Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPS)
Transféré par
Margaveth P. Balbin0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues3 pagesGlobal positioning systems (GPS) and differential GPS (DGPS) use satellites to precisely locate vessels. Automatic identification systems (AIS), radar, and echo sounders also help with navigation by displaying nearby vessels, course plotting to avoid collisions, and measuring water depth. Electronic chart display systems make navigation easier by allowing crews to pinpoint locations and directions more easily than paper charts. Other navigation systems include long range tracking identification (LRIT), rudder angle indicators, voyage data recorders, rate of turn indicators, navigational lights, and ship whistles.
Description originale:
assignment
Titre original
Assignment Panot
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentGlobal positioning systems (GPS) and differential GPS (DGPS) use satellites to precisely locate vessels. Automatic identification systems (AIS), radar, and echo sounders also help with navigation by displaying nearby vessels, course plotting to avoid collisions, and measuring water depth. Electronic chart display systems make navigation easier by allowing crews to pinpoint locations and directions more easily than paper charts. Other navigation systems include long range tracking identification (LRIT), rudder angle indicators, voyage data recorders, rate of turn indicators, navigational lights, and ship whistles.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
9 vues3 pagesDifferential Global Positioning Systems (DGPS)
Transféré par
Margaveth P. BalbinGlobal positioning systems (GPS) and differential GPS (DGPS) use satellites to precisely locate vessels. Automatic identification systems (AIS), radar, and echo sounders also help with navigation by displaying nearby vessels, course plotting to avoid collisions, and measuring water depth. Electronic chart display systems make navigation easier by allowing crews to pinpoint locations and directions more easily than paper charts. Other navigation systems include long range tracking identification (LRIT), rudder angle indicators, voyage data recorders, rate of turn indicators, navigational lights, and ship whistles.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
Bejino Willienel G.
MT13-A5
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPS)
Are enhancements to the Global Positioning System (GPS) which provide improved
location accuracy, in the range of operations of each system, from the 15-meter nominal GPS
accuracy to about 10 cm in case of the best implementations.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Is a satellite-based navigation system made up of at least 24 satellites. GPS works in any
weather conditions, anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day, with no subscription fees or setup
charges. The U.S. Department of Defense (USDOD) originally put the satellites into orbit for
military use, but they were made available for civilian use in the 1980s.
Each satellite transmits a unique signal and orbital parameters that allow GPS devices to decode and
compute the precise location of the satellite. GPS receivers use this information and trilateration to
calculate a user's exact location.
Automatic Identification System
Is an automated tracking system that displays other vessels in the vicinity. It is a broadcast
transponder system which operates in the VHF mobile maritime band. Your own ship also shows
on the screens of other vessels in the vicinity, provided your vessel is fitted with AIS. If AIS is not
fitted or not switched on, there is no exchange of information on ships via AIS. The AIS onboard
must be switched on at all times unless the Master deems that it must be turned off for security
reasons or anything else. The working mode of AIS is continuous and autonomous.
Automatic Radar Plotting Aid (ARPA)
Displays the position of a ship and other vessels nearby. The radar displays the position of
the ships in the vicinity and selects the course for the vessel by avoiding any kind of collision.
Echo Sounder
This instrument is used to measure the depth of the water below the ship’s bottom using
sound waves.
Electronic Chart Display Information System
Is a development in the navigational chart system used in naval vessels and ships. With the
use of the electronic chart system, it has become easier for a ship’s navigating crew to pinpoint
locations, and attaining directions are easier than before.
Automatic Identification system
AIS is a system which helps to pinpoint the location and other navigational statistics of ships. AIS
uses VHF radio channels as transmitters and receivers to send and receive messages between ships
which endeavors to fulfill a lot of responsibilities.
Long Range Tracking and Identification (LRIT) System
LRIT is an international tracking and identification system incorporated by the IMO under its SOLAS
convention to ensure a thorough tracking system for ships across the world.
Rudder Angle Indicator
Rudder angle indicator, as the name indicates, provide the angle of the rudder. The display is provided
on bridge to control the rate of turn and rudder angle of the ship.
Voyage Data Recorder
A VDR or voyage data recorder is an instrument safely installed on a ship to continuously record vital
information related to the operation of a vessel. It contains a voice recording system for a period of
at least last 12 hours. This recording is recovered and made use of for investigation in events of
accidents
Rate of turn indicator
It indicates how fast the ship is turning at steady rate, normally shown as number of degree turned.
Navigational Lights
All boats – whether big or small are required to have night lights as a part of the navigation systems.
This system was introduced in the year 1838 by the United States and then was followed by the United
Kingdom in 1849. In the year 1889, the International Maritime Conference was established by the
United States to establish proper guidelines to prevent marine accidents. In the year 1897, these rules
were officially adopted internationally.
Ship Whistle
A ship’s horn is known as a whistle and it is generally provided in duplicate. One is driven by air and
the other is electrically operated.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Difference Between AIS and LRITDocument1 pageDifference Between AIS and LRITRahul Kumar100% (2)
- PROBLEM 1: P Company Had 90% Ownership Interest Acquired Several Years Ago in S Company. TheDocument4 pagesPROBLEM 1: P Company Had 90% Ownership Interest Acquired Several Years Ago in S Company. TheMargaveth P. Balbin75% (4)
- Bridge Equipment (Short DescriptionDocument5 pagesBridge Equipment (Short DescriptionMigyeliESivira100% (4)
- Debeg 3400Document8 pagesDebeg 3400dsumicPas encore d'évaluation
- AIS .PpsDocument27 pagesAIS .PpsVaruna Shantha100% (1)
- Batumi State Maritime AcademyDocument5 pagesBatumi State Maritime AcademyTemo Turmanidze100% (1)
- Electrnic Navigational Devices On ShipDocument53 pagesElectrnic Navigational Devices On ShipBerke100% (3)
- Unit 1 - Bridge LayoutDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Bridge Layoutmecete8514Pas encore d'évaluation
- 30 Types of Navigation Equipment and Resources Used Onboard Modern ShipsDocument12 pages30 Types of Navigation Equipment and Resources Used Onboard Modern ShipsGiorgi Kandelaki100% (2)
- Ais (Automatic Identification System) : BackgroundDocument23 pagesAis (Automatic Identification System) : Backgroundwastlon100% (1)
- Instrument 1Document5 pagesInstrument 1Sean Lingat100% (1)
- Bridge EquipmentDocument4 pagesBridge EquipmentDanik Kr100% (3)
- Dwatch 2Document14 pagesDwatch 2Karuro SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gyro CompassDocument2 pagesGyro CompassDIONISIO Jonathan IanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nav AidDocument8 pagesNav Aidanmay kadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Identification System: Vasile Radu Adrian ET32Document4 pagesAutomatic Identification System: Vasile Radu Adrian ET32AdrianPas encore d'évaluation
- KITXVEBIDocument8 pagesKITXVEBIsuxosheremetPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 Types of Navigation Equipment and Resources Used Onboard Modern ShipsDocument8 pages30 Types of Navigation Equipment and Resources Used Onboard Modern Shipsmark john batingalPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Identification System (AIS) : System Ships Vessel Traffic Services Vessels Data Ships Marine RadarDocument4 pagesAutomatic Identification System (AIS) : System Ships Vessel Traffic Services Vessels Data Ships Marine RadarGurkanwar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- NavigationDocument15 pagesNavigationJenalen O. MiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project TV CadetDocument34 pagesProject TV Cadetandria.shanidzePas encore d'évaluation
- Elective 3 Act 1Document5 pagesElective 3 Act 1Rex MaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Electronics: Submitted By: John Miko Moral Terso Jimenez Francis Jay OrehuelaDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics: Submitted By: John Miko Moral Terso Jimenez Francis Jay OrehuelaJohn Miko MoralPas encore d'évaluation
- The Bridge EquipmentDocument6 pagesThe Bridge EquipmentBerhanu KebedePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 - SART - SEARCH AND RESCUE TRANSPONDERSDocument19 pagesChapter 16 - SART - SEARCH AND RESCUE TRANSPONDERSmendes100% (1)
- 2nd Mates Handout ARI F1 Bridge EquipmentsDocument95 pages2nd Mates Handout ARI F1 Bridge EquipmentsravelobePas encore d'évaluation
- Navigation EquipmentDocument6 pagesNavigation EquipmentJeric PremaleonPas encore d'évaluation
- AIS - Lesson-03Document7 pagesAIS - Lesson-03Zobaer AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- AISDocument8 pagesAISdrogo021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Nav 1Document14 pagesPresentation Nav 1Carl Angelo Jocson FlosaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIS Lesson-02Document4 pagesAIS Lesson-02Zobaer AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- VtmsDocument2 pagesVtmsLorenz YatcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidated BEQ+Gyro NotesDocument95 pagesConsolidated BEQ+Gyro NotesShubham Saurav100% (1)
- What Are The Concept of AIS SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Concept of AIS SystemAnonymous K286lBXoth100% (1)
- Navigation Imu-Bsc Prevzzz-ImpDocument53 pagesNavigation Imu-Bsc Prevzzz-ImpJOGESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Consolidated Nav Aids+Gyro Notes - PH2Document94 pagesConsolidated Nav Aids+Gyro Notes - PH2Rajat Bahuguna100% (1)
- Automatic Identification SystemDocument7 pagesAutomatic Identification Systemசிம்பு சண்டியர்Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIS NotesDocument2 pagesAIS NotesAmar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- AIS Notes PDFDocument6 pagesAIS Notes PDFRahulPrakash100% (1)
- A Is White PaperDocument13 pagesA Is White PaperNairdna P Led OirasorPas encore d'évaluation
- List of NavaidsDocument14 pagesList of Navaidstharesh nicholasPas encore d'évaluation
- D Watch 2Document2 pagesD Watch 2Delos Reyes, Ron Angeliqe B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIS Notes PDFDocument7 pagesAIS Notes PDFSandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- BEQ Notes Incl Compasses-2M (Consolidated)Document136 pagesBEQ Notes Incl Compasses-2M (Consolidated)Hriday Soin100% (1)
- Ais PDFDocument6 pagesAis PDFGlenn VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Q. What Does The Term AIS Mean?Document4 pagesQ. What Does The Term AIS Mean?Asus Fonepad100% (1)
- Class A AISDocument10 pagesClass A AISMark VlogsPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Identification Systems (AIS) Are Designed To Be Capable of Providing Information About The Ship To Other Ships and To Coastal Authorities AutomaticallyDocument43 pagesAutomatic Identification Systems (AIS) Are Designed To Be Capable of Providing Information About The Ship To Other Ships and To Coastal Authorities AutomaticallyAnonymous ppae1EVbPas encore d'évaluation
- Jiddoo ReportDocument3 pagesJiddoo Reporttobi powpowPas encore d'évaluation
- AIS Guide: Automatic Identification SystemDocument5 pagesAIS Guide: Automatic Identification SystemsbdmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigational EquipmentsDocument26 pagesNavigational EquipmentsParth Sarathi100% (1)
- P A G e H o W A I S W o R K S ?Document13 pagesP A G e H o W A I S W o R K S ?atinder13Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Long Range Tracking and Identification (Lrit)Document5 pagesThe Long Range Tracking and Identification (Lrit)kishore kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Identification System: ModelDocument6 pagesAutomatic Identification System: ModelAsael Marquez100% (1)
- Public Speech: Presenter: Moon, JangwookDocument24 pagesPublic Speech: Presenter: Moon, JangwookRaghav MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Low-Cost Microcontroller-Based Weather Monitoring SystemDocument43 pagesA Low-Cost Microcontroller-Based Weather Monitoring SystemChirag MistryPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigational EquipmentDocument61 pagesNavigational EquipmentFranz Joseph IwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Identification Systems (AIS)Document13 pagesAutomatic Identification Systems (AIS)Mike MSBPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Navigation for the Modern Boat Owner: Navigate Effectively by Getting the Most Out of Your Electronic DevicesD'EverandPractical Navigation for the Modern Boat Owner: Navigate Effectively by Getting the Most Out of Your Electronic DevicesPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Pick The Perfect Portable GPS Unit: A Guide To Stress Free TravelD'EverandHow To Pick The Perfect Portable GPS Unit: A Guide To Stress Free TravelPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Continuous Probability Density: Math ReviewerDocument2 pagesProperties of Continuous Probability Density: Math ReviewerMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1 - Strategic Cost Management Assignment #2 E.U.P. Using Weighted Average MethodDocument1 pageBalbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1 - Strategic Cost Management Assignment #2 E.U.P. Using Weighted Average MethodMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1 - Strategic Cost Management Assignment #4Document1 pageBalbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1 - Strategic Cost Management Assignment #4Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. Assignment #1Document7 pagesBalbin, Ma. Margarette P. Assignment #1Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
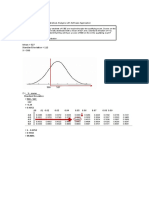
- Mean 527 Standard Deviation 112 X 500Document1 pageMean 527 Standard Deviation 112 X 500Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats D#4 HypothesisDocument1 pageStats D#4 HypothesisMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats A#4Document1 pageStats A#4Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1: Quantity To Be Accounted ForDocument2 pagesBalbin, Ma. Margarette P. ACCTG 021-ACTCY31S1: Quantity To Be Accounted ForMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats D#4Document1 pageStats D#4Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Stats D#4Document1 pageStats D#4Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5Document1 pageModule 5Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Sufficiency Group: Abrugar, Mariti Balbin, Ma. Margarette Pantaleon, Ericka Radomes, Jessie Torino, CheeneDocument2 pagesSelf Sufficiency Group: Abrugar, Mariti Balbin, Ma. Margarette Pantaleon, Ericka Radomes, Jessie Torino, CheeneMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Self Sufficiency: Abrugar, Mariti Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. Pantaleon, Ericka Anne Domingo Radomes, Jessie Torino, CheeneDocument11 pagesSelf Sufficiency: Abrugar, Mariti Balbin, Ma. Margarette P. Pantaleon, Ericka Anne Domingo Radomes, Jessie Torino, CheeneMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Picture Analysis - BalbinDocument1 pagePicture Analysis - BalbinMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Hbo Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesHbo Finals ReviewerMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate The Leaders - BalbinDocument2 pagesRate The Leaders - BalbinMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- OrdersDocument1 pageOrdersMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Questions in Obligations and Contracts by MilesDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions in Obligations and Contracts by MilesMary Ann Gumpay RagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Activity - HboDocument1 pageStudent Activity - HboMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Development Program: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument20 pagesStudent Development Program: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Development Program: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument20 pagesStudent Development Program: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- CC Material 8326384281957292162Document22 pagesCC Material 8326384281957292162Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Module 12Document3 pages04 Module 12Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between Dgps and GPS: Local Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesDifference Between Dgps and GPS: Local Coordinate SystemMargaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing The Winning Mindset: Culture and Gender Sensitivity SDP 4.3Document15 pagesDeveloping The Winning Mindset: Culture and Gender Sensitivity SDP 4.3Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing The Winning Mindset: Culture and Gender Sensitivity SDP 4.3Document15 pagesDeveloping The Winning Mindset: Culture and Gender Sensitivity SDP 4.3Margaveth P. BalbinPas encore d'évaluation
- IGL-RA15 - Reference GuideDocument10 pagesIGL-RA15 - Reference GuideLwin PhyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Advances On Hybrid Integration of 2D Materials On Integrated Optics PlatformsDocument24 pagesRecent Advances On Hybrid Integration of 2D Materials On Integrated Optics PlatformsArka GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Jasper SchematicDocument10 pagesJasper SchematiccrackintheshatPas encore d'évaluation
- Gateway 450ROG SchematicDocument40 pagesGateway 450ROG SchematicMark McKinsnkeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Document26 pagesPresentation Topic: GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)Anonymous xsK0G4IPas encore d'évaluation
- Metal Detector Circuit ReportDocument4 pagesMetal Detector Circuit Reportpratik kushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Embedded Systems: Unit No:-1 CO:-R16C406A.1 PO's:-PO1, PO2, PO3, PO12Document48 pagesEmbedded Systems: Unit No:-1 CO:-R16C406A.1 PO's:-PO1, PO2, PO3, PO12Mohammed AbdulAzizPas encore d'évaluation
- ChartsDocument17 pagesChartsHoàng Minh ThịnhPas encore d'évaluation
- 2108i 026277 1 PDFDocument8 pages2108i 026277 1 PDFAn DrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Melody Technical Manual - IndexDocument8 pagesMelody Technical Manual - IndexNassima BELILPas encore d'évaluation
- Data and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsDocument30 pagesData and Computer Communications: Tenth Edition by William StallingsHasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Open Systems Interconnection Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) (OSI)Document33 pagesOpen Systems Interconnection Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) (OSI)g_4uPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Call Processing: Source: InternetDocument11 pagesGSM Call Processing: Source: InternetAditya RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- MOSFET Device Operation: AccumulationDocument8 pagesMOSFET Device Operation: AccumulationMohit SoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Operational Amplifier: PA01 - PA73Document5 pagesPower Operational Amplifier: PA01 - PA73khawar mukhtarPas encore d'évaluation
- RGB Control SwitchDocument1 pageRGB Control SwitchLucian LupaşcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfamax NurseCall EnglishDocument4 pagesAlfamax NurseCall EnglishYacine MesnataPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.3.1.1 WAN Device Modules Instructions - IGDocument5 pages2.3.1.1 WAN Device Modules Instructions - IGJavier Sacán50% (2)
- Product Brief Accelleran E4000 Series High Capacity Small CellsDocument2 pagesProduct Brief Accelleran E4000 Series High Capacity Small Cellscopey861883Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adc MCQDocument9 pagesAdc MCQTrojanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fulltext MosfetDocument192 pagesFulltext MosfetMuhammad Khosyi'inPas encore d'évaluation
- GaN & SiC Power Semiconductors - Why These Devices Are Gaining Popularity - NewsDocument15 pagesGaN & SiC Power Semiconductors - Why These Devices Are Gaining Popularity - NewsAmanuel Amare GebrekidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Troubleshooting GuideDocument2 pagesTroubleshooting GuideAngelo PalamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Relay Output Module: Technical DataDocument2 pagesRelay Output Module: Technical DataguilhermegomPas encore d'évaluation
- EED LabDocument7 pagesEED LabVINITA AGARWALPas encore d'évaluation
- Model LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDocument2 pagesModel LA-ST120: AC Distribution Panel UnitDaniel JovelPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Motion Controls B25A20ACDocument9 pagesAdvanced Motion Controls B25A20ACServo2GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei Improve SDSRDocument9 pagesHuawei Improve SDSRAhmadArwani88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cut-Out Fuse (92123R3-P-D)Document1 pageCut-Out Fuse (92123R3-P-D)Genius DacpanoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Output Power Doubler Line Amplifier Features: 1000 MHZ, 21.5Db GainDocument10 pagesHigh Output Power Doubler Line Amplifier Features: 1000 MHZ, 21.5Db GainYung SangPas encore d'évaluation