Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Grid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction Generator
Transféré par
Sunil JainCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Grid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction Generator
Transféré par
Sunil JainDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
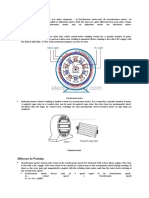
Grid connected induction Generator and Self
Excited Induction Generator...
Just like a DC Machine, a same induction machine can be used as an induction motor as
well as an induction generator, without any internal modifications. Induction generators
are also called as asynchronous generators.
Before starting to explain how an induction (asynchronous) generator works, I
assume that you know the working principle of an induction motor. In an induction motor,
the rotor rotates because of slip (i.e. relative velocity between the rotating magnetic field
and the rotor). Rotor tries to catch up the synchronously rotating field of the stator but
never succeeds. If rotor catches up the synchronous speed, the relative velocity will be
zero, and hence rotor will experience no torque.
But what if the rotor is rotating at a speed more than synchronous speed?
How induction generators work?
Consider, an AC supply is connected to the stator terminals of an induction
machine. Rotating magnetic field produced in the stator pulls the rotor to run behind
it (the machine is acting as a motor).
Now, if the rotor is accelerated to the synchronous speed by means of a prime
mover, the slip will be zero and hence the net torque will be zero. The rotor current
will become zero when the rotor is running at synchronous speed.
If the rotor is made to rotate at a speed more than the synchronous speed, the slip
becomes negative. A rotor current is generated in the opposite direction, due to the
rotor conductors cutting stator magnetic field.
This generated rotor current produces a rotating magnetic field in the rotor which
pushes (forces in opposite way) onto the stator field. This causes a stator voltage
which pushes current flowing out of the stator winding against the applied voltage.
Thus, the machine is now working as an induction generator (asynchronous
generator).
Induction generator is not a self-excited machine. Therefore, when running as a
generator, the machine takes reactive power from the AC power line and supplies active
power back into the line. Reactive power is needed for producing rotating magnetic field.
The active power supplied back in the line is proportional to slip above the synchronous
speed.
Self-excited induction generator
It is clear that, an induction machine needs reactive power for excitation, regardless
whether it is operating as a generator or a motor. When an induction generator is
connected to a grid, it takes reactive power from the grid. But what if we want to use an
induction generator to supply a load without using an external source (e.g. grid)?
A capacitor bank can be connected across the stator terminals to supply reactive power
to the machine as well as to the load. When the rotor is rotated at an enough speed, a
small voltage is generated across the stator terminals due to residual magnetism. Due to
this small generated voltage, capacitor current is produced which provides further
reactive power for magnetization.
Applications of induction generators: Induction generators produce useful power
even at varying rotor speeds. Hence, they are suitable in wind turbines.
Advantages: Induction or asynchronous generators are more rugged and require no
commutator and brush arrangement (as it is needed in case of synchronous generators).
One of the major disadvantage of induction generators is that they take quite large
amount of reactive power.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- AC Synchronous GeneratorDocument8 pagesAC Synchronous Generatoraswardi8756Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Rail Fuel Injection SystemDocument56 pagesCommon Rail Fuel Injection SystemMarcos Maciel100% (1)
- Synchronous MotorsDocument27 pagesSynchronous MotorsSyed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain50% (2)
- King Engine Bearings Catalog 2015Document552 pagesKing Engine Bearings Catalog 2015Walid Benazi50% (2)
- Principle Operation of Synchronous MotorDocument9 pagesPrinciple Operation of Synchronous MotorGideon MoyoPas encore d'évaluation
- PERKINS 2206-E13 Desarm. Armado 2008Document120 pagesPERKINS 2206-E13 Desarm. Armado 2008Jorge Luis BahamondeAzcarate63% (8)
- Camshaft Timing M62 VanosDocument10 pagesCamshaft Timing M62 Vanosmjassbong100% (1)
- Toyota 1kd-ftv Pares de Apriete PDFDocument1 pageToyota 1kd-ftv Pares de Apriete PDFTAMIRU TESFAYE100% (1)
- Synchronous MotorDocument8 pagesSynchronous MotorMsKaroly100% (1)
- Rolls-Royce: 250-B17F Series Operation and MaintenanceDocument2 pagesRolls-Royce: 250-B17F Series Operation and MaintenanceAnonymous 298xlo3uUPas encore d'évaluation
- 6bt Cummins PDFDocument136 pages6bt Cummins PDFbhushan kalwa100% (4)
- Induction Motors Unit 3Document26 pagesInduction Motors Unit 3babu KaroliPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motor: This Article Does NotDocument24 pagesInduction Motor: This Article Does Notyashraj786100% (1)
- 06b - Prop ControlDocument1 page06b - Prop Controljbert55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase MotorsDocument24 pagesThree Phase MotorsRobert MarcoliniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Last 100 Meters: Optimized Drop Cables For FTTHDocument19 pagesThe Last 100 Meters: Optimized Drop Cables For FTTHSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- AC MotorsDocument48 pagesAC MotorsBrandon SookdeoPas encore d'évaluation
- PS Checklist Motor GraderDocument1 pagePS Checklist Motor Graderyogi ganda pratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument14 pagesSynchronous MotorVishnu Nayak100% (1)
- Ac Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsDocument18 pagesAc Motors: (A) Synchronous Motors. (B) Asynchronous MotorsStudy portalPas encore d'évaluation
- Wärtsilä 20 Product GuideDocument178 pagesWärtsilä 20 Product Guidedaniel adam0% (1)
- Mack T13 Engine Lubricant TestDocument2 pagesMack T13 Engine Lubricant TestFrank FarePas encore d'évaluation
- Grid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction Generator..Document3 pagesGrid Connected Induction Generator and Self Excited Induction Generator..Sunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Generator Working TheoryDocument2 pagesInduction Generator Working TheorykalpanadeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Dubly Fed Induction GeneratorDocument2 pagesDubly Fed Induction GeneratorHafiz Ali AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction GeneratorDocument4 pagesInduction GeneratorAaryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Synchronous MotorDocument3 pagesAuto Synchronous Motorojunga.samuel21Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument8 pagesSynchronous MotorAvinash Kumar RaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Constructional Difference: Synchronous MotorDocument5 pagesConstructional Difference: Synchronous Motormirza121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Motor: AC Motor Rotor Alternating Current Rotating Magnetic FieldDocument5 pagesSynchronous Motor: AC Motor Rotor Alternating Current Rotating Magnetic FieldDeepak SekarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Synchronous Motor From A Hammond OrganDocument8 pagesA Synchronous Motor From A Hammond Organsiva prakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac MotorsDocument10 pagesAc MotorsJonas Marco CaguetePas encore d'évaluation
- Fig Showing Picture of ADocument6 pagesFig Showing Picture of ADemeico DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motor:: Electrical Motor Asynchronous Motor Magnetic FieldDocument1 pageInduction Motor:: Electrical Motor Asynchronous Motor Magnetic FieldShaheerPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument6 pagesSynchronous MotorSelvasundar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Synchronous MotorDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Synchronous Motorਰੌਣਕ ਸ਼ੇਰਗਿੱਲPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator ListrikDocument48 pagesGenerator ListrikJM4 - APas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles of Synchronous Motor OperationDocument16 pagesBasic Principles of Synchronous Motor OperationJesse Jones SeraspePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-5 SMDocument27 pagesUnit-5 SMShaik ShaheenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument6 pagesSynchronous MotorPraveen Ramesh KarnamPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motor Discussion of TheoryDocument5 pagesInduction Motor Discussion of TheoryRadtech SboPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.18 Ac MotorsDocument25 pages3.18 Ac Motorsdeleted Yt acc.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Motor PDFDocument3 pagesSynchronous Motor PDFAdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- SynchronousDocument2 pagesSynchronousSubhuPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Generator MotorDocument86 pagesDC Generator MotorShemin T JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Paper Of: Basic Electrical and Electronics ECE131Document6 pagesTerm Paper Of: Basic Electrical and Electronics ECE131Er Karan AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Powerpoint Presentation: Prasanta SarkarDocument22 pagesPowerpoint Presentation: Prasanta SarkarMazhar HaqPas encore d'évaluation
- DC & Ac MotorsDocument13 pagesDC & Ac MotorsYash Jude NathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Motor & Its Applications & Power Factor ImprovementDocument4 pagesSynchronous Motor & Its Applications & Power Factor ImprovementYash BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Motor N TypeDocument28 pagesAc Motor N TypesypultrazPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction MotorDocument23 pagesInduction Motorsai netPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Drives: Content 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9Document48 pagesElectrical Drives: Content 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9TadeleHailePas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas AjaDocument4 pagesTugas AjaIka Bayu RamadhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous GeneratorDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between Asynchronous and Synchronous Generatorbik_mesilovePas encore d'évaluation
- EES (Lec20)Document16 pagesEES (Lec20)Muhammad SagheerPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Generator and Synchronous Induction Motor: Presented By: Namani Srilahari Pavithran SelvamDocument16 pagesInduction Generator and Synchronous Induction Motor: Presented By: Namani Srilahari Pavithran SelvamRaghulPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Machine TrainerDocument29 pagesInduction Machine TrainerBabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 6 VincoyDocument16 pagesAssignment 6 VincoyVincoy JohnlloydPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical MachinesDocument7 pagesElectrical Machinesusama jabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction GeneratorDocument5 pagesInduction GeneratorAmarjeetRanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2403 SEM 2 Marks PDFDocument15 pagesEE2403 SEM 2 Marks PDFkesavantPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Motor: Citations VerificationDocument11 pagesInduction Motor: Citations VerificationChamika Dilshan WickramawardenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit V: Krishan Arora Assistant Professor Lovely Professional UniversityDocument52 pagesUnit V: Krishan Arora Assistant Professor Lovely Professional UniversityVinay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Induction Generator: Principle of OperationDocument4 pagesInduction Generator: Principle of OperationASHIM KUMAR SAHU100% (1)
- Induction Motor CharacteristicsDocument14 pagesInduction Motor CharacteristicsAnnaRajPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator SynchronizationDocument7 pagesGenerator Synchronizationbanukiran sambojuPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Synchronous GeneratorDocument5 pagesClassification of Synchronous Generatormuhammad afaq IEEEPas encore d'évaluation
- The Meaning of Electric MotorsDocument11 pagesThe Meaning of Electric MotorsMelindaTamrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous Motor Application and OperationDocument3 pagesSynchronous Motor Application and OperationRajesh TipnisPas encore d'évaluation
- Reluctance Motor: University of The Philippines Los Baños, Laguna AY 2010-2011Document16 pagesReluctance Motor: University of The Philippines Los Baños, Laguna AY 2010-2011Dela Cruz リッチェルPas encore d'évaluation
- Een 11 Finals Lec2Document43 pagesEen 11 Finals Lec2lavadiajhonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-I:: Explain With The Help of Circuit Diagram The Working of High Pressure Mercury Vapour LampDocument3 pagesUnit-I:: Explain With The Help of Circuit Diagram The Working of High Pressure Mercury Vapour LampSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- NEW Details Video LinksDocument6 pagesNEW Details Video LinksSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat Lab NumericalDocument72 pagesMat Lab NumericalSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 2 Electric ChargeDocument24 pagesPhysics 121: Electricity & Magnetism - Lecture 2 Electric ChargeSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines PDFDocument6 pagesGuidelines PDFSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution de 50Document6 pagesSolution de 50Sunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- My Party On The MountainDocument1 pageMy Party On The MountainSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Duplicate Word Highlight Code From You TubeDocument2 pagesDuplicate Word Highlight Code From You TubeSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Remaining Sections. Remaining SectionsDocument3 pagesRemaining Sections. Remaining SectionsSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Document4 pagesAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Single & Multistage Amplifier: AEC AssignmentDocument2 pagesSingle & Multistage Amplifier: AEC AssignmentSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- AE Paper With Solution2013Document6 pagesAE Paper With Solution2013Sunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Q3. Explain The Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test On A Single PhaseDocument5 pagesQ3. Explain The Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test On A Single PhaseSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET High Frequency Model and Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument17 pagesMOSFET High Frequency Model and Amplifier Frequency ResponseSunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Setup and System Equations: Photo CourtesyDocument5 pagesPhysical Setup and System Equations: Photo CourtesySunil JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesEngine Data Sheet PDFabhay dubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Parts Catalog - Option Detail Option Group Graphic Film Card DateDocument4 pagesElectronic Parts Catalog - Option Detail Option Group Graphic Film Card DateRussell HayesPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyphase Induction MotorDocument38 pagesPolyphase Induction MotorSaad KhaliqPas encore d'évaluation
- Kit Contents: Shown in Fig 1 1-Stainless Steel Valley Covers Plate 6-Button Socket Head ScrewsDocument3 pagesKit Contents: Shown in Fig 1 1-Stainless Steel Valley Covers Plate 6-Button Socket Head ScrewsGabriel ChiavettoPas encore d'évaluation
- VMX VMAX 1200 1996Document22 pagesVMX VMAX 1200 1996demoracingedu100% (1)
- Ravenol Hls Sae 5W-30Document2 pagesRavenol Hls Sae 5W-30Alin StancaPas encore d'évaluation
- McCormick C-L Europa Tier 3 (2008-2015) - RS51 - C80L Tractor Service Repair Manual PDFDocument29 pagesMcCormick C-L Europa Tier 3 (2008-2015) - RS51 - C80L Tractor Service Repair Manual PDFfjkkekmdmPas encore d'évaluation
- M3 Engine BookletDocument16 pagesM3 Engine BookletEliePas encore d'évaluation
- Rumus Rumus PerhitunganDocument27 pagesRumus Rumus PerhitunganErwin BagarPas encore d'évaluation
- LC165F-1H Owner's ManualDocument31 pagesLC165F-1H Owner's Manualrb cloudPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 5 Theory of Stirling EnginesDocument51 pagesChap 5 Theory of Stirling EnginesjosperdelPas encore d'évaluation
- ProblemsDocument25 pagesProblemsJohn Paul JuegoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3zr ToyotaDocument9 pages3zr ToyotaDavid ParariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecu Hyundai Starex Contiental - Google SearchDocument2 pagesEcu Hyundai Starex Contiental - Google SearchNofriagara Davit Harnawan0% (1)
- 40 BN 100 BN: Service Letter SL2019-686/JUSVDocument3 pages40 BN 100 BN: Service Letter SL2019-686/JUSVOctavian DinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2: Engine Performance Measures: BAE 517 - Lecture 2Document40 pagesChapter 2: Engine Performance Measures: BAE 517 - Lecture 2Siraj BussePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Drawing 12Document1 pageElectrical Drawing 12Nam NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Feed Pump: Wärtsilä Vasa 32 Engine SPC 174-0019ADocument4 pagesFuel Feed Pump: Wärtsilä Vasa 32 Engine SPC 174-0019ASaasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Flow System of GAS TURBINEDocument8 pagesFluid Flow System of GAS TURBINEAlanPas encore d'évaluation