Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5.venturi & Orifice - Set 2
Transféré par
ahm531Titre original
Copyright
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
5.venturi & Orifice - Set 2
Transféré par
ahm531Droits d'auteur :
A H M 531 Venturi & Orifice By: Mu'men Al-Otoom
1 ﻣﺆﻣﻦ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﻖ اﺣﻤﺪ اﻟﻌﺘﻮم ATOOMUS
The Civil Engineering Center 1 Visit www.AHM531.com for more lecture notes and E-books!
A H M 531 Venturi & Orifice By: Mu'men Al-Otoom
Objective:
Venturi:
To study the principles of Venturi meter and to determine its coefficient Cd
by comparing the measure flow rate with the ideal flow rate.
Orifice:
1- To determine the coefficient Cd of an orifice meter by comparing the
measured flow rate with the ideal flow rate.
2- To calibrate the rotameter.
Theory:
Venturi:
The Venturi meter is a device which is used for measuring the discharge of a
long pipe. The fluid flowing in the pipe is lead through a contraction section to a
throat, which has a smaller cross-sectional area than the pipe, so that the velocity of
the fluid through the throat is higher than that in the pipe. This increase of velocity
is accompanied by a fall in pressure, the magnitude of which depends on the rate of
flow, so that by measuring the pressure drop, the discharge may be calculated from
the equation:
Qtheoretical = ( A1A2 ) x √(2g(h1 – h2))
√(A12 – A22 )
= K ( h1 – h2 )( 1 / 2 )
where A1, A2 are the cross sectional area of the entry and the throat section, and h1-
h2 is the differential manometer reading across the entry and the throat of the
meter. In practice, there is some loss of the energy between sections 1 and 2, as a
result, measured values of Q usually fall a little short of coefficient Cd which is
introduced as follows:
Qac t= Cd.Qtheo
This coefficient may be established by experiment.
Orifice:
The Orifice and rota meter are devices for measuring the flow rate along a
pipe. An Orifice in a pipe line may be used as a meter in the manner as the Venturi
meter. The Orifice meter consist of a concentric square-edged circular hole in thin
plate which is clamped between the flanges of the pipe. The arrangement is cheap
compared to the cost of a Venturi meter, but there are substantial energy losses.
The theoretical floe rate can be calculated from the equation:
2 ﻣﺆﻣﻦ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﻖ اﺣﻤﺪ اﻟﻌﺘﻮم ATOOMUS
The Civil Engineering Center 2 Visit www.AHM531.com for more lecture notes and E-books!
A H M 531 Venturi & Orifice By: Mu'men Al-Otoom
Qtheoritical = ( A1A2 ) x √(2g(h6 – h7 ))
√(A62 – A72 )
= K ( h6 – h7 )( 1 / 2 )
But the actual flow rate may be as little as tow-thrids ,of this value .A coefficient of
discharge Cd must be introduced in the same way as for the venturi meter , the
actual flow rate through as orifice meter is :
Qac t= Cd.Qtheo
Where : A6 & A7 are the cross sectional area of the pipe & orifice respectively & (h6
– h7 ) is the differantial manometer reading across the up & down stream of the
orifice & the coefficient Cd may simplest device for measuring the flow in a pipe line
.It consist of a vertical glass tube that is slightly tapered , in which the metering float
is suspended by the upward motion of the fluid around it .
Directional notches cut in the float keep it rotating & thus free of wall of wall
friction .
The rate of flow Q determine the equilibrium height of the float , the tube is
graduated to read the flow directly .
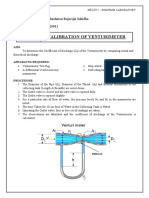
Apparatus : ( For both venturi & orifice )
At a no. of points along the length of the convergent divergent passage of venturi ,
piezometer tubes are drilled into the wall & connection are from each of there to
vertical manometer tubes .
The manometer tubes are connected at their top ends to a common reservoir in
which the amount of air may be controlled by a small air value at one end .the whole
assembly of venturi meter ,manometer tube , scale & reservoir is supported on a
base mounted on screwed feet which may be adjusted to level the equipment .
3 ﻣﺆﻣﻦ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﻖ اﺣﻤﺪ اﻟﻌﺘﻮم ATOOMUS
The Civil Engineering Center 3 Visit www.AHM531.com for more lecture notes and E-books!
A H M 531 Venturi & Orifice By: Mu'men Al-Otoom
CALCULATION :
Resultant of the venturi meter :
A1 = 7.91 x 10-4 m2
A2 = 1.76715 x 10 -4 m2
Rotameter Vol. Time Qactual h1 h2 h3 Qtheoritical Cd Re
(L/min.) ( L (sec.) x10-3 mm mm mm x 10-3
) m3/sec. m3/sec
5 5 80 0.0625 175 160 167 0.0931994 0.670605176 5052.669022
10 5 30.67 0.163026 212 155 185 0.181679 0.897329906 13179.46272
15 5 25.52 0.195925 256 142 211 0.256933 0.762552883 15839.10685
20 5 16.40 0.304878 305 122 244 0.325532 0.936553088 24647.16202
22 5 13.52 0.369822 335 100 264 0.368894 1.002515628 29897.41061
V
0.3536768
0.9225363
1.1087061
1.7252525
2.0927595
Sample of calculation :
For the fires reading :
Qactual = ( Vol. / Time ) = 0.0625 x 10 -3 m3/sec.
Qtheoretical = ( A1A2 ) x √(2g(h1 – h2)) = 0.0932 x 10 -3
√(A12 – A22 )
Cd = ( Qactual / Qtheoritical ) = 0.67061
V = (Qactual / A2 ) = (0.0625 x 10 -3 / 1.76715 x 10 -4 ) = 0.3537 m / sec.
Re = ( ρ x V x D2 ) / ( μ ) = ( 1000 x x0.015)/ ( 1.05 x 10-3 ) = 5052.669
4 ﻣﺆﻣﻦ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﻖ اﺣﻤﺪ اﻟﻌﺘﻮم ATOOMUS
The Civil Engineering Center 4 Visit www.AHM531.com for more lecture notes and E-books!
A H M 531 Venturi & Orifice By: Mu'men Al-Otoom
Resultant of the orifice meter :
Rotameter Vol. Time Qactual h6 h7 h8 Qtheoritical Cd Re
(L/min.) (L) (sec.) x10-3 mm mm mm m3/sec
m3/sec.
5 5 80 0.0625 99 93 95 0.000117 0.532588469 3791.325
10 5 30.67 0.163026 114 86 96 0.000254 0.643080328 9889.354
15 5 25.52 0.195925 135 75 93 0.000371 0.527960702 11885.05
20 5 16.40 0.304878 160 68 96 0.00046 0.663467327 18494.27
22 5 13.52 0.369822 179 61 97 0.00052 0.710622749 22433.85
V
0.199045
0.519191
0.623965
0.970949
1.177777
Sample of calculation :
For the first reading :
Qactual = ( Vol. / Time ) = 0.0625 x 10 -3 m3/sec.
Qtheoritical = ( A1A2 ) x √(2g(h6 – h7 )) = 0.000117 m3/sec.
√(A62 – A72 )
Cd = ( Qactual /Qtheoritical ) = 0.532588469
V = (Qactual / A7 ) = (0.0625 x 10 -3 /3.14 x 10-4 ) = 0.199 m / sec.
Re = ( ρ x V x D7 ) / ( μ ) = ( 1000 x 0.199 x 0.02 )/ ( 1.05 x 10-3 ) = 3790.48
☺Plot Q vs. ( h1 – h2 )( 1 / 2 )
then find K-value . ( Y-intercept point )
☺Plot Q vs. Cd .
Discussion & Conclusion :
We can see the large difference between the Cd value = 0.9 & Cd calculated .
And we can see the h1 > h3 > h2 in the venturi ……
And we can see the h6 > h8 > h7 in the orifice ……
5 ﻣﺆﻣﻦ ﺗﻮﻓﻴﻖ اﺣﻤﺪ اﻟﻌﺘﻮم ATOOMUS
The Civil Engineering Center 5 Visit www.AHM531.com for more lecture notes and E-books!
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Experiment 3 Flow Over WeirsDocument20 pagesExperiment 3 Flow Over Weirsfadhilahmad100% (3)
- Ralph L. Webb, Nae-Hyun Kim - Principles of Enhanced Heat Transfer-CRC Press (2005)Document816 pagesRalph L. Webb, Nae-Hyun Kim - Principles of Enhanced Heat Transfer-CRC Press (2005)arif aktaş100% (1)
- Calibration of Venturi MeterDocument9 pagesCalibration of Venturi Meterseminarproject40% (5)
- Dometic Manual Refrigerator Diagnostic Service ManualDocument52 pagesDometic Manual Refrigerator Diagnostic Service ManualDan Pound100% (5)
- Calibration of VenturimeterDocument5 pagesCalibration of VenturimeterRahul KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrology and Hydraulics PDFDocument193 pagesHydrology and Hydraulics PDFGeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC Project Report 2.0Document16 pagesHVAC Project Report 2.0Màñëësh RèddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws Practice Test - Ans. KeyDocument4 pagesGas Laws Practice Test - Ans. Keycabbiemartinez100% (1)
- Water DesalinationDocument142 pagesWater DesalinationKhaleel Jaberov100% (1)
- Kronig Penny Model: Engineering Physics by Dr. Amita Maurya, Peoples University, Bhopal. Unit 5Document7 pagesKronig Penny Model: Engineering Physics by Dr. Amita Maurya, Peoples University, Bhopal. Unit 5Wulandari PrimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document31 pagesChapter 6Camille LardizabalPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)Document10 pagesFlowmeter Apparatus (Venturi, Orifice, Rotameter)meghaparinPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturimeter Lab Submitfinal (1) PDFDocument6 pagesVenturimeter Lab Submitfinal (1) PDFchinmay dasPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Document6 pagesCalibration of Venturimeter: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Amisha SharonPas encore d'évaluation
- Universiti Teknologi Malaysia: Title of ExperimentDocument20 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Malaysia: Title of ExperimentKhairil IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document31 pagesChapter 6Camille LardizabalPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.turbulent Pipe Flow - Set 2Document5 pages7.turbulent Pipe Flow - Set 2ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Report 2 Venturimeter IDocument9 pagesLaboratory Report 2 Venturimeter IReyven ReconPas encore d'évaluation
- VENTURIMETERDocument10 pagesVENTURIMETERKrishan PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- (1st Revise) Experiment-1-Study-of-flow-through-an-orifice-meterDocument6 pages(1st Revise) Experiment-1-Study-of-flow-through-an-orifice-meterFozlerabbi AnandoPas encore d'évaluation
- FM (Practical) PDFDocument44 pagesFM (Practical) PDFPrathmesh BakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Over A Rectangular and Vee NotchesDocument7 pagesFlow Over A Rectangular and Vee NotchesfarahanisiliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice Plate Long ReportDocument16 pagesOrifice Plate Long ReportLuqman HakimPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument5 pages1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterRaghavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Over WeirsDocument12 pagesFlow Over WeirsItemogeng Bernatt Babe100% (1)
- Paul Gabriel Report No 4Document7 pagesPaul Gabriel Report No 4gelledPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturimeter 28Document10 pagesVenturimeter 28Agyeman EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Coefficient of Discharge Test.Document9 pagesCoefficient of Discharge Test.AhmadGhanemPas encore d'évaluation
- Title: Orifice and Free Jet FlowDocument5 pagesTitle: Orifice and Free Jet Flowamean_anuar100% (1)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Fluid Machinery Lab (MEPC 319)Document5 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Fluid Machinery Lab (MEPC 319)Brijesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Urban Drainage System: HydrologyDocument15 pagesUrban Drainage System: HydrologyAmira HachemPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Academy of Engineering AlandiDocument5 pagesMIT Academy of Engineering AlandiManish UikePas encore d'évaluation
- Orifice and MouthpieceDocument8 pagesOrifice and MouthpieceAdithya MathivananPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 5: Flow Measurement Using Venturi Meter (Flow Through A Venturi Meter)Document6 pagesExperiment 5: Flow Measurement Using Venturi Meter (Flow Through A Venturi Meter)Cece SesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - OrificeDocument14 pagesLab - OrificeSzelee Kuek100% (1)
- American University of Madaba: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics LabDocument7 pagesAmerican University of Madaba: Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics LabEng-Mohammad Nabel AlqamPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Measuring Device (ME-310P) Lab Report: Aim of The ExperimentDocument3 pagesFlow Measuring Device (ME-310P) Lab Report: Aim of The Experimentb21270Pas encore d'évaluation
- Determination Coefficient of Velocity From Jet TrjectoryDocument13 pagesDetermination Coefficient of Velocity From Jet TrjectoryMohd Syafiq Akmal81% (31)
- Venturi ReportDocument8 pagesVenturi Reportstephen kangerePas encore d'évaluation
- CABINTOYDocument6 pagesCABINTOYMatt Kristopher DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceb 601 Lab 6Document7 pagesCeb 601 Lab 6divikesh kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- To Determine Coefficient of DischargeDocument7 pagesTo Determine Coefficient of DischargeUmair NawazPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturi MeterDocument4 pagesVenturi Meterprince.patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1: Flow Over A NotchDocument15 pagesExperiment 1: Flow Over A NotchLai YenPas encore d'évaluation
- Dip - Orifices and Mouth PiecesDocument19 pagesDip - Orifices and Mouth PiecesDan KiswiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce8381 FMDocument65 pagesCe8381 FMAyyanrajPas encore d'évaluation
- Title: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter ApparatusDocument4 pagesTitle: Estimation The Volume Flow Rate Using Venturi-Meter Apparatuslya AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3: Determination of The Coefficient of Discharge With Outflow Under Constant Head ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment 3: Determination of The Coefficient of Discharge With Outflow Under Constant Head ObjectiveUsman AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No 3 HM LabDocument5 pagesExperiment No 3 HM Labprajwalwanjari5524Pas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessDocument51 pagesOptimization and Design of Dehydration Unit and NGL ProcessHoracio RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermofluids LabDocument14 pagesThermofluids Labحسين عمريPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ManualDocument46 pagesLab ManualAizaz HabibPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Over Wiers: Water Chanel Vernier HookDocument4 pagesFlow Over Wiers: Water Chanel Vernier HookEsra BelhajPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice Meterf20221047Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 5Document9 pagesExperiment 5Dr.AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Over WeirsDocument22 pagesFlow Over WeirsNurfayyadhahtul Syafawani100% (1)
- Venturimeter ExptDocument9 pagesVenturimeter Exptatif irshadPas encore d'évaluation
- Eyad All ReportsDocument25 pagesEyad All ReportsHazemPas encore d'évaluation
- Venturimeter ExpDocument12 pagesVenturimeter ExpAmoluck BhatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge CoefficientDocument11 pagesDischarge Coefficientsisai12u2420% (2)
- Friction of Pipe 2Document5 pagesFriction of Pipe 2Ranu GamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mech Orifice 3Document9 pagesFluid Mech Orifice 3TatendaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDocument15 pagesFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsAngelica Joyce BenitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume ID'EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrometer - Data SheetDocument5 pagesHydrometer - Data Sheetahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shrinkage Limit Test - Data SheetDocument1 pageShrinkage Limit Test - Data Sheetahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atterberg Limits - Data SheetDocument1 pageAtterberg Limits - Data Sheetahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Triaxial Test - Data SheetDocument2 pagesTriaxial Test - Data Sheetahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compaction Test - Data SheetDocument1 pageCompaction Test - Data Sheetahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unconfined Test - Set 2Document7 pagesUnconfined Test - Set 2ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Triaxial Test - Set 2Document8 pagesTriaxial Test - Set 2ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atterberg Limits - Set 1Document8 pagesAtterberg Limits - Set 1ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Specific Gravity - Set 1Document3 pagesSpecific Gravity - Set 1ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Directed Shear - Set 2Document11 pagesDirected Shear - Set 2ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atoomus مﻮﺘﻌﻟا ﺪﻤﺣا ﻖﻴﻓﻮﺗ ﻦﻣﺆﻣDocument7 pagesAtoomus مﻮﺘﻌﻟا ﺪﻤﺣا ﻖﻴﻓﻮﺗ ﻦﻣﺆﻣahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrometer - Set 2Document7 pagesHydrometer - Set 2ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Permeability Measurement - Set 1Document6 pagesPermeability Measurement - Set 1ahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.chloride & ConductivityDocument6 pages3.chloride & Conductivityahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.Ph & AcidityDocument6 pages1.Ph & Acidityahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atoomus مﻮﺘﻌﻟا ﺪﻤﺣا ﻖﻴﻓﻮﺗ ﻦﻣﺆﻣDocument4 pagesAtoomus مﻮﺘﻌﻟا ﺪﻤﺣا ﻖﻴﻓﻮﺗ ﻦﻣﺆﻣahm531Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 2 - ColloidsDocument15 pagesExperiment 2 - ColloidsRodelyn CantorPas encore d'évaluation
- Haldor Topsoe Hter First ExperiencesDocument8 pagesHaldor Topsoe Hter First ExperiencesGeorge Van BommelPas encore d'évaluation
- American Water Works AssociationDocument25 pagesAmerican Water Works AssociationZafirahAhmadFauziPas encore d'évaluation
- PLP P-2-2003, Glycol Dehydration-2nd Ed-RosenDocument41 pagesPLP P-2-2003, Glycol Dehydration-2nd Ed-Rosenivanov5559100% (1)
- Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 15,16,18 2022 (Omit 18.3)Document3 pagesChemistry Study Guide Chapter 15,16,18 2022 (Omit 18.3)JocelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Name (S) :: Quick - Phet Gas Intro (Google "Phet Gas Intro Choose" Gases Intro" Click On The Arrow Button)Document2 pagesName (S) :: Quick - Phet Gas Intro (Google "Phet Gas Intro Choose" Gases Intro" Click On The Arrow Button)Menasita MayantasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Grinding and CuttingDocument20 pagesGrinding and Cuttinggaur1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Pyq 2024Document217 pagesChemistry Pyq 2024sam.gamer.sg.opPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics - BuoyancyDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics - BuoyancyAbduljalil AlabidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesDocument59 pagesEngineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesSK crushPas encore d'évaluation
- Q2M3Document22 pagesQ2M3Sophia Jhayne AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering HydrologyDocument98 pagesEngineering HydrologyAnonymous 1n5HpBjPas encore d'évaluation
- TP201.3A Determination of 5 Inch WC Static Pressure Performance of Vapor Recovery Systems of Dispensing FacilitiesDocument10 pagesTP201.3A Determination of 5 Inch WC Static Pressure Performance of Vapor Recovery Systems of Dispensing FacilitiesCésar Oswaldo Aguilera OjedaPas encore d'évaluation
- MHD Power GenerationDocument25 pagesMHD Power Generationomg786Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 SynthesisDocument33 pages2 SynthesisSukanya Choudhary100% (1)
- Pumps CalculationDocument16 pagesPumps CalculationEkundayo JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Substitution of MN With Fe or CR in Heusler Alloy of Co2MnsnDocument11 pagesEffect of Substitution of MN With Fe or CR in Heusler Alloy of Co2MnsnΙήήΘςέήτ βόγPas encore d'évaluation
- VCR Theory NewDocument18 pagesVCR Theory NewPranay TinkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation of Internship ProjectDocument34 pagesPresentation of Internship ProjectReinaldo Ongky Billy AnandoPas encore d'évaluation
- 5555555Document58 pages5555555Ahmed MangoudPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.phase Diagrams PDFDocument24 pages10.phase Diagrams PDFMumpuniLuthfiPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear and Planar DensitiesDocument22 pagesLinear and Planar DensitiesIpul MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Valve Sizing Calculation - Docx INEGAS 3Document2 pagesValve Sizing Calculation - Docx INEGAS 3jhon.rojas.ery1489Pas encore d'évaluation
- Steam Trap ManualDocument61 pagesSteam Trap Manualbarrysmith77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethylene Recovery Through Dephlegmator TechnologyDocument9 pagesEthylene Recovery Through Dephlegmator TechnologyMohamed Abushrida100% (1)