Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids
Transféré par
sairam046Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids
Transféré par
sairam046Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Module 6 : Structure and Functions of Nucleic Acids
DNA-structure, properties and function
Structure of DNA :
• The discovery of DNA structure is one of the hall mark of the modern molecular biology.
• Based on the assumptions of Chargoff and utilizing X-ray diffraction data, obtained from
crystals of DNA by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, James Watson and Francis Crick
proposed a model for the structure of DNA in 1953.
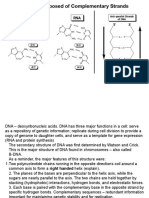
• They established that DNA has a double helical structure comprising of two complementary
antiparallel polynucleotide strands, wound around each other in a rightward direction.
• The backbone of the helix is sugar-phosphate and the bases are in the interior of the helix and
extended at 900perpendicular to the axis of the helix. Bases from opposite helix pair with each
other. Purines form base pairs with pyrimidene as a thumb rule- A will pair with T, and C with G.
According to this pattern, known as Watson-Crick base-pairing.
Specific features of DNA structure :
• It is double helical structure. One polynucleotide chain forms one strand. Two such strands
form double helix.
• Chain has sugar phosphate backbone and the bases are arranged perpendicular to the chain.
• Two strands are antiparallel to each other: one in 5' ---> 3' direction and the other in the 3' ---
> 5' direction.
• A and T ; and G and C occur as complementary and form base pair with corresponding
complementary base in opposite strand.
• One turn of the helix is 36 A and 10 base pairs are found per turn with rise of 3.6A.
• On the surface of double helix two deep grooves are found which are called major and minor
grooves.
• Helix is right handed along the axis.
The bases pairs are hydrogen bonds with each other and impart stability to the structure. The
base-pairs composed of G and C contain three H-bonds, whereas those of A and T contain two H-
bonds. For this reason G-C base-pairs are stronger than A-T base-pairs. The outcome will be that
DNA having more GC base pairs will be more stable than the one having more AT pairs.
• Bases are stacked over each other in the double helix.
• Hydrophobic interactions between stacked bases also stabilize the DNA.
• The sugar phosphate backbone of each strand is negatively charged (due to phosphate group
(pKa being near to zero). These charges are stabilized by Mg2+.
Various conformations of DNA :
• One of the properties of the DNA is that it shows conformational flexibility, and could exist in
alternative structural forms. The Watson-Crick structure is the B-form DNA or B-DNA.
• The B from is the most stable structure for a random sequence DNA molecule under
physiological conditions and is therefore “the standard point of reference in any study of the
properties of DNA”.The B-DNA predominates in the cell.
• There are two other structural variants of DNA that have been well characterized in crystal
structures. They are the A-DNA and Z-DNA. These DNA variants differ in their helical sense,
diameter, base pairs per helical turn, helix rise per base pair, base tilt normal to the helix axis,
sugar pucker conformation, and glycosyl bond conformation.
Dimensions of different DNA :
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Module 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsDocument15 pagesModule 6: Structure and Functions of Nucleic AcidsMadhuri Gupta100% (1)
- Nucleic AcidsDocument113 pagesNucleic AcidsBabak Nami100% (3)
- Nucleic Acids (Class 3)Document15 pagesNucleic Acids (Class 3)Swetank SahaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 10 Structure of DNA 2Document13 pagesLesson 10 Structure of DNA 2bavoca8322Pas encore d'évaluation
- 09NucAMO SuarezDocument14 pages09NucAMO SuarezscasuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Genetics (MCB202) Lecture 04Document64 pagesMicrobial Genetics (MCB202) Lecture 04ShamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Biochemistry of The DNADocument38 pagesModule 1 Biochemistry of The DNAdagame.marianlouise.shsPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Assignment 2Document12 pagesDna Assignment 2api-253560385100% (1)
- Lecture 1-DNA StructureDocument22 pagesLecture 1-DNA StructureLujain AlshiekhPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitrogenous Base Nucleoside DeoxynucleosideDocument14 pagesNitrogenous Base Nucleoside DeoxynucleosideIan WongPas encore d'évaluation
- LipidsDocument40 pagesLipidsNIRMALYA BAGCHIPas encore d'évaluation
- 09NucAMO MamalapatDocument7 pages09NucAMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatPas encore d'évaluation
- Handouts Unit-IVDocument11 pagesHandouts Unit-IVmukeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 1Document2 pagesNotes 1api-279318070Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2pt6 DNA and RNA Structure StudentDocument17 pages2pt6 DNA and RNA Structure StudentBig CinemaPas encore d'évaluation
- BME 203 - Lecture No. 13-15Document131 pagesBME 203 - Lecture No. 13-15SagorPas encore d'évaluation
- Nes and DnaDocument29 pagesNes and DnaGeeta P HanchatePas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology - IDocument122 pagesMolecular Biology - IBhanvi PaliwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationDocument50 pagesLecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationnizobellPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of DNA To Be UploadedDocument11 pagesStructure of DNA To Be UploadedBibhu Prasad RathPas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 2Document38 pagesSlide 2OdaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument52 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancezoologyPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 - Structure of DNADocument27 pages20 - Structure of DNAمحمد صالح ابراهيم محمدPas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesNucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaBauza, Stephanie Dawn T.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesDna Structure and FunctionAliah Aziz100% (1)
- Watson and Crick Model of DNADocument22 pagesWatson and Crick Model of DNAGanesh V Gaonkar100% (1)
- DNA Structure - ReplicationDocument22 pagesDNA Structure - Replicationapi-3763146100% (1)
- TOPIC 1 Organisation - Structure FunctionDocument41 pagesTOPIC 1 Organisation - Structure FunctionsyuhadahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 2Document142 pagesLecture 1 2ngocnm.bi12-320Pas encore d'évaluation
- DNA and RNA Are PolynucleotidesDocument35 pagesDNA and RNA Are PolynucleotidesnaomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology Unit 2 (DNA & RNA)Document40 pagesMolecular Biology Unit 2 (DNA & RNA)Fuz Nas100% (2)
- Kuliah DnaDocument47 pagesKuliah DnaRoby KieranPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Bioc1600-DnaDocument68 pages4 Bioc1600-DnaKellyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - DNA-The Genetic Material PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 2 - DNA-The Genetic Material PDFEman JandaliPas encore d'évaluation
- DNAstuctureDocument49 pagesDNAstuctureKhyati GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 MB CH 5Document88 pagesLecture 1 MB CH 5Raed Al-AtiyatPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA StructureDocument31 pagesDNA Structuremohammed aliPas encore d'évaluation
- Crick and Watson's Models of DNA StructureDocument10 pagesCrick and Watson's Models of DNA StructureSofi BellerPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010Document4 pagesDNA - Level 1 18 Jan 2010safemindPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesDocument35 pagesBIOC2600/MEDE2301 Lectures Overview: Dr. Alan Wong School of Biomedical SciencesSeo Eun KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Molecular Pathology - April 2012 - ZHDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Pathology - April 2012 - ZHtoxiczarrar.pubgPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene, Chromosomes and GenomesDocument31 pagesGene, Chromosomes and GenomesAfiq IzzatPas encore d'évaluation
- Nucleic AcidsDocument19 pagesNucleic AcidsKarmina SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3.2 MB DNA StruDocument62 pagesChapter 3.2 MB DNA StruMustee TeferaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sliced PDF CompressedDocument49 pagesSliced PDF Compressedfaheem.ashrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna ANDYDocument12 pagesDna ANDYAndy Morales100% (1)
- Lecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic AcidDocument64 pagesLecture. (1), Introduction & Structure of Nucleic Acidstudentactivity555Pas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of DNA PDFDocument7 pagesStructure of DNA PDFJamesPas encore d'évaluation
- SodapdfDocument49 pagesSodapdffaheem.ashrafPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA and RNA: Structure and Function: Arif RafidDocument32 pagesDNA and RNA: Structure and Function: Arif RafidSudipta MandolPas encore d'évaluation
- Concepts of Biology Chapter 09 XdGEOrpDocument99 pagesConcepts of Biology Chapter 09 XdGEOrpKonstantinos KosmidisPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and ProteinsDocument11 pagesMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and ProteinsRose HaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- BCH9 Pre1 - Central Dogma - DNADocument23 pagesBCH9 Pre1 - Central Dogma - DNAronPas encore d'évaluation
- RNA Secondary Structure PredictionDocument30 pagesRNA Secondary Structure PredictionsruthyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Seminar Report On DNA - The Code of Life.: Paper - II, Unit - IDocument48 pagesA Seminar Report On DNA - The Code of Life.: Paper - II, Unit - IEkta ManglaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Components of RNA and DNADocument26 pagesComponents of RNA and DNAKarla Javier PadinPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene It's Nature Expression and Regulation - Final PDF-4Document3 pagesGene It's Nature Expression and Regulation - Final PDF-4Aishwarya ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1DNA and RNADocument26 pages5.1DNA and RNAserficasoPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of ContentsDocument30 pagesTable of Contentssairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Process For Corporate Persons) Regulations, 2016) : Form D Proof of Claim by A Workman or An EmployeeDocument5 pagesProcess For Corporate Persons) Regulations, 2016) : Form D Proof of Claim by A Workman or An Employeesairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Consent Form To Be Filled by The Kailash Manasarovar Yatri: and I Am Consciously Aware of TheDocument1 pageConsent Form To Be Filled by The Kailash Manasarovar Yatri: and I Am Consciously Aware of Thesairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Chemical Engineering Front PageDocument2 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering Front Pagesairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Infra Structure ProjectDocument11 pagesInfra Structure Projectsairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thiyagu CVDocument3 pagesThiyagu CVsairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fluidization: ApplicationsDocument11 pagesFluidization: Applicationssairam046Pas encore d'évaluation
- RNAi NotesDocument6 pagesRNAi Notesaman jaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynein Achieves Processive Motion Using Both Stochastic and Coordinated SteppingDocument9 pagesDynein Achieves Processive Motion Using Both Stochastic and Coordinated SteppingNovVie VietTha Sccor IIPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOL200 PSet - Unit 6Document17 pagesBIOL200 PSet - Unit 6Lovey ChandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Staar Review Stations Day 3Document12 pagesBiology Staar Review Stations Day 3api-267841335Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marjorie I. Gawala - 4-MT108-DNA AND RNA WORKSHEETDocument2 pagesMarjorie I. Gawala - 4-MT108-DNA AND RNA WORKSHEETMarjorie GawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- PCR Questions and Answers Sep PagesDocument5 pagesPCR Questions and Answers Sep PagesMohita Chugh100% (1)
- An acidic, thermostable exochitinase with β - N - acetylglucosaminidase activity from Paenibacillus barengoltzii converting chitin to N - acetyl glucosamineDocument11 pagesAn acidic, thermostable exochitinase with β - N - acetylglucosaminidase activity from Paenibacillus barengoltzii converting chitin to N - acetyl glucosamineAlonsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument6 pagesAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisAhmad A. ArabiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5' Race System ManualDocument48 pages5' Race System ManualPrabu DhanasekaranPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.translation & Protein StructureDocument29 pages10.translation & Protein StructureRaunak JalanPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Document9 pages7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Radwa MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- II. Cot AnalysisDocument32 pagesII. Cot AnalysisSuraj BhattaraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein StructureDocument43 pagesProtein StructureZeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Strictosidine Synthase, A Key Gene in Biosynthesis of Mitragynine From Mitragyna SpeciosaDocument7 pagesMolecular Cloning and Characterization of Strictosidine Synthase, A Key Gene in Biosynthesis of Mitragynine From Mitragyna Speciosadarvien15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology of BacteriaDocument93 pagesMolecular Biology of BacteriaCamsy Wang100% (1)
- Lecture 4-Cell PolarityDocument52 pagesLecture 4-Cell PolarityFarrelita Nayla GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Evelyn Gabriela Gonzalez SimbañaDocument6 pagesEvelyn Gabriela Gonzalez SimbañaMOnzerratheManzzanitaSixxPas encore d'évaluation
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test Bank 1Document15 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Edition Nelson Test Bank 1kristine100% (48)
- TUNEL Assay - Ensaio TUNELDocument3 pagesTUNEL Assay - Ensaio TUNELMaurício Ferreira MacielPas encore d'évaluation
- Gel ElectroiphoresisDocument22 pagesGel ElectroiphoresisAqsa MazharPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectral Repeat Finder (SRF) : Identification of Repetitive Sequences Using Fourier TransformationDocument17 pagesSpectral Repeat Finder (SRF) : Identification of Repetitive Sequences Using Fourier TransformationSamir SabryPas encore d'évaluation
- Next-Generation DNA Sequencing: Diana Le Duc, M.D. Biochemistry Institute, Medical Faculty, University of LeipzigDocument40 pagesNext-Generation DNA Sequencing: Diana Le Duc, M.D. Biochemistry Institute, Medical Faculty, University of LeipzigDrAli Al-FendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test BankDocument13 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bankodettedieupmx23m100% (31)
- Expression of Biological InformationDocument7 pagesExpression of Biological InformationNur Amalina KhozariPas encore d'évaluation
- Unacademy 4 PDFDocument16 pagesUnacademy 4 PDFANUPAM ANAND KUMAR PANDEY MBA-IPas encore d'évaluation
- Epigenetic ModificationsDocument1 pageEpigenetic ModificationsFerny PintoPas encore d'évaluation
- SCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTDocument27 pagesSCIE1106 Lec 6 DNA Structure 2023 MSTJamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemistry Lab Review UNTDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Lab Review UNTSue WalthersPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene MutationDocument39 pagesGene MutationJanhaji PlotadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Puc 18Document2 pagesPuc 18xian zhangPas encore d'évaluation