Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2 (Continuity Equation)
Transféré par
Joshua TesoroCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lecture 2 (Continuity Equation)
Transféré par
Joshua TesoroDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EXAMPLES. EXERCISES.
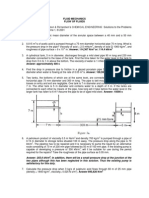
NCE 423: HYDRAULICS 1. Water runs through a water main of cross- 1. In the wind tunnel, the test-section wall is
sectional area of 0.4m2 with a velocity of 6 m/s. porous; fluid is sucked out to provide a thin
Calculate the velocity of water in the pipe when viscous boundary layer. The wall contains 800
the pipe tapers down to a cross-sectional area of holes of 7-mm diameter per square meter of
0.3m2. area. The suction velocity out each hole is Vs = 10
Lecture 2: Ans. v 2=8 m/s m/s, and the test section entrance velocity V1 =
46 m/s. Assuming incompressible flow of air,
2. A garden hose attached to a nozzle is used to fill compute:
a 10 gal bucket. The inner diameter of the hose is a. Vo , An s. 5.51 m/s
2 cm and it reduces to 0.8 cm at the nozzle exit. b. The total wall suction volume,
If it takes 50 sec to fill the bucket with water, An s. 3.48 m 3/s
Learning Objectives. determine: c. V2, An s. 40.53 m/s
1. To be able to derive the continuity equation. a. Volume and mass flow rates of water d. Vf, An s. 5.70 m/s
2. To be able to understand the concept of through the hose.
continuity equation and use this to solve related b. Average velocity of water at the nozzle exit.
problems. Ans. 7.5758 x 10 -4m3/s, 0.7576 kg/s,
15.0715 m/s
Required Knowledge in:
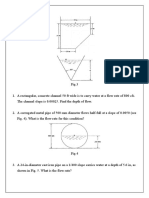
3. Pipe 1 diverges into two pipes namely Pipe 2 and
1. Rate of flow
Pipe 3. Pipe 1 is with a diameter of 50 mm and
mean velocity of 2 m/s. Pipe 2 is 40 mm in
diameter and takes only 30% of the total
Derivation of Continuity Equation. discharge. Pipe 3 is with a diameter of 60 mm.
Assumptions: What are the values of discharge and velocity in
Laminar flow-ideal fluid flow each pipe?
Ans. v 2= 0.936 m/s, v 3= 0.972 m/s
Incompressible-constant density
For compressible fluid:
For incompressible fluid:
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Topics Problem Set 6 - Hydraulics 3rd Term AY 2020-2021Document1 pageTopics Problem Set 6 - Hydraulics 3rd Term AY 2020-2021Mr. Mark B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limPas encore d'évaluation
- FM1 (3rd) May2020Document3 pagesFM1 (3rd) May2020Lakshay KoundalPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydau GeoDocument9 pagesHydau GeoAngelica TecsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 3Document4 pagesSheet 3Mohamed TallyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 02Document2 pagesTutorial 02shain begumPas encore d'évaluation
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallartePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsPraveen SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4Mimi SaffrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 Exercise ProblemsDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Exercise ProblemsHalima Sibayan SawanganPas encore d'évaluation
- Compre Hydraulics PSDocument5 pagesCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Boundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Document1 pageBoundary Layer Theory Problems Sheet - I - 2017 - 18Abhyuday SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial QN 6-10Document6 pagesTutorial QN 6-10clarence limPas encore d'évaluation
- NU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW)Document1 pageNU - Lecture 6 (UNSTEADY FLOW)Hernan BeñabonPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Fluid Mechanics TurorialDocument2 pagesAdvance Fluid Mechanics Turorialpinakramanuj11150% (2)
- CE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No. 2Document1 pageAssignment No. 2Charie EralinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Preboard 2 GeoDocument4 pagesPreboard 2 GeoLienardPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment on Orifice Meters and Pipe FlowDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment on Orifice Meters and Pipe FlowSwagata SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3 (Last Date For Submission: 3 OctDocument3 pagesAssignment 3 (Last Date For Submission: 3 OctSANDEEP SINGH100% (1)
- Topic 4 - (II)Document2 pagesTopic 4 - (II)daabgchiPas encore d'évaluation
- College engineering hydraulics problem setsDocument8 pagesCollege engineering hydraulics problem setsRia LauronPas encore d'évaluation
- Sw3 Answer KeyDocument1 pageSw3 Answer KeyPati DukaPas encore d'évaluation
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Document2 pagesPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Engineering Refresher CourseDocument7 pagesChemical Engineering Refresher CourseAstra BeckettPas encore d'évaluation
- Momentum Transfer: Sison, Kelly Sheine O. 4Che-CDocument16 pagesMomentum Transfer: Sison, Kelly Sheine O. 4Che-CKelly SisonPas encore d'évaluation
- CE 141 Hydraulic EngineeringDocument7 pagesCE 141 Hydraulic EngineeringAngelo Mathew ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Document1 pageNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER)Mr. Mark B.100% (1)
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFDocument1 pageNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFMr. Mark B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Document2 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 Fluid Dynamics Worksheet 1Khairunnisa FahrinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2mustefa kelilPas encore d'évaluation
- Visit: Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument9 pagesVisit: Civildatas - Blogspot.insankaran sPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFDocument2 pagesHydraulics - Series 1 (Fundamentals of Fluid Flow) - Sample Problems PDFNica Remollo100% (3)
- Hydraulics Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesHydraulics Practice QuestionsMarie AntonnetePas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Flow Rate CalculationDocument146 pagesPipe Flow Rate Calculationmalditaako66% (47)
- Unit 4 TrueDocument29 pagesUnit 4 TrueJojimar JulianPas encore d'évaluation
- FLUID MECHANICS AND MIXING CALCULATIONSDocument2 pagesFLUID MECHANICS AND MIXING CALCULATIONSGerry Lou Quiles100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics, Soil Mechanics, and Hydraulics ProblemsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics, Soil Mechanics, and Hydraulics ProblemsStudent555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 pagesProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- Hydraulik RezensentDocument148 pagesHydraulik RezensentScribdTranslationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFDocument32 pagesExam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFS. GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Code: 13A01303 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Regular Examinations December 2014 Time: 3 HoursDocument2 pagesCode: 13A01303 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R13) Regular Examinations December 2014 Time: 3 HoursBrahmaiah Vendipalli 184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flow Rate Calculation for PipeDocument146 pagesFlow Rate Calculation for PipeKarl Anne DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument6 pagesAssessment Exam 03: Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsAndrea MagtutoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixed TopicDocument105 pagesMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- MECH7Document1 pageMECH7Charles BryantPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsDocument1 pageCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsJustine Ejay MoscosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Equation and Its Applications in Fluid Mechanics ProblemsDocument3 pagesEnergy Equation and Its Applications in Fluid Mechanics Problemsmege1105Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ce8302 Iq UqDocument4 pagesCe8302 Iq UqAkxzPas encore d'évaluation
- HydraulicsDocument1 pageHydraulicsJerry Jake June HayaganPas encore d'évaluation
- AUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAUXILIARY LESSON - Water HammerFrancis HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- CE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question BankDocument9 pagesCE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering Question Banksankaran sPas encore d'évaluation
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsD'EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesD'EverandOne-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Junction Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsD'EverandJunction Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and ElectronicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolted and Riveted Connections Strength CalculationDocument1 pageBolted and Riveted Connections Strength CalculationJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- FlowchartDocument2 pagesFlowchartJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- "Transportation Engineering" Is The Application of Principles of Engineering, PlanningDocument17 pages"Transportation Engineering" Is The Application of Principles of Engineering, PlanningJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- University of The East - Manila: BS Civil Engineering On-the-Job Training On-The-Job Training / Practicum Weekly ReportDocument4 pagesUniversity of The East - Manila: BS Civil Engineering On-the-Job Training On-The-Job Training / Practicum Weekly ReportJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFDocument2 pagesLecture 3 (Bernoulli's Energy Equation) PDFJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicolas DSPDocument13 pagesNicolas DSPJoshua TesoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Pumps - Power CalculatorDocument4 pagesPumps - Power CalculatordpkPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart EssayDocument4 pagesHeart EssayQammar AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Directional Control Valve FundamentalsDocument18 pagesDirectional Control Valve Fundamentalsdoan lucPas encore d'évaluation
- Airfoil ConstructionDocument4 pagesAirfoil ConstructionMar Jerome TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Length Calcs For Pipes Valves and Fittings RevADocument9 pagesTotal Length Calcs For Pipes Valves and Fittings RevAlutfi awnPas encore d'évaluation
- ParametersDocument6 pagesParametersMark Kenneth BaldoquePas encore d'évaluation
- 5th Week - 2019 - Assignment - MOOC - Format PDFDocument11 pages5th Week - 2019 - Assignment - MOOC - Format PDFrobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Boundary Layed - NoteDocument3 pagesBoundary Layed - NoteMohammed AlshangitiPas encore d'évaluation
- Valves & Hose Bibs: How To Fix A Leaky Hose BibDocument2 pagesValves & Hose Bibs: How To Fix A Leaky Hose BibTheKeyPas encore d'évaluation
- P5-Fluid Flow PDFDocument13 pagesP5-Fluid Flow PDFJordi HengPas encore d'évaluation
- Short AnswerDocument10 pagesShort AnswerNarendra Singh Shekhawat100% (1)
- PSV Inspection ReportDocument4 pagesPSV Inspection ReportRonniPas encore d'évaluation
- CFX PreDocument74 pagesCFX PreMadhulaalasa KurmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Incompressible Flow PDFDocument10 pagesIncompressible Flow PDFjprvader0% (1)
- Aerodynamic Drag Reduction For A Simple Bluff Body Using Base BleedDocument7 pagesAerodynamic Drag Reduction For A Simple Bluff Body Using Base BleedJuantxoGarcia100% (1)
- Understanding NPSH & Cavitation in PumpsDocument11 pagesUnderstanding NPSH & Cavitation in PumpsArnab BhattacharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- SCM 025-108 M2Document8 pagesSCM 025-108 M2kazdanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 Hydraulic PressureDocument47 pagesLecture 5 Hydraulic PressureSAMUEL MAKATANEPas encore d'évaluation
- PT BMI Valve FAT Witness InviteDocument2 pagesPT BMI Valve FAT Witness Inviteahmad hafizPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPRESSOR SELECTION GUIDEDocument35 pagesCOMPRESSOR SELECTION GUIDEIan LuyaoPas encore d'évaluation
- FireDos Brochure Proportioners For Stationary Extinguishing Systems WebDocument12 pagesFireDos Brochure Proportioners For Stationary Extinguishing Systems WebDylan RamasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- X10686ME8093 WatermarkDocument2 pagesX10686ME8093 WatermarkMuthu SelvamPas encore d'évaluation
- Pamphlet 5 Bulk Storage of Liquid Chlorine - CiDocument29 pagesPamphlet 5 Bulk Storage of Liquid Chlorine - Cifagb1978Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Flow in Porous MediaDocument66 pagesFluid Flow in Porous MediaNicholas GawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Name:Azriel Varrand Khalevi NRP: 5019211026Document6 pagesName:Azriel Varrand Khalevi NRP: 5019211026Azriel Varrand KhaleviPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics PosterDocument1 pagePhysics PosterSamuel ParishPas encore d'évaluation
- Fan Performance Lab ProcedureDocument6 pagesFan Performance Lab ProcedureMax MichaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesDocument4 pagesExperiment 10: Find State Properties of Air State and Steady Flow Equation ObjectivesTAIMUR NASIRPas encore d'évaluation
- Afterburner Fall Poster ME393Document1 pageAfterburner Fall Poster ME393fatPas encore d'évaluation
- Qty Description RateDocument4 pagesQty Description RateAmir HabibPas encore d'évaluation