Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Uti
Transféré par
tsunami_cutie0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2K vues1 pageUrinary tract infection (UTI) may occur in the bladder, where it is called cystitis, or in the urethra, where it's called urethritis. Most UTI's results from ascending infection by bacteria that have entered through the urinary meatus but some may be caused by hematogenous spread. Parents will be aware and practice preventive measures for further growth or spread of infection.
Description originale:
Titre original
ncp uti (1)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentUrinary tract infection (UTI) may occur in the bladder, where it is called cystitis, or in the urethra, where it's called urethritis. Most UTI's results from ascending infection by bacteria that have entered through the urinary meatus but some may be caused by hematogenous spread. Parents will be aware and practice preventive measures for further growth or spread of infection.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
2K vues1 pageNCP Uti
Transféré par
tsunami_cutieUrinary tract infection (UTI) may occur in the bladder, where it is called cystitis, or in the urethra, where it's called urethritis. Most UTI's results from ascending infection by bacteria that have entered through the urinary meatus but some may be caused by hematogenous spread. Parents will be aware and practice preventive measures for further growth or spread of infection.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
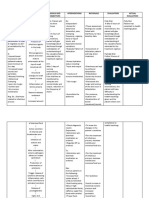
Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: High risk for A urinary tract infection After Independent:
“Nahihirapan infection related to (UTI) may occur in the rendering 1. Increased Expected Outcome:
nga siya urinary stasis. bladder, where it is called nursing care 1. Encourage hydration flushes Parents will be able to
umihi” as cystitis, or in the urethra, the parents increased fluid intake bacteria and toxins. demonstrate the
verbalized by where it is called urethritis. will be if not contraindicated. preventive measures.
the patient’s Upper urinary tract aware and
mother” infection results in practice 2. Investigate report of 2. Urinary retention
pyelonephritis. Most preventive bladder fullness. may develop,
Objective: UTI’s results from measures for causing tissue
ascending infection by further distension (bladder
-with bacteria that have entered growth or or kidney), and
indwelling through the urinary spread of potentially risk for
foley catheter. meatus but some may be infection. further infection.
caused by hematogenous
-urinalysis spread. UTI’s are much 3. Provide comfort 3. Promotes
shows pus common in females measures like back relaxation,
cells 6-10hpf because the shorter female rub, helping patient refocuses attention,
urethra makes them more assume position of and may enhance
vulnerable to entry of comfort. coping abilities.
organisms from
surrounding structures 4. Foley catheter care. 4 to prevent further
(vagina, periurethral growth of
glands, and rectum). microorganism.
Urinary stasis is a Dependent :
Stoppage or diminution 1. Administer 1. Reduces bacteria
of flow. Urinary stasis may antibiotics as present in urinary
be caused by prescribed. tract and those
abnormalities in structure introduced by
of the urinary system or drainage system.
in the nervous system
controlling it.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)deric95% (97)
- Nursing Care Plan ExampleDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan ExampleBrittanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Reports No Pain During Urination. There Will Be No Tension in Bladder The Patient Will Appear CalmDocument4 pagesReports No Pain During Urination. There Will Be No Tension in Bladder The Patient Will Appear CalmDenise Louise PoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- Sanjay Sharma's Notes For MRCPDocument7 pagesSanjay Sharma's Notes For MRCPMoe Zaw Lin100% (2)
- Immuno FinalDocument18 pagesImmuno FinalBroadway HardwarePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapters of Immunology - Janis KubyDocument1 pageChapters of Immunology - Janis Kubyapi-373112475% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTIDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTITrida Hermano CabansagPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan - UtiDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Utisweet_karisma05100% (6)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP UtiDocument2 pagesNCP UtiAlyanna Arañez50% (2)
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- UTIDocument2 pagesUTIdesh_dacanay100% (1)
- Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesSkin IntegrityJonica CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- Uti NCPDocument1 pageUti NCPAngelique Vinoya100% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infection - NCPDocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection - NCPIssa Farne0% (1)
- n320 Peds NCP wk3Document2 pagesn320 Peds NCP wk3api-301826049Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitRuby AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Uti NCPDocument3 pagesUti NCPHamdy Pagilit Dimaporo0% (1)
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaMiguelMartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Betty Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument2 pagesBetty Impaired Skin IntegrityBenjie DimayacyacPas encore d'évaluation
- Uti NCPDocument4 pagesUti NCPaagujar100% (4)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionJet Bautista100% (1)
- NCP UtiDocument2 pagesNCP UtiLeslie Anne Alcibar Tababa100% (1)
- NCP For UtiDocument3 pagesNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- Constipation LeukemiaDocument1 pageConstipation LeukemiamawelPas encore d'évaluation
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocument1 pageThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For SVTDocument6 pagesNCP For SVTRen VillenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Goal/s: After 20 Minutes of Nurse-Client Interaction, Client Will Be Knowledgeable About Newly Diagnosed Condition (Acute Appendicitis)Document3 pagesGoal/s: After 20 Minutes of Nurse-Client Interaction, Client Will Be Knowledgeable About Newly Diagnosed Condition (Acute Appendicitis)Rhn pjtPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP HemoDocument2 pagesNCP HemoJigs HechPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Inactivity ToleranceDocument16 pagesNCP Inactivity ToleranceChrisTine M. MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionJea Joel Mendoza100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Expected Outcome Implementation Rationale EvaluationRazzel Daza100% (1)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNCP HyperthermiaKirby ContaoiPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendectomy Nursing Care Plan - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesAppendectomy Nursing Care Plan - Risk For InfectionChebz Zy0% (1)
- PEDIA NCP Risk For BleedingDocument2 pagesPEDIA NCP Risk For BleedingTricia DogilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVecky TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3Grae TaclobPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diarrhea NCPDocument3 pagesDiarrhea NCPCharles Michael AzagraPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP ConstipationRoseben Somido100% (1)
- F. NCP ProperDocument4 pagesF. NCP ProperAle SandraPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicolePas encore d'évaluation
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocument1 pageTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceePas encore d'évaluation
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Uti Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Uti Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationmark327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Disorders of Renal Function Calculi - UTIDocument21 pagesDisorders of Renal Function Calculi - UTICres Padua QuinzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024Document11 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024Amanda EscorciaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPP 2Document8 pagesNCPP 2GEN COLLANTESPas encore d'évaluation
- The Thing For Sunday Pneumonia FlavouredDocument3 pagesThe Thing For Sunday Pneumonia FlavouredkasjdkasPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024 American Journal KidneyDocument11 pagesUrinary Tract Infections Core Curriculum 2024 American Journal Kidneycharliz diazPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract Infections: Practical Interpretations of Commonly Used TermsDocument6 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract Infections: Practical Interpretations of Commonly Used TermsPaullette SanjuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument6 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsSemut BarbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia SICDocument7 pagesPedia SICFrancheska Nicole Delos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisDocument34 pagesSeminar On: Urinary Tract Infections and NephritisGargi MPPas encore d'évaluation
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFDocument3 pagesEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - UTI NCP - NCM 112 Lec PDFGen Paulo EstoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Triptico ITUDocument2 pagesTriptico ITUClaudi Tperez0% (1)
- KQB 7002 Bioinstrumentation Case StudyDocument14 pagesKQB 7002 Bioinstrumentation Case StudyShafiq JSeahPas encore d'évaluation
- Bonus: Here's Your Perfect By: Jamie MILLERDocument47 pagesBonus: Here's Your Perfect By: Jamie MILLERJack KayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Human MAIT Cells Are Devoid of Alloreactive Potential: Prompting Their Use As Universal Cells For Adoptive Immune TherapyDocument34 pagesHuman MAIT Cells Are Devoid of Alloreactive Potential: Prompting Their Use As Universal Cells For Adoptive Immune TherapyJános JuhászPas encore d'évaluation
- Cri-Du-Chat Syndrome: Presenter: Dr. Neethu K Nandan Moderator: Dr. Sanghamitra GodiDocument35 pagesCri-Du-Chat Syndrome: Presenter: Dr. Neethu K Nandan Moderator: Dr. Sanghamitra GodiSanghamitra GodiPas encore d'évaluation
- GES 107 - Introduction To HIV&AIDSDocument39 pagesGES 107 - Introduction To HIV&AIDSSafiyah IzuagiePas encore d'évaluation
- MM Cheat Sheet 2011Document2 pagesMM Cheat Sheet 2011ehgeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Rate List 2017 NewDocument17 pagesTest Rate List 2017 NewParakram BhattPas encore d'évaluation
- Polydactyly PamphletDocument2 pagesPolydactyly PamphletAlan100% (1)
- BMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CADocument148 pagesBMB 515 Electronic Course Pack Sessions 21 - CANabeel ShahzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis in PLHIV SRDocument27 pagesEpidemiology of Viral Hepatitis in PLHIV SRUsman Kazali AbdulkadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Physio CAT 2 AnsweredDocument34 pagesPhysio CAT 2 AnsweredJohn KennedyPas encore d'évaluation
- Inheritance Chap 17Document23 pagesInheritance Chap 17Rayan KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fibroblast Growth Factors: A Controlling Mechanism of Skin AgingDocument8 pagesFibroblast Growth Factors: A Controlling Mechanism of Skin Agingnorma reyes contrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ribosomes and Protein SynthesisDocument15 pagesRibosomes and Protein SynthesisRichard ShakespearePas encore d'évaluation
- Aqa Gcse 9 1 Biology Collins EducationDocument35 pagesAqa Gcse 9 1 Biology Collins EducationRainPas encore d'évaluation
- Grand Guess Paper 1Document103 pagesGrand Guess Paper 1Shaik Mohammad AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ScienceDocument24 pagesBasic ScienceDioPas encore d'évaluation
- Biokimia Syaraf Dan Otak: Biochemistry Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument52 pagesBiokimia Syaraf Dan Otak: Biochemistry Department Hasanuddin Universityraynhard b. fandresPas encore d'évaluation
- Breast CancerDocument13 pagesBreast CancerJean Pierre ArangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Picture (CBP), EDTA Whole Blood: Master - SushanthDocument4 pagesComplete Blood Picture (CBP), EDTA Whole Blood: Master - SushanthAbdul MuqeemPas encore d'évaluation
- MoxifloxacinDocument3 pagesMoxifloxacinWaseem HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- GROUP-D (Entomology and Nematology) : JRF 2015 Time: 2.5HrsDocument10 pagesGROUP-D (Entomology and Nematology) : JRF 2015 Time: 2.5HrsDada PeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics MCQDocument19 pagesGenetics MCQSonam RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular and Biological Characterization of Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus (CABYV) Causing The Namamarako (NMK) Syndrome in AmpalayaDocument32 pagesMolecular and Biological Characterization of Cucurbit Aphid-Borne Yellows Virus (CABYV) Causing The Namamarako (NMK) Syndrome in AmpalayaUPLB Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research and Extension100% (1)
- Syllabus PDFDocument253 pagesSyllabus PDFVivek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- November 2008 QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument29 pagesNovember 2008 QP - Paper 2 CIE Biology A-Levelaimee simarnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument30 pagesUnit 5 Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemBea Bianca Cruz100% (1)