Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Paper 1
Transféré par
Nyakweba DenisCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Biology Paper 1
Transféré par
Nyakweba DenisDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name … …………… …………………………Index Number…................/………….
231/1
BIOLOGY Candidate’s Signature………………………
Paper 1
(Theory) Date…………………………………………..
March/April 2012
2 hours
Aplus Trial examination
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
BIOLOGY
Paper 1
(Theory)
2 hours
Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
For examiner’s use only
Question Maximum Candidate’s
score score
1-29 80
This paper consists of 10 printed pages
Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all
the pages are printed as indicated and no questions are missing.
@ 2012 Turn over
A plus Series Pre-Mock Examinations (2012) Trial 1
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 1
1. State two aim of studying biology. (2 marks)
2. State two glands whose secretions are released into the human duodenum.
(2mks)
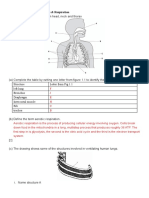
3. The diagram below represent female reproductive system in humans. Use it to answer the
questions that follow.
(a) Name the labeled parts: (2 mks)
III
IV
(b) (i) State the chromosomal state of the cells scooped from part I and labeled parts II. (1 mks)
I–
II-
(ii) Explain your answer in b (i) above. (1mks)
4. Describe the term eutrophication. (3 mks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 2
5. (a) What do you understand by the term transpiration. (1 mark)
(b) State two environmental factors that increase the rate of transpiration. (2 marks)
6. List four ways by which materials can circulate within and around the cells. (4 mks)
7. In fish, gaseous exchange occur across certain respiratory surfaces called gills. Water and
blood flow in opposite direction.
(a) What is the name given to the above phenomenon? (1mk)
(b) Explain the advantage of the above phenomenon. (2 mks)
8. (a) Suggest two reasons to explain why members of the division Pteridophyta are
considered to be more advanced than members of kingdom fungi.
(2mks)
(b). Name the spore producing structures in pteridophyta. (1mk)
9. (a) What is the function of hair-like structures on the walls of the fallopian tube in
mammalian female? (1mk)
(b). Name any other structure in humans in which similar hair-like structures are found (1mk)
10. State the enzymes present in each of the secretion released by the glands above. (3
mks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 3
11. (a) Differentiate co-enzymes from co-factors. (2 mks)
(b) Name two food substance that is not digested in human alimentary canal. (1mk)
12. Give the names corresponding to the following taxa as applied to humans; (3
mks)
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
13. Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) In the diagram, sketch the missing organelle.
(1 mk)
(b) Name the labeled parts B and C. (2 mks)
(c) State one function of part labeled A. (1mk)
14. The diagram below shows a human eye that is defective.
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 4
Name the eye defect illustrated in the diagram above. (1mk)
(a) What causes this defect? (1mk)
(b) How would this defect be corrected. (1mk)
15. (a) What is sex-linkage? (1mk)
(b) Give a reason to explain pre-mature baldness, tufts of hair in ear and nose are
characteristics found in men only. (2mks)
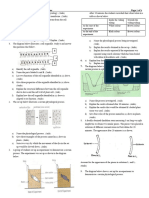
16. The diagram below represents a mammalian bone.
(i) Name the bone drawn above. (1mk)
(ii) Which part articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvic girdle? 1mk
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 5
(iii) State one function of an animal skeleton apart from support. (2 mks)
17. State three structural differences between Xylem vessels and Phloem. (4mks)
18. Name the blood vessel that nourishes the heart and the Kidney. (2mk)
19. (a) What does the term ventilation means with reference to gaseous exchange. (1 mk)
(b) State two respiratory surfaces in animals. (2 mks)
20. (a) Which hormone controls the concentration of urine produced in the kidney. (1mk)
(b) Name the main nitrogenous wastes material excreted by the following organisms;
(2 mks)
Fresh water fish.
Birds.
21. (a) State the causative agent of syphilis. (1 mk)
(b) List two methods of curbing the spread of HIV/AIDS. (2mks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 6
22. Explain the term Dormancy as used in Biology and state its significance.
Explanation (2mks)
Significance (1 mk)
23. Explain the term analogous structures as used in evolution. (3 mks)
24. (a) How does leaf folding in xerophytic plants aid in reducing the rate of transpiration?
(1 mk)
(b) State one other physiological adaptations that these plants employ in reducing the
rate of transpiration. (1 mks)
25. One gramme of fat yields twice as much energy as 1 gramme of carbohydrates when fully
oxidized. State two reasons why fat is not a suitable respiratory substrate in most animals.
(2mks)
26. Distinguish carefully between Excretion and Secretion. (2mks)
27. An experiment was set as shown below to compare the amount of carbon (iv) oxide in expired
and inspired air.
(a) State the purpose of clip
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 7
(i) P (1mark)
(ii) Q (1mark)
(b) Compare observations in tube A and B after experiment. Give reasons for your answer.
(2marks)
28. Give two reasons why it is important to screen the blood tissue before transfusion is done.
(2 mks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 8
Marking scheme- 231/1 paper 1
1. help to know how to use natural resources more efficiently; environment management;
medicine;improve agricultural yields through scientific research; improve on home
management techniques;
2. - Liver/gall bladder;
- pancrease;
3. III
- uterus/uterine cavity;
IV
- cervix;
. (1 mks)
I – diploid;
II- haploid
- I are somatic cells while II is a sex cell; (1mks)
4. - it is a natural process of excessive enrichment of water with nutrients; by which large
amounts of living organic materials grow in the water; slowly develop large concentrations of
aquatic plant life which eventually decay; (3 mks)
5. (a) it the process by which plants lose water to the atmosphere in form of vapour;
(1 mark)
(b) high temperatre; high light intensity; wind; a lot of water; low relative humidity;
first two. Rej temperature, light intensity, water, humidity. (2 marks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 9
6. - diffusion; cytoplasmic streaming/ cyclosis; cell movement and special organelles
microfilaments; endoplasmic reticulum; (4 mks)
7.
(a) counter current flow; (1mk)
(b) it maintains a steep concentration gradient; ensuring maximum gaseous exchange;
(2 mks)
8. (a) - are autotrophic; have vascular bundles; Show alteration of generation; (2mks)
(b). - sori; sorus. (1mk)
9. (a) -to propel egg/ovum zygote to uterus; (1mk)
(b). -Trachea/wine pip.; (1mk)
10. -amylase; lipase; trypsin; nuclease; (3 mks)
11. (a) -a co-enzyme is an organic substance that enable the enzyme to function effectively
e.g vitamins.
A co-factor is an inorganic substance that enhance performance of the enzyme e.g mineral ions.
(2 mks)
(b) - vitamins/ water/ mineral ions/ glucose; (1mk)
12. Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Animalia
Chordata
Mammalian(3 mks)
13. B- cell wall; (2 mk)
C- nucleus
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 10
-serves as continous bounding envelope for the entire cell; (1mk)
- it plays an active role in controlling and regulating the flow of molecules into and out of the cell;
14. (a)- short sightedness/ myopia; (1mk)
(b)- long eye ball; (
(c)- concave/ diverging lenses; (1mk)
15. (a) - occurrence of gene on sex chromosomes hence transmitted together with
those that determine sex; (1mk)
(b) - it is because are located on Y chromosomes that is exclusively found in
men; (2mks)
16. The diagram below represents a mammalian bone.
(j) Name the bone drawn above. (1mk)
- femur;
(ii) Which part articulates with the acetabulum of the pelvic girdle? 1mk
- part 1/ head;
(iii) State one function of an animal skeleton apart from support. (2 mks)
- protection of soft/delicate organs; formation of red blood cells in bone marrow;
movement;
17. .
Xylem Phloem
1.- are lignified -not lignified
2.- are dead tissues - are dead tissues
3. – no cytoplasmic filaments - have cytoplasmic filaments
4. – lack companion cells - have companion cells(4mks)
18 .- coronary artery and renal artery; (2mk)
19. (a) - it is the process of moving CO2 and O2 to and from the respiratory surfaces; (1
mk)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 11
(b) cell membrane; skin; alveoli; gills; (2 mks)
20. (a) antidiuretic hormone; (1mk)
(b) Fresh water fish.
- ammonia;
Birds.
- uric acid; (2 mks)
21. (a) - Treponema pallidium; (1 mk)
(b) - use of condoms; screening of blood before transfusion; abstinence from sex;
(2mks)
22. - Temporary stoppage/ceasation of growth process; in an organism/part of it; during which
metabolic activities fall to level sufficient/to keep cells/organisms alive; (2mks)
Significance (1 mk)
enable organism to survive periods of unfavourable environmental conditions e.g.
cold/heat; without exhausting food reserves; enable maturation of seeds/ production of
some growth hormones;
23. - these are structures of different embryonic origin; modified to perform similar function
due to exploitation of similar environments; this points towards convergent evolution. e.g
wings of birds and insects are modified for flight, (3 mks)
24. (a) - by not exposing stomata to environmental factors; (1 mk)
(b)- Reversed stomata rhythm; Shedding of leaves during drought; (1 mks)
25. -Requires more oxygen to oxidize
-Takes longer to release energy; (2mks)
26. -Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste products from the body-Secretion is the removal
of substances from a cell where it is formed and transfer to other ports where it is used;
(2mks)
27. (a) (i) Clip P – Closed to prevent exhaled air from entering into tube A/ when open allows
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 12
atmospheric air to enter into tube A; (1mark)
(ii) Clip Q – When closed prevents sucking in of the bicarbonate indicator/when open
allows exhaled air to enter into tube B; (1mark)
(b) A-bicarbonate indicator turns to orange-red; conditions are less acidic due to low
concentration of carbon (1marks)
B-bicarbonate indicator turns to yellow; showing high concentration of carbon (iv) oxide in
exhaled air. (1marks)
NB: Colours of bicarbonate indicator must be specific.
(iii)
28. - For pathogens e.g HIV; and compatibility; (2 mks)
Confidential and preparations.
- 50 cm3 liquid D- liquid D prepared by adding 40 cm3 of egg white and 5 g of glucose in a
liter of distilled water.
- Iodine solution
- Benedict’s solution
- Sodium bicarbonate
- 1% copper (II) sulphate
- 1% DCPIP
- Filter paper
- Droppers
- Means of heating
- White tile
- Glass rod
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 13
231/3
BIOLOGY
PAPER 3
(PRACTICAL)
March/ April 2012
1 ¾ HOURS
PREMOCK – KCSE PREDICTOR EXAMINATION
KENYA CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
BIOLOGY
PAPER 3
(PRACTICAL)
1 ¾ HOURS
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS
You are required to spend the first 15 minutes of the 1 ¾ hours allowed for this paper reading the
whole paper before commencing your work.
Answers must be written in the spaces provided.
For Examiners’ Use Only
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 14
QUESTION MAXIMUM CANDIDATES SCORE
1 17
2 13
3 10
TOTAL SCORE 40
A plus Series Pre-Mock Examinations (2012) Trial 1
1(a) You are provided with liquid D and a range of reagents and materials. Select the
appropriate requirements and carry out iodine, Benedict’s and paper tests and record in the
table below.
(12 marks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 15
(b) Put a little liquid D in a test tube and heat gently. Explain your observations. (2mks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 16
(c) (i) Name the classes of food in liquid D. (2 marks)
(ii) A tissue was found to be rich in oils. Was the tissue obtained from plant or
animal? (1 mark)
2. You are provided with photographs labeled J and K and . use them to answer the
questions that follow.
(a) Using the opened flowers photographs, count the number of flower parts listed below
and record your findings. (8 marks)
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 17
Floral part J K
Calyx
Corolla
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 18
Stamens
Pistil
(b) (i) Define the term pollination. (1 mk)
(ii) With reasons, suggest the type of pollination of specimens J and L. (2 marks)
(iii) Explain the biological significance of the type of reproduction exhibited by
flowering plants. (2 marks)
3. You are provided photographs below labeled A,B,C,D,E,F, G and a dichotomous key. use
them to answer the questions that follow.
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 19
(a) Fill the missing information in the dichotomous key below.
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 20
1 (a) Animal with jointed appendages……………….go to 3
(b) Animals without jointed appendages……….....go to 2
2 (a) Animals with a slender long body……………Nematoda
(b) Animals with a thick short body……………..Annelida
3 (a) …………………………..…………………….go to 5
(b) Animals without wings…………………go to 4
4 (a) Animals with numerous legs…………..Myrioponda
(b) ……………………………..…………..Hymenoptera
5 (a) Animals with short antenna…………..Diptera
(b) Animals with a pair of long antenna….go to 6
6 (a) Animals with cuticulized forewings…….Dictyoptera
(b) Animals with a pair of membranous wings…..Hymenoptera
(b) What name is given to the system of naming of organisms. (1mk)
(b)Use the completed dichotomous key to identify the family to which each plant belongs.
(7 marks)
Identity Steps followed
A…………………………….. …………………………
B ……………………………. …………………………
C …………………………… …………………………
D …………………………… ………………………….
E ……………………………. …………………………
F ……………………………… ………………………….
G ……………………………… …………………………….
Marking scheme
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 21
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 22
(b) (i) the solution coagulates;
(ii) proteins in the solution denatured leading to coagulation
(c) (i) Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids;
(ii) Plant;
Floral part J K
Calyx 5 fused 5 fused
Corolla 5 fused 5 free
Stamens 4 and 1 staminode many
Pistil 1 5 fused
(b) (i) Transfer of pollen grains from anthers to stigma;
(ii) insects; brightly coloured to attract insects; presenceof nectarines; landing platform;
rej. scented to attract insects.
(iii) Bring about genetic variation hence better adaptation/ survival of plants/ high yields/
drought /disease resistance;
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 23
(b)Fill the missing information in the dichotomous key below. (2 mks)
1 (a) Animal with jointed appendages……………….go to 3
(c) Animals without jointed appendages……….......go to 2
2 (a) Animals with a slender long body………………Nematoda
(b) Animals with a thick short body…………………Annelida
3 (a) Animal with wings…….………………………..go to 5
(b) Animals without wings………………………….go to 4
4 (a) Animals with numerous legs……………………Myrioponda
(b) Animals with3 pairs of legs…….………………Hymenoptera
5 (a) Animals with short antenna…………………….Diptera
(b) Animals with a pair of long antenna……………go to 6
6 (a) Animals with cuticulized forewings…………..Dictyoptera
(b) Animals with a pair of membranous wings…..Hymenoptera
(b) -binomial nomenclature; (1 mk)
Identity Steps followed (7mks)
A…1b,3b,4b………………… Hymenoptera
B …1b,3a,5a………………… Diptera
C …1b,3a,4a………………… Myriopoda
D …1b,3a,5b,6a……………… Dictyoptera
E …1a,2a…………………… Nematoda
F … .1b,5b,6b……………… Hymenoptera
G …1a,2b………………… Mollusca
A Plus Examinations series (2012) Printed by WEGO Publishers Page 24
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemD'EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 22072021 012 pp1Document13 pagesBio 22072021 012 pp1MARK SIMIYUPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology f2 2022 QsDocument8 pagesBiology f2 2022 QsMAGDALENE MWANGANGIPas encore d'évaluation
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationVernonPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Revision Booklet PDFDocument36 pagesBiology Revision Booklet PDFLus KamlPas encore d'évaluation
- F3 Bio Et3 QNDocument11 pagesF3 Bio Et3 QNBenjamin mwanikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 2023 Mocks BookletDocument167 pagesBiology 2023 Mocks BookletMasega Daniel ManaliPas encore d'évaluation
- F3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticeDocument10 pagesF3 Topic 11 & 12 PracticePianna IeongPas encore d'évaluation
- Kcse Physics Prediction 2023-2Document308 pagesKcse Physics Prediction 2023-2odhiambodalvin892Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification 1 and 2.Document4 pagesClassification 1 and 2.VernonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 Paper 1Document9 pages2008 Paper 1onokaanne9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topical Questions Form 3 - BiologyDocument32 pagesTopical Questions Form 3 - BiologyBadmind Jnr100% (2)
- English Open Day Oral Poetry: QuestionsDocument1 pageEnglish Open Day Oral Poetry: QuestionsZeddy AnjiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water and HydrogenDocument4 pagesWater and HydrogenomarPas encore d'évaluation
- K.C.S.E Past Papers Questions Form 21Document29 pagesK.C.S.E Past Papers Questions Form 21Mutula NashonPas encore d'évaluation
- Uace Growth & Development Questions and AnswerDocument29 pagesUace Growth & Development Questions and AnswerNelima Stella mercyPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretion and HomeostasisDocument6 pagesExcretion and HomeostasisVernonPas encore d'évaluation
- Form Six Aee 1 Examination. Physics 02: ST Peter Claver High SchoolDocument4 pagesForm Six Aee 1 Examination. Physics 02: ST Peter Claver High SchoolCharles GhatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 231/ 1 BIOLOGY-Paper 1: (Theory) Trial 2Document7 pages231/ 1 BIOLOGY-Paper 1: (Theory) Trial 2sharon kamnyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell PhysiologyDocument4 pagesCell PhysiologyVernon100% (1)
- Transport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants and Animals Questions and Answers - Biology Form 2 Topical Revision Transport in Plants - QuestionsOTIENO ELIJAHPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy P1Document105 pagesPhy P1Godfrey Muchai100% (1)
- Form Three Biology Set 1 QSDocument3 pagesForm Three Biology Set 1 QSTiffany100% (1)
- Kcse Mocks Set 1Document312 pagesKcse Mocks Set 1Micah IsabokePas encore d'évaluation
- Crosscountry Mocks 1Document300 pagesCrosscountry Mocks 1Micah IsabokePas encore d'évaluation
- Page 1 of 7Document7 pagesPage 1 of 7Eric NjoguPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Pp2 Quick Revision Series Exams 2Document208 pagesPhy Pp2 Quick Revision Series Exams 2griticenanjalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.7 Waves IDocument8 pages2.7 Waves IReg UlusPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1 2023 End T3 Mathematics QS - Teacher - Co - .Ke - Set - ADocument15 pagesForm 1 2023 End T3 Mathematics QS - Teacher - Co - .Ke - Set - AYussuf Hirow100% (1)
- Form 1 Physics End Term 2 2023 Holiday AssignmentDocument11 pagesForm 1 Physics End Term 2 2023 Holiday AssignmentOkumu KevinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Kcse Physics Mocks Set 1Document246 pagesKcse Physics Mocks Set 1Citron AkhalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fathers of Nations Guide BookDocument62 pagesFathers of Nations Guide BookMonny MoniquePas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY ... F3 - Ecology Summary NotesDocument52 pagesBIOLOGY ... F3 - Ecology Summary NotesKiama Gitahi100% (2)
- Kcse Extra-County Mocks s1Document235 pagesKcse Extra-County Mocks s1micah isabokePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Notes Form 1 4Document248 pagesBiology Notes Form 1 4Sha MeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Longhorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 4Document345 pagesLonghorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 4anabelle.pangatungan1998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cre Top National Schools 2024Document21 pagesCre Top National Schools 2024engineerbwiboPas encore d'évaluation
- Kcse Biology Revision SeriesDocument39 pagesKcse Biology Revision Seriestingai jacob habakkukPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 3 ChemDocument6 pagesForm 3 ChemFestus NanokPas encore d'évaluation
- Excretion and Homeostasis: VacuoleDocument24 pagesExcretion and Homeostasis: Vacuolemark lwanga100% (2)
- Ecology - QuestionsDocument14 pagesEcology - QuestionsDerrick M100% (1)
- KLB Biology F3 NoteDocument49 pagesKLB Biology F3 NoteSocdal Abdi100% (1)
- Gas Laws Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesGas Laws Chemistry Form 3 Topical Questions and AnswersBonface Kenani67% (3)
- 3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineDocument28 pages3.3 Work Energy Power and MachineGladys KPas encore d'évaluation
- ReproductionDocument162 pagesReproductionchumbavictor459100% (2)
- Chemistry Mocks Set 1Document167 pagesChemistry Mocks Set 1Citron AkhalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pangani Post Mock Examination: Kenya Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument3 pagesPangani Post Mock Examination: Kenya Certificate of Secondary EducationFestus NanokPas encore d'évaluation
- KCSE PREMOCKS Set 1Document245 pagesKCSE PREMOCKS Set 1Micah IsabokePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2013Document3 pagesBiology Paper1 Questions and Answers Kcse 2013JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- History K.C.S.E Pp2-Questions Updated2Document55 pagesHistory K.C.S.E Pp2-Questions Updated2AlfrickPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE-Biology Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperDocument8 pagesICSE-Biology Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibrium Positions at Instant T 10 CM: A B C D E F G H IDocument17 pagesEquilibrium Positions at Instant T 10 CM: A B C D E F G H IVincent haPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Question and Answer 2013-2017Document52 pagesChemistry Question and Answer 2013-2017Chikuta ShingaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8a Integrated Science Test 3Document2 pagesGrade 8a Integrated Science Test 3Davies Masumba100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Chemistry PracticalsDocument41 pagesBasic Principles of Chemistry PracticalsMufaro NyamutoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kcse Computer Studies Database QSTNS 2005 - 2021Document21 pagesKcse Computer Studies Database QSTNS 2005 - 2021Makueni Girls ICT Students100% (1)
- Geography 2023 Revision Materials.Document90 pagesGeography 2023 Revision Materials.nyabinge silvesterPas encore d'évaluation
- Cre Form 3 Based QuestionsDocument5 pagesCre Form 3 Based QuestionsPhelix Ouma OdhiamboPas encore d'évaluation
- C.R.E PP2Document24 pagesC.R.E PP2frank kipkoech100% (1)
- BIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY Form 3 Holiday Assignment QuestionsgurlavatarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 3Document6 pagesBiology Paper 3Nyakweba Denis100% (1)
- Biology Paper 2 Marking SchemeDocument2 pagesBiology Paper 2 Marking SchemeNyakweba DenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Paper 1 Marking SchemeDocument5 pagesBiology Paper 1 Marking SchemeNyakweba Denis0% (1)
- 443/2 Agriculture Paper 2 Time: 2 Hours: A Plus Examinations Series Trial 1Document11 pages443/2 Agriculture Paper 2 Time: 2 Hours: A Plus Examinations Series Trial 1Nyakweba DenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Agriculture Paper 2 Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesAgriculture Paper 2 Marking SchemeNyakweba DenisPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced MicroeconomicsDocument605 pagesAdvanced MicroeconomicsNyakweba Denis100% (1)
- Business Plan On GypsumDocument19 pagesBusiness Plan On GypsumAbdulbar kelilPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan. Phase ChangeDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan. Phase ChangeChupapi Munyanyo80% (5)
- Verka Complete Traning FilrDocument46 pagesVerka Complete Traning FilrSaab Rana100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Assertion-Reason QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Assertion-Reason Questionsteresa tsoiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comprehensive Review of Thermal Energy StorageDocument32 pagesA Comprehensive Review of Thermal Energy StorageRetneshwaaran GanesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Detergent Types LibroDocument22 pagesDetergent Types LibroRonaldo CMPas encore d'évaluation
- TOEFL Reading Practice 3-12Document10 pagesTOEFL Reading Practice 3-12OpacarophilePas encore d'évaluation
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument11 pagesMaterial Safety Data SheetRUDDY ALFAN SUBAKTIPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B16Document4 pagesAQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B16Mahebul MazidPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised National Plumbing Code of The Philippines - 1 PDFDocument112 pagesRevised National Plumbing Code of The Philippines - 1 PDFKyra Aleson100% (1)
- 1-First Quarter Experiment - Grade 6Document4 pages1-First Quarter Experiment - Grade 6cecil tayagPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Fixit Coal Tar EpoxyDocument3 pagesDR Fixit Coal Tar EpoxyPritha DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Loctite Frekote 770-NCDocument6 pagesLoctite Frekote 770-NCreussavelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gap Analysis of Kandla Site With Respect To Fire Protection and Control Document Number 0101Document13 pagesGap Analysis of Kandla Site With Respect To Fire Protection and Control Document Number 0101kirandevi1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tray DryerDocument22 pagesTray DryerHari KishorePas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science - Tarbuck - Chapter 5 - Running Water and GroundwaterDocument40 pagesEarth Science - Tarbuck - Chapter 5 - Running Water and GroundwaterLeon Jordan100% (1)
- Rajiv Dixit Talk On Sutra of Maharishi VagbhatDocument17 pagesRajiv Dixit Talk On Sutra of Maharishi VagbhatIshwar ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Exemplar: First Quarter-Q1, Wk1Document19 pagesLesson Exemplar: First Quarter-Q1, Wk1Ailljim Remolleno ComillePas encore d'évaluation
- Oil & Gas SeperationDocument34 pagesOil & Gas Seperationassatpute100% (2)
- Msds Grote UltrasealDocument2 pagesMsds Grote UltrasealBrett OzeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Carney 1996 Technology and CultureDocument32 pagesCarney 1996 Technology and CultureErica DiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sika 1 PDFDocument6 pagesSika 1 PDFAan TeePas encore d'évaluation
- Jingen PK MS-100 MSDS UpdatedDocument7 pagesJingen PK MS-100 MSDS UpdatedMainulHoquePas encore d'évaluation
- PDS en-GB 45751Document2 pagesPDS en-GB 45751Anuar SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Der 10Document233 pagesDer 10mantujataliPas encore d'évaluation
- Conplast F292M8: Foam Cement AdmixtureDocument5 pagesConplast F292M8: Foam Cement AdmixtureNaufal Ari NugrahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges and Socio-Economic Importance of Fish Production in Ethiopia:ReviewDocument5 pagesChallenges and Socio-Economic Importance of Fish Production in Ethiopia:ReviewZelalem EjiguPas encore d'évaluation
- Coconut Food Production - Coconut HandbookDocument19 pagesCoconut Food Production - Coconut Handbooksyahirah abubakarPas encore d'évaluation
- 9B - Dredge Crawler Technology - WODCON XXI - Leo W. Van Ingen MKII PDFDocument38 pages9B - Dredge Crawler Technology - WODCON XXI - Leo W. Van Ingen MKII PDFUdit AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- K Range PumpsDocument7 pagesK Range Pumpsnacho quispe0% (1)