Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5 Question Bank 1 DOM 2161901 Even 2019
Transféré par
FuxCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
5 Question Bank 1 DOM 2161901 Even 2019
Transféré par
FuxDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Gandhinagar Institute of Technology
Mechanical Engineering Department
Dynamics of Machinery-2161901
Question Bank 1
1. Explain Rayleigh’s method for finding the natural frequency of vibratory system.
2. Discuss different cases showing the characteristics of the system performance for a damped
free vibration
3. Explain Equilibrium method to find the frequency of vibratory system.
4. Write short note on types of damping method.
5. Discuss the effect of inertia of constraint in longitudinal and transverse vibrations.
6. Define the following terms: (i) Periodic motion (ii) Simple Harmonic Motion (iii) Degree
of Freedom (iv) Natural Frequency (v) Damping Factor (vi) Logarithmic Decrement (vii)
Resonance.
7. Derive an expression for logarithmic decrement. What is the significance of logarithmic
decrement?
8. Derive the expression for naturally frequency for free vibration using energy method.
9. Write down detail Classification of vibrations. Define the terms: magnification factor,
displacement, transmissibility.
10. Explain an analytical method of balancing of several masses rotating in different planes.
11. Explain the balancing of several masses rotating in same plane by Graphical Method.
12. Explain the Forced vibration with rotating Unbalance.
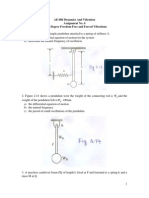
13. The mass 'm' is hanging from a chord attached to the circular homogeneous disc of mass
'M' and radius 'R' as shown in Figure. The disc is restrained from rotating by a spring
attached at radius 'r' from the center. If the mass is displaced downwards from rest position,
determine the frequency of oscillations.
14. A semicircular disc is suspended about its centre. Determine its natural frequency of
oscillation.
15. Find out natural frequency of the system shown in figure by energy method and
equilibrium method.
16. A damped vibrating system consisting of 40 Kg mass executes 20 oscillations in 5 seconds.
The amplitude of vibration decreases to one-eighth of the initial value after 8 complete
oscillations. Determine logarithmic decrement, damping factor, damping co-efficient and
spring stiffness.
17. In a single degree viscously damped vibrating system, the suspended mass of 16 kg makes
45 oscillation in 27 seconds. The amplitude of natural vibration decreases to one- seventh
of initial value after 5 oscillation. Determine:
Logarithmic decrement
Damping factor and damping co-efficient
Stiffness of spring.
18. A machine having a mass of 100 kg is supported on a spring which deflects 20mm under
the load of machine, a dashpot id fitted to reduce the amplitude of vibration to 10 % of its
initial value in two complete oscillations. Determine the stiffness of the spring, critical
damping co-efficient, logarithmic decrement, damping factor and frequency of damped
free vibration.
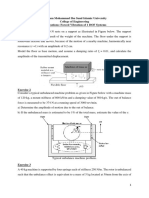
19. A line shaft carries five pulleys P, Q, R, S & T equally spaced along the shaft. The masses
of the pulleys P,R & S are 10, 8, and 16 kg respectively. The eccentricity of all pulley
masses can be assumed equal. The angular distance between P and R is 900, and R & S is
1350 measured in the same direction. Find the masses of pulleys Q and T and their angular
position, so that the shaft is completely balanced.
20. A, B C, & D are four masses attached on a shaft at radii 0.1m, 0.225m, 0.15m and 0.15m
respectively. Planes in which masses revolve are spaced 0.6m apart and the weights of B,
C and D are 10kg, 5.5kg and 3.6kg respectively. Estimate the required mass at A and the
relative angular positions of all the four masses so that the shaft is in complete balance.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Unit-Iii (Free Vibration) Part-A (2 Marks)Document2 pagesUnit-Iii (Free Vibration) Part-A (2 Marks)Asep HidayatPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Subject: Vibration Control EngineeringDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: Vibration Control EngineeringOmPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank For VceDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank For Vcecpt.ghostPas encore d'évaluation
- BE - 2019 - Dynamics of MachineryDocument5 pagesBE - 2019 - Dynamics of Machineryparthadhav2020.mech1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesImportant QuestionsdineshbabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Previous Year QuestionsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Previous Year QuestionsnikhilasoknPas encore d'évaluation
- DEC Mechanical Vibration Worksheet 1Document6 pagesDEC Mechanical Vibration Worksheet 1ephrembusiness2Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME34ME505 - Vibration and Noise ControlPractice Problems IDocument20 pagesME34ME505 - Vibration and Noise ControlPractice Problems IMUHAMMAD ASJAD AAMIR AAMIR AMINPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Vibration Part-A: Dynamics of MachineryDocument3 pagesFree Vibration Part-A: Dynamics of MachineryMonojit KonarPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing and VibrationDocument5 pagesBalancing and VibrationSridhar KanagarajPas encore d'évaluation
- 5826Document6 pages5826zubbbuPas encore d'évaluation
- Model QuestionsDocument4 pagesModel Questions6nkumar_vnrPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery Question BankDocument1 pageDynamics of Machinery Question Bankhumkisisekamnahi 82Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME304 Dynamics of Machinery, September 2020Document3 pagesME304 Dynamics of Machinery, September 2020Alok DineshPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Mechanical VibrationsDocument10 pages8 Mechanical VibrationsTsihatesfaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsDocument18 pagesME 6505 - Dynamics of Machines: Fifth Semester Mechanical Engineering (RegulationsshivendrakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Me6505 DM Mech VST Au Unit III PDFDocument18 pagesMe6505 DM Mech VST Au Unit III PDFMechanical EngineeringPas encore d'évaluation
- ME6505-Dynamics of MachinesDocument5 pagesME6505-Dynamics of Machinesshrikant belsarePas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machines QP DOM UPTO 2010Document32 pagesDynamics of Machines QP DOM UPTO 2010Chennai TuitionsPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM Question BankDocument4 pagesDOM Question BankAMIT SOLANKIPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 353 - Assgn1Document4 pagesME 353 - Assgn1Amar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Forced Vibration123Document4 pagesForced Vibration123Himanshu KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment-1 Vibrations 2017Document3 pagesAssignment-1 Vibrations 2017Arpit Sharma0% (1)
- Important Question BankDocument5 pagesImportant Question BankChhagan kharolPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentxing007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics Lab Manual - ME6511Document66 pagesDynamics Lab Manual - ME6511vinothPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Vibration of An Undamped Translational System: Worksheet-2Document6 pagesFree Vibration of An Undamped Translational System: Worksheet-2FasilPas encore d'évaluation
- T1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14Document2 pagesT1403 Mom Ii 24.6.14STUDENTS OF DOE CUSATPas encore d'évaluation
- 13n08me2302 5Document4 pages13n08me2302 5Thamizh Selvan SPas encore d'évaluation
- KomDocument11 pagesKompradeepPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM QuestionPaperPattern-IA-2 - PrintDocument4 pagesDOM QuestionPaperPattern-IA-2 - PrintThamizh Selvan SPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM Cycle Test - II 2022 AnswerkeyDocument7 pagesDOM Cycle Test - II 2022 AnswerkeyL04 BHÀRÁTHÏ KÀÑÑÁÑPas encore d'évaluation
- at ResonantDocument10 pagesat ResonantAlhji AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM Unit 4 & 5 QBDocument6 pagesDOM Unit 4 & 5 QBRayleighPas encore d'évaluation
- 振動學題庫 2Document11 pages振動學題庫 2San DugoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery Question BankDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question BankArun ShawnPas encore d'évaluation
- Numericals of Forced Vib Lec#06Document7 pagesNumericals of Forced Vib Lec#06Qamar Uz ZamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Btme-402 - Theory of Machines: Two Marks QuestionsDocument6 pagesBtme-402 - Theory of Machines: Two Marks QuestionsNavneet Singh DhamiPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsDocument4 pagesME 354 VIBRATION & CONTROL (2018-19) Problems On Single-Degree-of-Freedom SystemsMukul Chandra0% (1)
- Be Winter 2020Document3 pagesBe Winter 2020Naitri BatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Problems Set-3Document6 pagesPractice Problems Set-3ganeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of MachineryDocument2 pagesDynamics of MachineryAbhijeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Part BDocument3 pagesPart BMuthu RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Engg - Mechanics - Question BankDocument5 pagesEngg - Mechanics - Question BankShresth SanskarPas encore d'évaluation
- VibrationDocument6 pagesVibrationchandan_j4uPas encore d'évaluation
- S6 QB MeDocument18 pagesS6 QB MevenkiteshksPas encore d'évaluation
- ICSE X FORCE REMEDIAL REVISION-mergedDocument8 pagesICSE X FORCE REMEDIAL REVISION-mergedanimeshtechnosPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentDocument4 pagesMachine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentVijay ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machines Qpaper Nov-Dec 2010 Nit Raipur Mech 5th SemDocument2 pagesDynamics of Machines Qpaper Nov-Dec 2010 Nit Raipur Mech 5th SemShashi Bhushan PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery Question PapersDocument22 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question PapersMohan Babu S0% (1)
- Tutorial + Correction Mechanical Vibration Chapter 4Document12 pagesTutorial + Correction Mechanical Vibration Chapter 4Mohammed Al HelaylPas encore d'évaluation
- Me2302: Dynamics of Machinery Question BankDocument14 pagesMe2302: Dynamics of Machinery Question BankNagendar SelvakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUniversity QuestionsMartin De Boras PragashPas encore d'évaluation
- Anna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)Document4 pagesAnna University Madras Institute of Technology: 718 R.P.M N 843 R.P.M)veeyeskay_2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11D'EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ultrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsD'EverandUltrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Production Technology: Electron Beam MachiningDocument14 pagesProduction Technology: Electron Beam MachiningFuxPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank CAD 2161903 Even 2019Document3 pagesQuestion Bank CAD 2161903 Even 2019FuxPas encore d'évaluation
- RAC Answer Key Set B CT-2Document2 pagesRAC Answer Key Set B CT-2FuxPas encore d'évaluation
- DomDocument2 pagesDomFuxPas encore d'évaluation
- IE CT-1 Even 2017 Answer Key Set BDocument2 pagesIE CT-1 Even 2017 Answer Key Set BFuxPas encore d'évaluation
- DomDocument2 pagesDomFuxPas encore d'évaluation
- Breakthrough For Brake Design Automotive AA V8 I1Document3 pagesBreakthrough For Brake Design Automotive AA V8 I1FuxPas encore d'évaluation
- 2161901Document11 pages2161901FuxPas encore d'évaluation
- HTML Meta TagsDocument4 pagesHTML Meta Tagsmamcapiral25Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ds 50 BrochureDocument2 pagesDs 50 BrochureRaulMesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ammendement No.1 - List of Approved VendorsDocument3 pagesAmmendement No.1 - List of Approved VendorsLakhwant Singh KhalsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission and DistributionDocument10 pagesTransmission and Distributionprabhjot singh186% (21)
- Andreki, P. (2016) - Exploring Critical Success Factors of Construction Projects.Document12 pagesAndreki, P. (2016) - Exploring Critical Success Factors of Construction Projects.beast mickeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacom S72724+PDR32-RMT-HYB+ManualDocument130 pagesPacom S72724+PDR32-RMT-HYB+ManualDavidChisholmPas encore d'évaluation
- SQAP For Pumps 2017Document79 pagesSQAP For Pumps 2017MukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance On Mooring System Management Plans (MSMP)Document39 pagesGuidance On Mooring System Management Plans (MSMP)PJ Apostol Alpacas100% (4)
- Traction Motors E WebDocument16 pagesTraction Motors E WebMurat YaylacıPas encore d'évaluation
- Matrix APDDocument1 pageMatrix APDQHSE BTGPas encore d'évaluation
- TXL 025 12s Datasheet 1 en PDFDocument11 pagesTXL 025 12s Datasheet 1 en PDFJulianCitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Licenta - Algoritmi de Rezolvare A Cubului Rubik PDFDocument46 pagesLicenta - Algoritmi de Rezolvare A Cubului Rubik PDFRazvan SavucPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Technology Institute PresentationDocument14 pagesGas Technology Institute PresentationAris KancilPas encore d'évaluation
- GEN Reacool Maintenance Manual 1Document151 pagesGEN Reacool Maintenance Manual 1Md Saddam HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity9 PDFDocument5 pagesActivity9 PDFSmitPas encore d'évaluation
- Fresh Water GeneratorDocument48 pagesFresh Water GeneratorTarek Ashry100% (2)
- Databook Continental Agri 2006 PDFDocument0 pageDatabook Continental Agri 2006 PDFdanilo3073Pas encore d'évaluation
- Expansion Joint PDFDocument7 pagesExpansion Joint PDFPramit RajKarnikarPas encore d'évaluation
- UV-5R MenusDocument4 pagesUV-5R MenusRikardoviskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Roles in Solution Manager (SAP Library - SAP Solution Manager)Document3 pagesOverview of Roles in Solution Manager (SAP Library - SAP Solution Manager)Sravan Kumar PendyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- KMJT's Goldfarming GuideDocument36 pagesKMJT's Goldfarming GuideAnonymous oe4U3HCcPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Download Book Power Electronics Motor Drive Systems Fundamentals Experiments and Applications PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Power Electronics Motor Drive Systems Fundamentals Experiments and Applications PDFrichard.desouza769100% (10)
- Air PollutionDocument18 pagesAir PollutionKimjinPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume AkuDocument4 pagesResume AkukeylastPas encore d'évaluation
- Pds Microstran LTR en LRDocument2 pagesPds Microstran LTR en LRthaoPas encore d'évaluation
- MSDS - Molecular Sieve 4ADocument4 pagesMSDS - Molecular Sieve 4AadeliaaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsDocument22 pagesOhm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsTiarra MojelPas encore d'évaluation
- ABB Brakers 1SDC210004D0204Document286 pagesABB Brakers 1SDC210004D0204radugorceaPas encore d'évaluation
- Examen MesaDocument14 pagesExamen MesaFernando QuirogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsDocument18 pagesAnalysis+of+Non Symmetrical+Flapping+AirfoilsAsif HameedPas encore d'évaluation