Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Institutional Framework For International Trade
Transféré par
Megha SharmaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction To Institutional Framework For International Trade
Transféré par
Megha SharmaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction to Institutional Framework for International Trade:
India has a comprehensive institutional set up to promote international trade. Exporting firms
need to understand and appreciate the institutions involved and the functions carried out by
them. The Department of Commerce is the prime agency of the country to promote
international trade.
It is supported by a massive institutional set up (Exhibit 4.5) at the union and state government
levels, carrying out a range of trade facilitation activities.
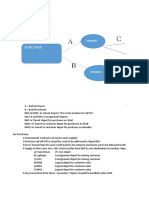
Institutional Framework –
A. Tier 1 Department of Commerce:
The Department of Commerce is the primary governmental agency responsible for developing and
directing foreign trade policy and programmes, including commercial relations with other countries,
state trading, various trade promotional measures and development, and regulation of certain export-
oriented industries.
The principal functional divisions of the Department of Commerce engaged in export promotion
activities are discussed as follows.
1. The Economic Division is engaged in
Export planning
formulating export strategies
Periodic appraisal
Review of policies
The Economic Division also maintains coordination with and control over other divisions and
various organizations set up by the Ministry of Commerce to facilitate export growth.
Besides, the Economic Division monitors work relating to technical assistance, management
services for exports, and overseas investment by Indian entrepreneurs.
2. The Trade Policy Division
keeps track of development in international organizations, such as WTO, UNCTAD,
Economic Commission of Europe, Africa, Latin America, and Asia and Far East
(ESCAP).
The Trade Policy Division is also responsible for India’s relationship with regional
trading agreements, such as EU, NAFTA, SAFTA, Commonwealth, etc.
It also looks after GSP and non-tariff barriers.
3. The Foreign Trade Territorial Division:
looks after the development of tirade with different countries and regions of the
world
It also deals with state trading and barter trade, organization of trade fairs and
exhibitions, commercial publicity abroad, etc
It maintains contact with trade mission abroad and carries out related administrative
work
4. The Export Product Division :
looks after problems connected with production, generation of surplus, and
development of products for exports. However, for products wherein the
administrative responsibility remains with concerned ministries, the Export Product
Division keeps in close touch with them to ensure that the production is sufficient to
realize the full export potential besides ensuring the home consumption.
The division is also responsible for the working of export organizations and
corporations, which deal with commodities and products under their jurisdiction.
5. The Exports Industries Division:
Responsible for development and regulation of rubber, tobacco, and cardamom.
It is also responsible for handling export promotion activities relating to textiles,
woolens, handlooms, readymade garments, silk, and cellulosic fibres, jute and jute
products, handicrafts, and coir and coir products.
6. The Export Services Division
1. Deals with the problems of export assistance, such as export credit, export house,
market development assistance (MDA), transport subsidies, free trade zones, dry
ports, quality control and pre-shipment inspection, assistance to import capital
goods, etc.
B. Tier 2 -Subordinate offices:
In addition to these divisions, attached and subordinate offices are also involved in the
promotion of foreign trade.
1. Directorate General of Foreign Trade: the directorate is responsible for execution of export-
import policy announced by the Government of India. It is headed by Director General of
Foreign Trade (DGFT). The directorate also looks after the work relating to issuing of licenses
and monitoring of export obligations.
2. Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics:
The Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCI&S) was set up
in 1962 and is headquartered at Kolkata. It is responsible for collection, compilation, and
dissemination of trade statistics and commercial information. The DGCI&S also brings
out a number of publications, mainly on inland and coastal trade statistics, revenue
statistics, shipping and air cargo statistics, etc.
its main publications, such as India Trade Journal (weekly) and Foreign Trade Statistics of
India (monthly) provide detailed information on export trade statistics. The DGCI&S uses
mainly the Daily Trade Returns (DTRs), an authentic source, for compiling and
generating export-import statistics.
3. Directorate General of Anti-Dumping and Allied Duties:
constituted in April 1998, the Directorate General of Anti-Dumping (DGAD) is
responsible for carrying out anti-dumping investigations and to recommend
wherever required, the amount of anti-dumping/countervailing duty under the
Customs Tariff Act, on identified articles which would be adequate to remove
injury to the domestic industry.
C. Tier 3 Institutional Framework – Advisory Bodies:
Advisory bodies provide an effective mechanism for continued interaction with trade and
industry and increased coordination among various departments and ministries concerned with
export promotion. The Government of India has set up the following advisory bodies for
promoting international trade.
1. Board of Trade:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleDocument3 pagesCAT G3500 Gas Engine Maintenance ScheduleQaiser Iqbal67% (6)
- Tanker Operators ReviewDocument9 pagesTanker Operators ReviewjoshiyoursPas encore d'évaluation
- RYA CompetentDocument221 pagesRYA Competentsimion stefan100% (7)
- Insurance Awareness PDF Capsule 2017 by AffairscloudDocument56 pagesInsurance Awareness PDF Capsule 2017 by AffairscloudMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecommerce On India MartDocument26 pagesEcommerce On India Martamit_5599Pas encore d'évaluation
- Baby Mait PDFDocument2 pagesBaby Mait PDFChris LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Out Going LettersDocument461 pagesOut Going LettersHemn Rafiq TofiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature ReviewDocument25 pagesLiterature ReviewMegha Sharma100% (1)
- Dicks Sporting GoodsDocument6 pagesDicks Sporting GoodsAnonymous 57oCRhtPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report On Supply Chain ManagemenDocument26 pagesProject Report On Supply Chain ManagemenVyankatesh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Bangladesh CAAB Personal Licensing HandbookDocument278 pagesBangladesh CAAB Personal Licensing Handbooks ramanPas encore d'évaluation
- GST VS VatDocument62 pagesGST VS VatMohit AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Import and Export Procedures at Atlas ShippingDocument35 pagesImport and Export Procedures at Atlas ShippingsumitPas encore d'évaluation
- Produce Mango Jelly with NSIC's Mango Processing Project ProfileDocument3 pagesProduce Mango Jelly with NSIC's Mango Processing Project ProfileAnonymous EAineTizPas encore d'évaluation
- Institutional Set Up For Export Promotion in IndiaDocument7 pagesInstitutional Set Up For Export Promotion in IndiaSammir MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project ReportDocument45 pagesA Project ReportShivani ParetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advertising Effectiveness of TATA MotorsDocument72 pagesAdvertising Effectiveness of TATA MotorsAmit0% (1)
- Itc LTD.: Minor Project Report (Pg34) ONDocument28 pagesItc LTD.: Minor Project Report (Pg34) ONBhavya BhartiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Accounting in National DevelopmentDocument14 pagesThe Role of Accounting in National DevelopmentPushpa BaruaPas encore d'évaluation
- CAse Study - CSEDocument2 pagesCAse Study - CSETrupti DeorePas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Mutual FundsDocument72 pagesProject On Mutual FundsHarshitha Harshitha S TumkurPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship Report MAHADDocument13 pagesInternship Report MAHADMahad aslam QureshiPas encore d'évaluation
- MITCODocument13 pagesMITCOSwati Milind RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- PestelDocument12 pagesPestelsamy7541100% (2)
- First Flight LogisticsDocument7 pagesFirst Flight Logisticsmahato28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire On Export Procedure and DocumentationDocument18 pagesQuestionnaire On Export Procedure and Documentationuma100% (1)
- CHEMEXIL - Chemical Exports From India (Report)Document37 pagesCHEMEXIL - Chemical Exports From India (Report)Mayank GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- ITC Mission, Vision, GoalsDocument3 pagesITC Mission, Vision, GoalsANJALI SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Digital Marketing Strategy Definition - Fundamentals of Digital Marketing, 2 - e - Dev TutorialsDocument54 pagesChapter 5 Digital Marketing Strategy Definition - Fundamentals of Digital Marketing, 2 - e - Dev TutorialsViruchika PahujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Car Industry ProposalDocument6 pagesAutomobile Car Industry Proposalsavaliyamahesh100% (1)
- VMOGSWS Strategies Report on ITC LtdDocument14 pagesVMOGSWS Strategies Report on ITC Ltdsamarth agarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail Communication MixDocument42 pagesRetail Communication Mixhandore_sachinPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Volkswagen Entering in The Indian MarketDocument5 pagesProject On Volkswagen Entering in The Indian Marketशुभांगी सक्सेनाPas encore d'évaluation
- Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Iribus - Iveco of ItalyDocument26 pagesMarket Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Iribus - Iveco of ItalySayeed IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Neva ProjectDocument51 pagesNeva ProjectRaj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Export PDFDocument15 pagesExport PDFSupriya KorePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Project of FTDocument26 pagesFinal Project of FTSharayu BavkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib-Class Assignment-Mitty CoolDocument10 pagesIb-Class Assignment-Mitty CoolPoonam_Khaitan_6836Pas encore d'évaluation
- Executive SummaryDocument2 pagesExecutive SummaryAnzar Imran67% (3)
- A Lifecycle Framework of Green Iot-Based Agriculture and Its Finance, Operation, and Management IssuesDocument32 pagesA Lifecycle Framework of Green Iot-Based Agriculture and Its Finance, Operation, and Management IssuesRavi GowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bata Final AssignmentDocument17 pagesBata Final Assignmenttanveerahmed05324420% (1)
- A Study On Material Control TechniqusDocument55 pagesA Study On Material Control Techniquskathirvelmba100% (1)
- Import - Export Policy of IndiaDocument13 pagesImport - Export Policy of Indiaravi pratapPas encore d'évaluation
- PR GUIDELINE 2020-21 - Minor Project 1Document20 pagesPR GUIDELINE 2020-21 - Minor Project 1mihirchopraPas encore d'évaluation
- HUL ProjectDocument47 pagesHUL Projectpothupalepu prabhuPas encore d'évaluation
- My Food Roller Flour Factory PVT - LTDDocument54 pagesMy Food Roller Flour Factory PVT - LTDSandeep Nair67% (3)
- AshrulDocument58 pagesAshrulNilabjo Kanti Paul100% (2)
- Bata Pakistan CEO Considers ChangesDocument10 pagesBata Pakistan CEO Considers ChangesJoel WaghchourePas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On ITC Limited With Reference To Its Stakeholders & CSR ActivitiesDocument26 pagesA Study On ITC Limited With Reference To Its Stakeholders & CSR ActivitiesGovind N VPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On The Influence of Packaging in Brand Selection in Toothpaste IndustryDocument12 pagesA Study On The Influence of Packaging in Brand Selection in Toothpaste IndustryAshish Garg100% (1)
- A Synopsis On Inventory Management AT: Heritage Foods LimitedDocument9 pagesA Synopsis On Inventory Management AT: Heritage Foods LimitedkiziePas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Global Market StrategiesDocument6 pagesDesigning Global Market StrategiesGeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Thomson Press, RavinderDocument73 pagesThomson Press, Ravinderrasi1719Pas encore d'évaluation
- Significant Accounting Policies TVS MotorsDocument12 pagesSignificant Accounting Policies TVS MotorsArjun Singh Omkar100% (1)
- Cma Tata MotorsDocument25 pagesCma Tata MotorsArchana MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- IB Notes - ConsolidatedDocument85 pagesIB Notes - Consolidatedraksha vasanthPas encore d'évaluation
- ITC equity research report summarizing diversified business segments, valuation, and future prospectsDocument2 pagesITC equity research report summarizing diversified business segments, valuation, and future prospectsISHPREET KAUR50% (2)
- Investment Opportunities in Automotive Sector in RAKDocument77 pagesInvestment Opportunities in Automotive Sector in RAKyudhie_7Pas encore d'évaluation
- GDP ProjectDocument11 pagesGDP ProjectNikhil Goyal 141Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 India Foreign Trade FeautresDocument12 pages1 India Foreign Trade FeautresvanshiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Government Influence On Trade and InvestmentDocument11 pagesGovernment Influence On Trade and InvestmentKrunal Maniyar100% (2)
- Life History of Sunil MittalDocument6 pagesLife History of Sunil MittalgunnaprasannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tata Motors Suv Segment ProjectDocument57 pagesTata Motors Suv Segment ProjectmonikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Micromax International Marketing ResearchDocument62 pagesMicromax International Marketing Researchgayatri nigade100% (1)
- Project On Financial Analysis Between Tata Motors and Ashok LeylanDocument23 pagesProject On Financial Analysis Between Tata Motors and Ashok LeylannafisurPas encore d'évaluation
- Precision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryD'EverandPrecision Turned Products World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Products A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionD'EverandGreen Products A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Tracking The Top Trends: 1.CSR Trend: Increased TransparencyDocument2 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility: Tracking The Top Trends: 1.CSR Trend: Increased TransparencyMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Method in MNGGDocument53 pagesResearch Method in MNGGShanthi HariharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Workers Rights in IndiaDocument6 pagesWorkers Rights in IndiaMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSR OverviewDocument29 pagesCSR OverviewMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bba Iii SemDocument1 pageBba Iii SemMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minutes of MeetingDocument1 pageMinutes of MeetingMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Great DepressionDocument77 pagesGreat Depressionrick cel mercialesPas encore d'évaluation
- Import FinanceDocument3 pagesImport FinanceMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Construct and VariableDocument8 pagesConcept Construct and VariableMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of Quality Control and PreDocument2 pagesMethods of Quality Control and PreMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fdi and India PerspectiveDocument32 pagesFdi and India PerspectiveMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Method in MNGGDocument20 pagesResearch Method in MNGGMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulative and Advisory Bodies 2Document38 pagesFormulative and Advisory Bodies 2Megha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Trade Policy Evolution: Pre-Independence to Post-LiberalisationDocument4 pagesIndia's Trade Policy Evolution: Pre-Independence to Post-LiberalisationMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Date Time Tuesday, 18 October 2016 9:30 11:30 2:00 3:00 4:00 5:30 6:30 7:30 8:00 10:00 11:00Document75 pagesDate Time Tuesday, 18 October 2016 9:30 11:30 2:00 3:00 4:00 5:30 6:30 7:30 8:00 10:00 11:00Megha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Export Import Trader Regulatory FrameworkDocument7 pagesExport Import Trader Regulatory FrameworkSammir MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Green MarketingDocument23 pagesGreen MarketingMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Logistics EDocument53 pages02 Logistics EMesh Bubbah MashPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Logistics EDocument53 pages02 Logistics EMesh Bubbah MashPas encore d'évaluation
- BPSM - Business policy and strategic management introductionDocument35 pagesBPSM - Business policy and strategic management introductionMegha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cranfield Information Use ReviewDocument53 pagesCranfield Information Use ReviewGuna SekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Special Member PDFDocument20 pagesApplication Special Member PDFGelbert SilotPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis in Fluid MachineriesDocument71 pagesThesis in Fluid MachineriesSiN XPas encore d'évaluation
- Tiket MartinDocument3 pagesTiket MartinMartin Yulia SaputriPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Classifieds in India, Classified Ads in India, Online Classified Advertising - OLX DOT COMDocument3 pagesFree Classifieds in India, Classified Ads in India, Online Classified Advertising - OLX DOT COMVenkatrao GarigipatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Marine Trader Double Cabin Cruiser Under $50KDocument8 pagesMarine Trader Double Cabin Cruiser Under $50KGert SteynPas encore d'évaluation
- Employer Liability for Employee's NegligenceDocument2 pagesEmployer Liability for Employee's NegligenceRomz NunePas encore d'évaluation
- Tata NanoDocument13 pagesTata NanoShraddha DadhichPas encore d'évaluation
- Travelling Role Plays and DialoguesDocument4 pagesTravelling Role Plays and DialoguesRodica Ioana BândilăPas encore d'évaluation
- Batik Air Eticket 10 May (Ecuvqw) - Mr. Ardani 2paxDocument4 pagesBatik Air Eticket 10 May (Ecuvqw) - Mr. Ardani 2paxSatria FajriPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Read A Tire SidewallDocument3 pagesHow To Read A Tire SidewallClutchSatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Karnataka DL application statusDocument5 pagesKarnataka DL application statusOkgfrPas encore d'évaluation
- Gencon 94Document4 pagesGencon 94Víctor Andrés AlarcónPas encore d'évaluation
- Mee362 Two-And-three-wheeler TH 1.00 Ac21Document2 pagesMee362 Two-And-three-wheeler TH 1.00 Ac21yashvantPas encore d'évaluation
- FAA Form 8500-7Document4 pagesFAA Form 8500-7Taha ArousPas encore d'évaluation
- Quotation of Backhoe Loader (2022.04.25)Document8 pagesQuotation of Backhoe Loader (2022.04.25)Nicolau TechPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Cycle Assessment of Packaging Materials For Milk and Dairy ProductsDocument12 pagesLife Cycle Assessment of Packaging Materials For Milk and Dairy Productsmanisha maniPas encore d'évaluation
- Highway Link Design - 2002Document70 pagesHighway Link Design - 2002Welly Pradipta bin MaryulisPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 NSXDocument491 pages2018 NSXZoltan FabianPas encore d'évaluation
- ENI CONGO - Bambini Spa Bridging DocumentDocument45 pagesENI CONGO - Bambini Spa Bridging DocumentBitsindouPas encore d'évaluation
- Botswana Jde MappingDocument7 pagesBotswana Jde MappingKiran KagitapuPas encore d'évaluation
- ADMS Assignment Spring 2011Document8 pagesADMS Assignment Spring 2011muneermuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Standfast 43Document4 pagesStandfast 43Elison Farias OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Christopher Columbus Letter To The King and Queen of SpainDocument3 pagesChristopher Columbus Letter To The King and Queen of Spainapi-252149221Pas encore d'évaluation