufacturer
will rebate, to the ultimate boiler owner, five thousand dollars ($5,000) for every full
efficiency point (1.0%) that the actual efficiency is below the guaranteed level. The
specified boiler efficiency is based on the following conditions.
1. Fuel specification used to determine boiler efficiency:
• Natural Gas
Carbon,% (wt) = 69.98
Hydrogen,% (wt) = 22.31
Sulfur,% (wt) = 0.0
Heating value, Btu/lb = 21,830
• No. 2 Oil
Carbon,% (wt) = 85.8
Hydrogen,% (wt) = 12.7
Sulfur,% (wt) = 0.2
Heating value, Btu/lb = 19,420
• No. 6 Oil
Carbon,% (wt) = 86.6
Hydrogen,% (wt) = 10.9
Sulfur,% (wt) = 2.09
Heating value, Btu/lb = 18,830
2. Efficiencies are based on ambient air temperature of 80 °F, relative humidity of 30%,
and 15% excess air in the exhaust flue gas.
3. Efficiencies are based on the following radiation and convection losses. Firing rate of
25% - 1.2%, 50% - 0.6%, 75% - 0.4%, and 100% - 0.3%.
ENGINEERING DATA
The following engineering information is provided for CBL Boilers. Additional detail is
available from your local Cleaver-Brooks authorized representative.
Boiler Information
Table A5-12 shows steam volume and disengaging area for CBL boilers.
Table A5-10 lists quantity and outlet size for safety valves supplied on CBL boilers.
Table A5-11 gives recommended steam nozzle sizes on CBL Boilers.
Table A5-13 shows recommended non-return valve sizes for CBL Boilers.
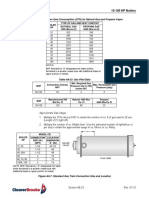
Blowdown Water Requirements
Some local codes require blowdown tanks to be constructed in accordance with
recommendations of the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
The National Board’s recommendations base the size of the blowdown tank on the
removal of at least 4 inches of water from the boiler.
Table A5-14 lists the approximate quantity of water represented by 4 inches of water at
normal operating level for Cleaver-Brooks CBL Boilers.
Section A5-11 Rev. 03-08
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers
Burner/Control Information
Burner Characteristics
Note that altitude correction and burner changes are required for higher altitudes which
may alter dimensions, motor hp and gas pressures. Also 50 Hz applications and low NOx
options should be reviewed by the Cleaver-Brooks authorized representative.
Gas-Fired Burners
Table A5-15 gives gas train connection sizes and gas pressure requirements.
Table A5-16 shows correction factors for gas pressure at elevations over 1000 ft. above
sea level.
For oversized or undersized gas trains or altitude above 1,000 feet, contact your local
Cleaver-Brooks authorized representative.
Fuel Connections - Gas
The local gas company should be consulted for requirements and authorization for
installation and inspection of gas supply piping. Installation of gas supply piping and
venting must be in accordance with all applicable engineering guidelines and regulatory
codes. All connections made to the boiler should be arranged so that all components
remain accessible for inspection, cleaning and maintenance.
A drip leg should be installed in the supply piping before the connection to the gas
pressure regulator. The drip leg should be at least as large as the inlet fitting supplied
with the boiler. Consideration must be given to both volume and pressure requirements
when choosing gas supply piping size. Refer to the boiler dimension diagram provided by
Cleaver-Brooks for the particular installation. Connections to the burner gas train should
be made with a union, so that gas train components or the burner may be easily
disconnected for inspection or service. Upon completion of the gas piping installation, the
system should be checked for gas leakage and tight shutoff of all valves.
Fuel Connections - Oil
Oil-fired burners are equipped with an oil pump, which draws fuel from a storage tank and
supplies pressurized oil to the burner nozzle(s). The burner supply oil pump has a greater
capacity than the burner requires for the maximum firing rate. Fuel not delivered to the
nozzle is returned to the storage tank. A two-pipe (supply and return) oil system is
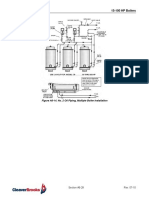
recommended for all installations. Figure A5-5 shows a typical fuel oil supply
arrangement. Oil lines must be sized for the burner and burner supply oil pump
capacities.
The burner supply oil pump suction should not exceed 10" Hg. If a transfer pump is used,
it must have a pumping capacity at least equal to that of the burner pump(s). Supply
pressure to the burner pump should not exceed 3 psig.
A strainer must be installed in the supply piping upstream of the burner supply pump in
order to prevent entry of foreign material into the pump, fuel control valves, or burner
nozzle(s). The strainer must be sized for the burner supply pump capacity. A strainer
mesh of 150 microns (0.005") is recommended.
Install a check valve in the line to prevent draining of the oil suction line when the burner
is not in operation. Location of the check valve varies with the system, but usually it is
located as close as possible to the storage tank.
Installation of a vacuum gauge in the burner supply line between the burner oil pump and
the strainer is recommended. Regular observation and recording of the gauge indication
will assist in determining when the strainer needs servicing.
Upon completion of the oil piping installation, the system should be checked for oil or air
leakage and tight shutoff of all valves.
Section A5-12 Rev. 03-08
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers
Boiler Room Information
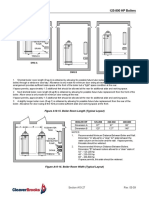
Figure A5-7 shows typical boiler room length requirements.
Figure A5-8 shows typical boiler room width requirements.
Stack Support Capabilities
CBL Boilers can support up to 2000 lbs. without additional support. CBL Boilers can be
reinforced to support up to 3000 lbs.
Boiler Room Combustion Air
When determining boiler room air requirements, the size of the room, air flow, and
velocity of air must be reviewed as follows:
1. Size (area) and location of air supply openings in boiler room.
A. Two (2) permanent air supply openings in the outer walls of the boiler room are
recommended. Locate one (1) at each end of the boiler room, preferably below a
height of 7 feet. This allows air to sweep the length of the boiler.
B. Air supply openings can be louvered for weather protection, but they should not
be covered with fine mesh wire, as this type of covering has poor air flow
qualities and is subject to clogging by dust or dirt.
C. A vent fan in the boiler room is not recommended, as it could create a slight
vacuum under certain conditions and cause variations in the quantity of
combustion air. This can result in unsatisfactory burner performance.
D. Under no condition should the total area of the air supply openings be less than
one (1) square foot.
E. Size the openings by using the formula:
Area (sq-ft) = CFM/FPM
2. Amount of air required (cfm).
A. Combustion Air = Rated bhp x 8 cfm/bhp.
B. Ventilation Air = Maximum bhp x 2 cfm/bhp or a total of 10 cfm/bhp - up to 1000
feet elevation. Add 3 percent more per 1000 feet of added elevation.
3. Acceptable air velocity in Boiler Room (fpm).
A. From floor to (7) foot height - 250 fpm.
B. Above (7) foot height - 500 fpm.
Example: Determine the area of the boiler room air supply openings for (1) 1000 hp boiler
at 800 feet altitude. The air openings are to be 5 feet above floor level.
• Air required: 1000 x 10 = 10000 cfm (from 2B above).
• Air velocity: Up to 7 feet = 250 fpm (from 3 above).
• Area Required: Area = cfm/fpm = 10000/250 = 40 Sq-ft total.
• Area/Opening: 40/2 = 20 sq-ft/opening (2 required).
Stack/Breeching Size Criteria
Notice
Consult local codes, which may supersede these requirements.
The design of the stack and breeching must provide the required draft at each boiler flue
gas outlet. Proper draft is critical to burner performance.
Section A5-13 Rev. 03-08
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers
Although constant pressure at the flue gas outlet of the CBL is not required, it is
necessary to size the stack/breeching to limit flue gas pressure variation. The allowable
pressure range is –0.50" W.C. to +0.50" W.C. The maximum pressure variation at any
firing rate for the boiler is 0.50" W.C.
The low NOx option allowable pressure range is -0.25" W.C. to +0.25" W.C. The
maximum pressure variation at any firing rate for the boiler is 0.25" W.C.
For additional information, please review Section I4, General Engineering Data (Stacks)
and Section F, Stacks. Stack and breeching sizes should always be provided by a
reputable stack supplier who will design the stack and breeching system based on the
above criteria. Your local Cleaver-Brooks authorized representative is capable of
assisting in your evaluation of the stack/breeching design.
Table A5-4. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies Table A5-6. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies
(%) CBL Boilers - 125 psig, Natural Gas, (%) CBL Boilers - 125 psig, No. 6 Oil,
5 sq. ft./BHP, 4-Pass 5 sq. ft./BHP, 4-Pass
FIRING RATE (%) BOILER HP FIRING RATE (%)
BOILER HP
25 50 75 100 25 50 75 100
800 82.0 82.3 82.7 82.5 800 86.5 86.0 86.5 86.8
900 82.3 82.0 82.5 82.5 900 86.6 86.5 86.5 86.9
1000 82.0 82.6 82.7 82.6 1000 86.5 86.6 86.5 86.8
1100 82.3 82.7 82.7 82.7 1100 86.5 86.7 86.6 86.9
1200 82.2 83.0 83.2 83.2 1200 86.5 87.0 87.0 87.0
1300 82.5 82.8 83.0 83.0 1300 86.3 86.6 87.0 87.0
1400 82.3 82.3 82.8 82.8 1400 86.0 86.5 86.8 86.7
1500 82.0 83.0 83.0 83.0 1500 86.0 86.5 86.8 86.6
Table A5-5. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies Table A5-7. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies
(%) CBL Boilers - 125 psig, No. 2 Oil, (%) CBL Boilers - 125 psig, Natural Gas,
5 sq. ft./BHP, 4-Pass 4 sq. ft./BHP, 3-Pass
FIRING RATE (%) FIRING RATE (%)
BOILER HP BOILER HP
25 50 75 100 25 50 75 100
800 85.2 85.9 85.9 86.0 1000 81.4 81.5 81.5 81.5
900 85.3 85.8 86.0 86.0 1100 81.3 81.6 82.0 82.0
1000 85.8 86.0 86.0 86.2 1200 81.2 81.4 82.0 82.0
1100 85.5 85.6 85.6 86.0 1300 81.0 81.3 81.6 82.0
1200 85.8 86.0 86.3 86.5 1400 81.0 81.3 81.4 81.8
1300 85.3 86.0 86.4 86.6 1500 81.0 81.4 81.4 81.9
1400 85.9 86.0 86.4 86.5
1500 86.0 86.6 86.5 86.6
Section A5-14 Rev. 03-08
Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers
Table A5-8. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies Table A5-9. Predicted Fuel-to-Steam Efficiencies
(%) CBL Boilers- 125 psig, No. 2 Oil, 4 sq. (%) CBL Boilers- 125 psig, No. 6 Oil, 4 sq.
ft./BHP, 3-Pass ft./BHP, 3-Pass
FIRING RATE (%) FIRING RATE (%)
BOILER HP BOILER HP
25 50 75 100 25 50 75 100
1000 84.8 85.0 85.0 85.0 1000 86.2 86.2 85.8 85.6
1100 84.7 85.0 85.0 85.0 1100 86.3 86.4 86.1 85.9
1200 85.0 85.2 85.4 85.2 1200 86.2 86.2 85.8 86.0
1300 85.0 85.0 84.8 85.5 1300 86.0 86.4 86.1 85.8
1400 85.0 85.6 84.8 85.5 1400 86.0 86.4 86.0 85.8
1500 85.0 85.5 84.9 85.6 1500 86.0 86.3 86.2 85.9
Table A5-10. CBL Steam Boiler Safety Valve Outlet Size
VALVE
15 PSIG STEAM 150 PSIG STEAM 200 PSIG STEAM 250 PSIG STEAM
SETTING
NO. OF NO. OF NO. OF NO. OF
OUTLET OUTLET OUTLET OUTLET
BOILER HP VALVES VALVES VALVES VALVES
SIZE (“FPT) SIZE (“FPT) SIZE (“FPT) SIZE (“FPT)
REQ'D REQ'D REQ'D REQ'D
1-3 1 - 2 1/2
800 - - 2 2 2 2 1/2
1-4 1-3
1-3 1 - 2 1/2
900 - - 2 2 3 2
1-4 1-3
2-8 1 - 2 1/2
1000 3 2 4 2 3 2
1-6 1-3
2-8 1-3
1100 3 2 4 2 2 3
1-6 1-4
1-3
1200 2 8 2 4 2 - -
1-4
2-3 1 - 2 1/2
1300 3 8 3 3 - -
1-4 2-3
1-3
1400 3 8 3 3 3 - -
2-4
1-3
1500 3 8 3 3 3 - -
2-4
NOTES:
Table A11-8 only applies to 5 Sq Ft/BHP units.
Valve manufacture is Kunkle.
Valve requirements can vary with special pressure settings.
Section A5-15 Rev. 03-08
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chronic Pain GuidelinesDocument56 pagesChronic Pain GuidelinesOporadhBiggan100% (1)
- Packaged steam generators: Custom designs have advantages over standard onesDocument90 pagesPackaged steam generators: Custom designs have advantages over standard onespinenamuPas encore d'évaluation
- Eng & FLS Standards Rev.1 (Dec. 2018)Document72 pagesEng & FLS Standards Rev.1 (Dec. 2018)Nalan BAHCEKAPILIPas encore d'évaluation
- Trends in Packaged Boiler Design PDFDocument10 pagesTrends in Packaged Boiler Design PDFpertspyPas encore d'évaluation
- SADC System ExplainedDocument8 pagesSADC System ExplainedpallavishraddhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens Boiler Control OverviewDocument12 pagesSiemens Boiler Control OverviewAnonymous zMWvcTPas encore d'évaluation
- Fine Tuning A CFBC Boiler PDFDocument12 pagesFine Tuning A CFBC Boiler PDFrikumohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Checkl List For Boiler Specification by K.K.parthibanDocument8 pagesCheckl List For Boiler Specification by K.K.parthibanparthi20065768Pas encore d'évaluation
- Buffer Tank Hydraulic SeparatorDocument4 pagesBuffer Tank Hydraulic SeparatorJohn MorePas encore d'évaluation
- BurnerDocument4 pagesBurnerAhmed Mohamed KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerala BOE-2014 Paper-1 SolutionDocument10 pagesKerala BOE-2014 Paper-1 SolutionAlok DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Aux Power CalculationDocument22 pagesAux Power Calculationssheart_mindPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Instrumentation and ControlDocument54 pagesBoiler Instrumentation and ControlSunny Gupta100% (2)
- Slide Fuel Valves Reduce EmissionsDocument5 pagesSlide Fuel Valves Reduce EmissionsParthiban NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion Optimization Study Improves Boiler PerformanceDocument44 pagesCombustion Optimization Study Improves Boiler Performancekarikalcholan m100% (1)
- Yoga Nidra MethodDocument13 pagesYoga Nidra MethodPrahlad Basnet100% (2)
- Boiler UtilizationDocument24 pagesBoiler UtilizationLarisa Viorica FlorianPas encore d'évaluation
- Install An Automatic Blowdown Control System: BackgroundDocument5 pagesInstall An Automatic Blowdown Control System: BackgroundNaPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler BurnerDocument12 pagesBoiler BurnerSumeet SawantPas encore d'évaluation
- Choudhari Et Al. (2012) - Distilation Optimization by Vapor RecompressionDocument7 pagesChoudhari Et Al. (2012) - Distilation Optimization by Vapor Recompressionvazzoleralex6884Pas encore d'évaluation
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersD'EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler RatingDocument5 pagesBoiler RatingEdy Suprayitno0% (1)
- Byco Refinery Boiler Inspection Report SummaryDocument23 pagesByco Refinery Boiler Inspection Report SummaryZia Abbasi100% (1)
- Coca Cola Primary Activities: 1. Inbound Logistics Include Functions Like Receiving, Warehousing, and Managing InventoryDocument5 pagesCoca Cola Primary Activities: 1. Inbound Logistics Include Functions Like Receiving, Warehousing, and Managing InventoryJaene L.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBEX Elite Boilers 1300-2200HP Engineering DataDocument4 pagesCBEX Elite Boilers 1300-2200HP Engineering DatasebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model ICB 100-800 HP Boilers: Performance DataDocument4 pagesModel ICB 100-800 HP Boilers: Performance DatasebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 4WG 100 - 800 HP Boilers: Fuel Connections - OilDocument4 pagesModel 4WG 100 - 800 HP Boilers: Fuel Connections - OilsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPEC Model CB Steam Jan11Document12 pagesSPEC Model CB Steam Jan11Stanford BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient 15-100 HP Boilers for BuildingsDocument5 pagesEfficient 15-100 HP Boilers for BuildingssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 4WI 100 - 800 HP Boilers: Figure A2-7. No. 2 Oil Piping, Multiple Boiler InstallationDocument4 pagesModel 4WI 100 - 800 HP Boilers: Figure A2-7. No. 2 Oil Piping, Multiple Boiler InstallationsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: 2.05 Efficiency GuaranteeDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: 2.05 Efficiency GuaranteesebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dunkirk PSB Boiler Installation ManualDocument28 pagesDunkirk PSB Boiler Installation ManualaprichPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-19. Breeching ArrangementDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-19. Breeching ArrangementsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- CB-7768 Gen - Boiler Efficiency TablesDocument4 pagesCB-7768 Gen - Boiler Efficiency TablestthennisPas encore d'évaluation
- Series 1: Forced Draft Dual Fuel BurnersDocument4 pagesSeries 1: Forced Draft Dual Fuel Burnersdiogenes torresPas encore d'évaluation
- Model 4WI Boiler Warranty, Tests and StartupDocument4 pagesModel 4WI Boiler Warranty, Tests and StartupsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Models: ELP-110 /199 Btu / HR: Typical Elite Plus Boiler ®Document2 pagesModels: ELP-110 /199 Btu / HR: Typical Elite Plus Boiler ®shreyanshPas encore d'évaluation
- BOC Technical Webinar Series: Boiler Tune-Up and MaintenanceDocument33 pagesBOC Technical Webinar Series: Boiler Tune-Up and MaintenanceAnonymous u0wETydFPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A1 Model Cb-Le Steam Boiler Specifications (125-800 HP, STEAM 15-300 PSIG)Document4 pagesSection A1 Model Cb-Le Steam Boiler Specifications (125-800 HP, STEAM 15-300 PSIG)sebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fig. 8.1: A Shell Boiler With An EconomizerDocument11 pagesFig. 8.1: A Shell Boiler With An EconomizerMuhammad Alam Zaib KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions and Answers For Primary ReformerDocument3 pagesQuestions and Answers For Primary ReformerMaged HegabPas encore d'évaluation
- Hurst Boiler & Welding Co., IncDocument4 pagesHurst Boiler & Welding Co., IncChristian Veliz CamargoPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Efficiency Combustion EfficiencyDocument8 pagesBoiler Efficiency Combustion EfficiencyBelalNorPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Front Feedwater TankDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Front Feedwater TanksebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPEC ModelCBR Steam Mar4Document10 pagesSPEC ModelCBR Steam Mar4Jason PoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Hurst Boiler & Welding Company, Inc.: SERIES 500 STEAM BOILER (100-1500 HP, STEAM 15-300 Psig) Sample SpecificationsDocument5 pagesHurst Boiler & Welding Company, Inc.: SERIES 500 STEAM BOILER (100-1500 HP, STEAM 15-300 Psig) Sample SpecificationsDaniel GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbines and ExpandersDocument8 pagesTurbines and ExpandersMusa KaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Economizers: Colin FrenchDocument6 pagesEconomizers: Colin Frenchsathesh100% (1)
- Series 4vt Steam SpecificationsDocument5 pagesSeries 4vt Steam Specificationsagusti24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Series 500 Water SpecDocument5 pagesSeries 500 Water SpecChristhofer Arroyo ChacónPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Data: Model CBLE 100-800 HP BoilersDocument4 pagesPerformance Data: Model CBLE 100-800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- General: Model ICB 100-800 HP BoilersDocument4 pagesGeneral: Model ICB 100-800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared By: Hemanthkrishnan R Roll No 44 S5Ma NssceDocument22 pagesPrepared By: Hemanthkrishnan R Roll No 44 S5Ma NssceKingPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Burner (Steam Jet)Document4 pagesBoiler Burner (Steam Jet)Win Min0% (1)
- OIL HANDBOOKDocument32 pagesOIL HANDBOOKolhevlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerant Piping: By: Cecil R. Visger, Past International PipingDocument18 pagesRefrigerant Piping: By: Cecil R. Visger, Past International PipingBehnam AshouriPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler efficiency tips for improving heat transferDocument28 pagesBoiler efficiency tips for improving heat transferBaher SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Better Burner SpecificationsDocument2 pagesBetter Burner SpecificationsKARAVOS13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Firetube BoilersDocument2 pagesSteam Firetube BoilersmichtenbPas encore d'évaluation
- Op Eff16122023Document38 pagesOp Eff16122023Sharath BogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SD'EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficient 15-100 HP Boilers for BuildingsDocument5 pagesEfficient 15-100 HP Boilers for BuildingssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers: Table A5-11. CBL Recommended Steam Nozzle SizeDocument5 pagesModel CBL 900-1800 HP Boilers: Table A5-11. CBL Recommended Steam Nozzle SizesebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 900-1800 HP Steam Boilers: Features, Dimensions and Engineering DataDocument5 pages900-1800 HP Steam Boilers: Features, Dimensions and Engineering DatasebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 15-100 HP Boilers Dimensions SpecsDocument5 pages15-100 HP Boilers Dimensions SpecssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-14. No. 2 Oil Piping, Multiple Boiler InstallationDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-14. No. 2 Oil Piping, Multiple Boiler InstallationsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: 1.04 Burner and ControlsDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: 1.04 Burner and ControlssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-19. Breeching ArrangementDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Figure A6-19. Breeching ArrangementsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Features and Benefits: Model CB 15-100 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesFeatures and Benefits: Model CB 15-100 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Sound LevelDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Sound LevelsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Table A6-22. Maximum Gas Consumption (CFH) For Natural Gas and Propane VaporDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Table A6-22. Maximum Gas Consumption (CFH) For Natural Gas and Propane VaporsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Boiler HP View All Dimensions in Inches A B C D EDocument5 pagesModel CB 15-100 HP Boilers: Boiler HP View All Dimensions in Inches A B C D EsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 900-1800 HP Boiler SpecsDocument5 pages900-1800 HP Boiler SpecssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A5: Model CBL 900-1800 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesSection A5: Model CBL 900-1800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Figure A10-10. Typical Gas Piping LayoutDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Figure A10-10. Typical Gas Piping LayoutsebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: 2.05 Efficiency GuaranteeDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: 2.05 Efficiency GuaranteesebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Front Feedwater TankDocument5 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Front Feedwater TanksebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 78Document5 pages78sebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBL 900-1800 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesModel CBL 900-1800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 81Document5 pages81sebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 125-800 HP Model CBR Boilers Technical Specs & Performance DataDocument5 pages125-800 HP Model CBR Boilers Technical Specs & Performance DatasebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 125-800 HP Model CBR Boilers Technical Specs & Performance DataDocument5 pages125-800 HP Model CBR Boilers Technical Specs & Performance DatasebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Figure A10-2. Model CBR Hot Water Boiler Dimensions - Sheet 1 of 2Document6 pagesModel CBR 125-800 HP Boilers: Figure A10-2. Model CBR Hot Water Boiler Dimensions - Sheet 1 of 2sebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- 75Document5 pages75sebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- Model ICB 100-800 HP BoilersDocument4 pagesModel ICB 100-800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- General: Model ICB 100-800 HP BoilersDocument4 pagesGeneral: Model ICB 100-800 HP BoilerssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- High-efficiency boiler specifications for 100-800 HP modelsDocument4 pagesHigh-efficiency boiler specifications for 100-800 HP modelssebaversaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECOSIADocument8 pagesECOSIAaliosk8799Pas encore d'évaluation
- JDP Rainbox Attenuation CratesDocument6 pagesJDP Rainbox Attenuation CratesBerat DalyabrakPas encore d'évaluation
- Gimnazjum Exam Practice GuideDocument74 pagesGimnazjum Exam Practice GuideVaserd MoaslePas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Adhesive Resin Cements Ph-Neutralization, HydrophilicityDocument7 pagesSelf-Adhesive Resin Cements Ph-Neutralization, HydrophilicityCarolina Rodríguez RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG ProjectDocument34 pagesECG Projectsamsai888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aripiprazole medication guideDocument3 pagesAripiprazole medication guidemissayayaya100% (1)
- CH 23 PDFDocument42 pagesCH 23 PDFkrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Corn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisDocument2 pagesCorn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisBonifacius Budi NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparative Study Between Various Models of Eco-Brick and Hollow BlocksDocument9 pagesA Comparative Study Between Various Models of Eco-Brick and Hollow BlocksMykaila Ysa ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Venkateshwara Institute of MedicalDocument10 pagesVenkateshwara Institute of Medicalbolhari070Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryDocument5 pages2016 Ruptured Pseudoaneurysm of The Middle Meningeal ArteryJulio Cesar Velasco CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Estimation of SlaughterhouseDocument25 pagesCost Estimation of Slaughterhousemohamed faahiyePas encore d'évaluation
- Home & Garden 2015Document32 pagesHome & Garden 2015The Standard NewspaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Blaylock Face Masks Pose Serious Risks To The HealthyDocument8 pagesBlaylock Face Masks Pose Serious Risks To The HealthyDonnaveo ShermanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Atelectasis Prevention & TreatmentDocument9 pagesAcute Atelectasis Prevention & TreatmentmetabolismeproteinPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Bulletin - Menopause Balance Complex Cooling LotionDocument2 pagesProduct Bulletin - Menopause Balance Complex Cooling Lotionshaklee480Pas encore d'évaluation
- Year 8 Drama ScriptDocument8 pagesYear 8 Drama ScriptTISMSecondaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Section III - Topic 3Document7 pagesSection III - Topic 3KARINE HOVSEPYANPas encore d'évaluation
- 016-5032-002-C - SmarTrax - Case IH STX-Steiger-Quadtrac (AccuGuide-Ready) and New Holland TJ-T90X0-T9XXX (IntelliSteer-Ready) - Installation ManualDocument26 pages016-5032-002-C - SmarTrax - Case IH STX-Steiger-Quadtrac (AccuGuide-Ready) and New Holland TJ-T90X0-T9XXX (IntelliSteer-Ready) - Installation ManualAndreyPas encore d'évaluation
- PRC 2017 Annual Report ENDocument88 pagesPRC 2017 Annual Report ENmuhammad suryadiPas encore d'évaluation
- FAQ: Product RegistrationDocument5 pagesFAQ: Product RegistrationCalvin WangPas encore d'évaluation
- DaloDocument2 pagesDalojosua tuisawauPas encore d'évaluation
- Kluge 2004 MetabolaDocument42 pagesKluge 2004 MetabolaBlah BlahPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex C Olp On The RoadDocument7 pagesAnnex C Olp On The RoadCabanglasanfs OLPPas encore d'évaluation
- Arthropods: A Guide to the Diverse PhylumDocument10 pagesArthropods: A Guide to the Diverse Phylumpkkalai112Pas encore d'évaluation
- Barangay Ordinance Vaw 2018Document7 pagesBarangay Ordinance Vaw 2018barangay artacho1964 bautista100% (3)