Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Vapor Liquid Equilibrium
Transféré par
Celvin DickyDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Vapor Liquid Equilibrium
Transféré par
Celvin DickyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II
VAPOR LIQUID
EQUILIBRIUM
Mala Hayati Nasution, S.T., M.T.
Chemical Engineering Department
UISI
2019
Value Matrix
Parameter Percentage A AB B BC C D E
Presence 5% 16 meetings Absent > 5
times
Quiz 1 10% Presence in 2 Presence in Absent in
Quiz 2 10% Quiz only 1 Quiz both 2 Quiz
Task 30% All Terlambat 1 Terlambat 2
assignments tugas tugas
on time
Mid Test 15% > 81
Final Test 25% > 81
The answer of True, True, True, True, False, False, False,
the Task, Quiz, Good Good Bad Bad Good Good Bad
Mid Test and language, Language, language, language, language, Language, Language,
Final Test structured, Not Not Not structured, Not Not
neat. structured, structured, structured, neat. structured, structured,
neat neat not neat neat Not neat
Politeness 5% Polite in class, Not polite at
outside the all
class, WA
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 2
Equilibrium
• Equilibrium is a static condition in which no
changes occur in the macroscopic properties
of a system with time.
• Temperature, Pressure and Phase
Compositions remain constant.
• Change in microscopic level.
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 3
Measures of Composition
• Mass Fraction and Mole Fraction
• Concentration
• Total Molar Mass
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 4
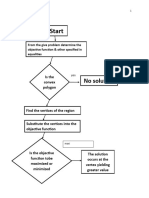
The Phase Rule & Duhem’s Theorem
• Intensive Variable does not depend on the
size of the system T, P, viscosity.
• Extensive Variable depends the size of the
Intensive Variable, P dan T Equation which connects system mass, volume, entropy, energy
variables
Duhem’s Theorem
“In a closed system, an equilibrium condition is reached when 2 variables are set”
2 phases
2 components
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 5
VLE Qualitative Behavior
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 6
VLE Qualitative Behavior
F=2–π+N Temperature (T)
= 2 – 1 (phase) + 2 (components) = 3 Pressure (P)
Composition (xi)
Upper surface : saturated liquid
Bubble point
Under surface : saturated vapor
Dew point
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 7
VLE Qualitative Behavior
• Point U – B – H – C1 Subcooled
• Point K – A – C2
Vapor – liquid
Superheated vapor
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 8
VLE Qualitative Behavior
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 9
VLE Qualitative Behavior
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 10
P-x,y and T-x,y Diagram
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 11
VLE Qualitative Behavior
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 12
P-T Diagram
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 13
Diagram P-T
Critical Point
Maximum Pressure
F- G : Retrograde Condensation
Bubble point ?
Saturated Vapor occurs
condensation because of
Dew point ?
pressure reduction
Pressure reduction, vaporization G-H : Vaporization because of
vaporization
Temperatur maksimum
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 14
Diagram P-T Azeotrop
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 15
Assignment
• Individual assignment.
• Handwriting only.
• Use reuse A4 paper.
• Write a resume of “Vapor Liquid Equilibrium Behavior” based on the presentation of 10 groups.
• Write the resume in Bahasa Indonesia.
Universitas Internasional Semen Indonesia Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II 16
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- DVS 2205-5-1987 Calculation of Thermoplastic TanksDocument7 pagesDVS 2205-5-1987 Calculation of Thermoplastic TanksAserty12100% (3)
- Measure and Integration: A Concise Introduction to Real AnalysisD'EverandMeasure and Integration: A Concise Introduction to Real AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- AirfoilDocument8 pagesAirfoilMOFEEZALAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayJeffrey YumangPas encore d'évaluation
- Sip-Aip Monitoring ToolDocument9 pagesSip-Aip Monitoring Toolbrave29heartPas encore d'évaluation
- Daily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayJeffrey YumangPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument16 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriesIshan NogiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 07-Solution Thermodynamics-Student PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 07-Solution Thermodynamics-Student PDFsupernova shinePas encore d'évaluation
- 1-1. Introduction and Fundamentals of Thermodynamics PDFDocument8 pages1-1. Introduction and Fundamentals of Thermodynamics PDFOctavianus RudyPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material: Downloaded From VedantuDocument11 pagesStudy Material: Downloaded From VedantuMudit KapoorPas encore d'évaluation
- LP - Percentage Composition - 2Document6 pagesLP - Percentage Composition - 2Khiyah RhuePas encore d'évaluation
- Nter Olecular Orces (IMF) : Saptarshi MajumdarDocument29 pagesNter Olecular Orces (IMF) : Saptarshi MajumdarHarish RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 9Document20 pagesLec 9Rohan TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Nuclear Chemistry Complete ModuleDocument97 pagesChemistry Chemical Kinetics Nuclear Chemistry Complete Moduleruchir angraPas encore d'évaluation
- CHME 312 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II Fall 2010: InstructorDocument4 pagesCHME 312 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II Fall 2010: InstructorAmro Ismail KashtPas encore d'évaluation
- Word 2Document6 pagesWord 2aadityaray2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-2021-PETA 1.1 States of MatterDocument4 pages2020-2021-PETA 1.1 States of Matternathaniel husolPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020-2021-PETA 1.1 States of MatterDocument4 pages2020-2021-PETA 1.1 States of Matternathaniel husolPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material: Free Master Class SeriesDocument12 pagesStudy Material: Free Master Class SeriessunilPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Report of TEST-03 Subjectwise ESE - Paper 2 - CE: BookmarkDocument26 pagesTest Report of TEST-03 Subjectwise ESE - Paper 2 - CE: BookmarkamitPas encore d'évaluation
- Preventive Maintenance Plan: Machine / Device Task Frequency Description of Maintenance TaskDocument12 pagesPreventive Maintenance Plan: Machine / Device Task Frequency Description of Maintenance TaskFlorin DamaroiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Equilibria SummaryDocument5 pagesChemical Equilibria SummaryKiara LimPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Chapter 04 - Part 1 - 05Document41 pages03 Chapter 04 - Part 1 - 05MmmmohPas encore d'évaluation
- 59d74544e4b0b990ba5c9fed 5ba3e3dae4b0639d7c27ddc3 1571732486470Document13 pages59d74544e4b0b990ba5c9fed 5ba3e3dae4b0639d7c27ddc3 1571732486470KingPas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter Basics HTML Guide - enDocument3 pagesStates of Matter Basics HTML Guide - enLloyd KauseniPas encore d'évaluation
- MSD Front PageDocument2 pagesMSD Front PageNicholas ZPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 HSC Bio Girraween Trial Written Marking GuidelinesDocument37 pages2012 HSC Bio Girraween Trial Written Marking GuidelinesshivmeetPas encore d'évaluation
- Nlewis65 204 208 Classroom Winnick 29 No 3 Summer 1995 CeeDocument5 pagesNlewis65 204 208 Classroom Winnick 29 No 3 Summer 1995 CeeFerdz RmrzPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Research I: Nabunturan, Compostela ValleyDocument3 pagesPractical Research I: Nabunturan, Compostela Valleyjocelyn dianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tos NEW TCWDocument1 pageTos NEW TCWJennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Record of Grades: Year: Student NameDocument4 pagesRecord of Grades: Year: Student NameMark Jacob Delos SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry: Target: Jee Main and Advanced 2022Document64 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Target: Jee Main and Advanced 2022sarvesh goyalPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Chapter 03 CompiledDocument78 pages02 Chapter 03 CompiledDwi Ramadhani100% (1)
- Physical Chemistry IDocument25 pagesPhysical Chemistry IClara CarreraPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB ACT 1 Feel The HeatDocument3 pagesLAB ACT 1 Feel The HeatFrancis AbalosPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Chapter 11 (Compiled)Document106 pages05 Chapter 11 (Compiled)Haziq KhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTP Finals TOSDocument2 pagesNSTP Finals TOSAntoneth AlviolaPas encore d'évaluation
- ENG 2019 UAS Kalkulus 3 PDFDocument5 pagesENG 2019 UAS Kalkulus 3 PDFkholiq giffariPas encore d'évaluation
- PETE202 - F181 - CH2 - Pure CompoundsDocument10 pagesPETE202 - F181 - CH2 - Pure CompoundshabnasforlfePas encore d'évaluation
- C-220 (20-22) Thermodynaics-3Document17 pagesC-220 (20-22) Thermodynaics-333-Siddharth NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Plan IB21 ChemDocument3 pagesPlan IB21 ChemMustafa Al-TaiePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemicalkinetics Presentation 150214034801 Conversion Gate02Document35 pagesChemicalkinetics Presentation 150214034801 Conversion Gate02BLACK HACKERPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 4 Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesClass 4 Zeroth Law of ThermodynamicsBharathiraja MoorthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Industry L1Document20 pagesChemical Industry L1Mohammed Salah JamalPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Chapter 10 (Compiled)Document86 pages07 Chapter 10 (Compiled)Sofea IzyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibrium Class 11Document11 pagesEquilibrium Class 11bt21102036anshulasharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test: Bachelor of Secondary Education (Mindanao State University)Document7 pages2nd Quarter Summative Test: Bachelor of Secondary Education (Mindanao State University)Anna Missy FunjPas encore d'évaluation
- 7B.2 IvyLearn - Last Homework Polls and Margin of Error - 2HH-Fall 2023-Quantitative ReasoningDocument1 page7B.2 IvyLearn - Last Homework Polls and Margin of Error - 2HH-Fall 2023-Quantitative Reasoningmaximogreen2003Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preventative Maintenance PlanDocument12 pagesPreventative Maintenance PlanlouayPas encore d'évaluation
- 0.0 Revised ChE 123 Syllabus (COVID-19)Document2 pages0.0 Revised ChE 123 Syllabus (COVID-19)googley71Pas encore d'évaluation
- AalysisDocument1 pageAalysisponveeraventhanpPas encore d'évaluation
- W8L2 - Review Concluding RemarksDocument8 pagesW8L2 - Review Concluding RemarksJay patelPas encore d'évaluation
- January 1999 PDFDocument27 pagesJanuary 1999 PDFATPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q2 - W8Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q2 - W8Garneth OrantoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Razon Raymond C. Problem Set No.2Document14 pagesRazon Raymond C. Problem Set No.2luna genilPas encore d'évaluation
- Rasheed Tyron 28Document1 pageRasheed Tyron 28Nareema RasheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Due Date: Week 12 (See MOODLE For Exam Dates) .: BIT243: Network Security Assignment 2 (20%) Total: 20 MarksDocument4 pagesDue Date: Week 12 (See MOODLE For Exam Dates) .: BIT243: Network Security Assignment 2 (20%) Total: 20 MarksJimmy CyrusPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 - Phase Equilibrium of One ComponentDocument24 pagesChapter 7 - Phase Equilibrium of One ComponentPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNPas encore d'évaluation
- Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program: Science - Grade 8 Practice TestDocument43 pagesTennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program: Science - Grade 8 Practice TestSunkyung KimPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q2 - W8Document8 pagesDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q2 - W8Thedanreb NagonusPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Light Scattering: Tables, Formulas, and ApplicationsD'EverandMultiple Light Scattering: Tables, Formulas, and ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Millimeter PaperDocument1 pageMillimeter PaperCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Uts Daik Celvin Dicky Wahyudi 2031710009Document43 pagesUts Daik Celvin Dicky Wahyudi 2031710009Celvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Water Treatment by Adsorption TechnoloDocument8 pagesAdvances in Water Treatment by Adsorption TechnoloCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- DDocument17 pagesDCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Termo Bu YuniDocument5 pagesTermo Bu YuniCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel TermoDocument7 pagesExcel TermoCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Goaalseek YoutubeDocument1 pageGoaalseek YoutubeCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Titrimetric MethodeDocument17 pagesTitrimetric MethodeCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Produksi Asam Lemak Dari Dedak Melalui Proses Hidrolisis Enzimatis Secara in Situ. Universitas Dipenogoro. SemarangDocument1 pageProduksi Asam Lemak Dari Dedak Melalui Proses Hidrolisis Enzimatis Secara in Situ. Universitas Dipenogoro. SemarangCelvin DickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical and Numerical Predictions of Burst Pressure of PipelinesDocument9 pagesTheoretical and Numerical Predictions of Burst Pressure of PipelinesA LamperougePas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlocal Theories For Bending, Buckling and Vibration of Beams - JN ReddyDocument21 pagesNonlocal Theories For Bending, Buckling and Vibration of Beams - JN ReddyShivareddy KondakindiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - SF AnwerDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics - SF AnwerKishore ChandPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation Investigation - Ballistic PendulumDocument3 pagesSimulation Investigation - Ballistic PendulumpixelhoboPas encore d'évaluation
- CE6306Strength of Materials - NotesDocument127 pagesCE6306Strength of Materials - Notesl8o8r8d8s8i8v8Pas encore d'évaluation
- By Ferdinand P. Beer & E. Russell Johnston Jr. With Notes by J. Walt Oler (Texas Tech University)Document20 pagesBy Ferdinand P. Beer & E. Russell Johnston Jr. With Notes by J. Walt Oler (Texas Tech University)Aizabelle FerrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Unreinforced Masonry Infill Walls in RC FramesDocument23 pagesEffect of Unreinforced Masonry Infill Walls in RC FramesAmandeepSandhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Saibel 1952Document4 pagesSaibel 1952Naturinda SarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Inclination, Length Pattern and Bending Stiffness of Soil NailsDocument12 pagesEffects of Inclination, Length Pattern and Bending Stiffness of Soil NailsyiklamPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL - Science 10 - Quarter 1 - Week 6Document7 pagesDLL - Science 10 - Quarter 1 - Week 6marianne viodorPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 2012 PDFDocument12 pagesExam 2012 PDFYuChenQianPas encore d'évaluation
- Research On Key Technologies of Four-Rotor UAV Flight Control System Based On STM32 MicrocontrollerDocument7 pagesResearch On Key Technologies of Four-Rotor UAV Flight Control System Based On STM32 MicrocontrollerSiddhesh PalodPas encore d'évaluation
- TensorDocument44 pagesTensorbilal5202050Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW3phy102Document3 pagesHW3phy102rajat12346Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydro 36 37 PDFDocument24 pagesHydro 36 37 PDFMuhammad Rafi RenaldyPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Exploration: Waves: Vocabulary: Amplitude, Compression, Crest, Frequency, Longitudinal Wave, Medium, PeriodDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Waves: Vocabulary: Amplitude, Compression, Crest, Frequency, Longitudinal Wave, Medium, PeriodNims DaydaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arche2 Module 1Document19 pagesArche2 Module 1Justine MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Under Uniaxial CompressionDocument11 pagesConcrete Under Uniaxial Compressionsreejithp1040% (1)
- Iii Semester: Ability Enhancement CourseDocument47 pagesIii Semester: Ability Enhancement Coursemujtaba siddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes For Section 13-5Document10 pagesLecture Notes For Section 13-5gPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy ConversionDocument24 pagesEnergy ConversionJohn Christian CoronadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Article: Study On Roll Instability Mechanism and Stability Index of Articulated Steering VehiclesDocument16 pagesResearch Article: Study On Roll Instability Mechanism and Stability Index of Articulated Steering VehiclesEric CPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohr Circle Hp35sDocument3 pagesMohr Circle Hp35sAlfredo Romero GPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - Vectors - Session-1 - AnswerDocument4 pagesAssignment - Vectors - Session-1 - AnsweraadityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy and Exergy Analysis of A Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Having Smooth and Corrugated Inner TubesDocument11 pagesEnergy and Exergy Analysis of A Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Having Smooth and Corrugated Inner TubesKar AbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Coefficient of RestitutionDocument13 pagesCoefficient of RestitutionDivina Mercedes FernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1Document41 pagesLecture 1norhaslina_aa33% (3)
- Fracture MechanicsDocument20 pagesFracture MechanicsShilpi KaushikPas encore d'évaluation